Do Cryptocurrency Prices Camouflage Latent Economic Effects? A Bayesian Hidden Markov Approach †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Summary & Results
- Q1. Do the same explanatory variables affect both the BTC and ETH cryptocurrencies?
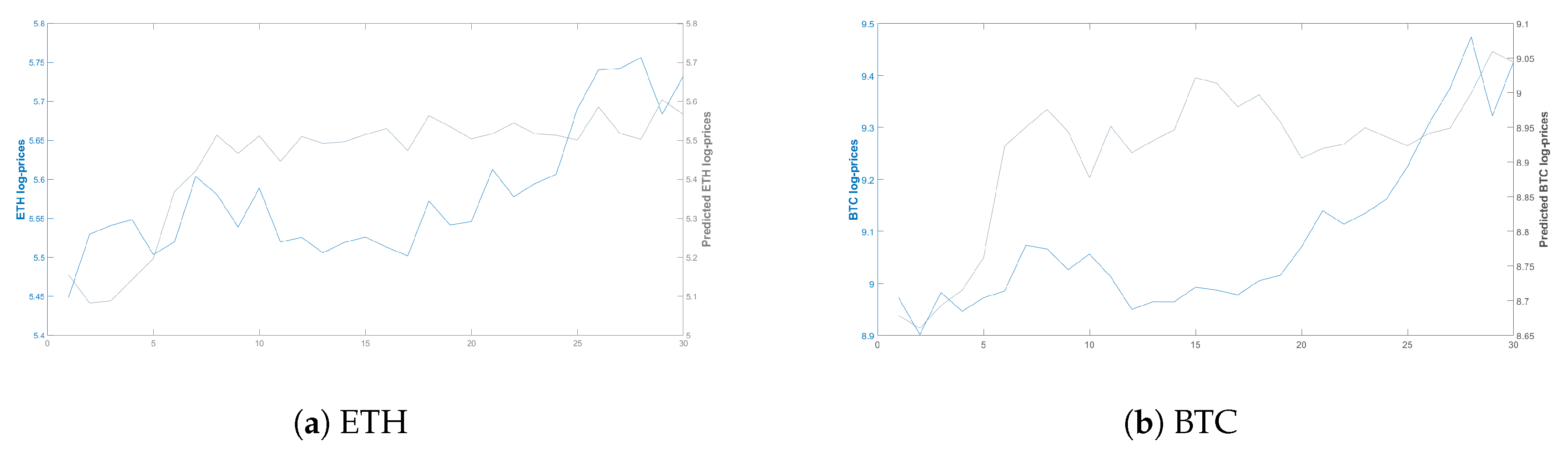
- Q2. What is the predictive power of the NHPG model on the BTC and ETH price series?
- Q3. Do the same explanatory variables affect the BTC price series both on the long and short run?
2. Modeling Cryptocurrency Price Series
The Non-Homogeneous Pólya-Gamma Hidden Markov Model
- Given the model’s parameters, the hidden states are simulated using the Scaled Forward Backward of algorithm of [42].
- The posterior mean regression parameters are simulated using the standard conjugate analysis, via a Gibbs sampler method.
- The logistic regression coefficients are simulated using the Pólya-Gamma data augmentation scheme [43], as a better and more accurate sampling methodology compared to the existing schemes.
- The set of covariates that affect the model linearly and non-linearly (via the transition probabilities) are updated using a double reversible jump algorithm.
- Predictions are made conditional on the simulated unknown quantities.
