Information Length as a New Diagnostic of Stochastic Resonance†
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Double-Well Potential Model
3. Results
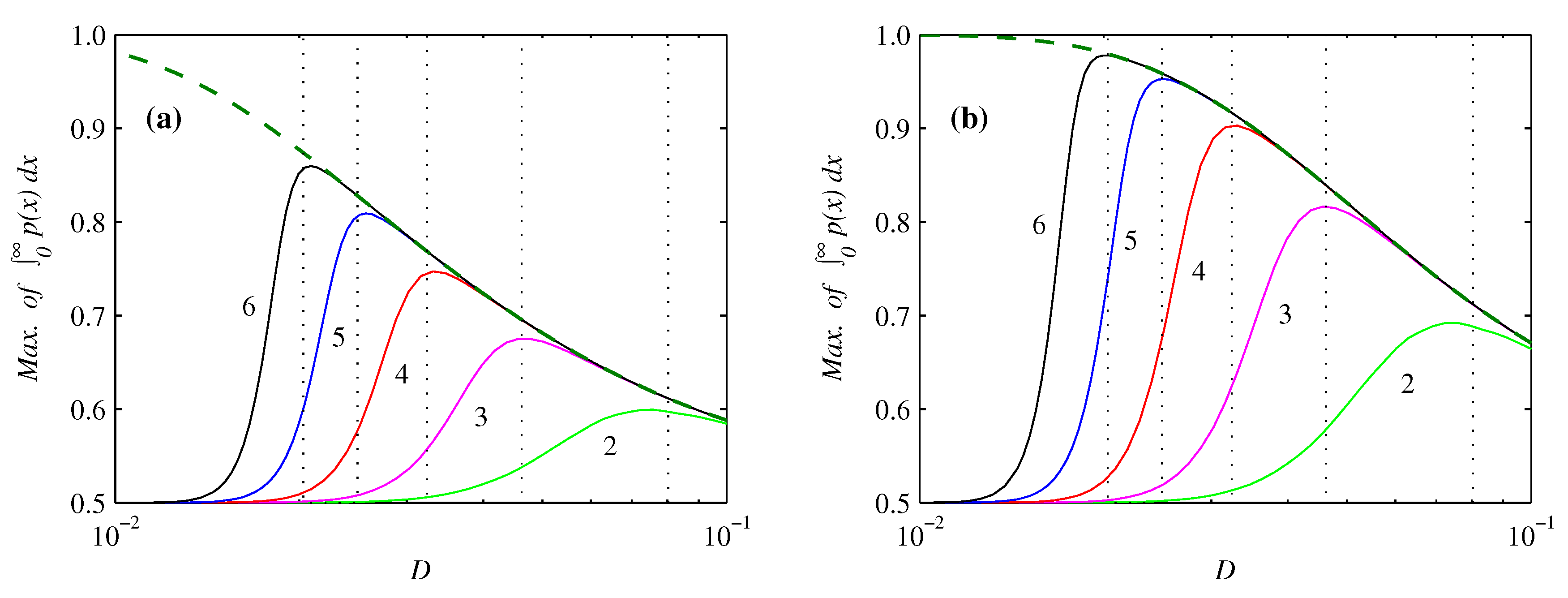
3.1. Probability Density Functions
3.2. Escape Times
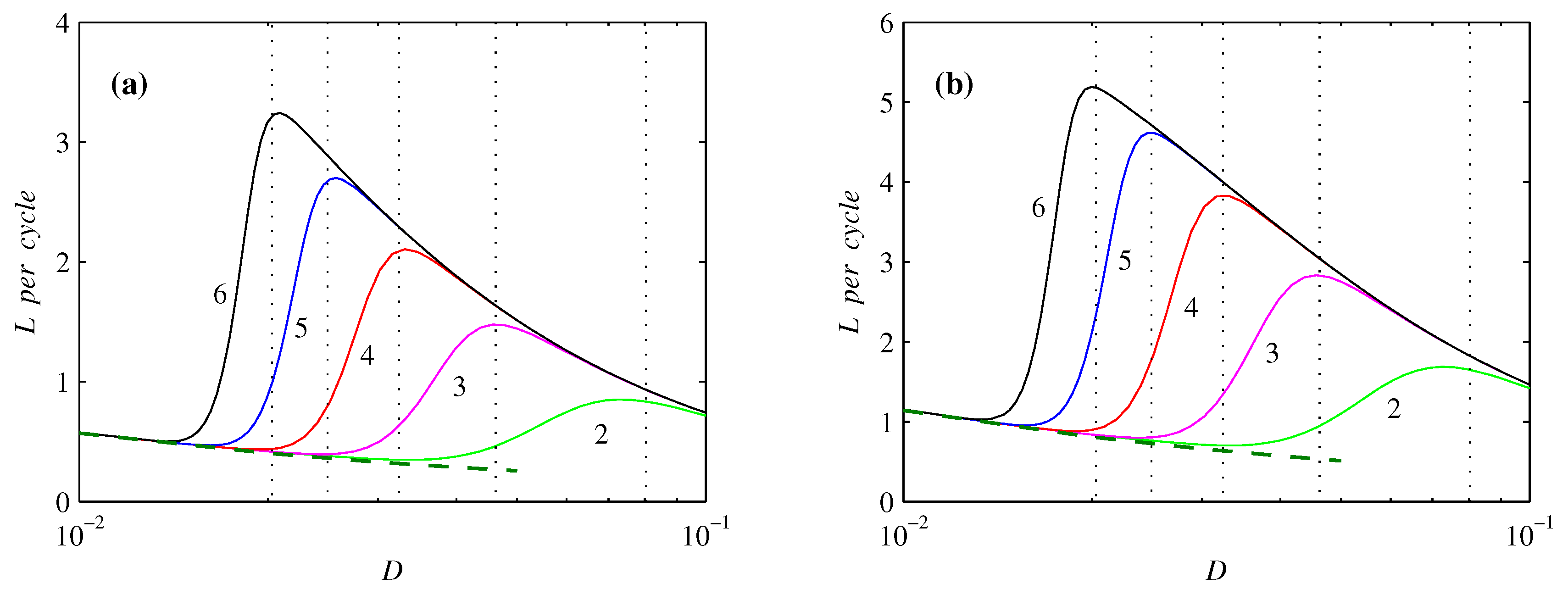
3.3. Information Length
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Information Length and Infinitesimal Relative Entropy
References
- Benzi, R.; Sutera, A.; Vulpiani, A. The mechanism of stochastic resonance. J. Phys. A 1981, 14, L453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolis, C.; Nicolis, G. Stochastic aspects of climate transitions-additive fluctuations. Tellus 1981, 33, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fauve, S.; Heslot, F. Stochastic resonance in a bistable system. Phys. Lett. 1983, 97, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, P.; Hänggi, P. Stochastic nonlinear dynamics modulated by external periodic forces. EPL 1989, 8, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, H.; Nicolis, G.; Nicolis, C. Periodically forced Fokker–Planck equation and stochastic resonance. Phys. Rev. A 1990, 42, 2030–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, P.; Hänggi, P. Amplification of small signals via stochastic resonance. Phys. Rev. A 1991, 44, 8032–8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, P. Periodically driven stochastic systems. Phys. Rep. 1993, 234, 175–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, P.; Schmid, G.J.; Hänggi, P. Universal equivalence of mean first-passage time and Kramers rate. Phys. Rev. E 1999, 60, R1–R4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Reimann, P.; Hänggi, P. Surmounting oscillating barriers: Path-integral approach for weak noise. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62, 6282–6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneghan, C.; Chow, C.C.; Collins, J.J.; Imhoff, T.T.; Lowen, S.B.; Teich, M.C. Information measures quantifying aperiodic stochastic resonance, Phys. Rev. E 1996, 54, R2228–R2231. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, J.W.C.; Asraf, D.E.; Bulsara, A.R.; Inchiosa, M.E. Information-theoretic distance measures and a generalization of stochastic resonance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 2850–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goychuk, I.; Hänggi, P. Stochastic resonance in ion channels characterized by information theory. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 61, 4272–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goychuk, I. Information transfer with rate-modulated Poisson processes: A simple model for nonstationary stochastic resonance. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 21909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonnell, M.D.; Stocks, N.G.; Pearce, C.E.M.; Abbott, D. Stochastic Resonance: From Suprathreshold Stochastic Resonance to Stochastic Signal Quantization; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Goychuk, I.; Hänggi, P. Nonstationary stochastic resonance viewed through the lens of information theory. Eur. Phys. J. B 2009, 69, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B. Optimal information transfer and stochastic resonance in collective decision making. Swarm Intell. 