2D Nanomaterial, Ti3C2 MXene-Based Sensor to Guide Lung Cancer Therapy and Management †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sensing Material Synthesis and Cell Lines Preparation
2.1.1. Ti3C2 Nanomaterial-Based Sensor Preparation
2.1.2. Cancer Cell Lines and Materials
2.1.3. Preparation of Cell Samples
2.1.4. Xenografted Lung Tumor Model on Nude Mice
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Normal Cells
2.2.2. A549 lung Cancer Cells
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Observation from the Non-Tumerogenic Sample Graph
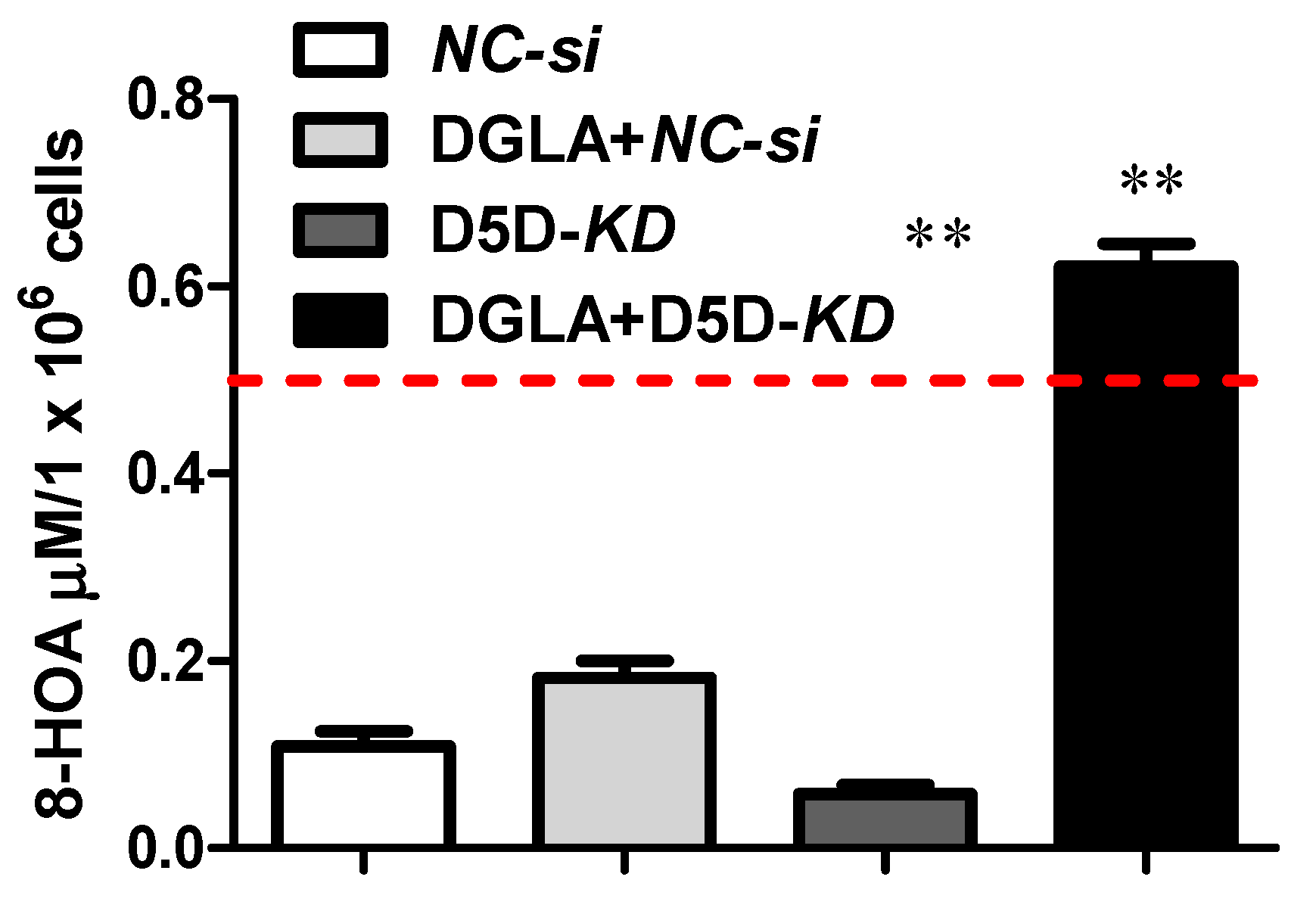
3.2. Observation from the CARCINOGENIC Samples (1st Trial)
4. Conclusions and Discussion
References
- Cancer. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Small Cell Lung Cancer—Cancer Therapy Advisor. Available online: https://www.cancertherapyadvisor.com/home/decision-support-in-medicine/imaging/small-cell-lung-cancer/ (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Molina, J.R.; Yang, P.; Cassivi, S.D.; Schild, S.E.; Adjei, A.A. Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LTorre, A.; Siegel, R.L.; Jemal, A. Lung cancer statistics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 893, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Asbestos Lung Cancer: Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment. Available online: https://www.asbestos.com/cancer/lung-cancer/ (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Deadliest Cancers Receive the Least Attention. Available online: https://www.asbestos.com/featured-stories/cancers-that-kill-us/ (accessed on 11 October 2020).
- Cruz, C.S.D.; Tanoue, L.T.; Matthay, R.A. Lung Cancer: Epidemiology, Etiology, and Prevention. CME 2011, 32, 605–644. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H. Chemotherapy for lung cancer in the era of personalized medicine. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. (Seoul) 2019, 82, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Jolly, S.; Quarshie, W.O.; Kapadia, N.; Vigneau, F.D.; Kong, F.M. Modern radiation further improves survival in non-small cell lung cancer: An analysis of 288,670 patients. