High-Lift Mechanism Motion Generation Synthesis Using a Metaheuristic †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Position Analysis of Four-Bar Mechanism
3. Optimization Problem and Constraint Handling
| Design variables for x are | Limits of the variables: |
| x = [r1, r2, r3, r4, L1, L2, xO2, yO2, ] | 0.01 ≤ r1 ≤ 0.3 |
| Target points are (xd, yd) and | 0.01 ≤ r2, r3, r4 ≤ 0.5 |
| (xd, yd) = [(0.059, 0.0032), (0.0642, −0.0455)] * 1.1173 | −0.1 ≤ L1, L2 ≤ 0.2 |
| = [0, 24.90] * pi/180 for case 1 | xO2 = 0 |
| (xd, yd) = [(0.059, 0.00032), (0.0703, −0.0454)] * 1.1173 | −0.05 ≤ yO2 ≤ 0.05 |
| = [0, 43.52] * pi/180 for case 2 | −60 ≤ ≤ −45 |
4. Design Results
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Dam, C.P.; Shaw, S.G.; Vander Kam, J.C.; Brodeur, R.R.; Rudolph, P.K.C.; Kinney, D. Aero-Mechanical Design Methodology for Subsonic Civil Transport High-Lift Systems. In Proceedings of the RTO AVT Symposium on “Aerodynamic