Effect of Gemcitabine on HOTAIR Expression Level in H596 and H1944 Cell Lines †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
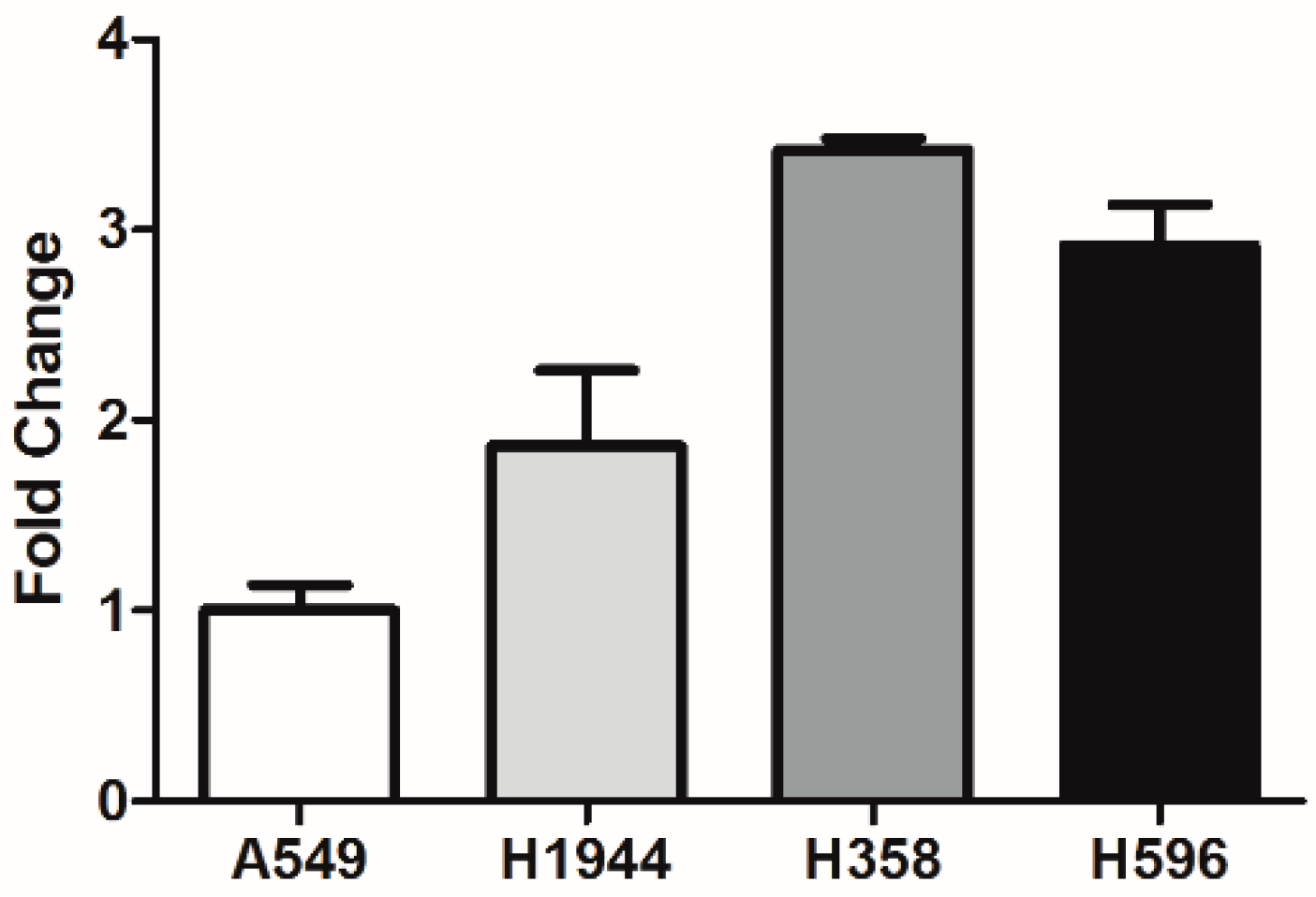
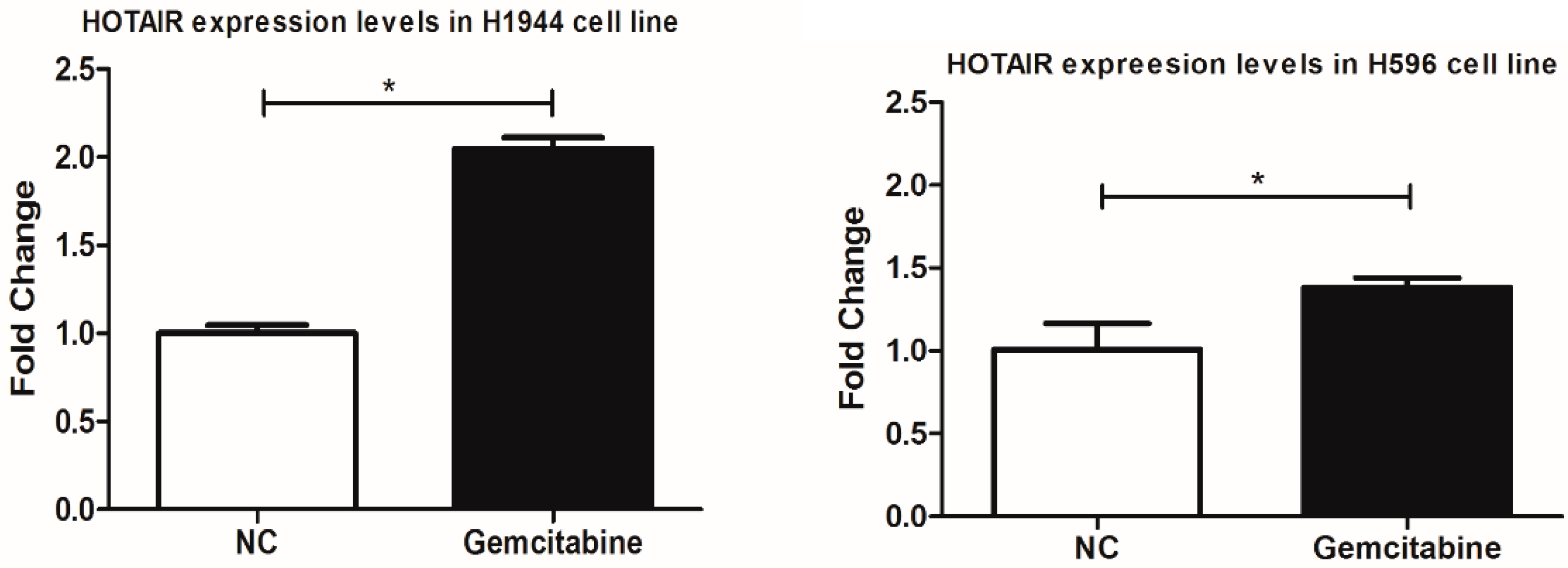
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruder, D.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.; Shien, K.; Behrens, C.; Kalhor, N.; Chen, H.; Shen, L.; Lee, J.J.; Hong, W.K.; Tang, X.; et al. Concomitant targeting of the mTOR/MAPK pathways: Novel therapeutic strategy in subsets of RICTOR/KRAS-altered non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 21, 33995–34008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Saavedra, D.; Neninger, E.; Rodriguez, C.; Viada, C.; Mazorra, Z.; Lage, A.; Crombet, T. CIMAvax-EGF: Toward long-term survival of advanced NSCLC. Semin. Oncol. 2018, 45, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, M.K.; Niknafs, Y.S.; Malik, R.; Singhal, U.; Sahu, A.; Hosono, Y.; Barrette, T.R.; Prensner, J.R.; Evans, J.R.; Zhao, S.; et al. The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human transcriptome. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parasramka, M.A.; Maji, S.; Matsuda, A.; Yan, I.K.; Patel, T. Long non-coding RNAs as novel targets for therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 161, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, Z. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR: A novel oncogene. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 5611–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toschi, L.; Cappuzzo, F. Gemcitabine for the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Targets Ther. 2009, 2, 209–217. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.W.; Wu, M.J.; Lin, Z.M.; Wang, C.Y.; Cheng, S.Y.; Lin, Y.K.; Chow, Y.H.; Ch’ang, H.J.; Chang, V.H.S. Therapeutic Effect of Repurposed Temsirolimus in Lung Adenocarcinoma Model. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Dong, P.; Wang, W.; Huang, M.; Tian, B. Gemcitabine treatment causes resistance and malignancy of pancreatic cancer stem-like cells via induction of lncRNA HOTAIR. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 4773–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kandemiş, E.; Domaniku, A.; Polat, İ.; Bulut, G. Effect of Gemcitabine on HOTAIR Expression Level in H596 and H1944 Cell Lines. Proceedings 2018, 2, 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2251590
Kandemiş E, Domaniku A, Polat İ, Bulut G. Effect of Gemcitabine on HOTAIR Expression Level in H596 and H1944 Cell Lines. Proceedings. 2018; 2(25):1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2251590
Chicago/Turabian StyleKandemiş, Emine, Aylin Domaniku, İrem Polat, and Gülay Bulut. 2018. "Effect of Gemcitabine on HOTAIR Expression Level in H596 and H1944 Cell Lines" Proceedings 2, no. 25: 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2251590
APA StyleKandemiş, E., Domaniku, A., Polat, İ., & Bulut, G. (2018). Effect of Gemcitabine on HOTAIR Expression Level in H596 and H1944 Cell Lines. Proceedings, 2(25), 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2251590



