Correlating Spatially Resolved Photoconductivity and Luminescence in Colloidal Quantum Dot Films †
Abstract
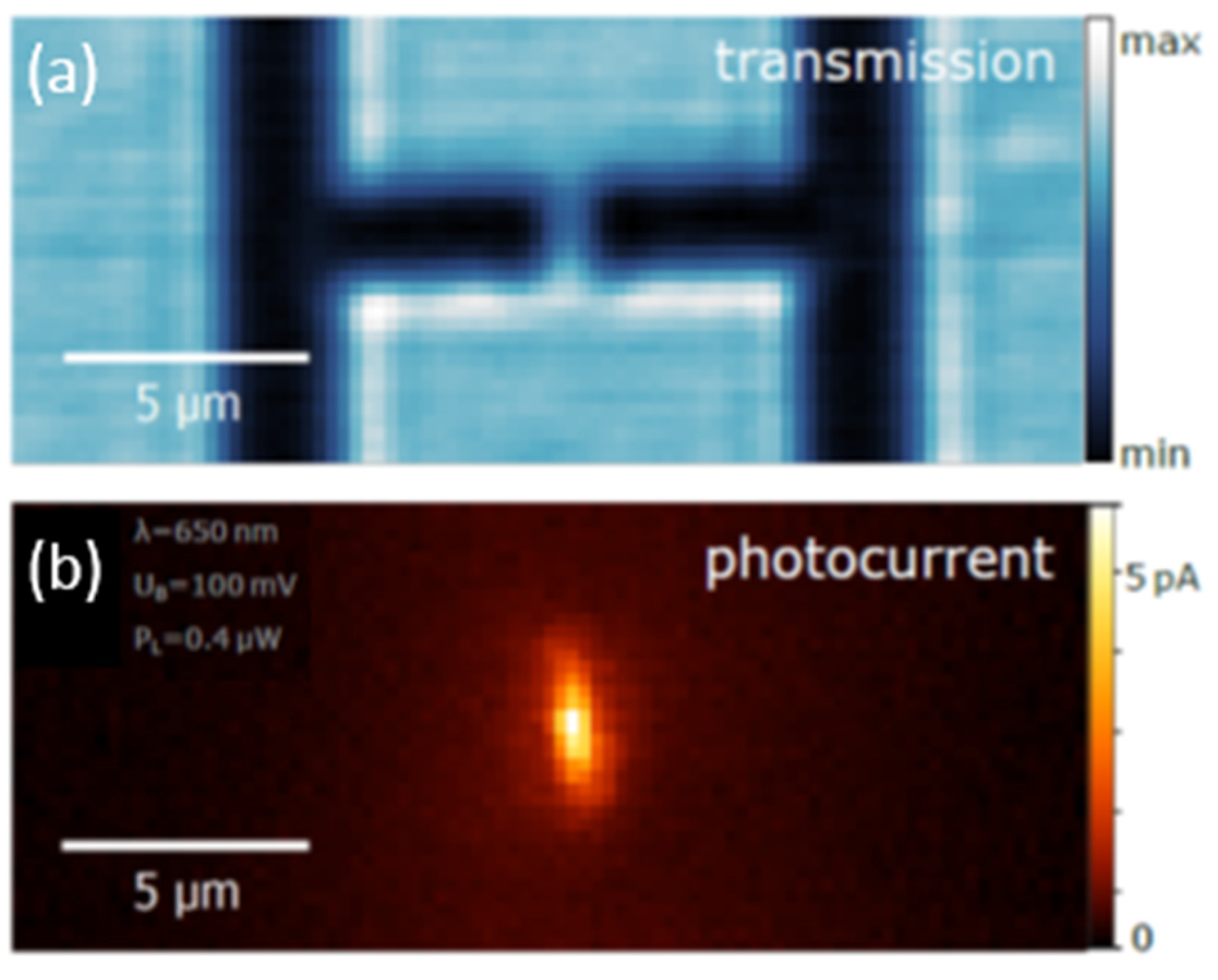
:1. Introduction
2. Correlation of Photoconductivity and Luminescence
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Konstantatos, G.; Sargent, E.H. Colloidal quantum dot photodetectors. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2011, 54, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, R.; Curry, R.J. Lead sulphide nanocrystal photodetector technologies. Nat. Photonics 2016, 10, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kelderer, E.; Grimaldi, D.; Hohenau, A.; Ditlbacher, H.; Krenn, J.R. Correlating Spatially Resolved Photoconductivity and Luminescence in Colloidal Quantum Dot Films. Proceedings 2020, 56, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020056039
Kelderer E, Grimaldi D, Hohenau A, Ditlbacher H, Krenn JR. Correlating Spatially Resolved Photoconductivity and Luminescence in Colloidal Quantum Dot Films. Proceedings. 2020; 56(1):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020056039
Chicago/Turabian StyleKelderer, Emil, Dario Grimaldi, Andreas Hohenau, Harald Ditlbacher, and Joachim R. Krenn. 2020. "Correlating Spatially Resolved Photoconductivity and Luminescence in Colloidal Quantum Dot Films" Proceedings 56, no. 1: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020056039
APA StyleKelderer, E., Grimaldi, D., Hohenau, A., Ditlbacher, H., & Krenn, J. R. (2020). Correlating Spatially Resolved Photoconductivity and Luminescence in Colloidal Quantum Dot Films. Proceedings, 56(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020056039



