Using Smart Wearables to Monitor Cardiac Ejection †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
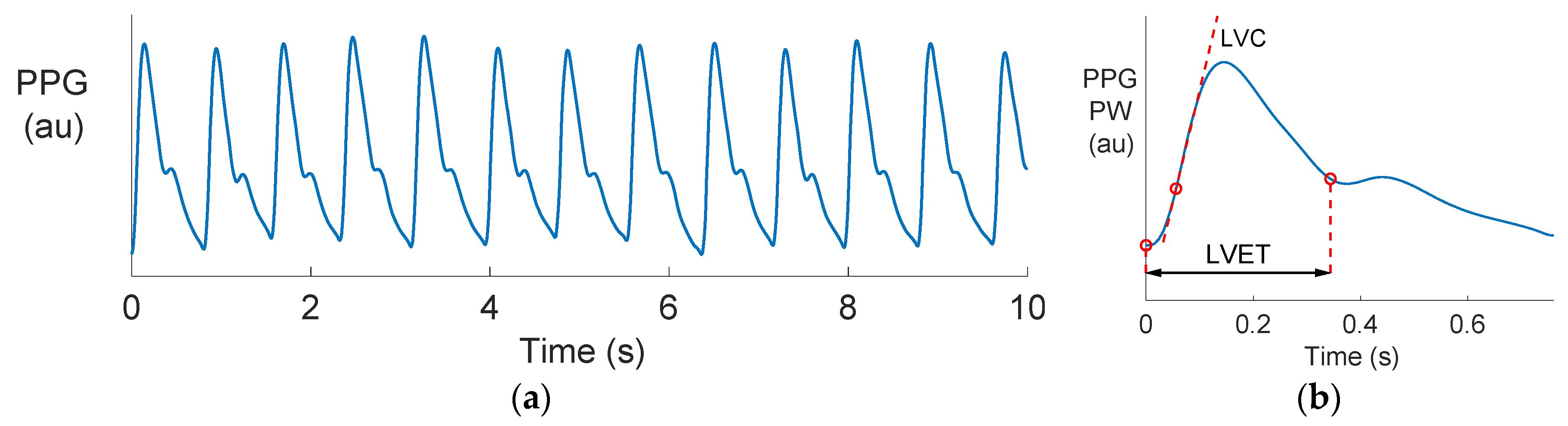
2.2. Estimating LVET and LVC from Radial BP and PPG Waves
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
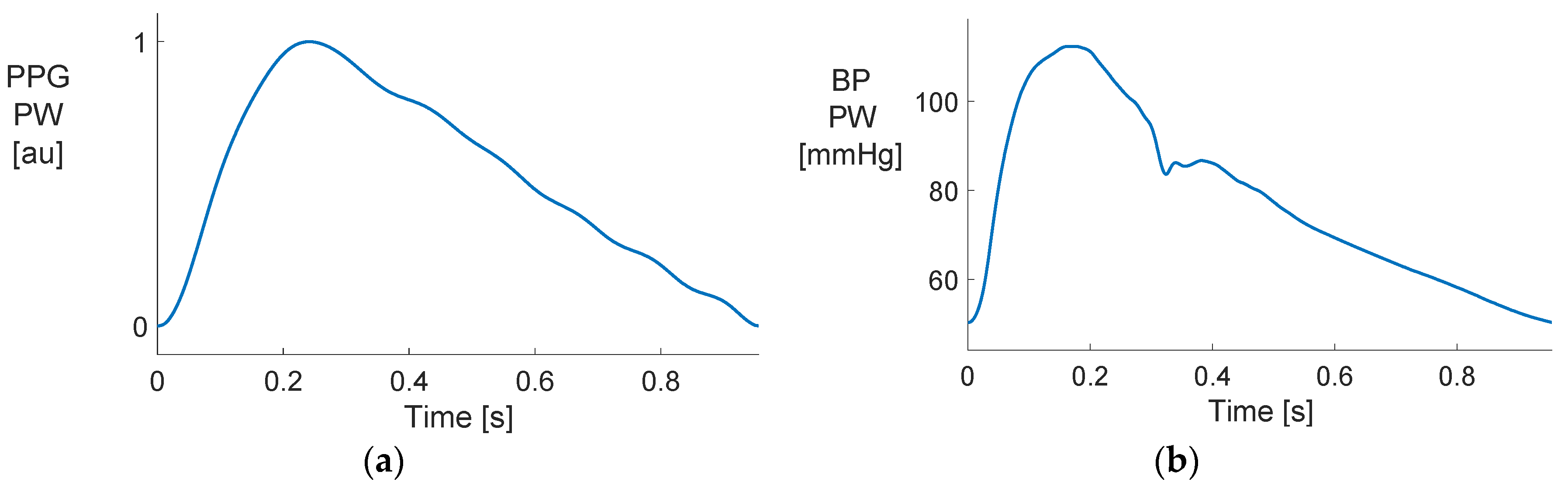
3.1. Comparing PPG and BP Waves
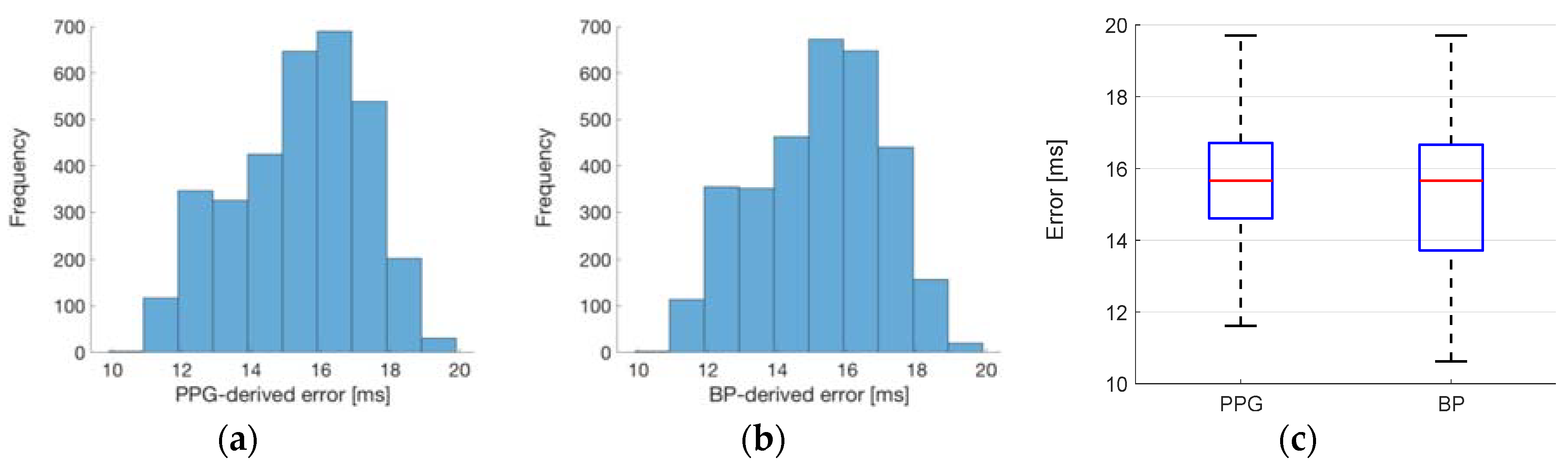
3.2. Estimating Left Ventricular Ejection Time (LVET)
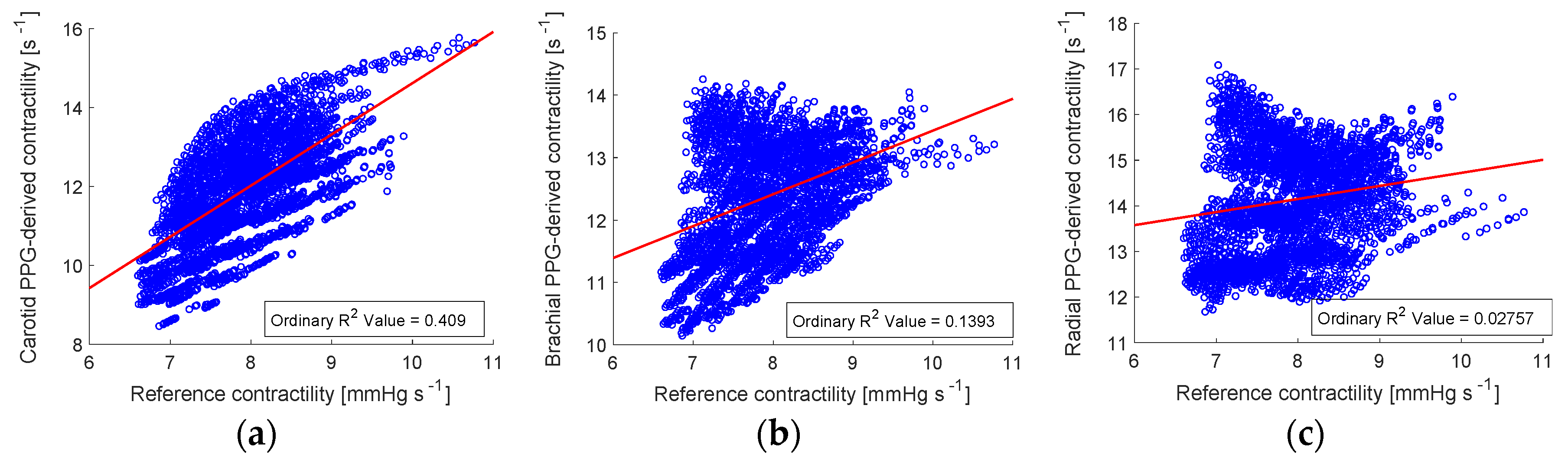
3.3. Estimating Left Ventricular Contractility (LVC)
3.4. Limitations and Future Work
3.5. Implications
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.; Pi, Z.; Liu, B. TROIKA: A general framework for heart rate monitoring using wrist-type photoplethysmographic signals during intensive physical exercise. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallen, M.P.; Gomersall, S.R.; Keating, S.E.; Wisløff, U.; Coombes, J.S. Accuracy of heart rate watches: Implications for weight management. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarchi, D.; Salvi, D.; Velardo, C.; Mahdi, A.; Tarassenko, L.; Clifton, D.A. Estimation of HRV and SpO2 from wrist-worn commercial sensors for clinical settings. In Proceedings of the IEEE 15th International Conference on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 4–7 March 2018; pp. 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- Millasseau, S.C.; Guigui, F.G.; Kelly, R.P.; Prasad, K.; Cockcroft, J.R.; Ritter, J.M.; Chowienczyk, P.J. Noninvasive assessment of the digital volume pulse. Comparison with the peripheral pressure pulse. Hypertension 2000, 36, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.; Turner, P. Systolic time intervals: A review of the method in the non-invasive investigation of cardiac