Detecting and Correlating Aircraft Noise Events below Ambient Noise Levels Using OpenSky Tracking Data †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Current Practice in Aircraft Noise Mapping and Noise Event Monitoring
1.2. Health Impact and Noise Annoyance of Aircraft Operations
1.3. Potential Improvements to Estimate Noise Exposure to Aircraft Operations
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. A Small Introduction to Noise Indicators for Non-Acousticians
2.2. Long-Term High-Quality Noise Measurements (Type 1 Equipment)
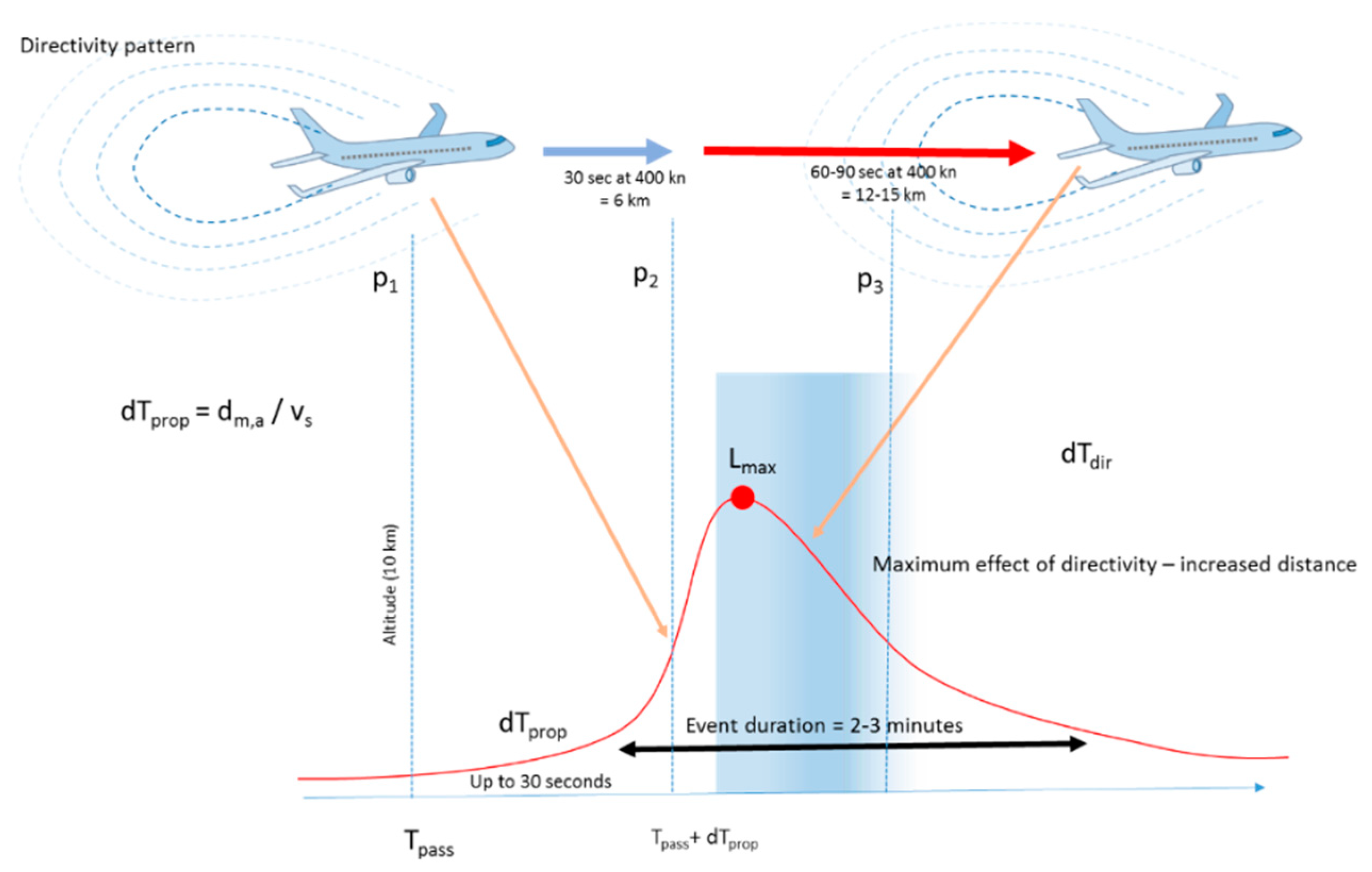
2.3. Long Distance Event Detection Is a Timely Question
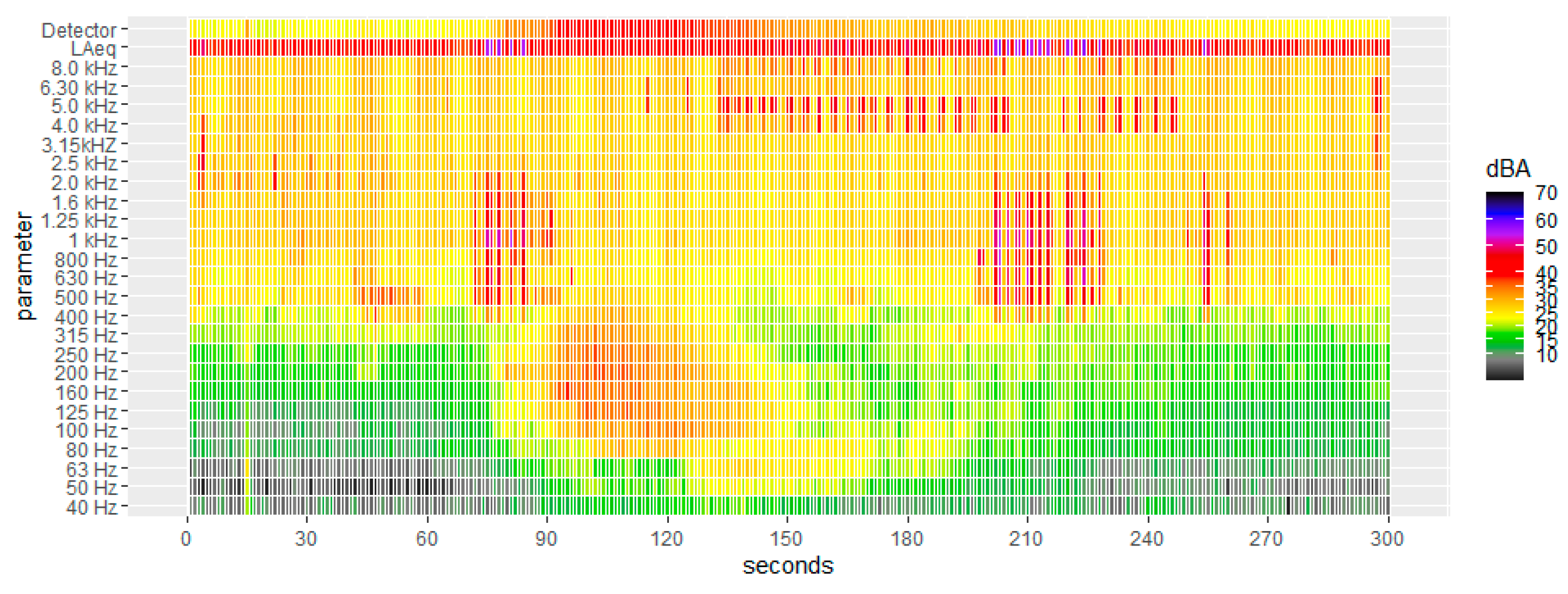
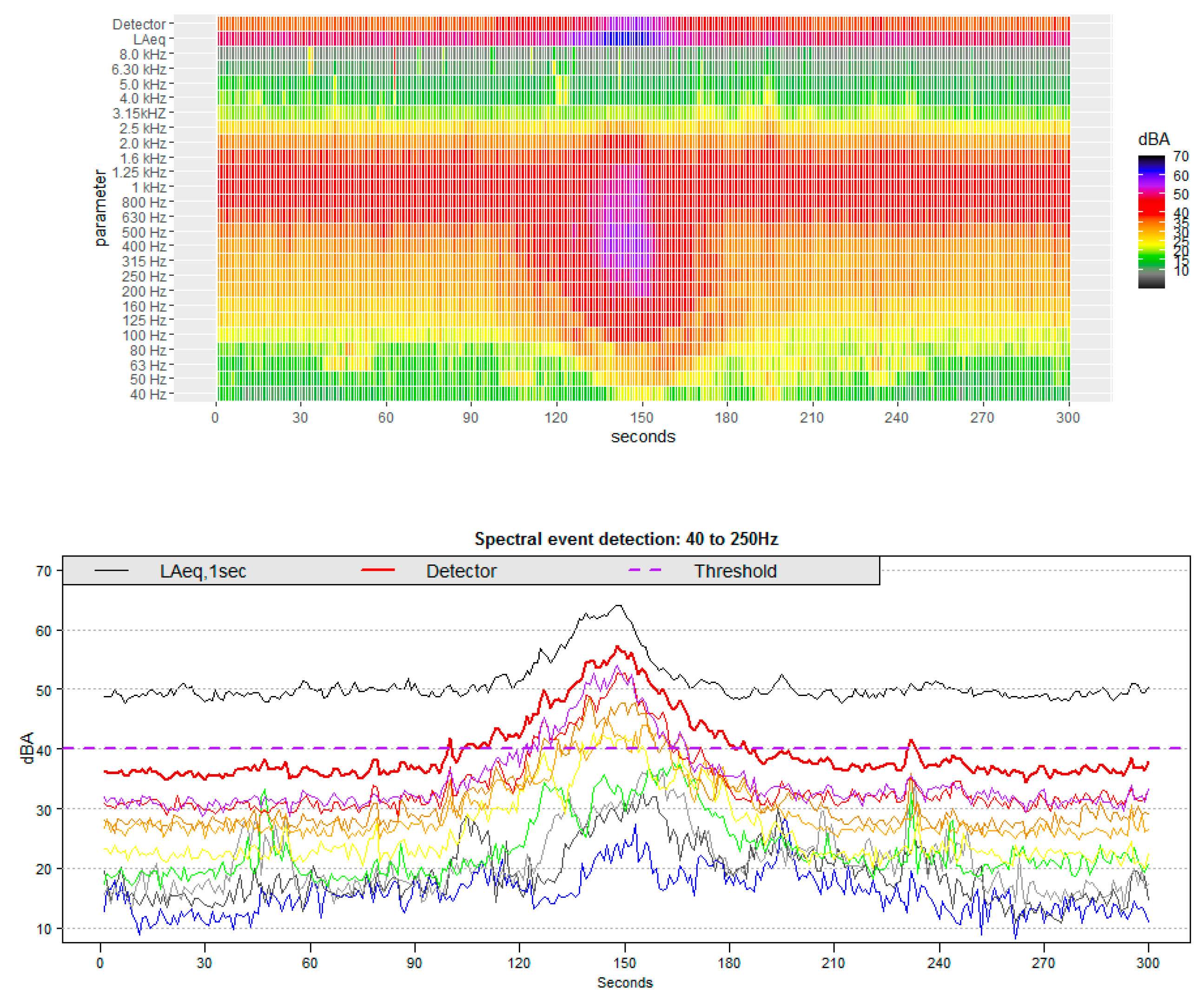
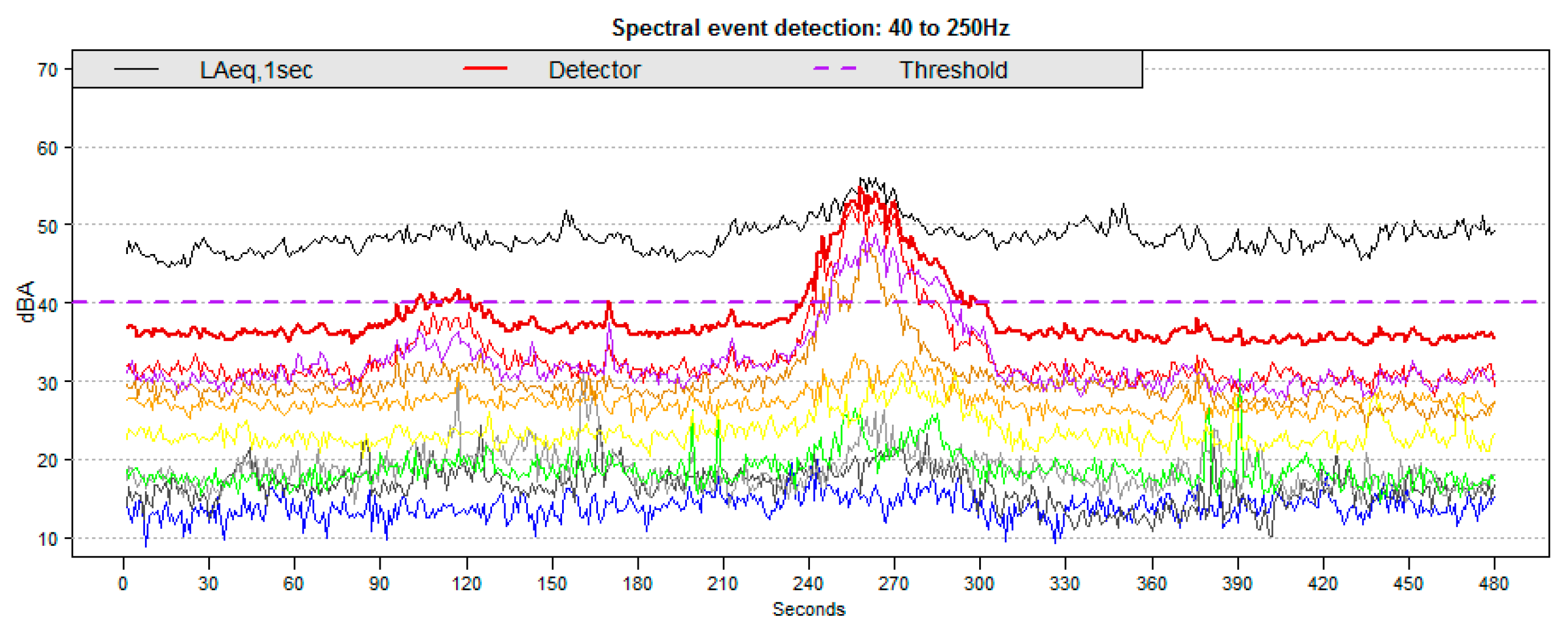
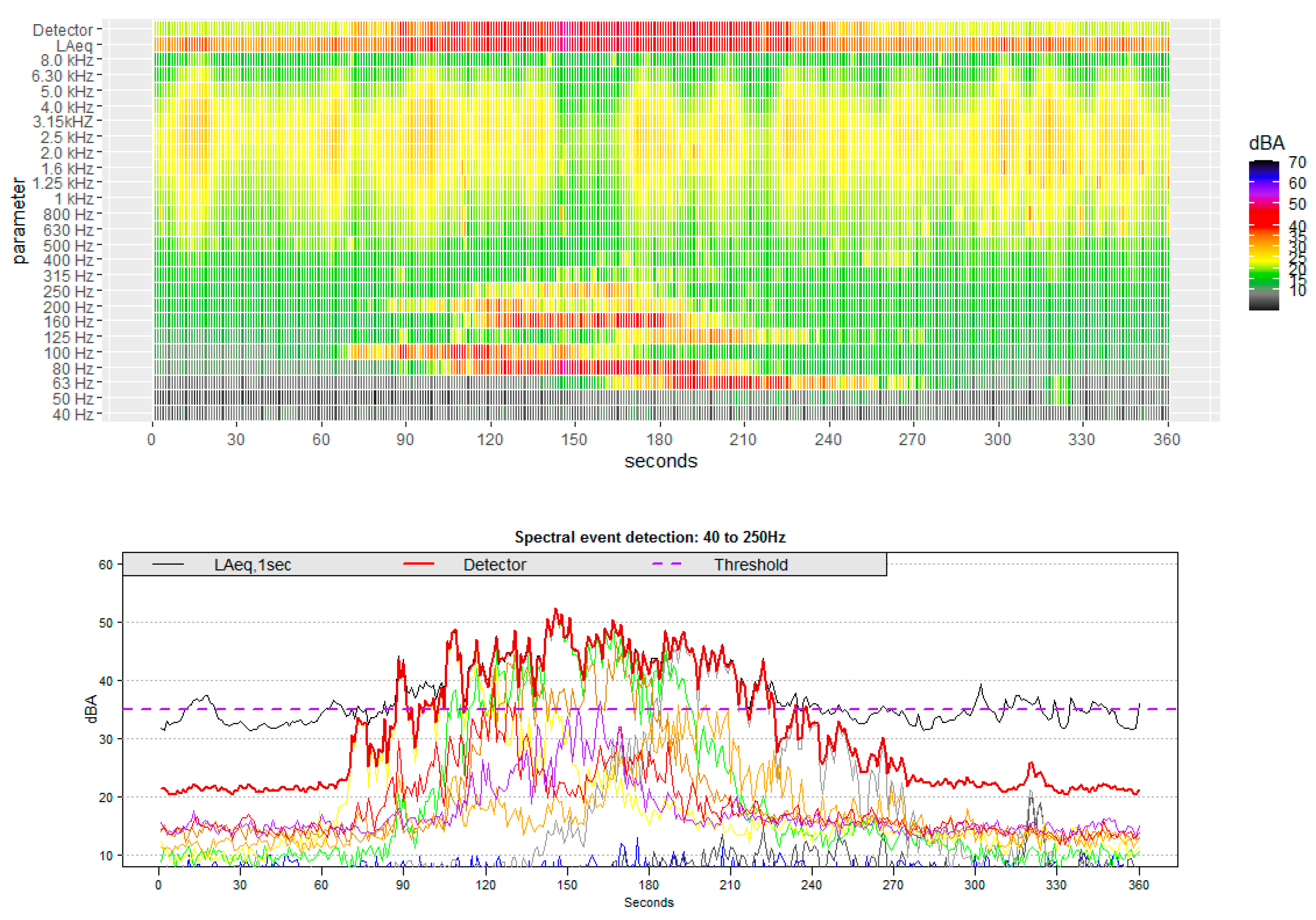
2.4. Event Detection Method
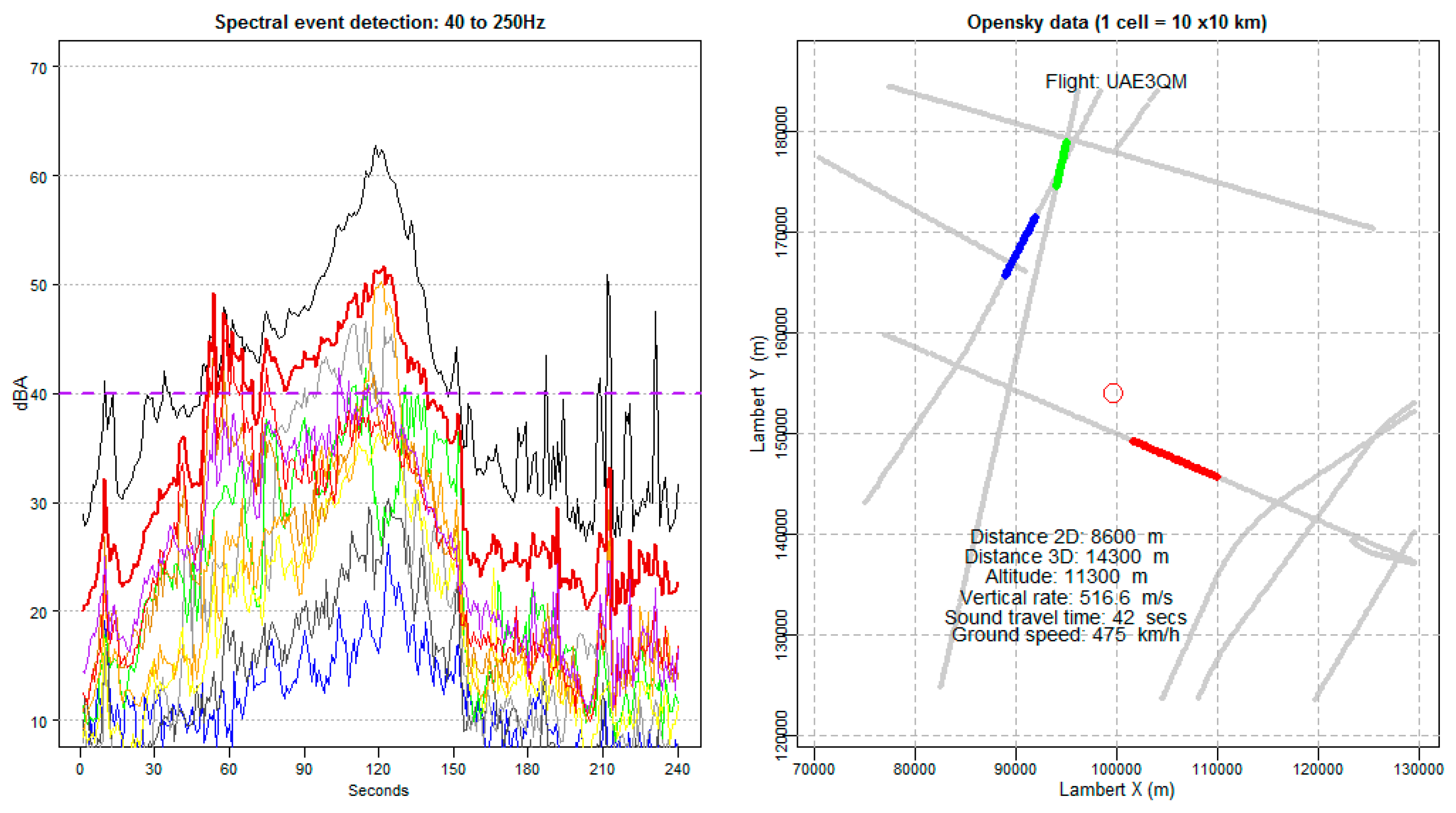
