The Analysis of Bayer Liquor by SPME-GC-MS of Derivatized Organic Poisons †
Conclusions
References
- Maher, Q.E. Structural Determination, Identification and Removal of Bayer Liquor Organic Poisons. Master’s Thesis, Macquarie University, Sydney, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Power, G.; Loh, J. Organic compounds in the processing of lateritic bauxites to alumina part 1: Origins and chemistry of organics in the Bayer process. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 105, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigma-Aldrich, Co. Supelco, Solid Phase Microextraction: Theory and Optimization of Conditions. Bulletin 1998, 923, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Schummer, C.; Delhomme, O.; Appenzeller, B.M.R.; Wennig, R.; Millet, M. Comparison of MTBSTFA and BSTFA in derivatization reactions of polar compounds prior to GC/MS analysis. Talanta 2009, 77, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, G.; Loh, J.S.C.; Wajon, J.E.; Busetti, F.; Joll, C. A review of the determination of organic compounds in Bayer process liquors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 689, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
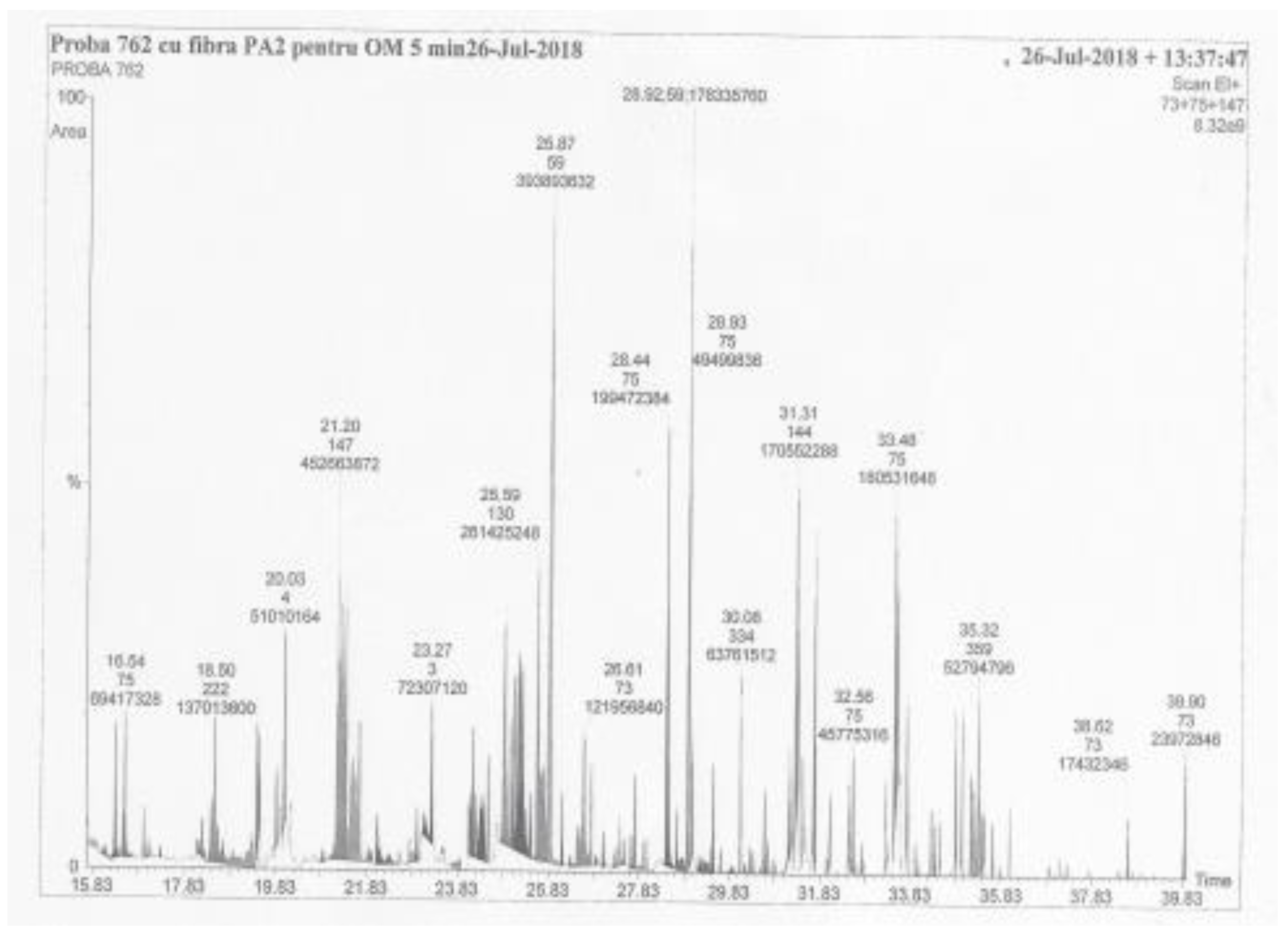
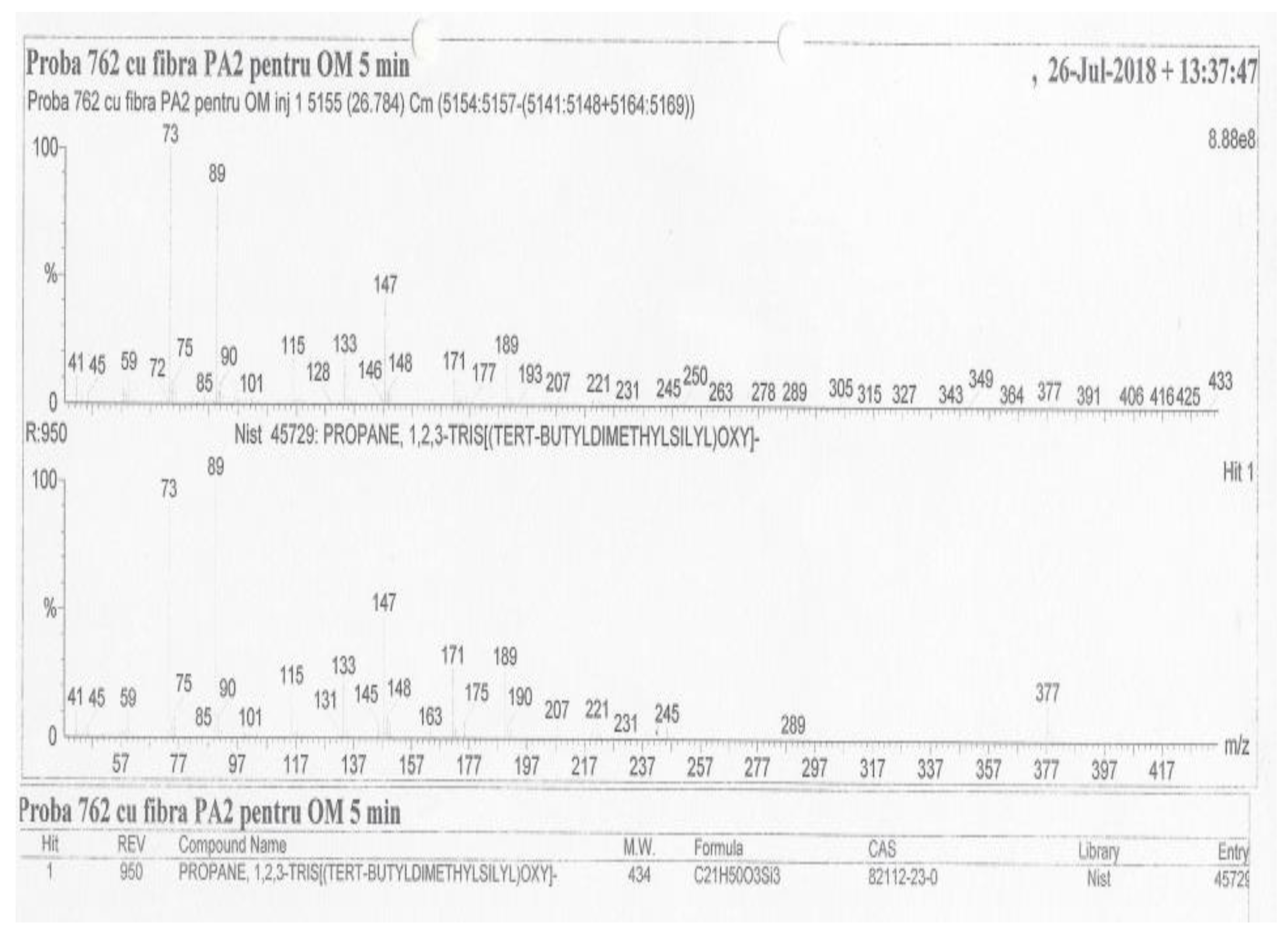
| No. | Name of Components | M | Concentration, (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Propanoic acid, 2-oxo-(pyruvic acid) | 88 | 0.3 |
| 2 | Butanoic acid, 3-methyl-(isovalerianic acid) | 102 | 1.3 |
| 3 | Pentanoic acid, 3-methyl- | 116 | 0.1 |
| 4 | Propandioic acid | 104 | 2.7 |
| 5 | Propanoic acid, 2-hydroxy | 90 | 3.1 |