| Algorithm 1 MCMC Sampling Scheme for Inference on Model Specification and Parameters |
|
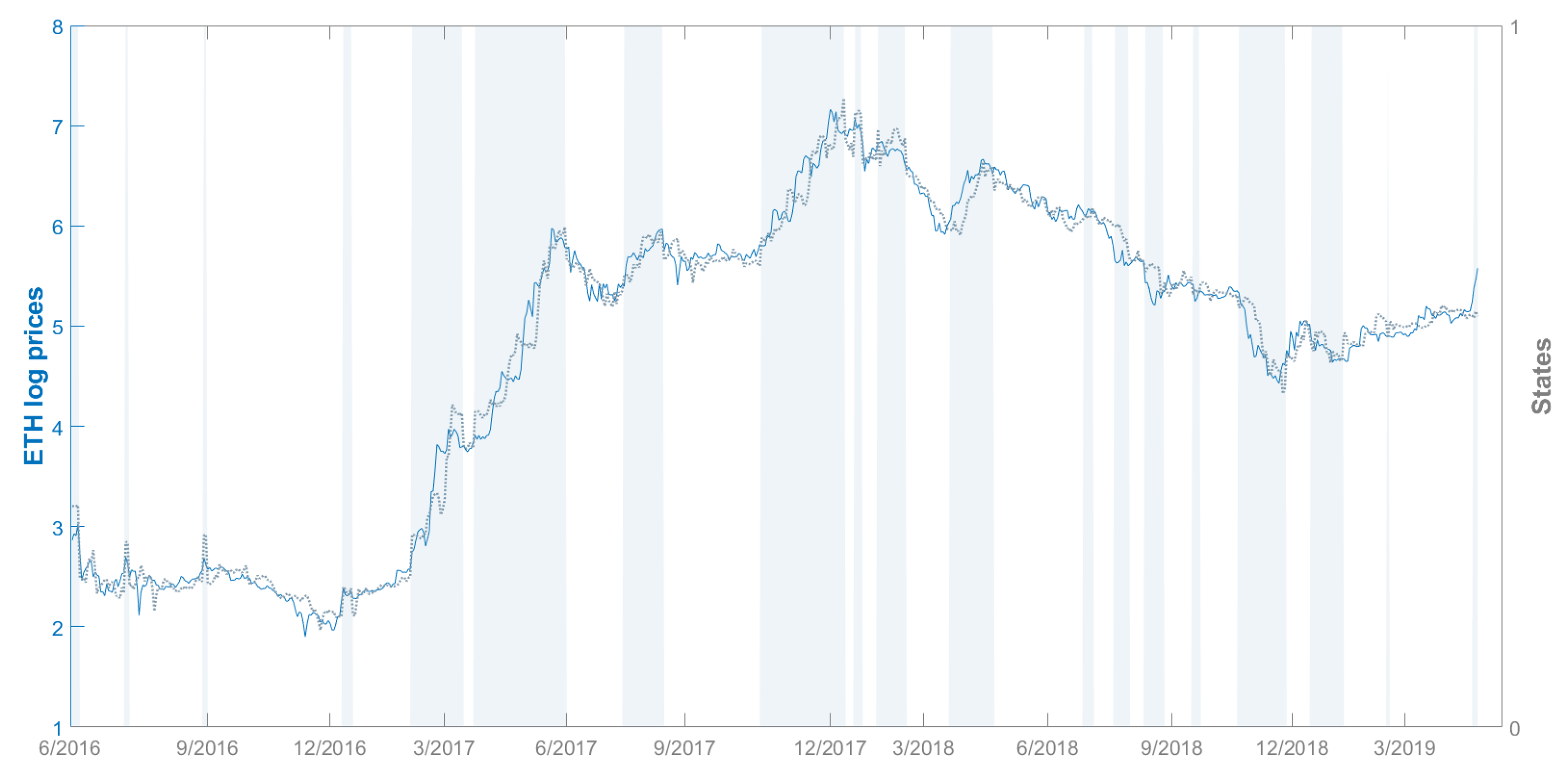
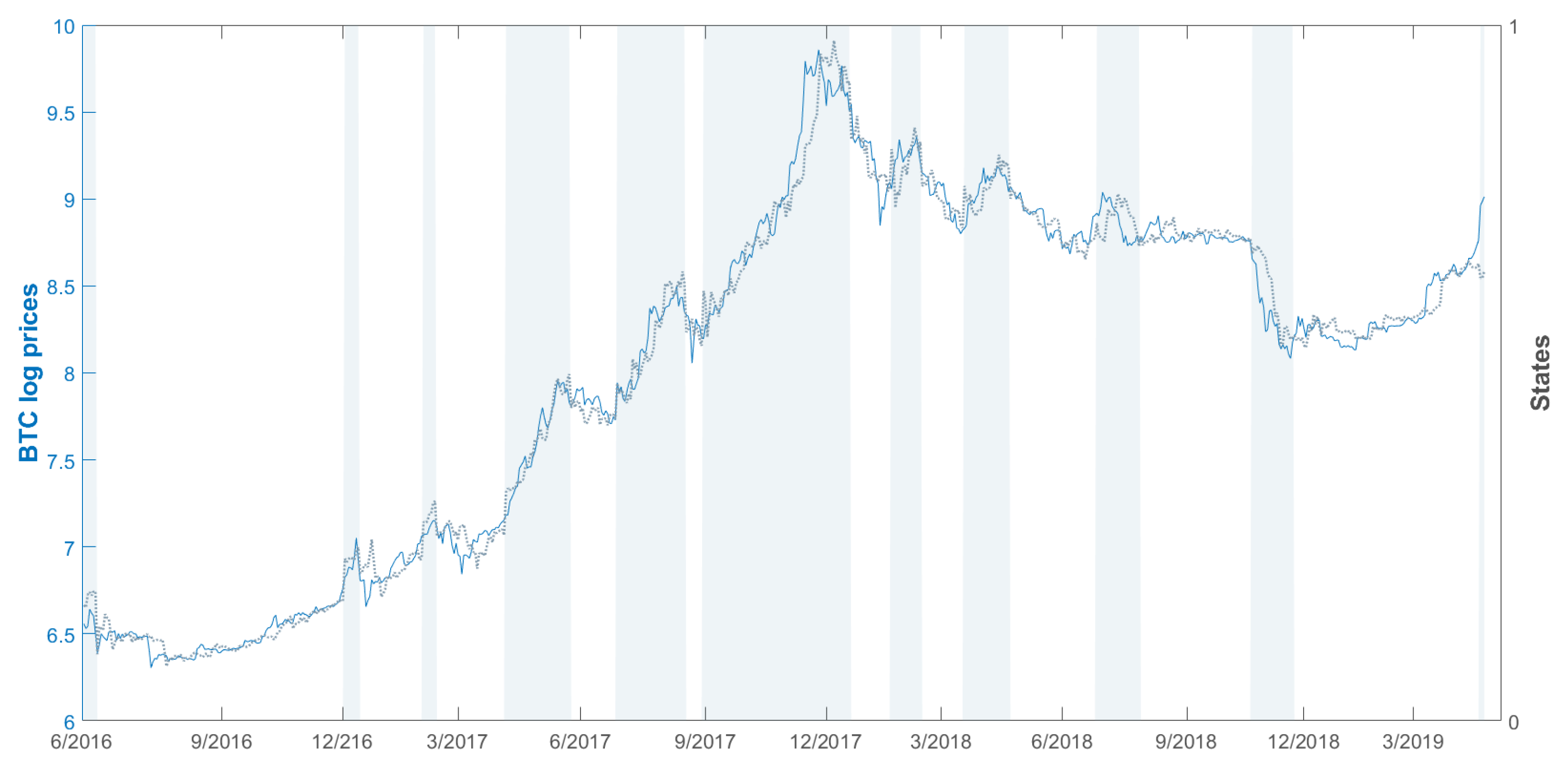
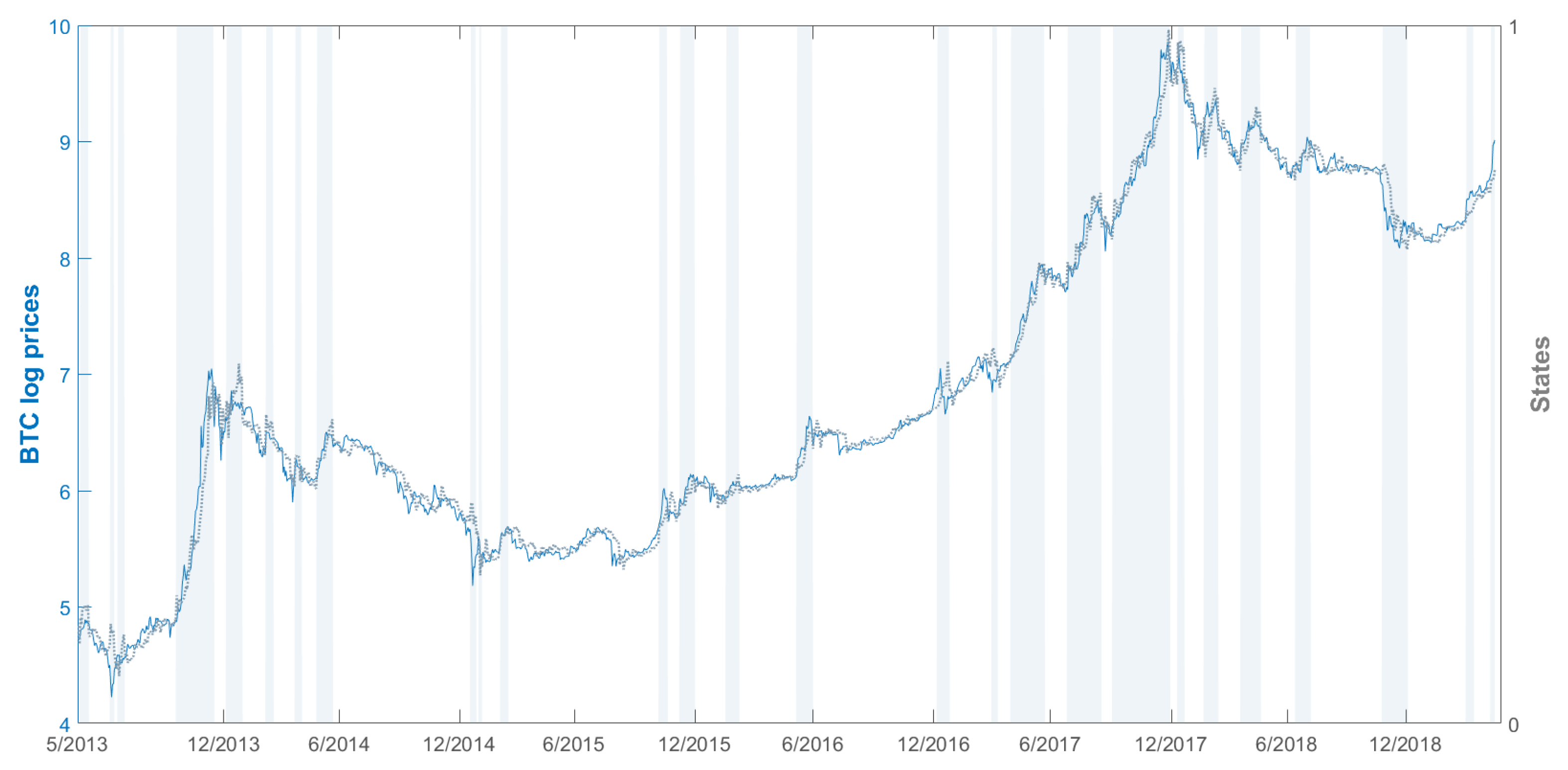
3. The Data-Experiment
| Explanatory Variables | ||
| Description | Symbol | Retrieved from |
| US dollars to Euros exchange rate | USD/EUR | investing.com |
| US dollars to GBP exchange rate | USD/GBP | investing.com |
| US dollars to Japanese Yen exchange rate | USD/JPY | investing.com |
| US dollars to Chinese Yuan exchange rate | USD/CNY | investing.com |
| Standard & Poor’s 500 index | SP500 | finance.yahoo.com |
| Dow Jones Industrial Average | DOW | finance.yahoo.com |
| NASDAQ Composite index | NASDAQ | finance.yahoo.com |