2.5. Flight Correlation Method
2.6. Modeling the Correlated Events
3. Results
3.1. Event Detection
3.2. Flight Correlation
4. Discussion
4.1. General
4.2. Aircraft Noise Emission Classification
4.3. Relevancy for Aircraft Annoyance, Complaints and Health Impact
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Europa, E.U. Directive 2002/49/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 June 2002 Relating to the Assessment and Management of Environmental Noise; Europa EU: Brussels, Belgium, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- EASA. European Aviation Environmental Report 2019; EASA: Cologne, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, C.; Recuero, M.; Ruiz, M. Aircraft noise-monitoring according to ISO 20906. Evaluation of uncertainty derived from the classification and identification of aircraft noise events. Appl. Acoust. 2012, 73, 209–217. [Google Scholar]
- Genesca, M.; Romeu, J.; Pamies, T.; Sanchez, A. Aircraft noise monitoring with linear microphone arrays. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2010, 25, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosin, C.; Barbo, B. Aircraft noise monitoring: Threshold overstepping detection vs. noise level shape and audio pattern recognition detection. Internoise 2013, 2011, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- The Aircraft Noise and Performance (ANP) Database: An International Data Resource for Aircraft Noise Modellers. Available online: https://www.aircraftnoisemodel.org/ (accessed on 1 October 2020).
- WORLD Health Organization. Burden of Disease from Environmental Noise: Quantification of Healthy Life Years Lost in Europe; World Health Organization, Regional Office for Europe: