Abstract
The present work reports the potential of a bio-inspired system based on spectrometry, also known as Electronic Eye (EE), capable of detecting different Tequila samples. The reported system analyzes small volumes of Tequila Reposado and Blanco by calculating samples’ absorbances, using a low cost and portable instrumentation employing a CCD camera. The absorbance imaging method consisted of exciting samples with light passes through an 8MP camera connected to a Raspberry Pi Card. The camera’s image data are analyzed using MATLAB 2018b to be represented in Red, Green and Blue (RGB) components for each pixel, in order to get an approximation of the absorbance and the Surface Color Index () associated with sample concentration. Using the developed EE, it was possible to identify seven different kinds and brands of Tequila. From the obtained results, it was observed that the average absorbance of the Tequila Reposado was greater than the absorbance of the Tequila Blanco. Otherwise, with the , the Tequila Blanco color index is lower concerning the Tequila Reposado’s. Finally, the EE allowed the identification of Tequila samples with reproducibility and repeatability.
1. Introduction
The growing interest of spirits producers to evaluate their authenticity, quality, and safety has motivated the development of efficient, portable, and low-cost analytical systems capable of monitoring these products’ characteristics. The use of analytical equipment has reached a level of sophistication that allows the investigation of foods’ properties. Regarding spirits and liquors, a consumer commonly wants and expects a product that is pleasant to taste and smell. In this regard, Tequila quality control is oriented toward understanding, characterizing, and controlling its aging, alcoholic content, and volatile composition, which define its characteristic color, flavor, and aroma.
Tequila is the traditional Mexican liquor whose worldwide consumption ranks fourth after whiskey, vodka, and rum. It has a significant presence in more than 120 countries and has sales of more than 200 million liters per year [1]. To control its production and quality specifications to export, it established the Protected Designation of Origin (POD) [2], recognized by the United States [3] and the European Union [4]. The Tequila is a distilled spirit from the cooked and fermented juice of the Agave Tequilana Weber blue variety, whose cultivation is authorized in the Mexican states of Jalisco, Nayarit, Tamaulipas, Michoacan, and Guanajuato.
Usually, Tequila’s quality assessment is performed using conventional analytical methods, mainly based on UV–Vis spectrophotometry, high-performance liquid chromatography, spectroscopy, chemical analysis [5], and sensory analysis performed by a human panel [6]. Despite these advantages, the conventional analytical methods are long protocols that require a period from hours to days to carry out the tests, expensive equipment and require an abundance of technically qualified personnel, considering its use as complete evaluations confined to a specialized laboratory with no possibilities of adaptation in applications with online quality control. Therefore, there is an urgent need for fast, cheaper, portable, and field effective alternatives that achieve reliable and non-destructive measurements.
This new perspective on analytical instrumentation has been focused on using bio-inspired systems that base their operation on the emulation of human senses to determine food characteristics, such as color, shape or size. In particular, the Electronic Eye (EE) has been designed to mimic human vision and analyze the color and some other attributes related to the sample’s appearance [7,8], and it is usually based on computer vision, colorimetric or spectrophotometry methods [9,10,11].
Electronic Eyes have proven advantageous in various foodstuff areas, such as process monitoring, quality control, freshness assessment, shelf life investigation, and authenticity assessment. Over the last few years, it has been possible to find applications related to the evaluation of the quality in alcoholic beverages [12,13], fruit ripening analysis [14,15,16], vegetables [17,18], cereals [19,20], meat products [21,22], fish and seafood [23,24,25], coffee [26,27], tea [28,29], olive oil [30,31], and others [32,33].
The main basis of electronic eyes is the acquisition of analytical information (Figure 1), typically using a Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) image sensor coupled with a camera [34,35,36]. After digital imaging, image processing is applied to enhance the acquired images for further analysis.
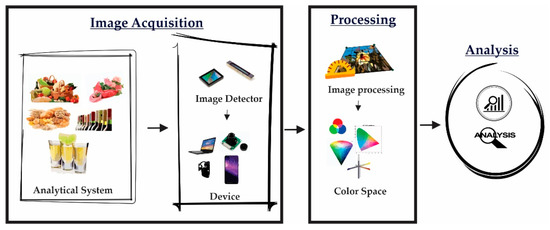
Figure 1.
Schematic structure of an image analysis system.