2017, 11, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillard, N.; Belin, E.; Chapeau-Blondeau, F. Enhancing qubit information with quantum thermal noise. Physica A 2018, 507, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.B.; Kim, E. Investigation of the statistical distance to reach stationary distributions. Phys. Lett. A 2015, 379, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heseltine, J.; Kim, E. Novel mapping in non-equilibrium stochastic processes. J. Phys. 2016, 49, 175002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Lee, U.; Heseltine, J.; Hollerbach, R. Geometric structure and geodesic in a solvable model of nonequilibrium process. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 93, 062127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.; Kim, E. Structures in sound: Analysis of classical music using the information length. Entropy 2016, 18, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenkès, L.-M.; Hollerbach, R.; Kim, E. Time-dependent probability density functions and information geometry in stochastic logistic and Gompertz models. J. Stat. Mech. 2017, 2017, 123201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Lewis, P. Information length in quantum systems. J. Stat. Mech. 2018, 2018, 043106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E. Investigating information geometry in classical and quantum systems through information length. Entropy 2018, 20, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquet, Q.; Kim, E.; Hollerbach, R. Time-dependent probability density functions and attractor structure in self-organised shear flows. Entropy 2018, 20, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Hashizume, Y. Expectation parameter representation of information length for non-equilibrium systems. Physica A 2019, 517, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frieden, B.R. Science from Fisher Information; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kramers, H.A. Brownian motion in a field of force and the diffusion model of chemical reactions. Physica 1940, 7, 284–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risken, H. The Fokker–Planck Equation: Methods of Solution and Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, E.-j.; Hollerbach, R. Information Length as a New Diagnostic of Stochastic Resonance†. Proceedings 2020, 46, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecea-5-06667
Kim E-j, Hollerbach R. Information Length as a New Diagnostic of Stochastic Resonance†. Proceedings. 2020; 46(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecea-5-06667
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Eun-jin, and Rainer Hollerbach. 2020. "Information Length as a New Diagnostic of Stochastic Resonance†" Proceedings 46, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecea-5-06667
APA StyleKim, E.-j., & Hollerbach, R. (2020). Information Length as a New Diagnostic of Stochastic Resonance†. Proceedings, 46(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecea-5-06667