København, Denmark, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Environmental Noise Guidelines for the European Region; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Geluidshinder—Evaluatie van de MIRA Indicatorset. Available online: https://www.milieurapport.be/publicaties/2020/geluidshinder-evaluatie-van-de-mira-indicatorset (accessed on 1 October 2020). (In Dutch).
- Dobruszkes, F.; Efthymiou, M. When environmental indicators are not neutral: Assessing aircraft noise assessment in Europe. J. Air Trans. Manag. 2020, 88, 101861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, M.; Strohmeier, M.; Lenders, V.; Martinovic, I.; Wilhelm, M. Bringing Up OpenSky: A Large-scale ADS-B Sensor Network for Research. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (IPSN), Berlin, Germany, 15–17 April 2014; pp. 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Pietrzko, S.; Hofmann, R.F. Prediction of A-weighted aircraft noise based on measured directivity patterns. Appl. Acoust. 1988, 23, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzko, S.; Bütikofer, R. FLULA-Swiss aircraft noise prediction program. In Proceedings of the Innovation in Acoustics and Vibration, Annual Conference of the Australian Acoustical Society, Adelaide, Australia, 13–15 November 2002; pp. 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zellmann, C.; Wunderli, J.M. Influence of the atmospheric stratification on the sound propagation of single flights. In Proceedings of the INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 16–19 November 2014; Volume 249, pp. 3770–3779. [Google Scholar]
- GitHub. Available online: https://github.com/xoolive/opensky_data (accessed on 1 October 2020).



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dekoninck, L. Detecting and Correlating Aircraft Noise Events below Ambient Noise Levels Using OpenSky Tracking Data. Proceedings 2020, 59, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020059013
Dekoninck L. Detecting and Correlating Aircraft Noise Events below Ambient Noise Levels Using OpenSky Tracking Data. Proceedings. 2020; 59(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020059013
Chicago/Turabian StyleDekoninck, Luc. 2020. "Detecting and Correlating Aircraft Noise Events below Ambient Noise Levels Using OpenSky Tracking Data" Proceedings 59, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020059013
APA StyleDekoninck, L. (2020). Detecting and Correlating Aircraft Noise Events below Ambient Noise Levels Using OpenSky Tracking Data. Proceedings, 59(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020059013



