Highly Sensitive H2S Sensing with Gold and Platinum Surface-Modified ZnO Nanowire ChemFETs †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ZnO Nanowire Growth
2.2. Gas Sensor Fabrication and Metal Surface Modification of ZnO Nanowires
2.3. Measurement Setup and Gas Sensor Evaluation
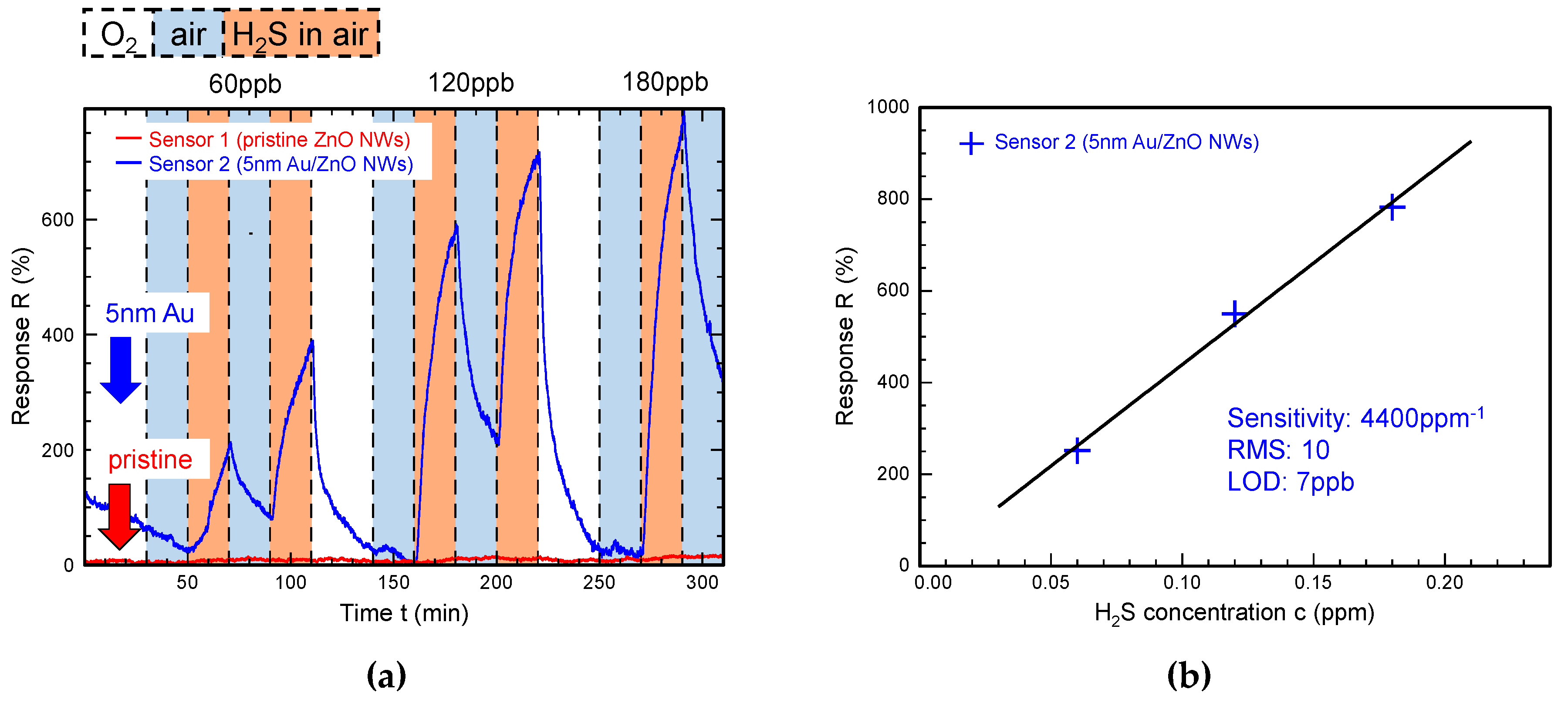
3. Results
3.1. Gas Sensing with Pristine, Au-Modified and Pt-Modified ZnO Nanowires
3.2. Systematic Au Surface Modification of ZnO NWs
3.3. LOD toward H2S Detection in Synthetic Air with Pristine and Surface-Modified ZnO NWs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
References
- Wang, P.; Zhang, G.; Wondimu, T.; Ross, R.; Wang, R. Hydrogen sulfide and asthma. Exp. Physiol. 2011, 96, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, C. Hydrogen sulphide and its therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2007, 6, 917–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, A.; Pennazza, G.; Santonico, M.; Martinelli, E.; Roscioni, C.; Galluccio, G.; Paolesse, R.; Di Natale, C. An investigation on electronic nose diagnosis of lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2010, 68, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millonig, G.; Praun, S.; Netzer, M. Non-invasive diagnosis of liver diseases by breath analysis using an optimized ion-molecule reaction-mass spectrometry approach: A pilot study. Biomarkers 2010, 15, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Yao, W. Correlation between levels of exhaled hydrogen sulfide and airway inflammatory phenotype in patients with chronic persistent asthma. Respirology 2014, 19, 1165–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wondimu, T.; Wang, R.; Ross, B. Hydrogen sulphide in human nasal air quantified using thermal desorption and selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, 036002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampolli, S.; Elmi, I.; Mancarella, F.; Betti, P.; Dalcanale, E.; Cardinali, G.C.; Severi, M. Real-time monitoring of sub-ppb concentrations of aromatic volatiles with a MEMS-enabled miniaturized gas-chromatograph. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2009, 141, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruci, J.; Cardoso, A.A.; Wilk, A.; Kokoric, V.; Mizaikoff, B. iCONVERT: An Integrated Device for the UV-Assisted Determination of H2S via Mid-Infrared Gas Sensors. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9580–9583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruci, J.; Cardoso, A.A.; Wilk, A.; Mizaikoff, B. Online Analysis of H2S and SO2 via Advanced Mid-Infrared Gas Sensors. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9605–9611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.G.; Jung, Y.; Han, S.D.; Shim, Y.; Shin, B.; Lee, T.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Jun, S.C.; Park, H.; et al. Chemiresistive Electronic Nose toward Detection of Biomarkers in Exhaled Breath. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 20969–20976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, R.; Hoel, A.; Granqvist, C.G.; Llobet, E.; Heszler, P. Low-level detection of ethanol and H2S with temperature-modulated WO3 nanoparticle gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2005, 104, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wu, J.; Cao, Y. Ultrasensitive H2S gas detection at room temperature based on copper oxide/molybdenum disulfide nanocomposite with synergistic effect. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2019, 287, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-J.; Jang, B.-H.; Lee, S.-J.; Min, B.K.; Rothschild, A.; Kim, I.