The objective of this work is to present an ongoing research related to the development of a portable Electronic Eye based on a typical computer vision system with the fundamental components: Lighting device, a frame-grabber, a CCD array camera, a personal computer, and a high-resolution color monitor, for identification of small volumes of Tequila samples by absorbance detection.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples of Tequila
This work focused on studying Blanco and Reposado Tequila from the Jalisco state region due to these types being the most popular and consumed. A total of seven commercial Tequila bottles were purchased from a local supermarket considering different well-known brands and certified by the Consejo Regulador del Tequila (CRT). Different samples share one or more characteristics (a complete description of the set is shown in Table 1).

Table 1.
Sample subdivision according to properties of interest.
2.2. Electronic Eye Design General Features
The EE designed prototype is integrated as a portable system, smoothly operated as a PC peripheric. The light source with which the system operates is based on a Light-Emitting Diode (LED), positioned in a centered zenith plane to improve accuracy and image acquisition (this position is widely used for samples with flat surfaces) [7]. There is a channel to place the sample to be analyzed and a CCD sensor to acquire digital images. The data’s control and processing are carried out through routines programmed in a small single-board computer that interacts with the user by a digital display. A general diagram of the device is shown in Figure 2.
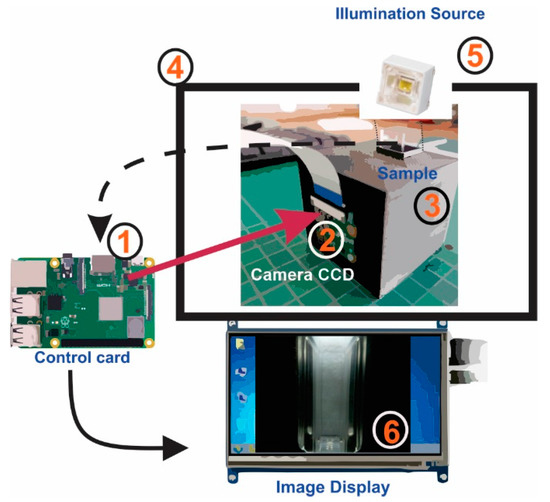
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of EE system for digital image measurements of Tequila samples. 1: Control card (Raspberry 3B+); 2: Digital camera CCD v2 Raspberry; 3: Fixed holder and cuvette; 4: Closed box for light control; 5: LED; 6: Image Display 7″.
2.3. Experimental
Some steps are necessary to operate the EE system. First, seven UV cuvettes are filled with 1 mL of each Tequila sample and one cuvette with the same volume of blank solution (distilled water). Figure 3 shows the result of the described process. The first sample to be measured corresponds to the blank solution in order to establish a reference signal. Afterward, the cuvettes containing different Tequila samples are measured one by one. Image capture readings are recorded using the designed Python-based manual control platform.

Figure 3.
(a) Commercial Tequila bottles; (b) set of samples prepared for analysis.
During each measurement, the lighting is always on, while the active Raspberry V2 camera sent the acquired image to the Raspberry Model 3B + development board. The entire procedure to capture a single sample takes around 10 s. Five subsequent tests with ten repetitions were carried out separately for each sample to observe the repeatability and reproducibility measures.
From the captured information, the RGB intensity histograms for each sample were obtained, in addition to the blank solution. Finally, the experimental absorbance value is obtained in terms of RGB intensity. Since the variation is minimal in the calculated absorbance values for each repetition of the experimental phase, it was decided to report only the average value. All calculations were made considering the 8-bit pixel value format.
2.4. Apparatus and Software
Digital images were obtained with the designed EE system under controlled light using a white 2xLED (model LYA-L29; Huawei Smartphones®) and a digital camera (Raspberry Pi Camera Module v2) with a Sony IMX219 8-megapixel sensor. They were controlled using a Raspberry Pi B Model 3+ with Python 2.7 software. Samples were placed in disposable plastic cuvettes (BRAND, UV-cuvettes) free of dust and dirt to obtain trustworthy images. The cuvettes’ filling volume has a range of 1.5 to 3.0 mL, with external dimensions of 4.5 mm × 23 mm that fits in a holder box that was located at a fixed distance (3 cm) from the camera focal plane. All digital images were processed offline to obtain RGB-data using MATLAB® 2018b (MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA).