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, A.B.; Dubinett, S.M. COX-2 inhibition and lung cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2004, 31, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, O.M.; Abkenari, S.; Tong, Z.; Tedman, A.; Huerta-Yepez, S. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Lung Cancer: Nutrition or Pharmacology? Nutr. Cancer 2020, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Sui, C.; Meng, F.; Ma, P.; Jiang, Y. The omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid inhibits proliferation and progression of non-small cell lung cancer cells through the reactive oxygen species-mediated inactivation of the PI3K /Akt pathway. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouremenos, K.A.; Johansson, M.; Marriott, P.J. Advances in gas chromatographic methods for the identification of biomarkers in cancer. J. Cancer 2012, 3, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer—Diagnosis and Treatment—Mayo Clinic. Available online: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cancer/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20370594 (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Problems with MRI for Cancer Diagnosis. Available online: https://www.ctoam.com/precision-oncology/why-we-exist/standard-treatment/diagnostics/mri/ (accessed on 12 October 2020).
- The Pros and Cons of PET/CT Scans | Independent Imaging. Available online: https://www.independentimaging.com/the-pros-and-cons-of-pet-ct-scans/ (accessed on 12 October 2020).
- Fred, H.L. Drawbacks and limitations of computed tomography: Views from a medical educator. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2004, 31, 345–348. [Google Scholar]
- Bitencourt, A.G.V.; Graziano, L.; Guatelli, C.S.; Albuquerque, M.L.L.; Marques, E.F. Ultrasound-guided biopsy of breast calcifications using a new image processing technique: Initial experience. Radiol. Bras. 2018, 51, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Endoscopy: Purpose, Procedure, Risks. Available online: https://www.webmd.com/digestive-disorders/digestive-diseases-endoscopy#1 (accessed on 13 October 2020).
- Gas Chromatography. Available online: http://www.chemforlife.org/teacher/topics/gas_chromatography.htm (accessed on 13 October 2020).