| Crude Oil Futures price | CO | finance.yahoo.com |
| Price of Gold | GOLD | finance.yahoo.com |
| CBOE Volatility index | VIX | finance.yahoo.com |
| Equity market related Economic Uncertainty index | EUI | fred.stlouisfed.org |
| Hash Rate | HR | quandl.com/etherscan.io |
| Average Block Size | AVS | quandl.com/etherscan.io |
| Mean Posterior Variance | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| BTC | BTC | ETH | |
| Sample period | 4/2013–6/2019 | 6/2016–6/2019 | 6/2016–6/2019 |
| Mean Square Forecast Error | |||
| MSFE | |||
4. Results
| Posterior probabilities of inclusion | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictors | BTC | BTC | ETH |
| Sample period | 4/2013 - 6/2019 | 6/2016-6/2019 | 6/2016-6/2019 |
| USD/EUR | 0.65 0.39 | 0.72 0.50 | 0.58 0.50 |
| USD/GBP | 1.00 0.36 | 0.62 0.48 | 0.47 0.48 |
| USD/JPY | 1.00 017 | 0.59 0.27 | 0.36 0.22 |
| USD/CNY | 1.00 0.39 | 0.81 0.44 | 0.67 0.36 |
| CO | 1.00 0.07 | 0.97 0.24 | 1.00 0.15 |
| VIX | 1.00 0.07 | 0.70 0.16 | 1.00 0.12 |
| SP500 | 0.46 0.13 | 0.42 0.20 | 0.47 0.18 |
| DOW | 0.95 0.08 | 0.48 0.16 | 0.45 0.11 |
| NASDAQ | 1.00 0.13 | 0.78 0.23 | 0.77 0.11 |
| GOLD | 1.00 0.12 | 0.97 0.32 | 1.00 0.13 |
| EUI | 0.05 0.01 | 0.07 0.01 | 0.00 0.00 |
| HR | 0.55 0.02 | 0.32 0.22 | 1.00 0.01 |
| AVS | 1.00 0.02 | 1.00 0.01 | 0.57 0.06 |
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakamoto, S. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. 2008. Available online: https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2019).
