Abstract
A computational study of the interaction between cardiac troponin I and its specific antibody is carried out. The aim of this study is to characterize the binding process by determining the binding sites, number of interactions and energies. Furthermore, a selectivity study of the binding efficiency of the cardiac troponin I antibody with the cardiac troponin I and with its principal interferon, the skeletal troponin I, is also performed to demonstrate that selectivity assays for sensing studies can be carried out computationally. Computational and simulation tools such as FTSite, FTMap, FTDock and pyDock were used to determine the binding sites and molecular docking performance, allowing us to obtain relevant information for a subsequent sensing system development.
1. Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases are the first cause of death worldwide [1] and heart failure is the end stage of almost all heart diseases. That heart failure is commonly produced by a damage of the heart myofilaments that can lead to systolic failure, resulting on a decrease of the blood circulation, not sufficing organism needs.
With a molecular mass of approximately 80 KDa, cardiac troponin (cTn) is a complex composed of three protein subunits having a different role in the myocardial contraction. Cardiac troponin T (cTnT) is a tropomyosin-binding subunit that regulates the interaction of the troponin complex with the thin filaments. Cardiac troponin I (cTnI) inhibits the interaction between myosin and actin, responsible of muscle contraction. Finally, cardiac troponin C (cTnC) is a Ca2+ binding subunit responsible of regulating the muscle contraction depending on the Ca2+ concentration. The binding of Ca2+ to cTnC produces a conformational change that reduces the inhibition of cTnI and thus leads to muscle contraction. That conformational change produced by cTnC is reversed when Ca2+ levels are restored, thus creating the contraction-relaxation cycle [2].
When a damage of the myofilaments of the cardiac muscle is produced, a breakage of the troponin complex takes place, leading to the release of the troponin subunits (cTnT, cTnI and cTnC) to the blood stream. Therefore, the levels of these cardiac troponin subunits in blood can be used as an indicator of myocardial damage. However, troponin is also found in the skeletal muscle, where it is also in charge of controlling the muscle contraction-relaxation cycle [3]. And as for the cTn, skeletal troponin (sTn) subunits (sTnT, sTnI and sTnC) are also released to the blood stream when the myofilaments of the skeletal muscle are damaged [4]. Due to the similarity between cardiac and skeletal troponin, sTn subunits may interfere in the detection of cTn ones, thus limiting the performance of cTn detection-based analysis systems [5].
Previous works indicate that, from the three cTn subunits, the utility of cTnC for cardiac damage diagnosis is limited by the fact that it presents the same structure than sTnC, the only difference is the number of Ca2+ binding sites between them [6]. Regarding cTnT and cTnI, cTnT presents several specific cardiac isoforms whereas cTnI presents one. From here, their use in cardiac diagnostic and prognostic applications [7]. Several comparative studies between cTnT cardiac isoforms and cTnI specific cardiac isoform have been carried out, concluding that cTnI exhibits a higher specificity and accuracy than cTnT for the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction at its early stage [8]. Therefore, cTnI has become the current gold-standard biomarker in clinical diagnosis for the identification of acute heart failures. However, it may presents a high cross reactivity with the sTnI regarding the interaction with cTnI antibody.
Within this context, in this work we report a computational study of the interaction of the cTnI antibody (αcTnI) capture probe with cTnI and sTnI. This study allows having a better understanding of the biochemical interactions between them and to computationally predict the binding performance and the selectivity of the αcTnI to cTnI versus sTnI. This information is very relevant for the development of analysis systems for myocardial failure diagnosis based on cTnI detection. First, FTSite and FTMap were used to determine and analyse the structure of the targets (cTnI and sTnI) and the antibody binding fragment (Fab). After the consideration of several possible conformations for cTnI and sTnI (more than 100), the most stable conformations (i.e., with the lowest total energy) were used to predict the binding sites. Next, FTDock and pyDock were used to study the molecular docking performance in order to select the most stable predicted conformations of the cTnI-αcTnI and sTnI-αcTnI complexes by their energies and coordinates. The 3D visualization of the molecules was done using PyMOL.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Molecules Structures
The X-ray structures of the molecules used in the study were obtained from the Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics (RCSB) protein data bank (PDB). The IDs of the sTnI and the αcTnI structures are 1VDI and 4P48, respectively. For the case of the cTnI, it was extracted from the whole cardiac troponin complex provided with the ID 4Y99 by cutting the specific sequence from the whole structure. Before their use, those molecules were purified by removing those atoms not corresponding with the molecules of interest from the PDB files and that might be present in the downloaded models (water residues and ions).