-D. Selective Detection of Acetone and Hydrogen Sulfide for the Diagnosis of Diabetes and Halitosis Using SnO2 Nanofibers Functionalized with Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanosheets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Chen, D.; Feng, M.; Ge, L.; Yang, D.; Song, Z.; Fan, B.; Zhang, R.; Shao, G. Hierarchical Fe2O3@WO3 nanostructures with ultrahigh specific surface areas: Microwave-assisted synthesis and enhanced H2S-sensing performance. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Fu, Q.; Luo, W.; Tong, X.; Xiong, J.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, Z. Enhanced H2S gas sensing properties of undoped ZnO nanocrystalline films from QDs by low-temperature processing. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2016, 224, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Sun, M.; Han, Sh.; Cai, C.; Shen, W.; Fu, Y. Ultrafast Response/Recovery and High Selectivity of the H2S Gas Sensor Based on α-Fe2O3 Nano-Ellipsoids from One-Step Hydrothermal Synthesis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 12761–12769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chu, X.; Wu, M. Detection of H2S down to ppb levels at room temperature using sensors based on ZnO nanorods. Sens. Actuators B: Chem 2006, 113, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.R.; Akbar, S.A.; Morris, P.A. Nanoscale metal oxide-based heterojunctions for gas sensing: A review. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2014, 204, 250–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, H.; Wang, S.; Duan, Z.; Jiang, Y. Evolution of breath analysis based on humidity and gas sensors: Potential and challenges. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2020, 318, 128104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Ramgir, N.S.; Goyal, C.P.; Datta, N.; Srivastava, S.; Kaur, M.; Debnath, A.K.; Aswal, D.K.; Vijay, Y.K.; Gupta, S.K. Effect of sensitizers on H2S sensing properties of ZnO nanowires. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Nanomaterials & Emerging Engineering Technologies, Sathyabama University, 600119 Chennai, India, 25 July 2013; pp. 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lin, X.; Yang, S.; Zhu, S.; Chen, X.; Dong, B.; Bai, X.; Wen, X.; Geyu, L.; Song, H. Highly dispersed Metal–Organic-Framework-Derived Pt nanoparticles on three-dimensional macroporous ZnO for trace-level H2S sensing. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2020, 309, 127802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.S.; Ellis, W.C. Vapor-liquid-solid mechanism of single crystal growth. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1964, 4, 89–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feneberg, M.; Reiser, A.; Schirra, M.; Enchelmaier, R.; Ladenburger, A.; Langlois, A.; Sauer, R.; Thonke, K. Au-catalyzed growth processes and luminescence properties of ZnO nanopillars on Si. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 054307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, F.; Riegert, S.; Madel, M.; Thonke, K. H2S sensing in the ppb regime with zinc oxide nanowires. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, H.A. Dielectrophoresis: The Behavior of Neutral Matter in Nonuniform Electric Field; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, J.; Lyutakov, O.; Rybka, V.; Kolská, Z.; Svorčík, V. Properties of gold nanostructures sputtered on glass. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2011, 6, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Al-Dossary, O.; Kumar, G.; Umar, A. Zinc Oxide Nanostructures for NO2 Gas–Sensor Applications: A Review. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Ding, H.; Yang, X.; Wei, Y.; Xiao, M.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X. Three-Dimensional-Structured Boron- and Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Hydrogel Enabling High-Sensitivity NO2 Detection at Room Temperature. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsan, N.; Weimar, U. Conduction model of metal oxide gas sensors. J. Electroceramics 2001, 7, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Shen, J. Hydrothermal synthesis of In2O3 for detecting H2S in air. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 115, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yong, K. Mechanism study of ZnO nanorod-bundle sensors for H2S gas sensing. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 7218–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.S.; Mirzaei, A.; Bang, J.H.; Oum, W.; Jung Kwon, Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, S.-W.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, H.W. Selective H2S-sensing performance of Si nanowires through the formation of ZnO shells with Au functionalization. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 289, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelson, H.B. The work function of the elements and its periodicity. J. Appl. Phys. 1977, 48, 4729–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; Katoch, A.; Sun, G.J.; Kim, S.S. Synthesis and gas sensing performance of ZnO-SnO2 nanofiber-nanowire stem-branch heterostructure. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 181, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Thomas, M.D.R.; Shephard, D.S.; Johnson, B.F.G. Suppressed electron hopping in a Au nanoparticle/H2S system: Development towards a H2S nanosensor. Chem. Commun 2005, 14, 1895–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Kim, Y.S.; Song, H.M.; Song, M.K.; Yu, Y.T. The role of gold catalyst on the sensing behavior of ZnO nanorods for CO and NO2 gases. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 165, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Sun, P.; Liu, F.; Lu, G. Design of Au@ZnO Yolk–Shell Nanospheres with Enhanced Gas Sensing Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 18661–18667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S.; Miyayama, M.; Koumoto, K.; Yanagida, H. Gas Sensing Characteristics of Porous ZnO and Pt/ZnO Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1985, 68, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balouria, V.; Ramgir, N.S.; Singh, A.; Debnath, A.K.; Mahajan, A.; Bedi, R.K.; Aswal, D.K.; Gupta, S.K. Enhanced H2S sensing characteristics of Au modified Fe2O3 thin films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 219, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Yoon, J.W.; Jeong, H.M.; Hwang, S.J.; Kwak, C.H.; Lee, J.H. Design of highly sensitive and selective Au@NiO yolk–shell nanoreactors for gas sensor applications. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 8292–8299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Sensor | ||
|---|---|---|
| pristine ZnO NWs | ||
| 1 nm Au/ZnO NWs | ||
| 2 nm Au/ZnO NWs | ||
| 3 nm Au/ZnO NWs | ||
| 4 nm Au/ZnO NWs | ||
| 5 nm Au/ZnO NWs |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaiser, A.; Ceja, E.T.; Huber, F.; Herr, U.; Thonke, K. Highly Sensitive H2S Sensing with Gold and Platinum Surface-Modified ZnO Nanowire ChemFETs. Proceedings 2020, 60, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECB2020-07070
Kaiser A, Ceja ET, Huber F, Herr U, Thonke K. Highly Sensitive H2S Sensing with Gold and Platinum Surface-Modified ZnO Nanowire ChemFETs. Proceedings. 2020; 60(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECB2020-07070
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaiser, Angelika, Erick Torres Ceja, Florian Huber, Ulrich Herr, and Klaus Thonke. 2020. "Highly Sensitive H2S Sensing with Gold and Platinum Surface-Modified ZnO Nanowire ChemFETs" Proceedings 60, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECB2020-07070
APA StyleKaiser, A., Ceja, E. T., Huber, F., Herr, U., & Thonke, K. (2020). Highly Sensitive H2S Sensing with Gold and Platinum Surface-Modified ZnO Nanowire ChemFETs. Proceedings, 60(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECB2020-07070





