Design of a Cable-Driven Actuator for Pronation and Supination of the Forearm to Integrate an Active Arm Orthosis †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Description and Characteristics of the Actuator
2.1. Biomechanics of the Forearm
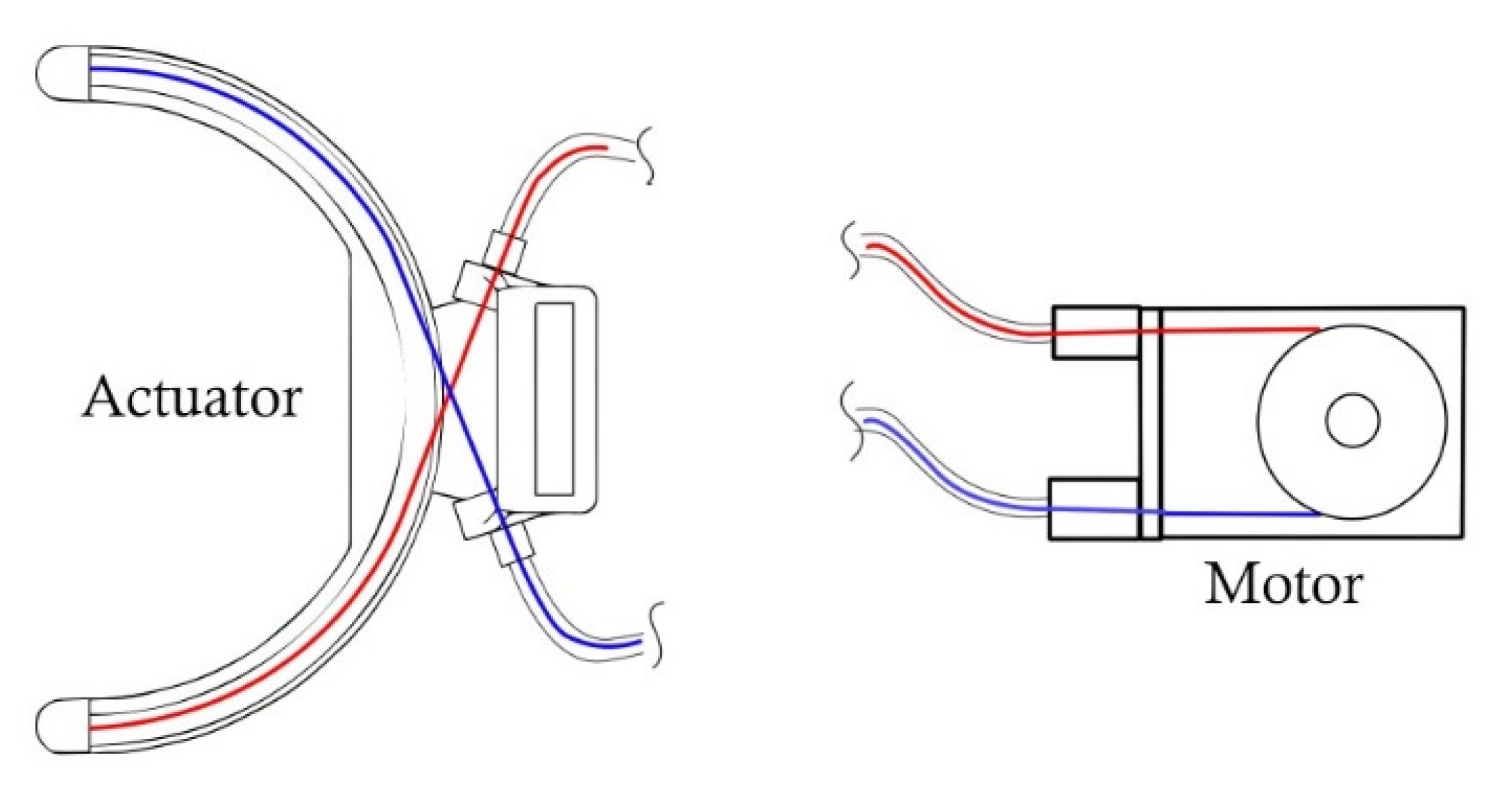
2.2. Design Concept and Methodology
2.3. Anthropometric Data Evaluation
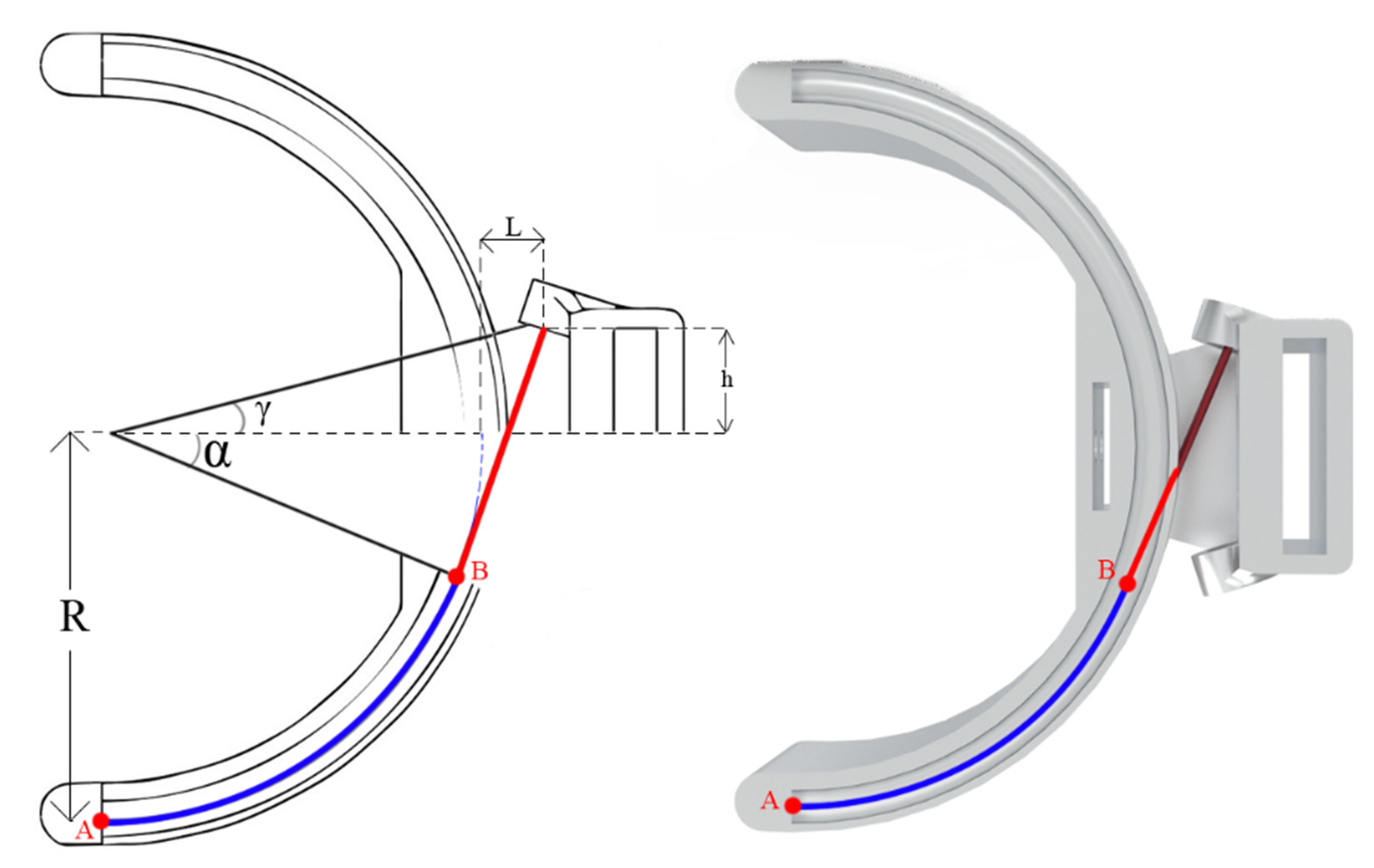
2.4. Mathematical Modelling
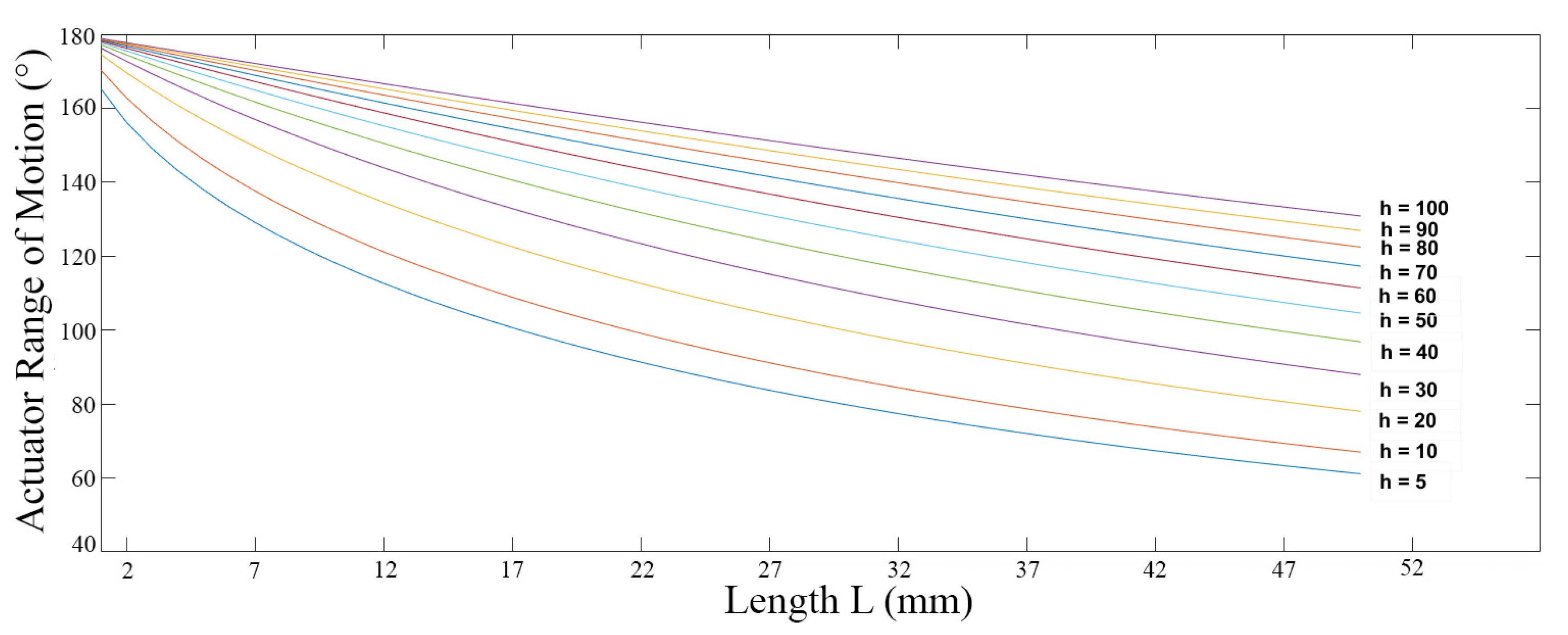
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stinear, C. Prediction of recovery of motor function after stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 1228–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.M.; Sapienza, S.; Bonato, P. Development of a “transparent operation mode” for a lower-limb exoskeleton designed for children with cerebral palsy. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 512–517. [Google Scholar]
- Kwakkel, G.; Kollen, B.J.; Krebs, H.I. Effects of Robot-Assisted Therapy on Upper Limb Recovery after Stroke: A Systematic Review. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2008, 22, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrholz, J.; Thomas, S.; Werner, C.; Kugler, J.; Pohl, M.; Elsner, B. Electromechanical-assisted training for walking after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 5, CD006185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Unger, J.; Zariffa, J.; Pakosh, M.; Jaglal, S.; Craven, B.C.; Musselman, K.E. Robot-assisted upper extremity rehabilitation for cervical spinal cord injuries: A systematic scoping review. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2018, 13, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klamroth-Marganska, V.; Blanco, J.; Campen, K.; Curt, A.; Dietz, V.; Ettlin, T.; Felder, M.; Fellinghauer, B.; Guidali, M.; Kollmar, A.; et al. Three-dimensional, task-specific robot therapy of the arm after stroke: A multicentre, parallel-group randomised trial. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.-Y.; Su, Y.-Y.; Yu, Y.-L.; Lin, C.-H.; Lan, C.-C. A 5-Degrees-of-Freedom Lightweight Elbow-Wrist Exoskeleton for Forearm Fine-Motion Rehabilitation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 2684–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.C.; Rosen, J. Design of a 7 Degree-of-Freedom Upper-Limb Powered Exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the First IEEE/RAS-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, 2006. BioRob 2006, Pisa, Italy, 20–22 February 2006; pp. 805–810. [Google Scholar]
- Pehlivan, A.U.; Celik, O.; O’Malley, M.K. Mechanical design of a distal arm exoskeleton for stroke and spinal cord injury rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Zurich, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2011; Volume 2011, p. 5975428. [Google Scholar]
- Rocon, E.; Ruiz, A.F.; Pons, J.L.; Belda-Lois, J.M.; Sanchez-Lacuesta, J.J. Rehabilitation Robotics: A Wearable Exo-Skeleton for Tremor Assessment and Suppression. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–22 April 2005; pp. 2271–2276. [Google Scholar]