- Buszewski, B.; Ligor, T.; Jezierski, T.; Wenda-Piesik, A.; Walczak, M.; Rudnicka, J. Identification of volatile lung cancer markers by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry: Comparison with discrimination by canines. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borer, J.S.; Simon, L.S. Cardiovascular and gastrointestinal effects of COX-2 inhibitors and NSAIDs: Achieving a balance. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Chan, D.; Felix, E.; Cartwright, C. Formation and antiproliferative effect of prostaglandin E3 from eicosapentaenoic acid in human lung cancer cells. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
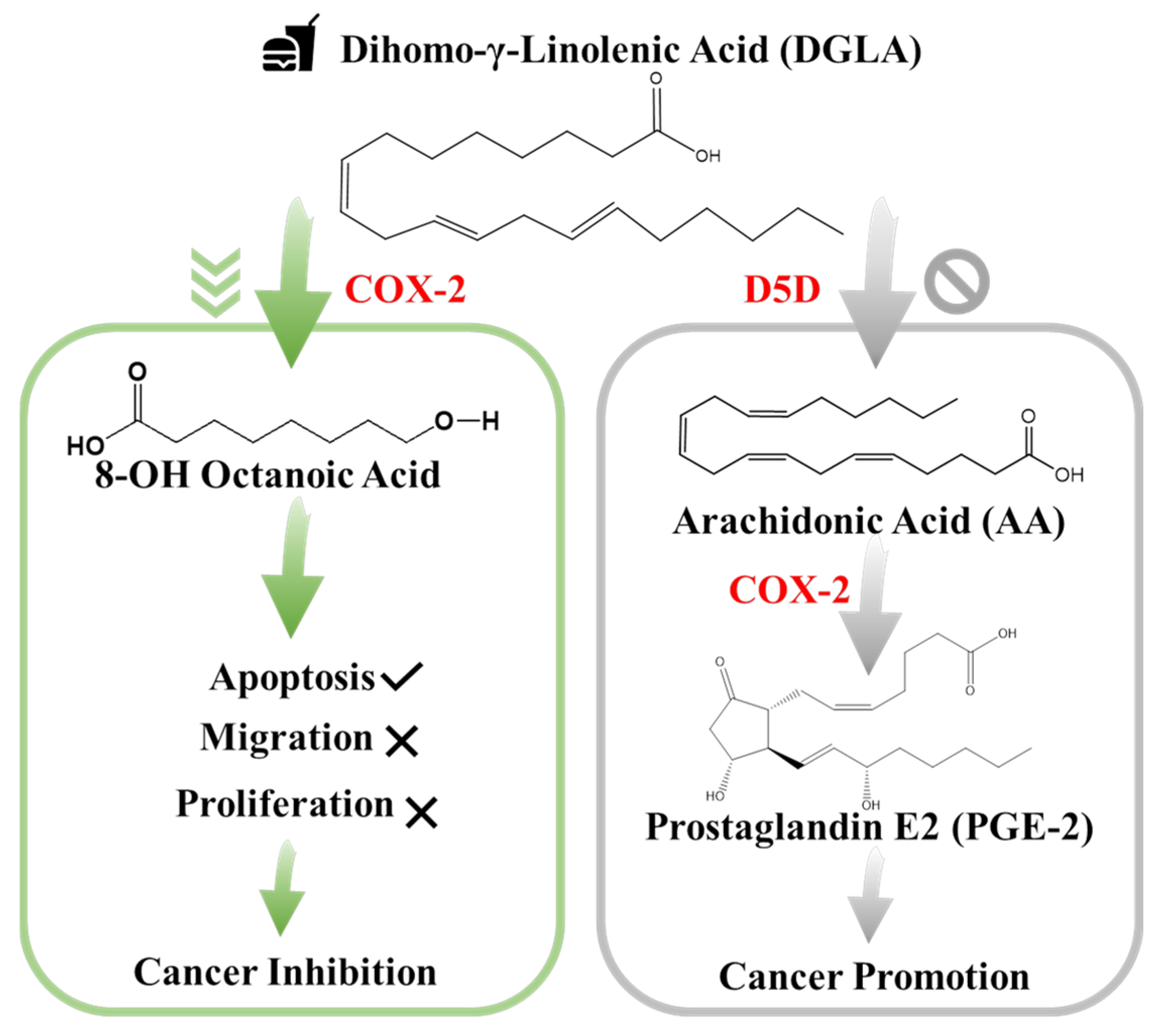
- Xu, Y.; Qi, J.; Yang, X.; Wu, E.; Qian, S.Y. Free radical derivatives formed from cyclooxygenase-catalyzed dihomo-γ-linolenic acid peroxidation can attenuate colon cancer cell growth and enhance 5-fluorouracil’s cytotoxicity. Redox Biol. 2014, 2, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, T.; Yang, L.; He, Y.; Miskimins, K.; Qian, S.Y. Knockdown delta-5-desaturase in breast cancer cells that overexpress COX-2 results in inhibition of growth, migration and invasion via a dihomo-γ-linolenic acid peroxidation dependent mechanism. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Shah, H.; Wang, H.; Shu, D.; Qian, S.Y.; Sathish, V. EpCAM-Targeted 3WJ RNA Nanoparticle Harboring Delta-5-Desaturase siRNA Inhibited Lung Tumor Formation via DGLA Peroxidation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 22, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Shu, D.; Guo, P.; Miskimins, K.; Qian, S.Y. Inhibition of cancer migration and invasion by knocking down delta-5-desaturase in COX-2 overexpressed cancer cells. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H.; Sayyar, Z.; Anarjan, N.; Berenjian, A. Nano-sensors in Food Nanobiotechnology. In Nanobiotechnology in Food: Concepts, Applications and Perspectives; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, W.; Cong, L.; Guo, Z.; Xie, Y.; Wang, L.; Tang, R.; Feng, Q.; Hamada, Y.; et al. Thermo-triggered Release of CRISPR-Cas9 System by Lipid-Encapsulated Gold Nanoparticles for Tumor Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1491–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Tang, L.; Xie, Y.; Xianyu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, P.; Hamada, Y.; Jiang, K.; Zheng, W.; Jiang, X. Gold nanoclusters-assisted delivery of NGF siRNA for effective treatment of pancreatic cancer. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wu, D.; Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Fan, G.; Li, G.; Wu, Y. Effective enrichment and detection of plant growth regulators in fruits and vegetables using a novel magnetic covalent organic framework material as the adsorbents. Food Chem. 2020, 306, 125455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Hossain, M.R.; Johnson, M. High Sensitive Breath Sensor Based on Nanostructured K2W7O22 for Detection of Type 1 Diabetes. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 4399–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, F.; Riegert, S.; Madel, M.; Thonke, K. H2S sensing in the ppb regime with zinc oxide nanowires. Sens. Actuatorsb Chem. 2017, 239, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chu, X.; Wu, M. Detection of H2S down to ppb levels at room temperature using sensors based on ZnO nanorods. Sens. Actuatorsb Chem. 2006, 113, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Majhi, S.M.; Yu, Y.T.; Lee, J.H. Noble metal@metal oxide semiconductor core@shell nano-architectures as a new platform for gas sensor applications. Rsc Adv. 2015, 5, 76229–76248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotcenkov, G.; Brinzari, V.; Cho, B.K. Conductometric gas sensors based on metal oxides modified with gold nanoparticles: A review. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1033–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.L.; Chen, A.T.; Zhang, Q.F.; Cao, G.Z. Room-Temperature Chemiresistive Effect of TiO2—B Nanowires to Nitroaromatic and Nitroamine Explosives. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Sun, H.; Chen, A.; Jang, S.H.; Jen, A.K.Y.; Szep, A. Chemiresistive response of silicon nanowires to trace vapor of nitro explosives. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2628–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Huang, D.; Yang, Z.; Xu, S.; He, G.; Li, X.; Hu, N.; Yin, G.; He, D.; Zhang, L. A Review on Graphene-Based Gas/Vapor Sensors with Unique Properties and Potential Applications. Nano-Micro Lett. 2016, 8, 95–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, K.; Furue, R.; Hayami, S. Recent progress in applications of graphene oxide for gas sensing: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 878, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Wen, J.; Shen, Y.; Lv, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y. Simultaneous Noncovalent Modification and Exfoliation of 2D Carbon Nitride for Enhanced Electrochemiluminescent Biosensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 11698–11701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Cao, X.; Wu, X.; He, Q. Recent Advances in Ultrathin Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6225–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Song, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhu, C.; Du, D.; Wang, S.; Asiri, A.; Lin, Y. Recent advances in emerging 2D nanomaterials for biosensing and bioimaging applications. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidiu, M.; Lukatskaya, M.R.; Zhao, M.Q.; Gogotsi, Y.; Barsoum, M.W. Conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide ‘clay’ with high volumetric capacitance. Nature 2015, 516, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xiang, J.; Liu, B.; Zhou, A.; Liu, R.; Tian, Y. Unique lead adsorption behavior of activated hydroxyl group in two-dimensional titanium carbide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4113–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Koh, H.; Ren, C.E.; Kwon, O.; Maleski, K.; Cho, S.; Anasori, B.; Kim, C.; Choi, Y.; Kim, J.; et al. Metallic Ti3C2Tx MXene Gas Sensors with Ultrahigh Signal-to-Noise Ratio. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, J.; Qifeng, Z.; Danling, W. Titanium carbide MXene: Synthesis, electrical and optical properties and their applications in sensors and energy storage devices. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2019, 9, 184798041882447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhabeb, M.; Maleski, K.; Anasori, B.; Lelyukh, P.; Clark, L.; Sin, S.; Gogotsi, Y. Guidelines for Synthesis and Processing of Two-Dimensional Titanium Carbide (Ti3C2Tx MXene). Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 7633–7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Shah, H.; Zhao, P.; Qian, S.; Sathish, V. New Delta-5-Desaturase Inhibitor Suppress Lung Cancer Progression: A Paradigm Shift on COX-2 Biology in Lung Cancer Treatment. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
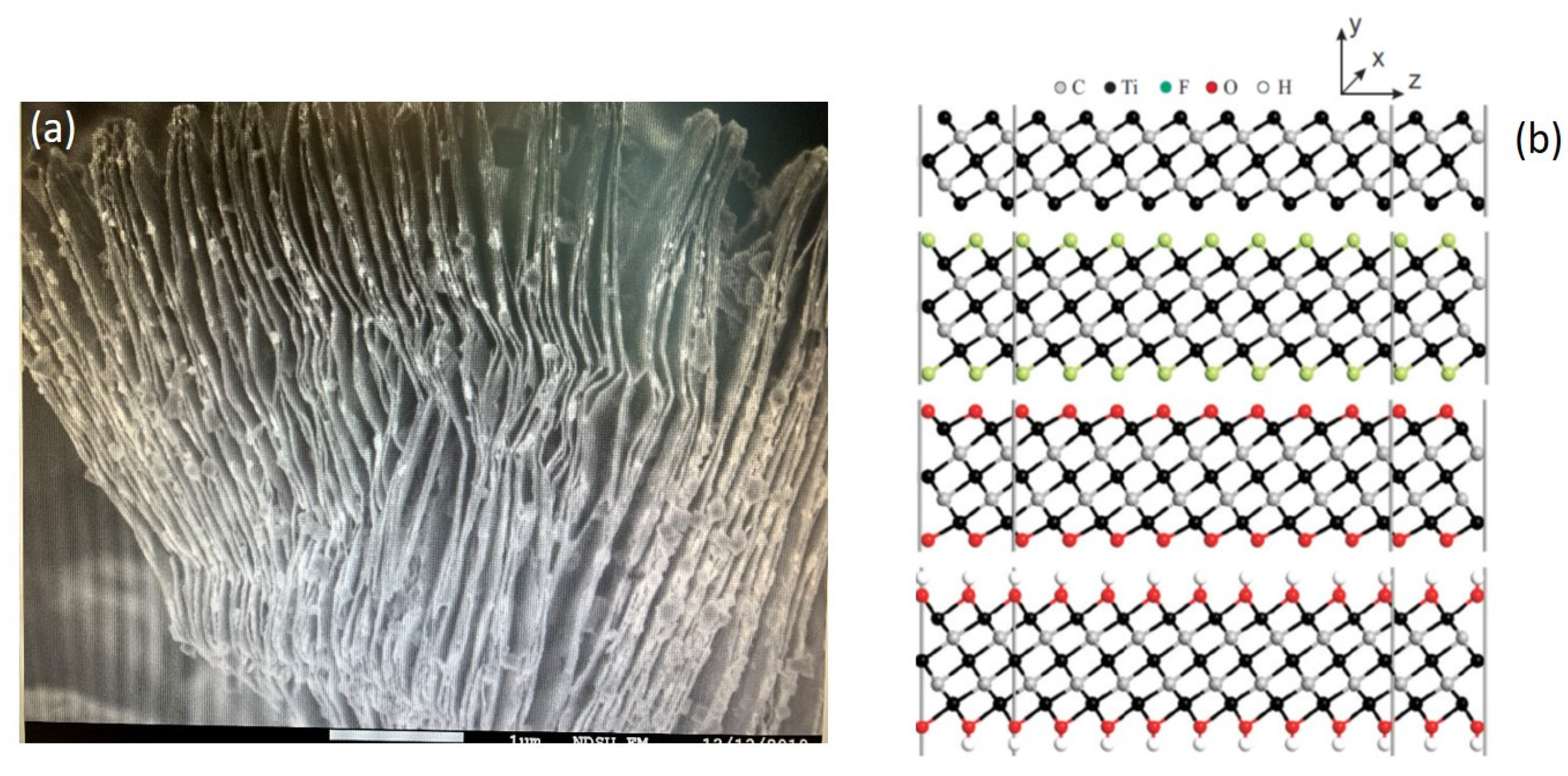
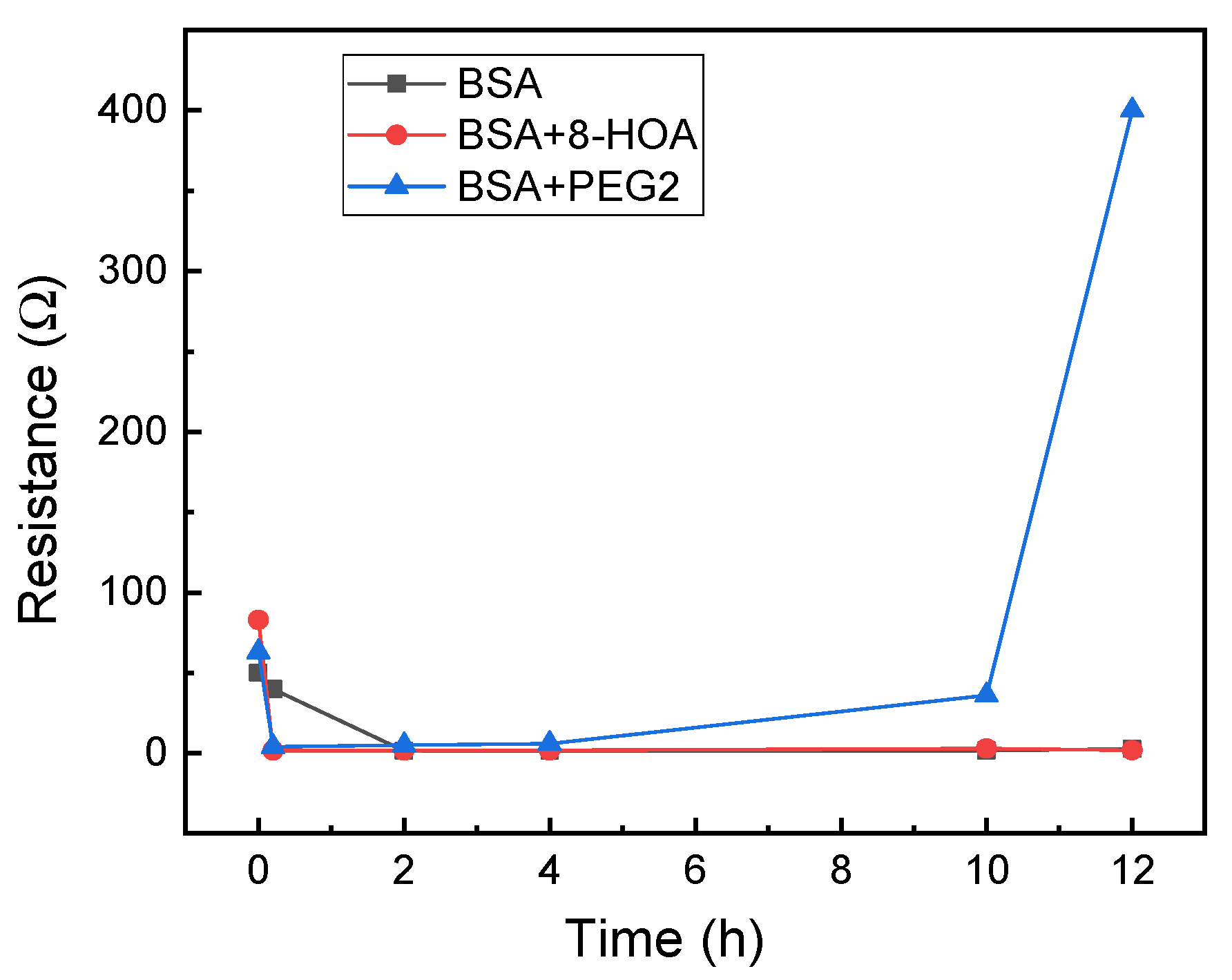

