Abstract
This communication presents ModSCO, a web application that supports systematic energy performance evaluation using Reduced Order Models (ROM). These models are particularly useful in scenario with missing, incomplete or uncertain building information. The paper describes the theory behind ROM grey-box modelling and presents case studies that support the smart operation of energy systems by generating Energy Conservation Opportunities (ESCOs) for instance, to help ISO 50001 implementation. The ROM demonstrated to provide accurate results with a reduced effort. The acceptable calibration tolerance provided by the ASHRAE Guideline 14 is been used to demonstrate the ROM’s accuracy. Additionally, the ModSCO architecture and user interface is also described.
1. Introduction
The energy performance gap between the building design and operation stages is well documented in literature. Common errors across the Building Life Cycle can reach to 150–250% increase in energy consumption [1]. Extensive energy retrofit programs are in place to tackle this gap. Based on a BPIE study, 5% of all renovations in Europe are extensive/nZEB renovations achieving 60% energy reduction [2]. However, some barriers for the uptake of nZEB deep-renovation remain such as: process complexity, poor skillsets, uncertainty about post-renovation’s energy performance and unclear financial mechanisms [3].
To overcome these barriers, the HIT2GAP Project (“Highly Innovative building control Tools Tackling the energy performance GAP”) [4], proposes the online BEMServer platform which advantage of building energy data and provides with a range of assessment tools [5].
This research paper presents one of these tools, the ModSCO module [6]. This module uses a Reduced Order Model (ROM) based on grey-box modelling methods to support the smart operation of energy systems and can be used to generate Energy Conservation Opportunities within the ISO 50,001 continuous improvement cycle [7]. This tool provides users with an interface to a ROM model without the need to install proprietary software. A grey box model structure was selected as underlying model thanks to the capability of these models of estimating the energy consumption in the typical scenario where the technical information about the building is missing and/or high uncertainty regarding the model parameters is present [8].
Section 2 presents the model used in the analysis and outlines the methods used for model development and calibration. A description of the ModSCO web interface is presented in Section 3. Pilot case studies are shown in Section 4, Section 5 discusses simulations results and finally, Section 6 summarizes the main conclusions.
2. Underlying Core Reduced Order Models Used in ModSCO
The ModSCO module makes use of Reduced Order Models based on grey box model developed by using the Modelica language programming [9]. Grey box models are a combination of black and white box models. They take the advantage of both methods by coupling the physical meaning and structure from the white box paradigm and the statistical approach and parameter estimation from the black box approach. In particular, the Modelica ROM used in ModSCO simplifies the physical description of the building using thermal network analogies and considering the system complexity as an electrical problem by means of resistances and capacitances. Figure 1 shows the RC-network diagram representing the ROM developed.
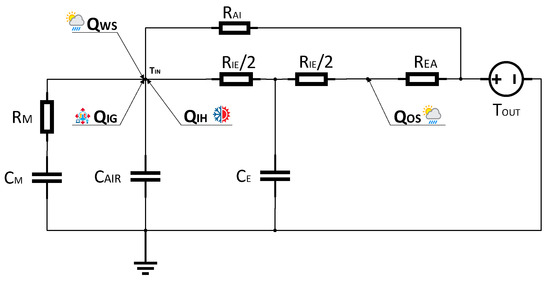
Figure 1.
The ModSCO ROM RC-network diagram.
The ModSCO ROM is composed of 5 resistances and 3 capacitances plus inputs regarding the internal gain, the solar radiation and the system heat gains. The resistances and capacitances of the ROM can be divided in two main groups: (1) The first aggregation (CM, RM) is used to lump the building internal wall and slabs and (2) the second cluster (REA, CE, RIE) is used to lump the whole building opaque and transparent envelope. RAI is the resistance used to simulate the air infiltration and natural ventilation and finally CAIR is the room capacitance represented in Modelica by using the MixingVolume element. QWS and QOS are the heat gain generated by the solar radiance through windows and opaque surfaces, a new component WeaterData has been created for evaluate these variables. QIG is estimated by the InternlGain component created in Modelica to calculate the heat gains due to people, lighting and electric equipment. Finally, QIH is the system heat gain which uses a new component H/CSystem for its calculation.