2.1.2. FTSite and FTMap
The binding surface of proteins contains the so-called `hot spots,’ specific regions that provide major contributions to the binding free energy. Such regions are more likely to bind small drug-like compounds with high affinity than the rest of the binding sites and hence are the prime targets in several fields such as immunology or drugs design. On the other hand, screening libraries of fragment-sized compounds obtained by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) or X-ray crystallography demonstrate that such ’hot spots’ regions can bind a large variety of molecules. Therefore, the challenge here is being able to determine those sites computationally rather than experimentally in order to predict their druggability [9].
In order to determine and analyse the binding regions of the cTnI, sTnI and αcTnI molecules, FTSite and FTMap computing tools were used. These tools perform a statistical search of the entire molecule surface using a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) based correlation approach in order to determine those regions prickly to bind other molecules [10]. For those binding regions, FTSite characterizes different properties such as volume, hydrophobicity, hydrogen bonding, energy potential, solvent accessibility, desolvation energy and residue propensity. On the other hand, FTMap allows representing the obtained energy expression on a grid, which includes attractive and repulsive van der Waals (VDW) terms, electrostatic interaction energies (Ele.), dissolvation energies (Dissolv.) based on Poisson–Boltzmann calculations, resulting in a very accurate way to identify low-energy spot clusters [11].
2.1.3. FTDock and pyDock
Molecular docking is a prediction methodology used to determine the preferred orientation of two molecules when bound to each other to form a stable complex. This preferred orientation can be used to predict their binding affinity, that is, the association strength between those two molecules.
FTDock and pyDock were used to model the biomolecular docking for the cTnI-αcTnI and sTnI-αcTnI complexes. Both computational tools perform a rigid-body docking of two biomolecules in order to predict their specific binding geometries and their probability/stability, given by their lowest total energy [12,13]. Predicted docked complexes were outputted in pdb files, which were displayed using PyMOL 3D viewer. FTDock and pyDock implement different molecular docking algorithms, what was used to confirm that the obtained results were valid. Finally, note that, besides providing the geometric description of the docked complex, pyDock also provides the best docking orientations as scored mainly by electrostatics and desolvation energy [14].
2.2. Methods
An initial mapping to determine the binding sites and hot spots was done using FTSite. Once the spots were determined, the corresponding binding sites for the proteins and the antibody were chosen based on the side chains around the binding sites for the flexibility and rotamers determination.
cTnI, sTnI and αcTnI were mapped by FTMap and maximally binding sites were selected and subsequently uploaded to the FTDock server for the corresponding biomolecular docking calculations. 10.000 statistically best conformations were generated and the most stable prediction was chosen for the next steps. In parallel, the same process was done using pyDock for a comparative study of the docking results obtained with FTDock. 100 best conformations were generated in pdb files, only considering the most stable of each complex. The results found by the two docking methods were similar.
3. Results and Discussion
First, the ligand binding sites and the `hot spots´ on the molecules surfaces were determined for the cTnI, sTnI and αcTnI. There is often more than one potential binding site on the surface of each molecule. Even when the structure of a molecule is determined by crystallography in a complex with a ligand, a complete description of its binding sites with that ligand cannot be determined because complex structures may not fully exploit the overall properties of the binding site. Moreover, knowledge of the possible binding sites in the structure of a molecule also enables us to analyse and classify them through their binding pocket profiles. Figure 1 shows the chosen binding sites and pockets for cTnI, sTnI and αcTnI determined using FTSite.
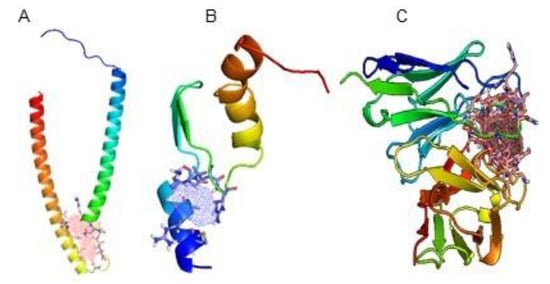
Figure 1.