- Kleim Jeffrey, A.; Jones Theresa, A. Principles of Experience-Dependent Neural Plasticity: Implications for Rehabilitation after Brain Damage. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2008, 51, S225–S239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dežman, M.; Asfour, T.; Ude, A.; Gams, A. Exoskeleton Arm Pronation/Supination Assistance Mechanism with A Guided Double Rod System. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE-RAS 19th International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–17 October 2019; pp. 559–564. [Google Scholar]
- Morrey, B.F.; Askew, L.J.; Chao, E.Y. A biomechanical study of normal functional elbow motion. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1981, 63, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardelli, M.; Tashjian, R.Z.; MacWilliams, B.A. Functional elbow range of motion for contemporary tasks. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2011, 93, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, M.A.; Yardley, A.; Johnson, G.R.; Carus, D.A. Dynamics of the upper limb during performance of the tasks of everyday living—A review of the current knowledge base. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 1996, 210, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, H.A.; Fai, Y.C.; Ming, E.S.L. Analysis of Human Hand Kinematics: Forearm Pronation and Supination. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2014, 4, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, T.M. Hand Anthropometry of US Army Personnel; No. TR-92/011; Army Natick Research Development and Engineering Center: Natick, MA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, D.; Qian, W.; Xiao, X.; Guo, Z. Modeling and Control of a Cable-Driven Rotary Series Elastic Actuator for an Upper Limb Rehabilitation Robot. Front. Neurorobot. 2020, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiele, A.; Letier, P.; Der Linde, R.V.; Der Helm, F.V. Bowden Cable Actuator for Force-Feedback Exoskeletons. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Beijing, China, 9–15 October 2006; pp. 3599–3604. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dias, E.A.F.; Andrade, R.M.d. Design of a Cable-Driven Actuator for Pronation and Supination of the Forearm to Integrate an Active Arm Orthosis. Proceedings 2020, 64, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/IeCAT2020-08511
Dias EAF, Andrade RMd. Design of a Cable-Driven Actuator for Pronation and Supination of the Forearm to Integrate an Active Arm Orthosis. Proceedings. 2020; 64(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/IeCAT2020-08511
Chicago/Turabian StyleDias, Eduardo A. F., and Rafhael M. de Andrade. 2020. "Design of a Cable-Driven Actuator for Pronation and Supination of the Forearm to Integrate an Active Arm Orthosis" Proceedings 64, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/IeCAT2020-08511
APA StyleDias, E. A. F., & Andrade, R. M. d. (2020). Design of a Cable-Driven Actuator for Pronation and Supination of the Forearm to Integrate an Active Arm Orthosis. Proceedings, 64(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/IeCAT2020-08511



