Multifunctional Smart Window Based on Dielectric Elastomer Actuator †
Abstract
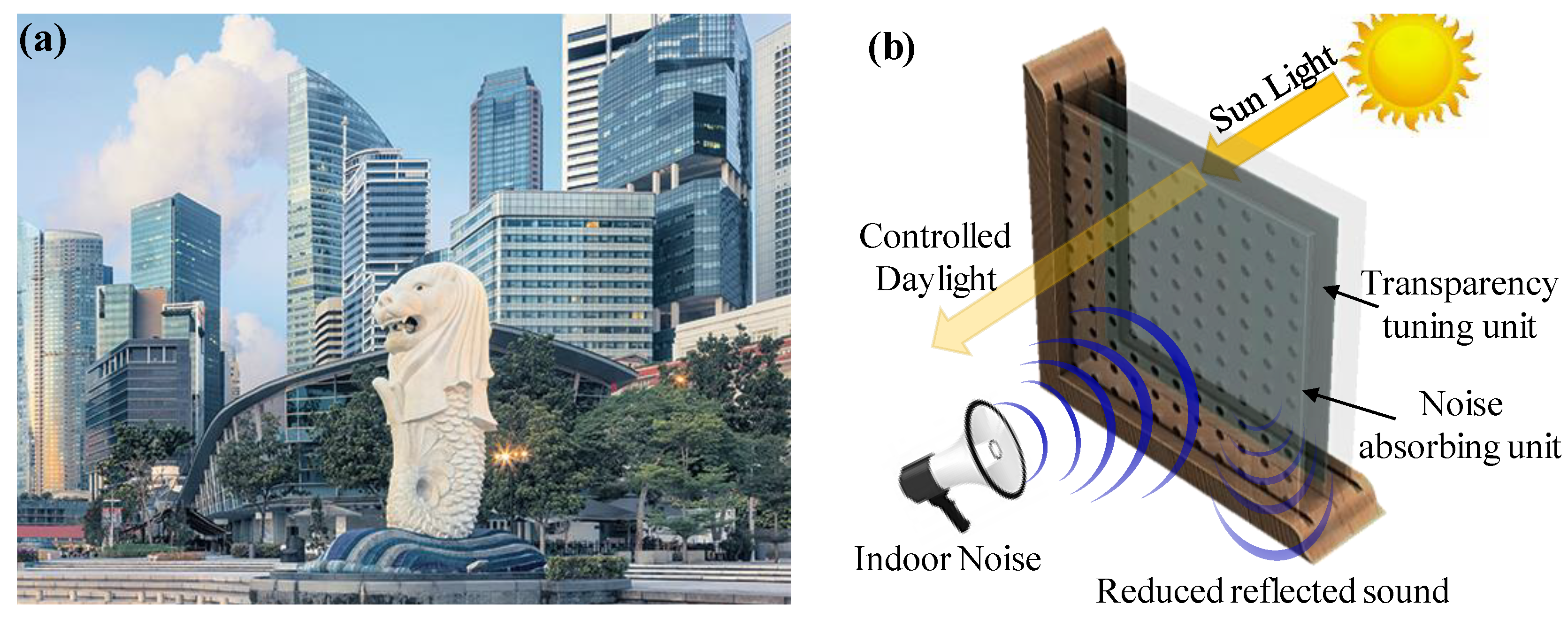
:1. Introduction
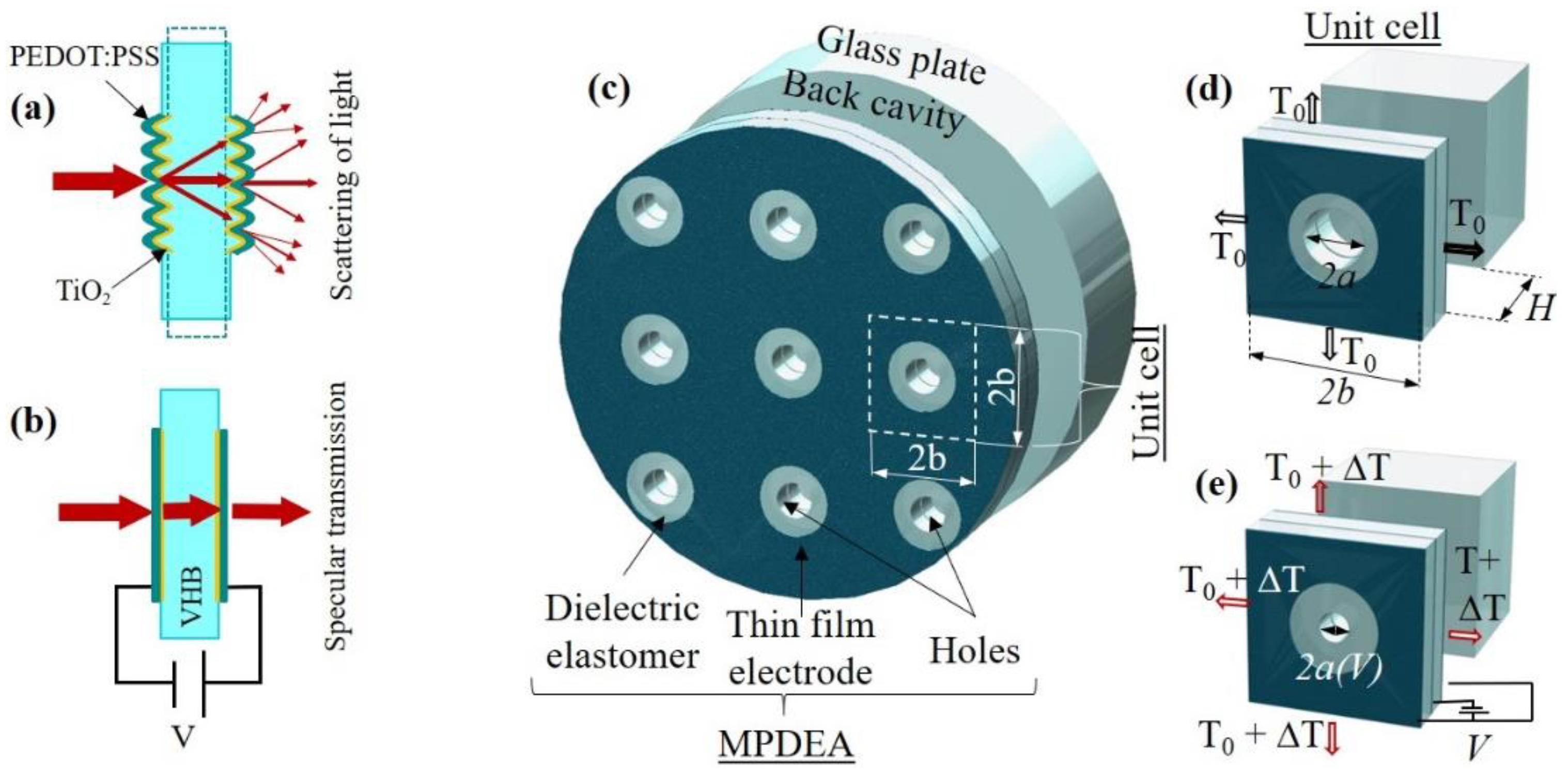
2. Theory
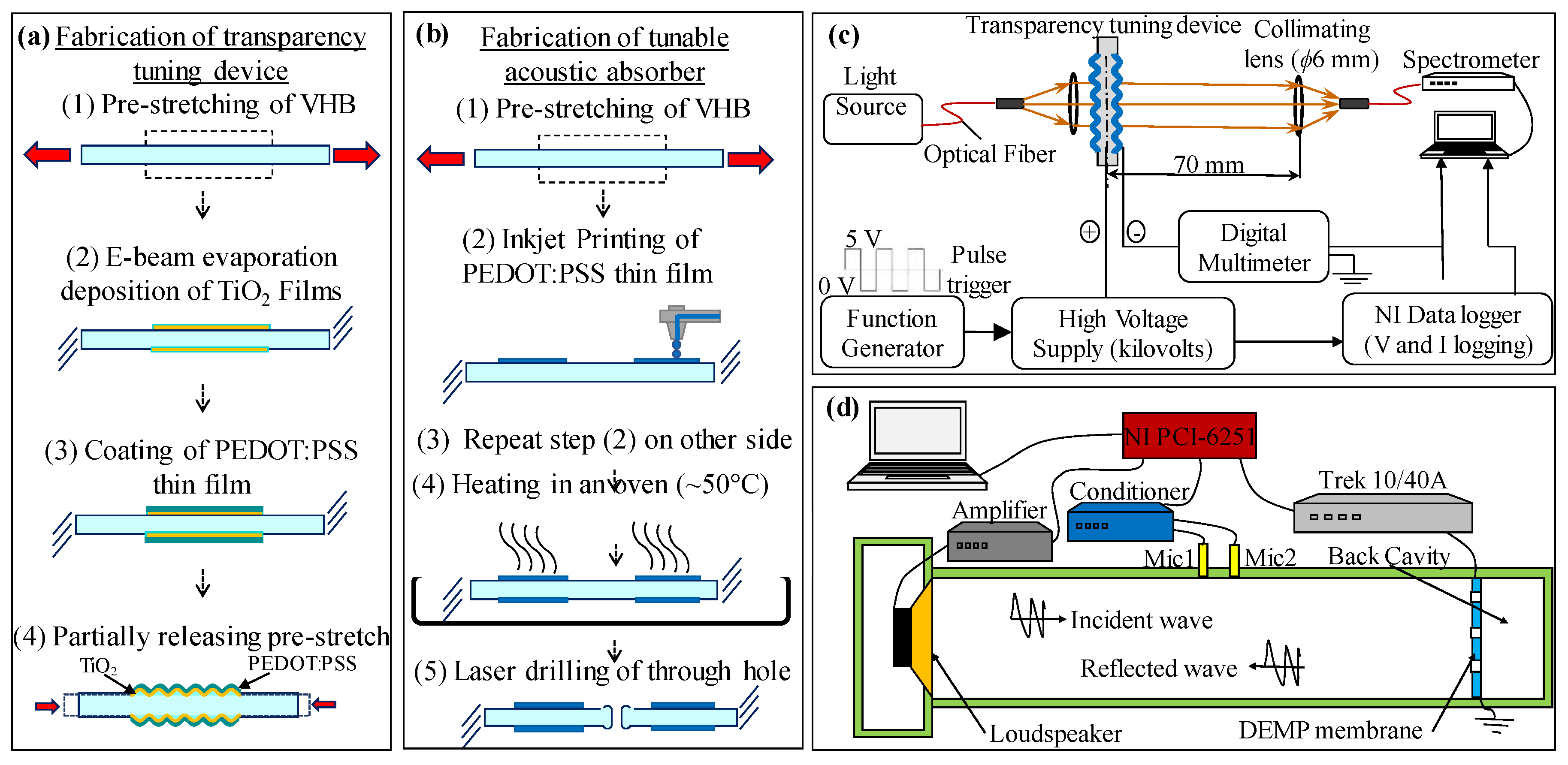
3. Experiments
4. Results and Discussion
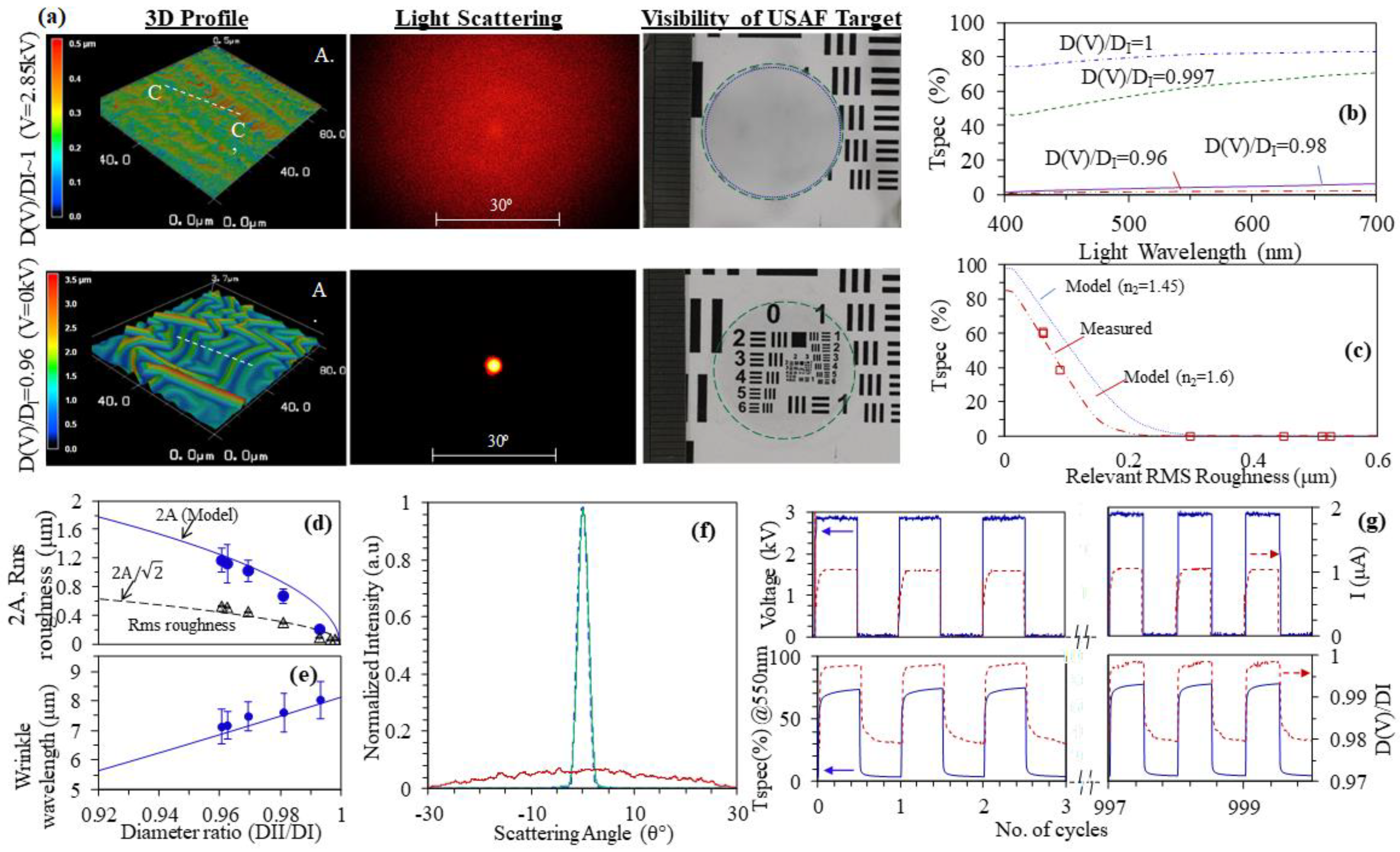
4.1. Transparency Tuning Device
4.2. Tunable Acoustic Absorber
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DEA | Dielectric elastomer actuators |
| MPP | Microperforated panel |
| MPDEA | Microperforated dielectric elastomer actuator |
References
- Cox, T.J.; D’antonio, P. Acoustic Absorbers and Diffusers: Theory, Design and Application; CRC Press: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gerriets-GmbH. Absorber Light. Available online: https://www.gerriets.com/us/absorber-light-8172 (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- Lampert, C.M. Chromogenic smart materials. Mater. Today 2004, 7, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granqvist, C.G. Electrochromics for smart windows: Oxide-based thin films and devices. Thin Solid Films 2014, 564, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doane, J.W.; Vaz, N.A.; Wu, B.G.; Žumer, S. Field controlled light scattering from nematic microdroplets. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1986, 48, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzaic, P.S. Polymer dispersed nematic liquid crystal for large area displays and light valves. J. Appl. Phys. 1986, 60, 2142–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baetens, R.; Jelle, B.P.; Gustavsen, A. Properties, requirements and possibilities of smart windows for dynamic daylight and solar energy control in buildings: A state-of-the-art review. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 2010, 94, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Ende, D.; Kamminga, J.D.; Boersma, A.; Andritsch, T.; Steeneken, P.G. Voltage-controlled surface wrinkling of elastomeric coatings. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3438–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görrn, P.; Cao, W.; Wagner, S. Isotropically stretchable gold conductors on elastomeric substrates. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 7177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Ryu, S.; Pugno, N.; Wang, Q.; Tu, Q.; Buehler, M.J.; Zhao, X. Multifunctionality and control of the crumpling and unfolding of large-area graphene. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, H.-Y.; Shrestha, M.; Lau, G.-K. Microscopically crumpled indium-tin-oxide thin films as compliant electrodes with tunable transmittance. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 132902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.V.; Andow, B.C.; Suresh, S.; Eksik, O.; Yin, J.; Dyson, A.H.; Koratkar, N. Controlled crumpling of graphene oxide films for tunable optical transmittance. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3256–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J. An acoustic window system with optimum ventilation and daylighting performance. Noise Vib. Worldw. 2006, 37, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asdrubali, F.; Pispola, G. Properties of transparent sound-absorbing panels for use in noise barriers. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 121, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struiksma, A.; Tenpierik, M.; Snijder, A.; Veer, F.; Botterman, B.; Hornikx, M.; van der Water, H.; Migchielsen, F. Sound absorbing glass: Transparent solution for poor acoustics of monumental spaces. SPOOL 2017, 4, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Soundproofing-windows.net. Soundproofing Windows with Double and Triple Glazing. Available online: http://soundproofing-windows.net/index.php/soundproofing-windows-with-double-and-triple-glazing (accessed on 1 December 2018).