FTSite results showing the pockets (coloured grid) and the binding sites (stick model) of (A) cTnI, (B) sTnI and (C) Fab region of the αcTnI. The visualization has been done using PyMOL.
FTSite provides binding sites sequences. Specific binding amino acids of those sequences of each protein interact with the antibody binding region forming the antibody-antigen complex. Table 1 shows all the amino acid sequences that form the binding sites previously depicted in Figure 1. Here, FTMap represents in a grid the highest bonded/non-bonded H (grids not shown) and the highest H-bonded amino acids forming the ‘hot spots’ from the whole binding sites.

Table 1.
Complete description of the binding sites sequences given by FTSite for cTnI, sTnI and αcTnI.
Table 2 shows the identified ‘hot spots’ hydrogen bond interactions for the cTnI-αcTnI and the sTnI-αcTnI complexes as defined by FTMap. Three H-bonds are identified for both complexes; however, while they are formed by three different amino acids for the cTnI-αcTnI complex, for the sTnI-αcTnI complex two of them are formed by the same amino acid GLY from the sTnI, what is translated into a weaker H-bonding than for cTnI-αcTnI. This fact determines the higher affinity of αcTnI towards cTnI than for sTnI.

Table 2.
Identified hydrogen bonds for the cTnI-αcTnI and the sTnI-αcTnI complexes as defined by FTMap.
After binding sites identification and mapping, the next step is studying molecular docking for the cTnI and sTnI to αcTnI binding. This process of docking provides the specific ‘hot spots’ amino acids of the whole sequence that interact, taking into account spatial distribution, van der Waals interactions and rotational restrictions among others. For the docking analysis, FTDock and pyDock were used. FTDock generates several output pdb files with docking probabilities organized from the highest to the lowest probable one. On the other hand, pyDock generates several pdb files of the docked complexes being randomly organized but results are accompanied by other generated files describing energies, positions and angles which can be used to order the predicted complexes. The ranking of molecular docking complexes obtained with both methods are the same, thus corroborating the simulation results. Figure 2 shows the docked complexes obtained for cTnI-αcTnI and sTnI-αcTnI, with highlighted binding zones.
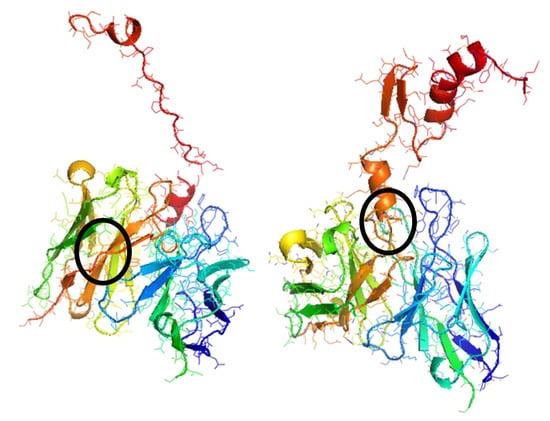
Figure 2.
Most stable docked configurations of (left) cTnI-αcTnI and (right) sTnI-αcTnI complexes. Binding zones are black circled.
Having identified the most stable predicted structures, the formed complexes were visualized using PyMol to depict the specific interactions between the ‘hot spots’ sequences previously identified. Figure 3 details the binding points between the cTnI, sTnI and the αcTnI as explained above. The obtained FTDock results were represented in the next figure, PyMOL was used to visually highlight the H-bonds between cTnI-αcTnI and sTnI-αcTnI.
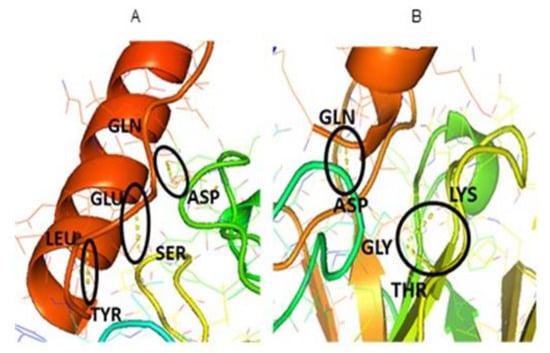
Figure 3.
Detailed view of the (A) cTnI-αcTnI and (B) sTnI-αcTnI docked complexes. H-bonds between binding amino acids are depicted with dash yellow line and highlighted with a black circle.