With the ROM resistances and capacitances described, a number of software tools were used to generate the core model used in ModSCO. Proprietary tools such as Dymola [10], and open source tools like JModelica [11] and Open Modelica [12] were used to generate the final Functional Mock-up Unit file (FMU) for the ModSCO core model. Some of the R-C elements of the models still need to be calculated using a spreadsheet provided online and customized for the users of ModSCO. The info needed at this spreadsheet can be collected through data collection and surveys. The formulas used to calculate these parameters are based on methods defined in a range of European Standards, e.g., calculation of walls resistance is based on ISO 6946 2007 [13]. A simplified calibration procedure is implemented by automatically comparing the resulting baseline model energy consumption simulated with the actual energy consumption data, and by verifying that the NMBE and the CV-RMSE indexes are into the ASHRAE 14 [14] recommendation of 5% and 15%. A simple calibration for the energy consumption was done by adjusting the uncertain parameters within an estimated range. The uncertain parameters were selected following the assumption made by Giretti et al. [8].
3. The ModSCO Web Interface to ROM
The ModSCO application main concept is to expose a generic ROM model where a number of variables (the model parameters) are modifiable and setup by the user. When parameter sets are generated then the model is simulated at the user request and results can be consulted. The core model sits statically in the application as an FMU file. This contains the equations, libraries and solvers to run the model so no critical dependencies or external firmware needs to be run. Once the FMU is generated, the model contained in it is called using a long open-source stack (PyFMI and dependencies) and integrated in the server side of ModSCO. Web interface to data, variables, parameter sets, results and HIT2GAP/BEMServer integration was developed using Django MVC framework [15]. The following is a summary of the main features as a result of the HIT2GAP project efforts. The features developed can be demonstrated for selected rooms at the Alice Perry Engineering Building pilot site:
- Simulation of the FMU contained model through a web interface. This is achieved by using python based FMI implementation PyFMI package and its dependencies. The web app runs this task asynchronously using a messages queue (RabbitMQ [16]) and asynchronous task scheduler (Celery [17]). ModSCO architecture is shown in Figure 2;
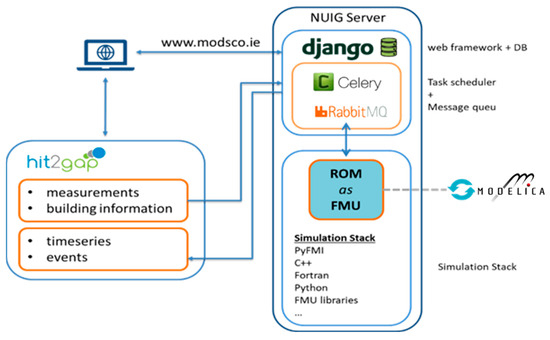 Figure 2. The ModSCO application architecture.
Figure 2. The ModSCO application architecture.
- Setup of different models using forms and handling of model administration actions such as edit, delete, save as new model or create a new model (see Figure 3);
 Figure 3. ModSCO models administration for a selected room.
Figure 3. ModSCO models administration for a selected room. - Retrieval of model results and visualization, this can be achieved using the web interface or downloading csv files for user manipulation;
- Generation of calibration jobs. Generation of a collection of different models and simulation with variations in a range of parameters in order to be calibrated by third party applications such as Calibro [18];
- Integration with HIT2GAP/BEMServer. This feature is only available through BEMServer/Hit2Gap portal authenticated access.
4. Case Studies
The models described has been used using three rooms of the Alice Perry Engineering Building of the National University of Ireland Galway (NUIG) as case studies. The first room was the Post Grads Areas 2053 and 3053 located on the second and third floor and served by AHU 103, the second room was the Lecture Theatre G47 placed on the ground floor and conditioned by the AHU 101A and finally the third has been the Computer Labs 2016 and 2017 situated on the second floor served by the AHU105. A survey has been done for all the three rooms to collect construction data, thermal and electric energy consumption of AHUs and thermal system for years 2015 and 2016.
5. Results and Discussion
Data for the three case studies selected was analysed and used following the method in Section 2. The data collected have been used to fill the spreadsheet and calculate the required R-C values. A semi-automated calibration routine was performed using a python script. Figure 4 summarizes the uncertain parameters changed during the calibration procedure for the Computer Lab.
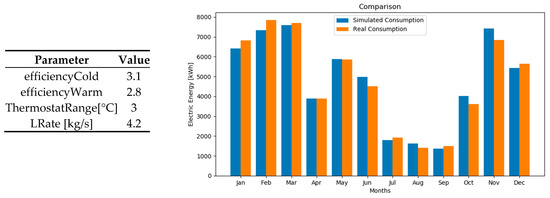
Figure 4.
Calibration uncertain parameters on the right and Comparison of Real vs Simulated energy consumption of the Computer Lab 2016 2017.
