Machine Learning to Compute Implied Volatility from European/American Options Considering Dividend Yield †
Abstract
:1. Problem Formulation
2. Methodology
2.1. ANN for European Implied Volatility
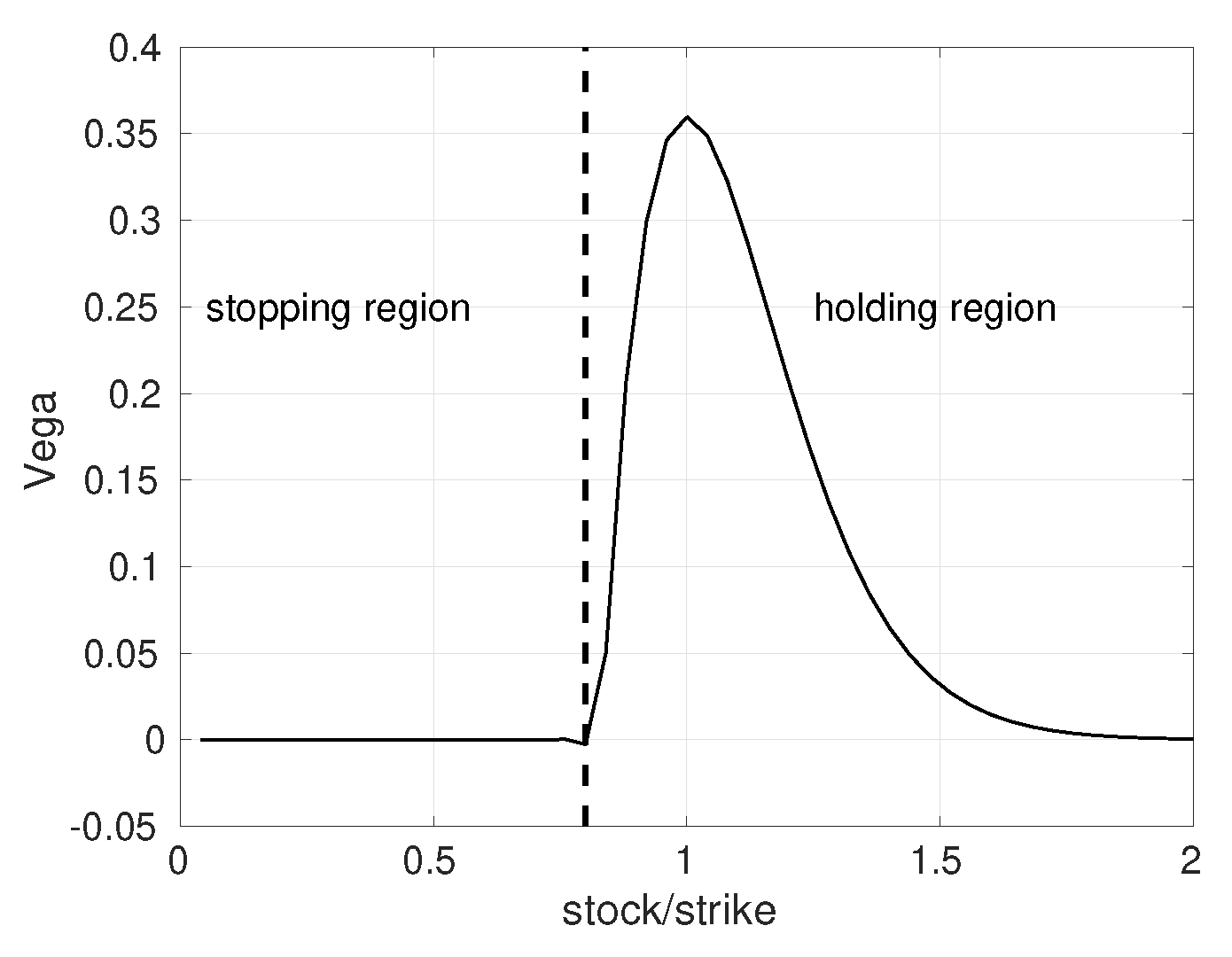
2.2. ANN for American Implied Volatility
3. Numerical Results
References
- Liu, S.; Leitao, A.; Borovykh, A.; Oosterlee, C.W. On Calibration Neural Networks for extracting implied information from American options. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.11786. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, F.; Oosterlee, C.W. Pricing early-exercise and discrete barrier options by Fourier-cosine series expansions. Numer. Math. 2009, 114, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Oosterlee, C.W.; Bohte, S.M. Pricing Options and Computing Implied Volatilities using Neural Networks. Risks 2019, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Hidden layers | 4 |
| Neurons(each layer) | 400 |
| Activation | ReLU |
| Initialization | Glorot |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Batch size | 1024 |
| Parameters | Range | |
|---|---|---|
| Inputs | Stock price () | [0.3, 1.8] |
| Time to maturity () | [0.08, 2.5] | |
| Risk-free rate (r) | [0.0, 0.25] | |
| Dividend yield (q) | [0.0, 0.25] | |
| Scaled time value () | - | |
| Output | Volatility () | (0.01, 1.05) |
| Phase | European Options | American Options | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSE | MAE | MAPE | MSE | MAE | MAPE | |||
| Training | 1.72 | 3.17 | 6.99 | 0.9999976 | 7.12 | 5.66 | 1.42 | 0.999990 |
| Testing | 1.94 | 3.35 | 7.39 | 0.9999972 | 1.93 | 6.52 | 2.35 | 0.999974 |
| Method | GPU (s) | CPU (s) | Robustness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Newton-Raphson | 19.68 | 23.06 | No |
| Brent | 52.08 | 60.67 | Yes |
| Bi-section | 337.94 | 390.91 | Yes |
| IV-ANN | 0.20 | 1.90 | Yes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Leitao, Á.; Borovykh, A.; Oosterlee, C.W. Machine Learning to Compute Implied Volatility from European/American Options Considering Dividend Yield. Proceedings 2020, 54, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020054061
Liu S, Leitao Á, Borovykh A, Oosterlee CW. Machine Learning to Compute Implied Volatility from European/American Options Considering Dividend Yield. Proceedings. 2020; 54(1):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020054061
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shuaiqiang, Álvaro Leitao, Anastasia Borovykh, and Cornelis W. Oosterlee. 2020. "Machine Learning to Compute Implied Volatility from European/American Options Considering Dividend Yield" Proceedings 54, no. 1: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020054061
APA StyleLiu, S., Leitao, Á., Borovykh, A., & Oosterlee, C. W. (2020). Machine Learning to Compute Implied Volatility from European/American Options Considering Dividend Yield. Proceedings, 54(1), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020054061