FTDock provides more than a thousand possible combinations for the docked proteins to αcTnI. Different parallel data were also given to distinguish the most stable configurations as previously mentioned. Table 3 and Table 4 show the parameters describing the most stable docking configuration for the cTnI-αcTnI and sTnI-αcTnI complexes.

Table 3.
Energy data (Kcal/mol) for the docked cTnI and sTnI with the αcTnI for the most stable formed complexes configuration.

Table 4.
Positions data for the docked protein with the antibody fab for the most stable formed complexes configuration.
From Table 3, the total energy of the cTnI-αcTnI complex is considerably lower than for the sTnI-αcTnI complex. Additionally, considering the previous results of the hydrogen bonding performance, the cTnI affinity towards αcTnI is higher than for the sTnI.
This study reveals that the selected αcTnI antibody is the adequate one for the experimental development of a cTnI-selective biosensing system in a subsequent stage. By performing this type of theoretical and computational analysis, we are able to determine the suitability of a certain capture antibody without the need of investing a large amount of resources on its experimental selection. This allows defining a better initial design of our biosensing experiments, with an enormous thrift on cost, effort and time.
4. Conclusions
In this work, we have demonstrated that a selectivity study can be performed computationally. As far as we know, this is the first time that a computational selectivity study is performed for biosensing purposes. The obtained affinity and selectivity results are highly important, since they compare the binding of cTnI and its principal interferon sTnI to bind the αcTnI for a cross reactivity study, with the aim of a correct selection of a bioreceptor for the development of a cTnI biosensor for an effective, selective, fast and direct early detection of a myocardial failure.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Horizon 2020 Framework Program of the European Union under the project H2020-PHC-634013 (PHOCNOSIS).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Status Report on Non-Communicable Diseases; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; Volume 176, pp. 9–11. ISBN 978 92 4 068645 8. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, A.V.; Potter, J.D.; Szczesna-Cordary, D. The role of Troponin in muscle contraction. Life 2002, 54, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yamazaki, M.; Shen, Q.W.; Swartz, D.R. Differences between cardiac and skeletal troponin interaction with the thin filament probed by troponin exchange in skeletal myofibrils. Biophys. J. 2009, 7, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, S.; Junikka, M.; Laitinen, P.; Majamaa-Voltti, K.; Alfthan, H.; Pettersson, K. Negative Interference in Cardiac Troponin I Immunoassays from a Frequently Occurring Serum and Plasma Component. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.C.; David, C.G.; Collinson, P.O.; Marber, M.S. Cardiac troponins: From myocardial infarction to chronic disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2017, 113, 1708–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, A.M.; Homsher, E.; Regnier, M. Regulation of contraction in striated muscle. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 853–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collinson, P.O.; Gaze, D.; Goodacre, S. The clinical and diagnostic performance characteristics of the high sensitivity abbott cardiac troponin I assay. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apple, F.S.; Ranka, L.; Murakami, M.M. Determination of 19 Cardiac Troponin I and T Assay 99th Percentile Values from a Common Presumably Healthy Population. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Pei, J.; Lai, L. Binding site detection and druggability prediction of protein targets for structure-based drug design. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 19, 2326–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Li, M.; Pineda-Sanabria, S.E.; Gelozia, S.; Lindert, S.; West, F.; Sykes, D.; Hwang, M. Structures reveal details of small molecule binding to cardiac troponin. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 101, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayan, B.; Kazakov, D.; Chuang, G.; Beglov, D.; Hall, D.R.; Landon, M.; Mattos, C.; Vajdal, S. Fragment based identification of druggable hot spots of proteins using fourrier domain correlation technique. Bioinformatics 2009, 1, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Blundell, L.; Fernandez-Recio, J. pyDock: Electrostatics and desolvation for effective scoring of rigid-body protein-protein docking. Proteins 2007, 68, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katchalski-Katzir, E.; Shariv, I.; Eisenstein, M.; Friesem, A.; Aftalo, C.; Vakser, A. Molecular surface recognition: Determination of geometric fit between proteins and their ligands by correlation techniques. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 2195–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez Garcia, B.; Pons, C.; Fernandez-Recio, J. pyDock web: A web server for rigid-body protein-protein docking using electrostatics and desolvation. Bioinformatics 2013, 1, 1698–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).