| 6 | Benzoic acid | 122 | 1.9 |
| 7 | Carboxylic acid, trans-3-(2,2-dichlorvinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane | 208 | 0.7 |
| 8 | Tryptophan | 204 | 1.1 |
| 9 | Succinic acid | 118 | 0.5 |
| 10 | Propantriol (glycerin) | 92 | 0.8 |
| 11 | Acetic acid, 2-hydroxy-2,2-diphenyl-(benzyl acid) | 228 | 0.9 |
| 12 | 5-Nonanol (dibutyl carbinol) | 144 | 0.1 |
| 13 | 2-Methylcyclohexanol | 114 | 0.9 |
| 14 | Octadecanoic acid | 284 | 1.4 |
| 15 | 9,12-Octadecadienoic acid | 280 | 0.3 |
| 16 | Pimaric acid | 302 | 1.1 |
| 17 | Isopimeric acid | 302 | 0.6 |
| 18 | Linolenic acid | 302 | 1.0 |
| 19 | Cyclopropanecarboxylic acid, 3-(2,2-dichlorvinyl)-2,2-dimethyl-, (3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl ester | 390 | 0.3 |
| No. | Name of Components | M | TR (min.) | P (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Propanoic acid, 2-oxo-, trimethylsilyl ester | 160 | 16.50 | 82.7 |
| 2 | Butanoic acid, 3-methyl-tert-butyldimethylsilyl ester | 216 | 16.54 | 91.2 |
| 3 | Pentanoic acid, 3-methyl-tert-butyldimethylsilyl ester | 230 | 18.13 | 90.3 |
| 4 | Propandioic acid, bis (trimethylsilyl) ester | 248 | 19.51 | 89.5 |
| 5 | Propanoic acid, 2-[(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)oxy]-tert-butyldimethylsilyl ester | 318 | 21.37 | 93.3 |
| 6 | Benzoic acid, tert-butyldimethylsilyl ester | 236 | 21.50 | 91.4 |
| 7 | Carboxylic acid, trans-3-(2,2-dichlorvinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane | 322 | 24.50 | 90.4 |
| 8 | N ,N’,O-tris (trimethylsilyl) tryptophan | 420 | 25.00 | 86.2 |
| 9 | Bis (tert-butyldimethylsilyl) succinate | 346 | 25.33 | 85.9 |