function in health, disease and clinical pharmacology. Postgrad. Med. J. 1983, 59, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstenblith, G.; Frederiksen, J.; Yin, F.; Fortuin, N.; Lakatta, E.; Weisfeldt, M. Echocardiographic assessment of a normal aging population. Circulation 1977, 56, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Werf, F.; Piessens, J.; Kesteloot, H.; De Geest, H. A comparison of systolic time intervals derived from the central aortic pressure and from the external carotid pulse tracing. Circulation 1975, 51, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.E.; Shaver, J.A.; Thompson, M.E.; Reddy, S.P.; Leonard, J.J. Direct correlation of external systolic time intervals with internal indices of left ventricular function in man. Circulation 1971, 44, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, G.S.H.; Middleton, P.M.; Celler, B.G.; Wang, L.; Lovell, N.H. Automatic detection of left ventricular ejection time from a finger photoplethysmographic pulse oximetry waveform: Comparison with Doppler aortic measurement. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 28, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Wowern, E.; Östling, G.; Nilsson, P.M.; Olofsson, P. Digital photoplethysmography for assessment of arterial stiffness: Repeatability and comparison with applanation tonometry. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blažek, R.B.; Lee, C. Multi-resolution linear model comparison for detection of dicrotic notch and peak in blood volume pulse signals. In Analysis of Biomedical Signals and Images; Brno University of Technology: Brno, Czech Republic, 2010; pp. 378–386. [Google Scholar]