2.5. Image Acquisition
Three hundred fifty Tequila images were captured (50 photos for each tequila sample). Each image was captured by the camera CCD Raspberry V2 and saved as an 8-bit JPG format on the Raspberry model 3B+ memory, the average size per image is 2.7 MB (8 Megapixels resolution, focus of f/2, 2592 × 1944 pixels). It was monitored during all experimental stages that the chassis remained closed during image capture, avoiding external light to get good quality images.
The white LED light source is placed at a zenith angle of the sample, where it is covered with white absorbent paper to avoid discrepancies with the lighting. The Raspberry 3B + card controls the camera v2. When the camera is turned on, the image is acquired and stored while displayed on the system screen. Subsequently, a preprocessing task is carried out, which consist on select and crop the region of interest (ROI). All images cropped were saved as a separate file with a constant pixel size (1244 × 231 pixels).
Considering that the obtained images are true-color images, it is possible to represent them as 3D matrixes associated with red, green, and blue components [37,38]. The key steps followed for the EE acquisition and elaboration of the regions RGB images are illustrated in the right side of Figure 4.
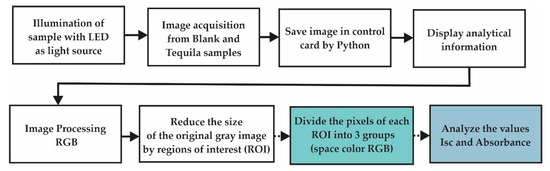
Figure 4.
A generalized block diagram of acquisition and identification of image processing EE.
2.6. Digital Image Analysis
When light passes through the sample, some of the light is absorbed [39,40]. Considering this phenomena, the response of the EE system can be modeled as shown in (1) where Aλ is the absorbance governed by the Lambert-Bee law [41], where is the intensity incident on the solution, is the intensity that comes out of the sample, λ is the wavelength of the applied light, C is the concentration of the absorbent sample , b is the optical path (thickness of the cell) and ε is the molar absorptivity coefficient.
This law expresses the proportional relationship between the absorbance and the concentration of certain compounds present in the sample under analysis. This equation represents a crucial element in evaluating the sample’s absorbance; therefore, it was part of the implemented algorithms for image processing in the MATLAB®.
Experimentally, once a beam of light passes through the cuvette of transparent material containing the sample, the intensity of that light will be absorbed, some will be reflected, and some will be transmitted. This way, it is possible to compare the transmitted intensity of a standard or blank solution and the interested sample’s transmitted intensity. This procedure allows not only the system calibration but also the obtaining of an experimental absorbance, as shown below in (2):
In order to complete the Tequila samples’ characterization, it was considered to use the average surface color index () for RGB space to describe the changes in color intensity and turbidity on the surface of a sample [42]. Due to a digital image is a two-dimensional collection of data, three values associated with vectors R, G, and B for each pixel, mean values can be calculated for the same phase and, in consequence, a total vector can be calculated to describe the entire surface. For a surface equal to one pixel, () is given by:
where is a magnification factor used to increase the numerical value of (here, use to in order to obtain values in the 0 - 100 scale) R, G and B are the magnitudes of vectors , and , respectively.
3. Results
The selected ROI is automatically defined and fixed for all analyzed sample images. The ROI was chosen considering the UV-Vis viewing window of the cuvette. In this way, the region of interest and its relative position regarding the sample support is always constant. Figure 5 shows three original images captured from some representative samples; the black dotted lines within the cuvette image denote the selected ROI, as well as the RGB intensity histogram associated with it. Furthermore, it can be seen in the histogram graphs that the color components are very close to each other, especially the green and blue ones. The three components reach a maximum intensity value of 255 (along the x-axis in graph).
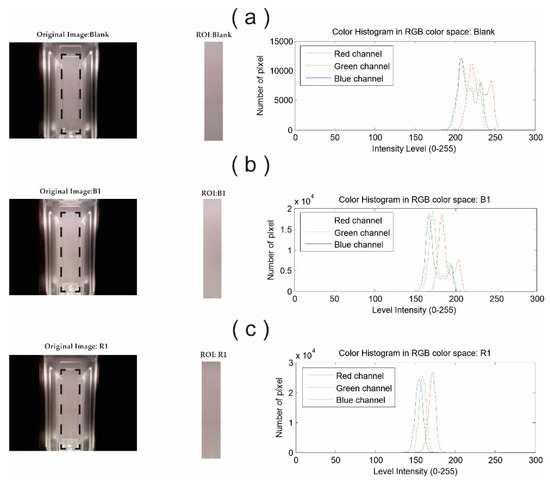
Figure 5.