- Shrestha, M.; Lau, G.-K. Tunable window device based on micro-wrinkling of nanometric zinc-oxide thin film on elastomer. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, M.; Asundi, A.; Lau, G.-K. Smart Window Based on Electric Unfolding of Microwrinkled TiO2 Nanometric Films. ACS Photonics 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, P.; Spizzichino, A. The Scattering of Electromagnetic Waves from Rough Surfaces; Artech House, Inc.: Norwood, MA, USA, 1987; p. 511. [Google Scholar]
- Eastman, J. Surface Scattering in Optical Interference Coatings; University of Rochester: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Zeman, M.; van Swaaij, R.A.C.M.M.; Metselaar, J.W.; Schropp, R.E.I. Optical modeling of a-Si:H solar cells with rough interfaces: Effect of back contact and interface roughness. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88, 6436–6443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keplinger, C.; Sun, J.-Y.; Foo, C.C.; Rothemund, P.; Whitesides, G.M.; Suo, Z. Stretchable, transparent, ionic conductors. Science 2013, 341, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, U.; Naujoks, N.; Dual, J. Mechanical characterization of PEDOT:PSS thin films. Synth. Metals 2009, 159, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, G.-K.; Heng, K.-R.; Ahmed, A.S.; Shrestha, M. Dielectric elastomer fingers for versatile grasping and nimble pinching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 182906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Shrestha, M.; Lau, G.-K. Electrically tunable and broader-band sound absorption by using micro-perforated dielectric elastomer actuator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 182901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, M.; Lu, Z.; Lau, G.-K. Transparent tunable acoustic absorber membrane using inkjet printed PEDOT: PSS thin-film compliant electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maa, D.-Y. Potential of microperforated panel absorber. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 104, 2861–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrin, D.; Liu, J. Properties and applications of microperforated panels. Sound Vib. 2011, 45, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ginn, K. Architectural Acoustics; Brüel & Kjaer: Naerum, Denmark, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Shian, S.; Clarke, D.R. Electrically tunable window device. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 1289–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosset, S.; Shea, H.R. Flexible and stretchable electrodes for dielectric elastomer actuators. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 110, 281–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, S.H.; Lau, G.K. Bi-axially crumpled silver thin-film electrodes for dielectric elastomer actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 125021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3M. Converting 3M Technology into Successful Applications; 3M Industrial Adhesives and Tapes Division: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shrestha, M.; Lau, G.-K.; Asundi, A.; Lu, Z. Multifunctional Smart Window Based on Dielectric Elastomer Actuator. Proceedings 2020, 64, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/IeCAT2020-08509
Shrestha M, Lau G-K, Asundi A, Lu Z. Multifunctional Smart Window Based on Dielectric Elastomer Actuator. Proceedings. 2020; 64(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/IeCAT2020-08509
Chicago/Turabian StyleShrestha, Milan, Gih-Keong Lau, Anand Asundi, and Zhenbo Lu. 2020. "Multifunctional Smart Window Based on Dielectric Elastomer Actuator" Proceedings 64, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/IeCAT2020-08509
APA StyleShrestha, M., Lau, G.-K., Asundi, A., & Lu, Z. (2020). Multifunctional Smart Window Based on Dielectric Elastomer Actuator. Proceedings, 64(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/IeCAT2020-08509