For all the three rooms the results have satisfied the ASHRAE calibration criteria. In particular, the Post Grad Area provided a NMBE = 0.39% and a CV-RMSE = 9.80%, the Lecture Theatre a NMBE = 0.09% and a CV-RMSE = 8.81%, and finally the Computer Lab a NMBE = 0.32% and a CV-RMSE = 7.08%. Figure 4 shows the comparison between real and simulated consumption. Additional graphs can be generated using ModSCO (e.g., monthly deviation or cumulative energy consumption).
For the Computer Lab the methodology was then further validated with the followed 2016 year data by changing weather file, occupancy schedules, AHU setpoints, and AHU heating and cooling switch. The results obtained are similarly positive and satisfy all calibration criteria with a NMBE = 1.42%, CV-RMSE = 11.10%. In the same room the script was also used to test the impact of a control scenario based on temperature setpoint. For 2015, the setpoint temperature of the Computer Lab was fixed to 22 °C. A control scenario by using 20 °C for the winter season and 24 °C for the summer season has been tested. This implementation results with a yearly electric energy saving of 2100 kWh.
6. Conclusions
Reduced Order Models were used to estimate the energy consumption of three university rooms. The models were tested and validated using real data from the Alice Perry Engineering Building at NUIG. Calibration results were in the acceptance range of ASHRAE Guideline 14 for yearly energy consumption prediction. The ROM then is used to test the impact of a control strategy. The use of ModSCO is illustrated, emphasising the user easy to setup, fast to run, and accurate ROM models can support impact evaluation of environmental and energy retrofit scenarios using a limited information and uncertain data.
Funding
This research work was funded by the Irish Research Council (IRC) - R2M Solution S.r.l Enterprise Partnership Scheme Postgraduate Scholarship 2017 under project ID EPSPG/2017/359 and by the European Union H2020 program under the HIT2GAP project with Grant agreement No. 680708.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Buildings Working Group of the Green Construction Board. Available online: http://www.greenconstruction-board.org/ (accessed on 28 May 2019).
- Astola, I.; Rademaekers, K.; Williams, R.; Yearwood, J. Boosting Building Renovation: What Potential and Value for Europe? Directorate-General for Internal Policies. Policy Department Economic and Scientific Policy, 2016. EU Publications. Available online: http://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/STUD/2016/587326/IPOL_STU(2016)587326_EN.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2019).
- Lee, P.; Lam, P.T.I.; Lee, W.L. Risks in Energy Performance Contracting (EPC) projects. Energy Build. 2015, 92, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hit2Gap Consortium. Hit2Gap: Highly Innovative Building Control Tools Tackling the Energy Performance Gap. Available online: http://www.hit2gap.eu/ (accessed on 28 May 2019).
- Hit2Gap Consortium. “BEMServer”. Available online: https://www.bemserver.org/ (accessed on 28 May 2019).
- IRUSE Group. ModSCO—Reduced Order Models to tackle the performance gap. Available online: https://www.modsco.ie/ (accessed on 28 May 2019).
- International Organization for Standardization. Energy Management Systems—Requirements with Guidance for Use (ISO 50001:2018); ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Giretti, A.; Vaccarini, M.; Casals, M.; Macarulla, M.; Fuertes, A.; Jones, R.V. Reduced-order modeling for energy performance contracting. Energy Build. 2018, 167, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modelica Association. Modelica Standard Library. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/modelica/ModelicaStandardLibrary (accessed on 28 May 2019).
- Dassault Systemes. “Dymola Systems Engineering”. Available online: https://www.3ds.com/-products-services/catia/products/dymola/ (accessed on 28 May 2019).
- Modelon, A.B. JModelica.org. Available online: https://jmodelica.org/ (accessed on 28 May 2019).
- Open Source Modelica Consortium (OSMC). OpenModelica. Available online: https://open-modelica.org/ (accessed on 28 May 2019).
- ISO. ISO 6946 2007 Building Components and Building Elements—Thermal Resistance and Thermal Transmittance—Calculation Method; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- American Society of Heating. Refrigeration & Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE 2014). In Guideline 14 Measurement of Energy, Demand, and Water Savings; ASHRAE: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Django Software Foundation. Django. Available online: https://www.djangoproject.com/ (accessed on 28 May 2019).
- Pivotal Software Inc. RabbitMQ. Available online: https://www.rabbitmq.com/ (accessed on 28 May 2019).
- Celery Software Foundation. Celery Project. Available online: http://www.celeryproject.org/ (accessed on 28 May 2019).
- University of Strathclyde, Glasgow. Calibro. Available online: https://www.strath.ac.uk/research/-energysystemsresearchunit/applications/calibro/ (accessed on 28 May 2019).
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).