Design and Optimization of Flight Vehicles in a Concurrent Multi-Disciplinary, Ottawa, QC, Canada, 18–21 October 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Li, D.; Qu, Q.; Kong, C. Two-Dimensional New-Type High-Lift Systems with Link/Straight Track Mechanism Coupling Downward Defection of Spoiler. J. Aircr. 2019, 56, 1524–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, A.D.; Castelli, M.R.; Benini, E. A Retrospective of high-lift device technology. Int. J. Aerosp. Mech. Eng. 2012, 6, 2561–2566. [Google Scholar]
- Zaccai, D.; Bertels, F.; Vos, R. Design methodology for trailing-edge high-lift mechanisms. CEAS Aeronaut. J. 2016, 7, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, J.A.; Nadal, F.; Muñoz, J.P.; Simon, A. Multiobjective constrained optimal synthesis of planar mechanisms using a new evolutionary algorithm. Mech. Mach. Theory 2007, 42, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleesongsom, S.; Bureerat, S. Four-bar linkage path generation through self-adaptive population size teaching-learning based optimization. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2017, 135, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleesongsom, S.; Bureerat, S. Alternative Constraint Handling Technique for Four-Bar Linkage Path Generation. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 324, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleesongsom, S.; Bureerat, S. Optimal Synthesis of Four-Bar Linkage Path Generation through Evolutionary Computation with a Novel Constraint Handling synthesis. Mech. Mach. Theory 2018, 44, 1784–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.Y. A GA–DE hybrid evolutionary algorithm for path synthesis of four-bar linkage. Mech. Mach. Theory 2010, 45, 1096–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuñuri, F.; Peón-Escalante, R.; Villanueva, C.; Pech-Oy, D. Synthesis of mechanisms