- Garay, J.; Kiayias, A.; Leonardos, N. The Bitcoin Backbone Protocol: Analysis and Applications. In Advances in Cryptology—EUROCRYPT 2015; Oswald, E., Fischlin, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 281–310. [Google Scholar]
- Crypto.com. 2019. Available online: https://coinmarketcap.com/all/views/all/ (accessed on 30 July 2019).
- Paper, L.W. 2019. Available online: https://libra.org/en-US/white-paper/?noredirect=en-US (accessed on 30 July 2019).
- Cheah, E.T.; Fry, J. Speculative bubbles in Bitcoin markets? An empirical investigation into the fundamental value of Bitcoin. Econ. Lett. 2015, 130, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, T.; Thu, H.; Walther, T. Bitcoin is not the New Gold—A comparison of volatility, correlation, and portfolio performance. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2018, 59, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaian, P.; Rajcaniova, M.; Kancs, A. The economics of BitCoin price formation. Appl. Econ. 2016, 48, 1799–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyhrberg, A.H. Bitcoin, gold and the dollar—A GARCH volatility analysis. Financ. Res. Lett. 2016, 16, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouri, E.; Gupta, R.; Tiwari, A.K.; Roubaud, D. Does Bitcoin hedge global uncertainty? Evidence from wavelet-based quantile-in-quantile regressions. Financ. Res. Lett. 2017, 23, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouri, E.; Azzi, G.; Dyhrberg, A.H. On the return-volatility relationship in the Bitcoin market around the price crash of 2013. Economics 2017, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouri, E.; Molnár, P.; Azzi, G.; Roubaud, D.; Hagfors, L.I. On the hedge and safe haven properties of Bitcoin: Is it really more than a diversifier? Financ. Res. Lett. 2017, 20, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, E.; Gozgor, G.; Lau, C.M.; Vigne, S.A. Does economic policy uncertainty predict the Bitcoin returns? An empirical investigation. Financ. Res. Lett. 2018, 26, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiampa, P. Volatility estimation for Bitcoin: A comparison of GARCH models. Econ. Lett. 2017, 158, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.S. Cryptocurrency value formation: An empirical study leading to a cost of production model for valuing bitcoin. Telemat. Inf. 2017, 34, 1308–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillip, A.; Chan, J.; Peiris, S. On generalized bivariate student-t Gegenbauer long memory stochastic volatility models with leverage: Bayesian forecasting of cryptocurrencies with a focus on Bitcoin. Econom. Stat. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgoula, I.; Pournarakis, D.; Bilanakos, C.; Sotiropoulos, D.; Giaglis, G.M. Using Time-Series and Sentiment Analysis to Detect the Determinants of Bitcoin Prices. MCIS 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colianni, S.G.; Rosales, S.M.; Signorotti, M. Algorithmic Trading of Cryptocurrency Based on Twitter Sentiment Analysis; CS229 Project; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Borri, N. Conditional tail-risk in cryptocurrency markets. J. Empir. Financ. 2019, 50, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, R. Ethereum Price Analysis: Ethereum (ETH) Needs To Discover The Magic Spell To Surge On Its Own. 2019. Available online: https://www.cryptonewsz.com/ethereum-price-analysis-ethereum-eth-needs-to-discover-the-magic-spell-to-surge-on-its-own/29402/ (accessed on 27 July 2019).