| Sample | Cell | 8-HOA | PGE2 | BSA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 106 BEAS2B | none | none | None |
| 2 | 106 BEAS2B | 0.6 ug/mL | none | None |
| 3 | 106 BEAS2B | none | 6 ug/mL | None |
| 4 | None | none | none | 1 mg/mL |
| Sample | Cell | DGLA | D5Di | 8-HOA | PGE2 | Estimated 8-HOA/PGE2Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 106 A549 | none | none | none | none | Low 8-HOA; low PGE2 |
| 2 | 106 A549 | none | none | 0.6 ug/mL | none | High 8-HOA; low PGE2 |
| 3 | 106 A549 | none | none | none | 6 ug/mL | Low 8-HOA; high PGE2 |
| 4 | 106 A549 | 100 uM | none | none | none | Low 8-HOA; high PGE2 |
| 5 | 106 A549 | none | 10 uM | none | none | Low 8-HOA; low PGE2 |
| 6 | 106 A549 | 100 uM | 10 uM | none | none | High 8-HOA; low PGE2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sadiq, M.; Pang, L.; Johnson, M.; Sathish, V.; Wang, D. 2D Nanomaterial, Ti3C2 MXene-Based Sensor to Guide Lung Cancer Therapy and Management. Proceedings 2020, 60, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECB2020-07055
Sadiq M, Pang L, Johnson M, Sathish V, Wang D. 2D Nanomaterial, Ti3C2 MXene-Based Sensor to Guide Lung Cancer Therapy and Management. Proceedings. 2020; 60(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECB2020-07055
Chicago/Turabian StyleSadiq, Mahek, Lizhi Pang, Michael Johnson, Venkatachalem Sathish, and Danling Wang. 2020. "2D Nanomaterial, Ti3C2 MXene-Based Sensor to Guide Lung Cancer Therapy and Management" Proceedings 60, no. 1: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECB2020-07055
APA StyleSadiq, M., Pang, L., Johnson, M., Sathish, V., & Wang, D. (2020). 2D Nanomaterial, Ti3C2 MXene-Based Sensor to Guide Lung Cancer Therapy and Management. Proceedings, 60(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECB2020-07055