Representative images of (a) Blank solution, (b) Blanco Tequila and (c) Reposado Tequila samples. From left to right you can see image captured by EE, ROI region and RGB intensity histogram.
Since the RGB model is the most common method used to detect color variations, this work was employed to detect color variations in Tequila samples. For this purpose, the images acquired were organized as a matrix 50 × 21, where the rows correspond to the total number of repetitions (5 tests with 10 repetitions for each test), and the columns represent the seven Tequila samples analyzed by triplicate. The RGB histogram was obtained from each element of the matrix and the average of the R, G and B components was associated with the experimental absorbance through of Equation (2). The evaluated absorbance values from each analyzed sample are shown in Table 2. Likewise, it can be observed that there is a distinction of maximum absorbance by the hue of the color sample when compared with the RGB components.

Table 2.
Absorbance values.
Figure 6 shows the absorbance with the dispersion, where the Blanco tequilas labeled as B1 and B2 have an absorbance value below 0.1. On the other hand, Reposado tequilas show an absorbance greater than 0.1; in particular, the sample labeled as R4 has the highest absorbance for the seven tequilas analyzed.

Figure 6.
Absorbance of analyzed samples.
To ensure that the internal lighting conditions do not affect the homogeneity of color (due to shadows or flashing reflections) in the sample, a validation of the homogeneous color distribution was carried out employing the Surface Color Index [41].
The changes in the RGB components indicate variations of color, which are associated with the composition of the sample. The vectors R, G, and B are the combination of values required to define the resultant vector’s magnitude in RGB space. In the case of digital images, the values of R, G and B are integers and range from 0 to 255, which allows generating 16,777,216 colors, where the color white is formed with the three primary colors at their maximum value (255, 255, 255). It is possible to identify the two analyzed Tequilas (Blanco and Reposado) by associating it with the .
Table 3 indicates the color index data for each sample of Tequila, and Figure 7 represents graphically the distribution for the seven Tequila samples analyzed. It is possible to find similarities in the Figure 6 and Figure 7, due to the absorbance and Surface Color Index have a similar relation in the Tequila samples. Less value in Blanco Tequilas and high values for Reposado Tequilas.

Table 3.
Surface color index intensity.
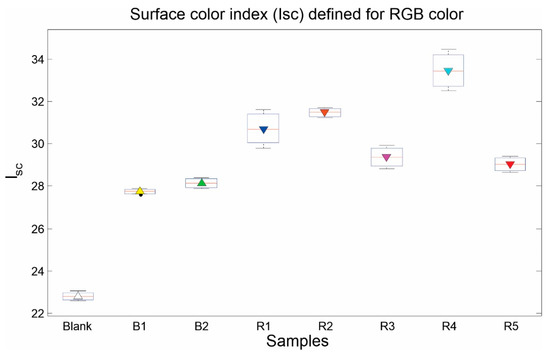
Figure 7.
Surface color index () of analyzed samples.
4. Discussion
Seven different kinds of Tequila and one sample of distilled water as blank were tested with the EE device. Once all sample images were acquired as Section 2.5 described, the ROI of the different samples was decomposed in its RGB components and the number of pixels were associated with the RGB level intensities.
The horizontal axis is divided into three imaginary zones, where the RGB histogram is plotted at the core; if the histogram is shifted to the left side in the horizontal axis provides information about the shadows in the image. The central zone represents the areas of medium luminosity, and the histogram shifted to the right side indicates the light areas at 100%. Figure 5 shows the blank sample’s histogram, where the three components have an approximate value of 255; these data allow to identify full luminosity in the EE system.
From the matrix 50 × 21, the values of the RGB components obtained were proceeded to calculate the . The value obtained allows validating the proposed methodology’s capacity by showing the possibility of discriminating different samples based on their magnitude. In this way, it was to distinguish between Blanco and Reposado Tequila samples by their color variation. Mathematically, value is represented as the ratio of the quotient between a factor and the root of the sum of the image’s RGB components.
Although the discrimination of the main groups of tequilas can be carried out based on the values of absorbance or the Surface Color Index, the results encourage carrying out individual discrimination of samples using some artificial intelligence tools such as artificial neural networks (ANN) or support vector machines (SVM). Both models could be fed with the color parameters obtained in order to build simple classifiers with two input parameters with linear/non-linear mapping to the output. Future experimental stages should be considered to increase the number of analyzed to strengthen the classification process and take advantage of these models’ generalization capability.