- Charlton, P.H.; Bonnici, T.; Tarassenko, L.; Clifton, D.A.; Beale, R.; Watkinson, P.J. An assessment of algorithms to estimate respiratory rate from the electrocardiogram and photoplethysmogram. Physiol. Meas. 2016, 37, 610–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijayasiri, L.; Rhodes, A.; Cecconi, M. Cardiac contractility. In Encyclopedia of Intensive Care Medicine; Vincent, J.-L., Hall, J.B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 46–462. ISBN 978-3-642-00417-9. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, D.T.; Braunwald, E.; Covell, J.W.; Sonnenblick, E.H.; Ross, J. Assessment of cardiac contractility. The relation between the rate of pressure rise and ventricular pressure during isovolumic systole. Circulation 1971, 44, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ifuku, H.; Taniguchi, K.; Matsumoto, H. Noninvasive assessment of cardiac contractility by using (dP/dt)/P of carotid artery pulses during exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1994, 69, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willemet, M.; Chowienczyk, P.; Alastruey, J. A database of virtual healthy subjects to assess the accuracy of foot-to-foot pulse wave velocities for estimation of aortic stiffness. Am. J. Physiol. Hear. Circ. Physiol. 2015, 309, H663–H675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haemodynamic Modelling Research Group Home Page. Available online: http://haemod.com (accessed on 4 February 2019).
- Charlton, P.H.; Celka, P.; Farukh, B.; Chowienczyk, P.; Alastruey, J. Assessing mental stress from the photoplethysmogram: A numerical study. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 054001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blažek, R.B.; Lee, C. Multi-resolution linear model comparison for detection of dicrotic notch and peak in blood volume pulse signals. In Analysis of Biomedical Signals and Images; Brno University of Technology: Brno, Czech Republic, 2010; pp. 378–386. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R.P.; Rittogers, S.E.; Froester, W.F.; Boudoulas, H. A critical review of the systolic time intervals. Circulation 1977, 56, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J. Photoplethysmography and its application in clinical physiological measurement. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 28, R1–R39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jubran, A. Pulse oximetry. Crit. Care 1999, 3, R11–R17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neff, T.A. Routine oximetry: A fifth vital sign? Chest 1988, 94, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendi, M. On the analysis of fingertip photoplethysmogram signals. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2012, 8, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mathieu, A.; Charlton, P.H.; Alastruey, J. Using Smart Wearables to Monitor Cardiac Ejection. Proceedings 2019, 4, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-5-05744
Mathieu A, Charlton PH, Alastruey J. Using Smart Wearables to Monitor Cardiac Ejection. Proceedings. 2019; 4(1):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-5-05744
Chicago/Turabian StyleMathieu, Aristide, Peter H. Charlton, and Jordi Alastruey. 2019. "Using Smart Wearables to Monitor Cardiac Ejection" Proceedings 4, no. 1: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-5-05744
APA StyleMathieu, A., Charlton, P. H., & Alastruey, J. (2019). Using Smart Wearables to Monitor Cardiac Ejection. Proceedings, 4(1), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-5-05744