- Koki, C.; Meligkotsidou, L.; Vrontos, I. Forecasting under model uncertainty:Non-homogeneous hidden Markov models with Polya-Gamma data augmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1802.02825. [Google Scholar]
- Meligkotsidou, L.; Dellaportas, P. Forecasting with non-homogeneous hidden Markov models. Stat. Comput. 2011, 21, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, C. Can the Markov switching model forecast exchange rates? J. Int. Econ. 1994, 36, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Chen, S.L. Why use Markov-switching models in exchange rate prediction? Econ. Model. 2006, 23, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frömmel, M.; MacDonald, R.; Menkhoff, L. Markov switching regimes in a monetary exchange rate model. Econ. Model. 2005, 22, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, J.; Schüssler, R. Forecasting exchange rates under parameter and model uncertainty. J. Int. Money Financ. 2016, 60, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, J.J.J.; Paap, R.; Ravazzolo, F. Real-Time Inflation Forecasting in a Changing World. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 2013, 31, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.H. Forecasting US inflation by Bayesian model averaging. J. Forecast. 2009, 28, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.H. Bayesian Model Averaging and exchange rate forecasts. J. Econ. 2008, 146, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamon, R.; Elliott, R. (Eds.) Hidden Markov Models in Finance: Further Developments and Applications, Volume II; International Series in Operations Research & Management Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Poyser, O. Exploring the dynamics of Bitcoin’s price: a Bayesian structural time series approach. Eurasian Econ. Rev. 2019, 9, 29–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, R.C.; Gorse, D. Predicting cryptocurrency price bubbles using social media data and epidemic modelling. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 November–1 December 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcilar, M.; Bouri, E.; Gupta, R.; Roubaud, D. Can volume predict Bitcoin returns and volatility? A quantiles-based approach. Econ. Model. 2017, 64, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Lee, J. An Empirical Study on Modeling and Prediction of Bitcoin Prices With Bayesian Neural Networks Based on Blockchain Information. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 5427–5437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichl, L.; Kaizoji, T. Volatility Analysis of Bitcoin Price Time Series. Quant. Financ. Econ. 2017, 1, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wijk, D. What can be expected from the BitCoin. Ph.D. Thesis, Erasmus Universiteit Rotterdam, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yermack, D. Chapter 2—Is Bitcoin a Real Currency? An Economic Appraisal. In Handbook of Digital Currency; Chuen, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, J.C.S. Analyzing Bitcoin Price Volatility. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hotz-Behofsits, C.; Huber, F.; Zörner, T.O. Predicting crypto-currencies using sparse non-Gaussian state space models. J. Forecast. 2018, 37, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, S.; Roche, J.; Caton, S. Predicting the Price of Bitcoin Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 26th Euromicro International Conference on Parallel, Distributed and Network-based Processing (PDP), Cambridge, UK, 21–23 March 2018; pp. 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C. Forecasting exchange rates: The multi-state Markov-switching model with smoothing. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2011, 20, 342–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, I.W. High-frequency Markov switching models in the foreign exchange market. J. Forecast. 2000, 19, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, S.L. Bayesian Methods for Hidden Markov Models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2002, 97, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polson, N.G.; Scott, J.G.; Windle, J. Bayesian Inference for Logistic Models Using Polya-Gamma Latent Variables. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2013, 108, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirignano, J.; Cont, R. Universal features of price formation in financial markets: Perspectives from deep learning. Quant. Financ. 2019, 19, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koki, C.; Leonardos, S.; Piliouras, G. Do Cryptocurrency Prices Camouflage Latent Economic Effects? A Bayesian Hidden Markov Approach. Proceedings 2019, 28, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019028005
Koki C, Leonardos S, Piliouras G. Do Cryptocurrency Prices Camouflage Latent Economic Effects? A Bayesian Hidden Markov Approach. Proceedings. 2019; 28(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019028005
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoki, Constandina, Stefanos Leonardos, and Georgios Piliouras. 2019. "Do Cryptocurrency Prices Camouflage Latent Economic Effects? A Bayesian Hidden Markov Approach" Proceedings 28, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019028005
APA StyleKoki, C., Leonardos, S., & Piliouras, G. (2019). Do Cryptocurrency Prices Camouflage Latent Economic Effects? A Bayesian Hidden Markov Approach. Proceedings, 28(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2019028005





