Intensive Training and Sex Influence Intestinal Microbiota Composition: A Preclinical Approach †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
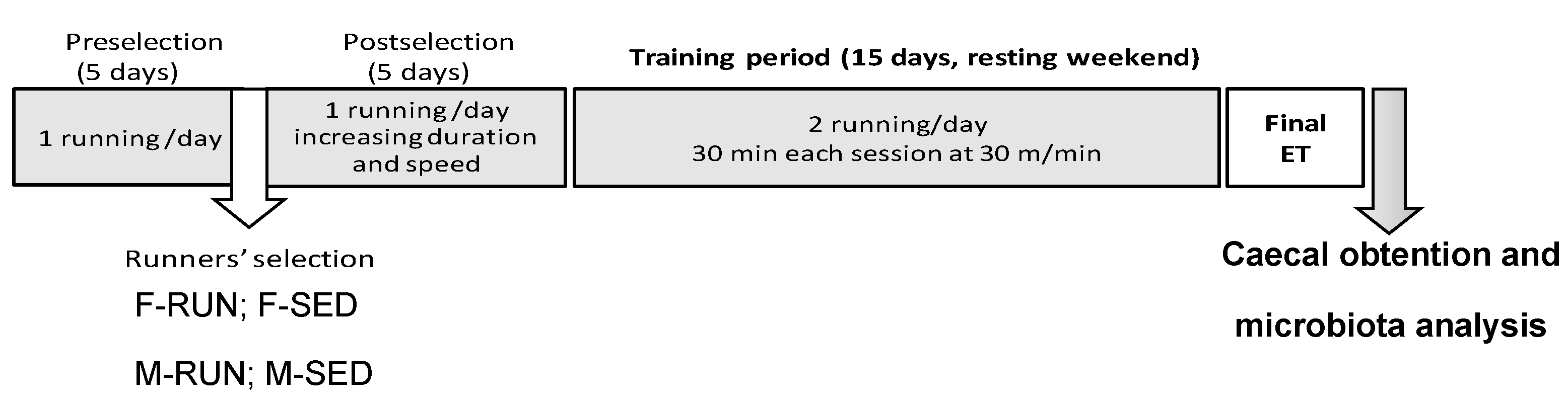
2.1. Animals and Training Program
2.2. Microbiota Determination
2.3. Statistical Analysis
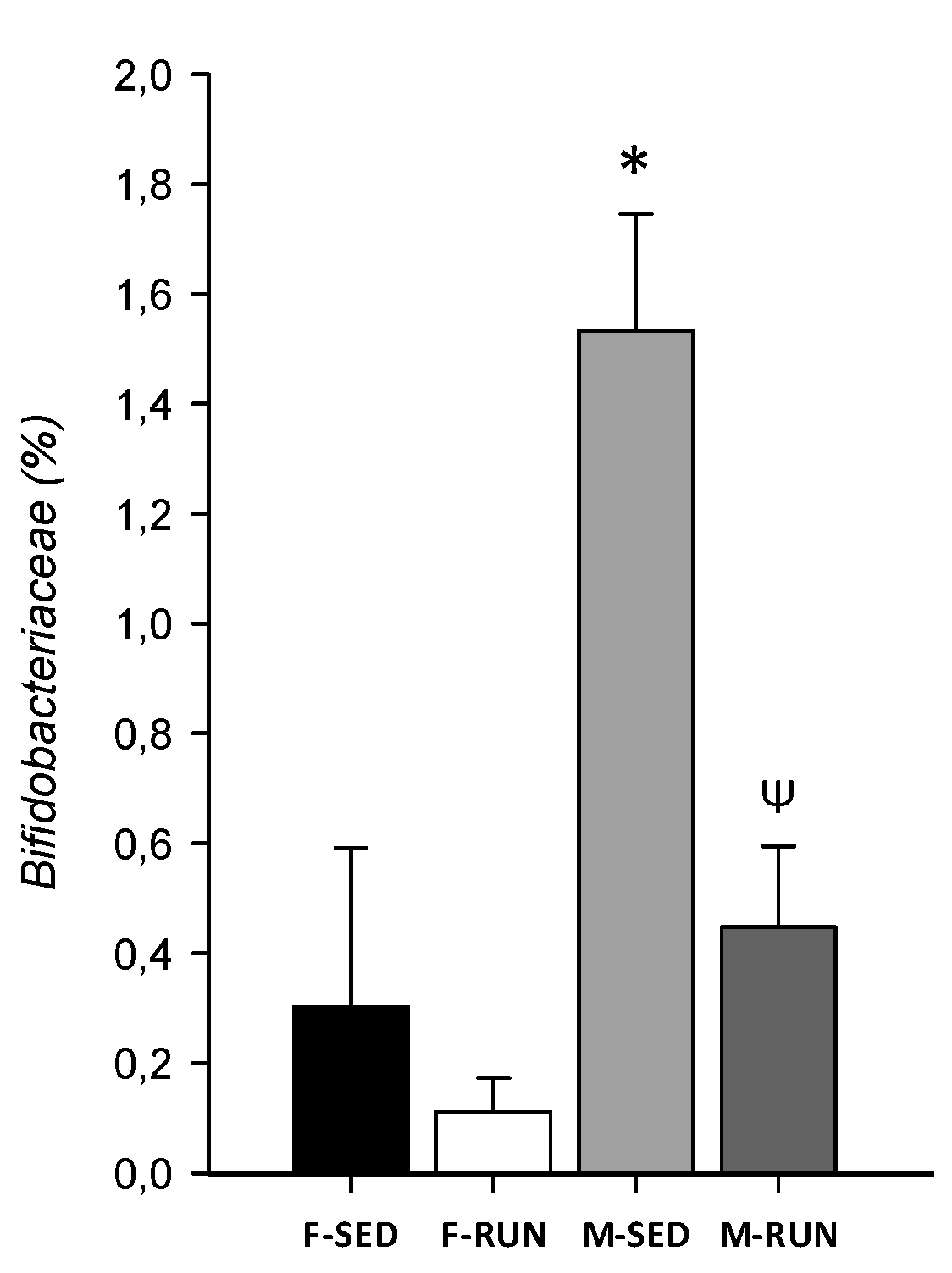
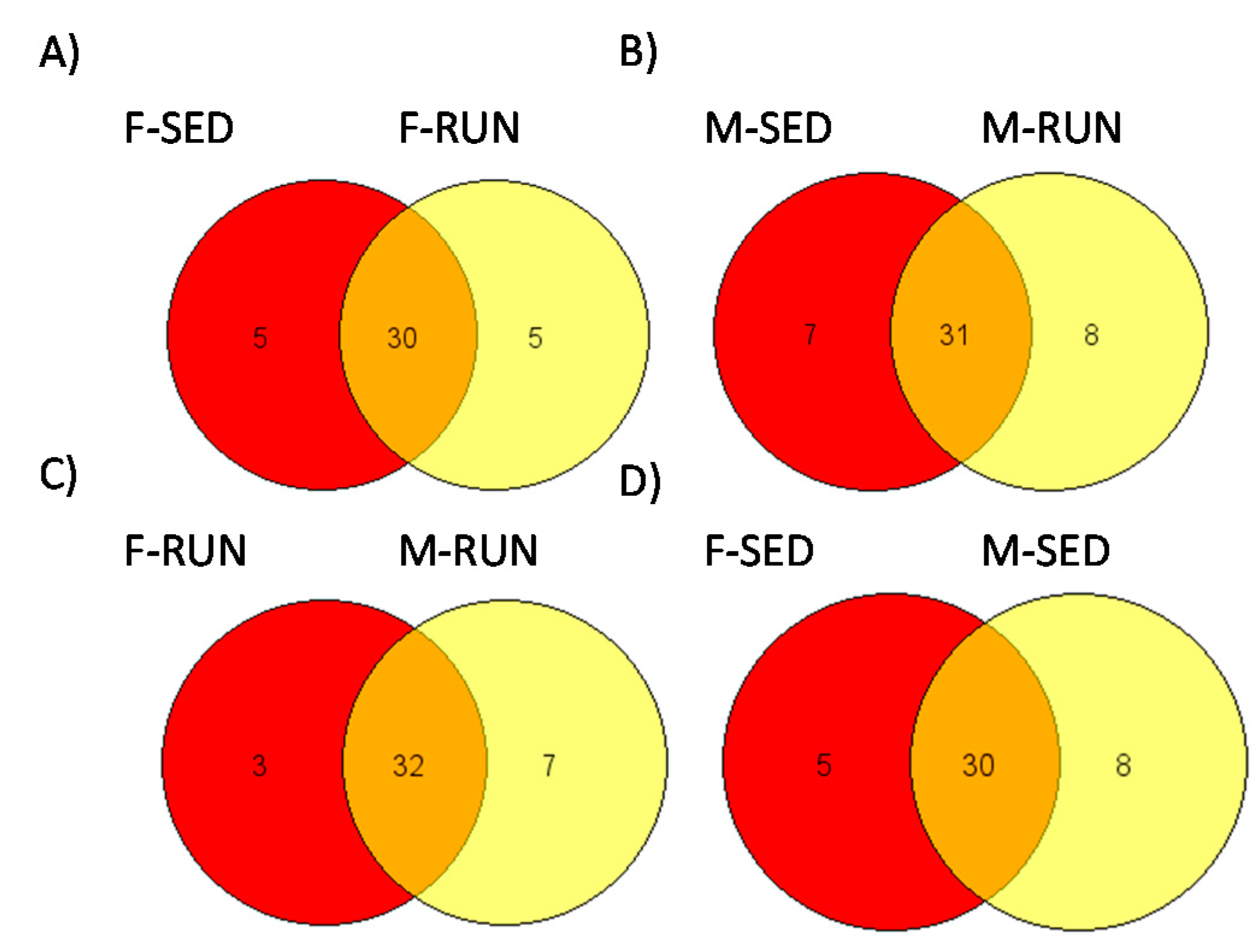
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keohane, M.; Woods, T.; O’Connor, P.; Underwood, S.; Cronin, O.; Whiston, R.; O’Sullivan, O.; Cotter, P.; Shanahan, F.; Molloy, M. Four men in a boat: Ultra-endurance exercise alters the gut microbiome. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2019, 22, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rettedal, E.A.; Cree, J.M.E.; Adams, S.E.; MacRae, C.; Skidmore, P.M.L.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Gant, N.; Blenkiron, C.; Merry, T.L. Short-term high-intensity interval training exercise does not affect gut bacterial community diversity or composition of lean and overweight men. Exp. Physiol. 2020. (online ahead of print). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersini, P.; Turroni, S.; Villafañe, J.H. Gut microbiota and physical activity: Is there an evidence-based link? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, M.A.; Bird, A.R. The Impact of Diet and Lifestyle on Gut Microbiota and Human Health. Nutrients 2015, 7, 17–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.S.; Li, W. How and Why Men and Women Differ in Their Microbiomes: Medical Ecology and Network Analyses of the Microgenderome. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1902054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estruel-Amades, S.; Camps-Bossacoma, M.; Massot-Cladera, M.; Pérez-Cano, F.J.; Castell, M. Alterations in the innate immune system due to exhausting exercise in intensively trained rats. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estruel-Amades, S.; Ruiz-Iglesias, P.; Périz, M.; Franch, À.; Pérez-Cano, F.J.; Camps-Bossacoma, M.; Castell, M. Changes in Lymphocyte Composition and Functionality After Intensive Training and Exhausting Exercise in Rats. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azagra-Boronat, I.; Tres, A.; Massot-Cladera, M.; Franch, À.; Castell, M.; Guardiola, F.; Pérez-Cano, F.J.; Rodríguez-Lagunas, M.J. Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 supplementation in rats during pregnancy and lactation affects mammary milk composition. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 2982–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz-Iglesias, P.; Massot-Cladera, M.; Estruel-Amades, S.; PérezCano, F.J.; Castell, M. Intensive Training and Sex Influence Intestinal Microbiota Composition: A Preclinical Approach. Proceedings 2020, 61, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECN2020-06989
Ruiz-Iglesias P, Massot-Cladera M, Estruel-Amades S, PérezCano FJ, Castell M. Intensive Training and Sex Influence Intestinal Microbiota Composition: A Preclinical Approach. Proceedings. 2020; 61(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECN2020-06989
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz-Iglesias, Patricia, Malén Massot-Cladera, Sheila Estruel-Amades, Francisco J. PérezCano, and Margarida Castell. 2020. "Intensive Training and Sex Influence Intestinal Microbiota Composition: A Preclinical Approach" Proceedings 61, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECN2020-06989
APA StyleRuiz-Iglesias, P., Massot-Cladera, M., Estruel-Amades, S., PérezCano, F. J., & Castell, M. (2020). Intensive Training and Sex Influence Intestinal Microbiota Composition: A Preclinical Approach. Proceedings, 61(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECN2020-06989