for single and hybrid tasks using differential evolution. Mech. Mach. Theory 2011, 46, 1335–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleesongsom, S.; Bureerat, S. Optimal synthesis of four-bar linkage path generation through evolutionary computation. Res. Appl. Mech. Eng. 2015, 3, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Nariman-Zadeh, N.; Felezi, M.; Jamali, A.; Ganji, M. Pareto optimal synthesis of four-bar mechanisms for path generation. Mech. Mach. Theory 2009, 44, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleesongsom, S.; Bureerat, S. Alternative Constraint Handling Technique for Four-Bar Linkage Motion Generation. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 501, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phukaokaew, W.; Sleesongsom, S.; Panagant, N.; Bureerat, S. Synthesis of four-bar linkage motion generation using optimization algorithms. Adv. Comput. Des. 2019, 4, 197–210. [Google Scholar]
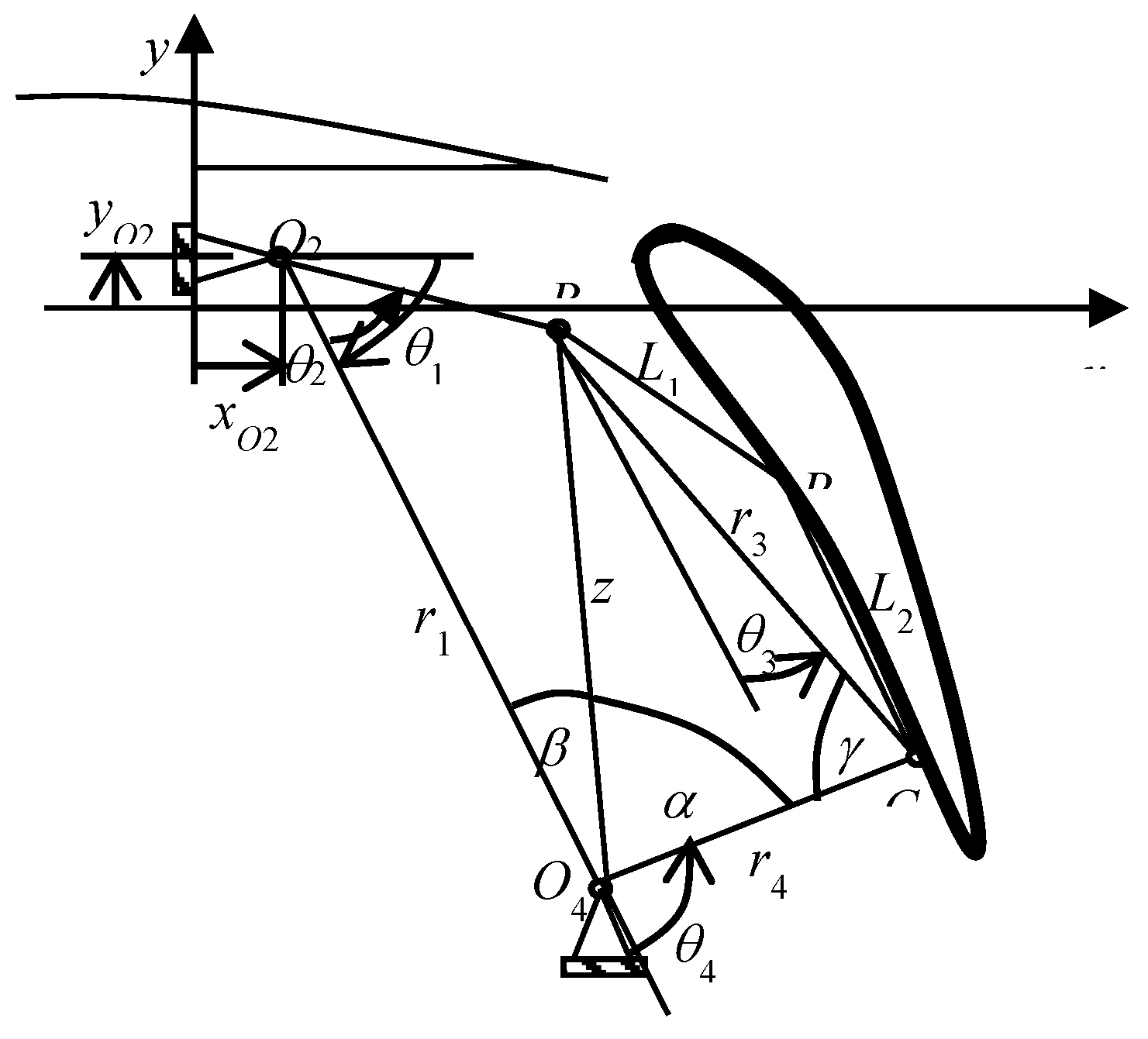
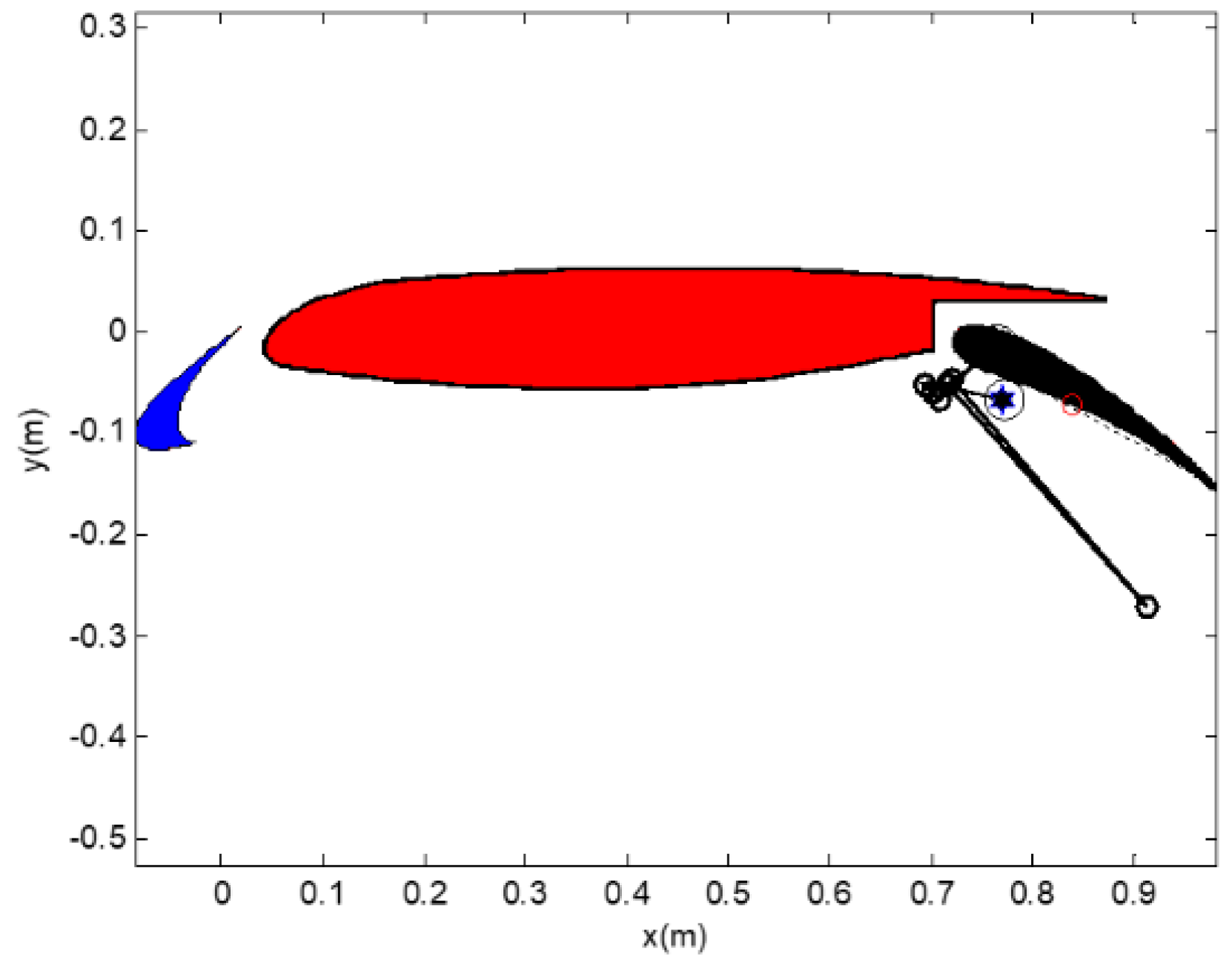
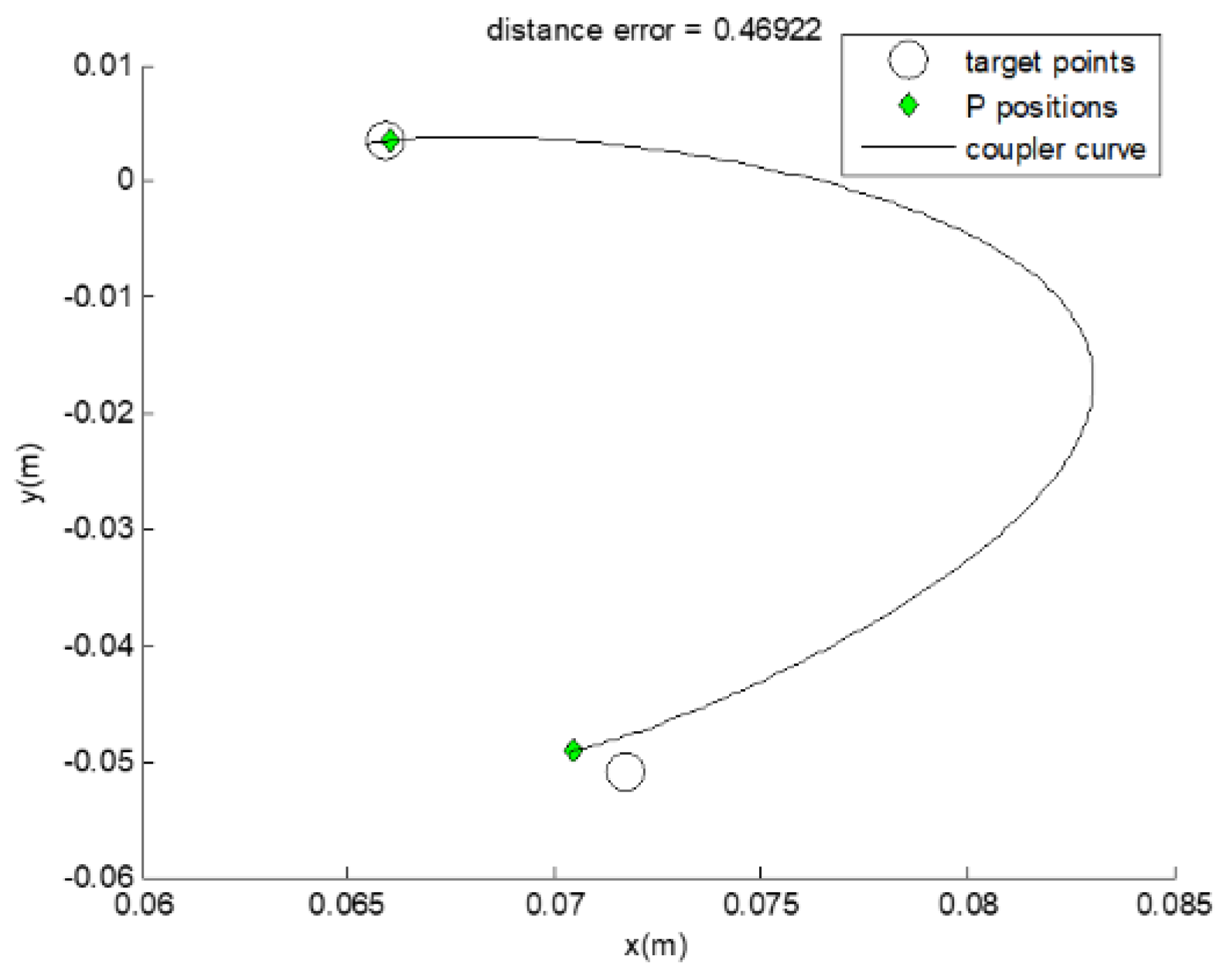
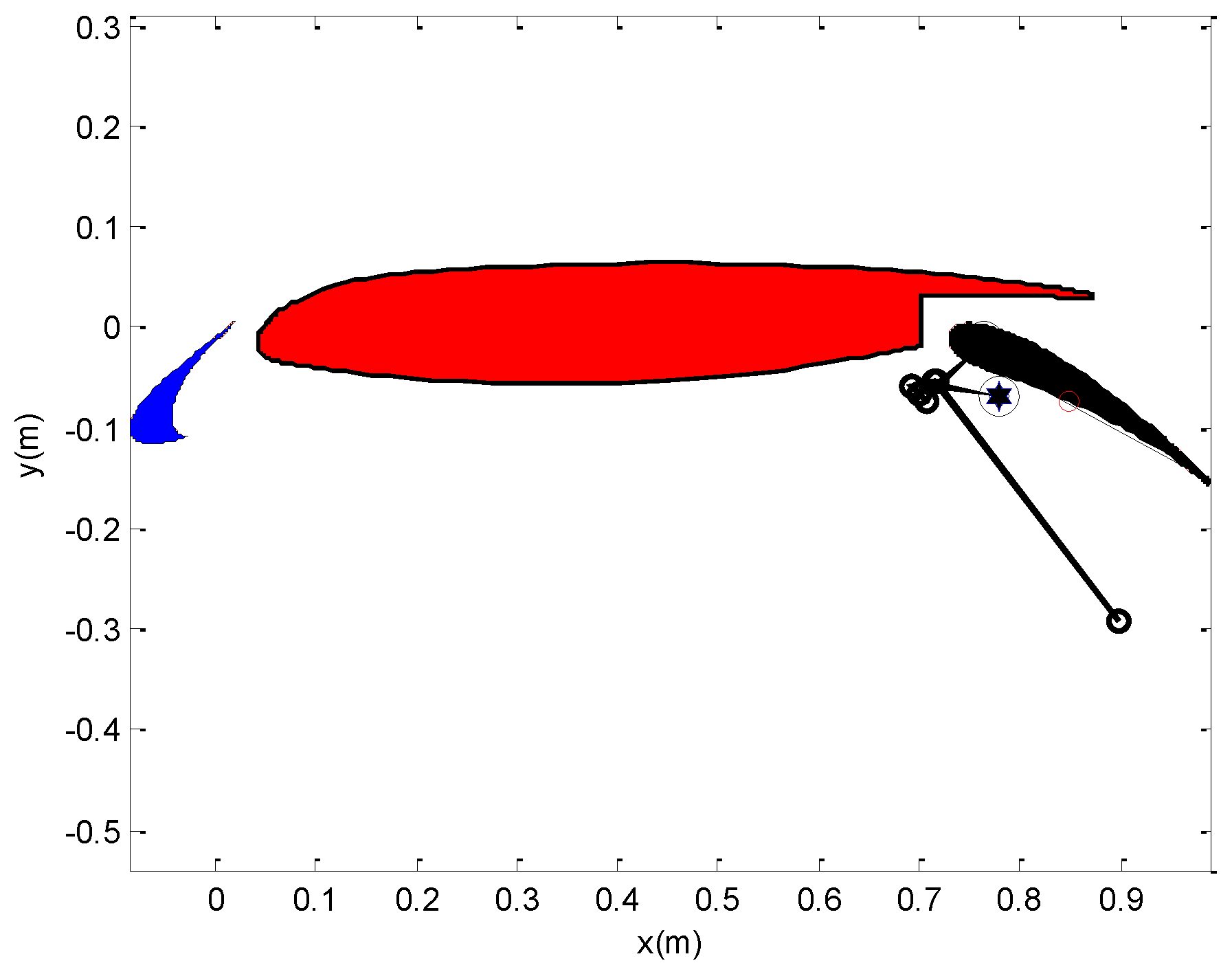
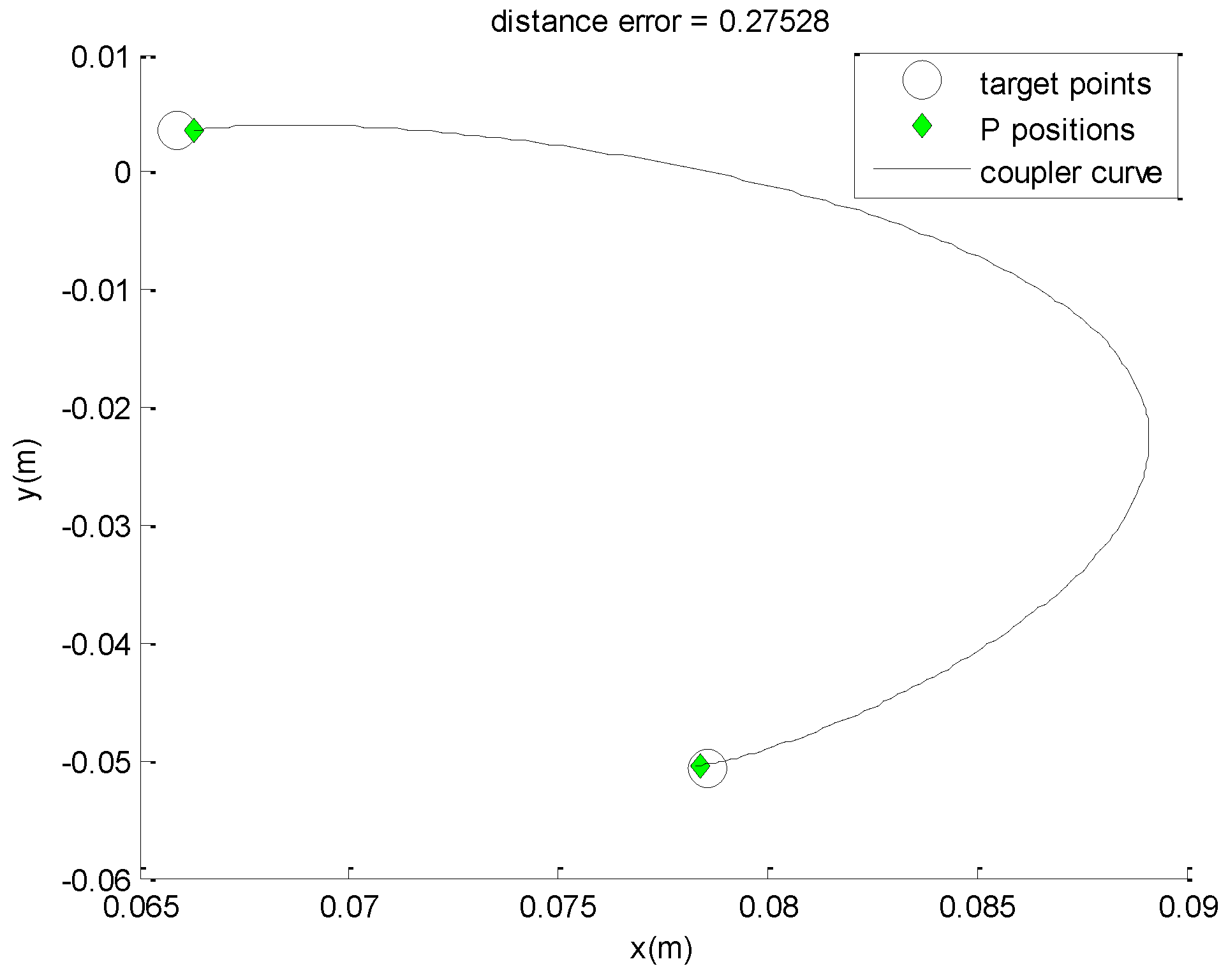
| Case | Position (xi, yi) * 1.1173 | Angle, δi (°) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Take-off | (0.059,0.0032), (0.0642, −0.0455) | 0, 24.90 |
| 2. Landing | (0.059,0.00032), (0.0703, −0.0454) | 0, 43.52 |
| TLBO | Parameters | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r1 | r2 | r3 | r4 | L1 | L2 | x0 | y0 | θ1 | Mean | Max | Min | std | |
| Case-1 | 0.2997 | 0.0381 | 0.2192 | 0.3989 | 0.0468 | 0.1724 | 0 | −0.0500 | −59.9423 | 0.023221 | 0.023425 | 0.02297 | 7.21 × 10−5 |
| Case-2 | 0.2999 | 0.0100 | 0.0232 | 0.2993 | −0.0853 | −0.0637 | 0 | −0.0500 | −48.2343 | 0.138061 | 0.138456 | 0.137642 | 0.000243 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chabphet, P.; Santichatsak, S.; Thalang, T.N.; Sleesongsom, S.; Bureerat, S. High-Lift Mechanism Motion Generation Synthesis Using a Metaheuristic. Proceedings 2019, 39, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019039005
Chabphet P, Santichatsak S, Thalang TN, Sleesongsom S, Bureerat S. High-Lift Mechanism Motion Generation Synthesis Using a Metaheuristic. Proceedings. 2019; 39(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019039005
Chicago/Turabian StyleChabphet, Poothanet, Supanat Santichatsak, Tunnatorn Na Thalang, Suwin Sleesongsom, and Sujin Bureerat. 2019. "High-Lift Mechanism Motion Generation Synthesis Using a Metaheuristic" Proceedings 39, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019039005
APA StyleChabphet, P., Santichatsak, S., Thalang, T. N., Sleesongsom, S., & Bureerat, S. (2019). High-Lift Mechanism Motion Generation Synthesis Using a Metaheuristic. Proceedings, 39(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019039005