5. Conclusions
The absorbance values and the Surface Color Index were employed as quantitative color characteristics based on the RGB model, used to describe the variations of color in the sample. The quantitative color characteristics based on image analysis show sensibility to detect coloration changes from apparently homogeneous samples. The results suggest that image analysis employing quantitative color characteristics can identify Blanco and Reposado Tequila samples. Finally, the absorbance and the Surface Color Index show a linear trend; in the absence of color, the value of absorbance and is minimal and increases for colored samples. Using the developed EE, it was possible to differentiate between the two kinds of Tequila samples with a portable and low-cost system.
Author Contributions
All the authors contributed equally to this work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to express their gratitude to the Mexican National Council of Science and Technology (CONACyT) for the financial support and Ph.D. fellowship for Anais Gomez.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Consejo Regulador del Tequila. Available online: https://www.crt.org.mx/index.php/en/pages-2/proteccion-del-tequila-a-nivel-internacional (accessed on 12 October 2020).
- Norma Oficial Mexicana. In NOM-006-SCFI-2012. 2012. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwjNitD-05rtAhXSIqYKHfFKD_IQFjAAegQIBBAC&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.dof.gob.mx%2Fnota_detalle.php%3Fcodigo%3D5282165&usg=AOvVaw3bdv7GSVb4Wt2Fm0dxYk5x (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Electronic Code of Federal Regulations. In Title 27, 5.22(g) Class 7; Agave Spirits. 1973. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/cgi-bin/text-idx?c=ecfr;sid=79589a2ef2d093ed0b73152fc7935f1b;rgn=div5;view=text;node=27%3A1.0.1.1.2;idno=27;cc=ecfr (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Council of the European Union. Agreement between the European Community and the United Mexican States on the Mutual Recognition and Protection of Designations for Spirit Drinks; Council of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva-Rodríguez, S.J.; Rodríguez-Garay, B.; Prado-Ramírez, R.; Gschaedler, A. Tequila: Raw Material, Classification, Process, and Quality Parameters. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Caballero, B., Finglas, P.M., Toldrá, F., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado-Jaramillo, N.; Estarrón-Espinosa, M.; Escalona-Buendía, H.; Cosío-Ramírez, R.; Martín-del-Campo, S.T. Volatile compounds generation during different stages of the Tequila production process. A preliminary study. LWT 2015, 61, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Sun, D.-W. Colour measurements by computer vision for food quality control—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.F.S.; Leta, F.R. Applications of computer vision techniques in the agriculture and food industry: A review. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 235, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, G.; Calvini, R.; Pigani, L.; Foca, G.; Vasile Simone, G.; Antonelli, A.; Ulrici, A. Electronic eye for the prediction of parameters related to grape ripening. Talanta 2018, 186, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, G.; Calvini, R.; Foca, G.; Ulrici, A. Automated quantification of defective maize kernels by means of Multivariate Image Analysis. Food Control 2018, 85, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Sun, D.W. Food colour measurement using computer vision. In Instrumental Assessment of Food Sensory Quality; Kilcast, D., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Chen, H.; Yu, Y.; Shen, C.; Fu, H.; She, Y. Colorimetric sensor array based on silver deposition of gold nanorods for discrimination of Chinese white spirits. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 320, 128256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, K.D.; Suarez, W.T.; dos Reis, M.F.; de Oliveira Krambeck Franco, M.; Moreira, R.P.L.; dos Santos, V.B. A digital image method of spot tests for determination of copper in sugar cane spirits. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 185, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Duan, J.; Zou, X.; Lin, G.; Song, S.; Ji, B.; Yang, Z. Banana detection based on color and texture features in the natural environment. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 167, 105057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, X.; Wang, Q.; He, X.; Zhang, C.; Huang, W. On line detection of defective apples using computer vision system combined with deep learning methods. J. Food Eng. 2020, 286, 110102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, A.; Bansal, A. Fruits and vegetables quality evaluation using computer vision: A review. J. King Saud Univ. Comp. Inf. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gong, L.; Zhou, B.; Huang, Y.; Liu, C. Detecting tomatoes in greenhouse scenes by combining AdaBoost classifier and colour analysis. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 148, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, C. A multimodal machine vision system for quality inspection of onions. J. Food Eng. 2015, 166, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xiong, J.; Guo, W.; Bu, R.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Lin, R. Colored rice quality inspection system using machine vision. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 88, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebatsion, H.K.; Paliwal, J.; Jayas, D.S. Automatic classification of non-touching cereal grains in digital images using limited morphological and color features. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2013, 90, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasevic, I.; Tomovic, V.; Milovanovic, B.; Lorenzo, J.; Đorđević, V.; Karabasil, N.; Djekic, I. Comparison of a computer vision system vs. traditional colorimeter for color evaluation of meat products with various physical properties. Meat Sci. 2019, 148, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinderup, C.H.; Dahl, A.; Jensen, K.; Carstensen, J.M.; Conradsen, K. Comparison of a multispectral vision system and a colorimeter for the assessment of meat color. Meat Sci. 2015, 102, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowlati, M.; Mohtasebi, S.S.; Omid, M.; Razavi, S.H.; Jamzad, M.; De La Guardia, M. Freshness assessment of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) by machine vision based on gill and eye color changes. J. Food Eng. 2013, 119, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, M.Ö.; Alçiçek, Z. Use of polarized light in image analysis: Application to the analysis of fish eye color during storage. LWT 2015, 60, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, M.O.; Misimi, E.; Ayvaz, Z. Quality Evaluation of Seafoods. In Computer Vision Technology for Food Quality Evaluation, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 243–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leme, D.S.; da Silva, S.A.; Barbosa, B.H.G.; Borém, F.M.; Pereira, R.G.F.A. Recognition of coffee roasting degree using a computer vision system. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 156, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.P.; Corrales, D.C.; Aubertot, J.N.; Corrales, J.C. A computer vision system for automatic cherry beans detection on coffee trees. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 136, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Qi, Y.; Wang, C.; Wan, X. Show me the color in your mind: A study of color-flavor associations in virtual reality. Food Qual. Prefer. 2020, 85, 103969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Xu, W.; Chen, Q. Determination of tea polyphenols in green tea by homemade color sensitive sensor combined with multivariate analysis. Food Chem. 2020, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buratti, S.; Malegori, C.; Benedetti, S.; Oliveri, P.; Giovanelli, G. E-nose, e-tongue and e-eye for edible olive oil characterization and shelf life assessment: A powerful data fusion approach. Talanta 2018, 182, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apetrei, C.; Apetrei, I.M.; Villanueva, S.; de Saja, J.A.; Gutierrez-Rosales, F.; Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L. Combination of an e-nose, an e-tongue and an e-eye for the characterisation of olive oils with different degree of bitterness. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 663, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, C. On the changing colour of food & drink. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, F.; Dejmek, P.; Aguilera, J.M. Calibrated color measurements of agricultural foods using image analysis. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2006, 41, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C. Electronic eye for food sensory evaluation. In Evaluation Technologies for Food Quality; Zhong, J., Wang, X., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Hipatl, C.; Muñoz-Aguirre, S.; Muñoz-Guerrero, R.; Castillo-Mixcóatl, J.; Beltrán-Pérez, G.; Gutiérrez-Salgado, J.M. Optical system based on a CCD camera for ethanol detection. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2013, 24, 105003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitán-Vallvey, L.F.; López-Ruiz, N.; Martínez-Olmos, A.; Erenas, M.M.; Palma, A.J. Recent developments in computer vision-based analytical chemistry: A tutorial review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 899, 23–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, C. Chapter Four—Color. In Information Visualization, 4th ed.; Ware, C., Ed.; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 95–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, D.; Valdez, L.F.; Gutiérrez Salgado, J.M.; Marty, J.L.; Muñoz, R. Colorimetric Analysis of Ochratoxin A in Beverage Samples. Sensors 2016, 16, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, A.I.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Muñoz, R. Design of an optical portable system for detection of pH. In Proceedings of the 2018 Global Medical Engineering Physics Exchanges/Pan American Health Care Exchanges (GMEPE/PAHCE), Porto, Portugal, 19–24 March 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Anh Bui, D.; Hauser, P.C. Absorbance measurements with light-emitting diodes as sources: Silicon photodiodes or light-emitting diodes as detectors? Talanta 2013, 116, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, M.; Diamond, D. Absorbance based light emitting diode optical sensors and sensing devices. Sensors 2008, 8, 2453–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palencia, M.; Lerma, T.; Palencia, V. Description of fouling, surface changes and heterogeneity of membranes by color-based digital image analysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 510, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).