| 10 | Propane, 1,2,3-tris[tert-butyldimethylsilyl)oxy]- | 434 | 26.78 | 95.0 |
| 11 | Acetic acid, 2-hydroxy-2,2-diphenyl-tert-butyldimethylsilyl ester | 342 | 29.48 | 85.0 |
| 12 | 5-Nonanol-trimethylsilyl ester | 216 | 30.88 | 87.5 |
| 13 | Silanes, trimeth[(2-methylcyclohexyl)oxy]-, cis- | 186 | 31.45 | 87.6 |
| 14 | Octadecanoic acid, tert-butyldimethylsilyl ester | 398 | 33.76 | 83.8 |
| 15 | 9,12-Octadecadienoic-tert-butyldimethylsilyl ester | 394 | 34.38 | 85.9 |
| 16 | Pimaric acid, trimethylsilyl ester | 374 | 34.84 | 80.8 |
| 17 | Isopimeric acid, trimethylsilyl ester | 374 | 34.97 | 82.4 |
| 18 | Linolenic acid, trimethylsilyl ester | 350 | 35.17 | 82.2 |
| 19 | Cyclopropanecarboxylic acid, 3-(2,2-dichlorvinyl)-2,2-dimethyl-, (3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl ester | 390 | 36.10 | 95.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Badescu, V.; Senin, R. The Analysis of Bayer Liquor by SPME-GC-MS of Derivatized Organic Poisons. Proceedings 2020, 57, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020057101
Badescu V, Senin R. The Analysis of Bayer Liquor by SPME-GC-MS of Derivatized Organic Poisons. Proceedings. 2020; 57(1):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020057101
Chicago/Turabian StyleBadescu, Virgil, and Raluca Senin. 2020. "The Analysis of Bayer Liquor by SPME-GC-MS of Derivatized Organic Poisons" Proceedings 57, no. 1: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020057101
APA StyleBadescu, V., & Senin, R. (2020). The Analysis of Bayer Liquor by SPME-GC-MS of Derivatized Organic Poisons. Proceedings, 57(1), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020057101




