Helicobacter Pylori Causes Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in DNA Double Strand Break Repair Inhibited Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
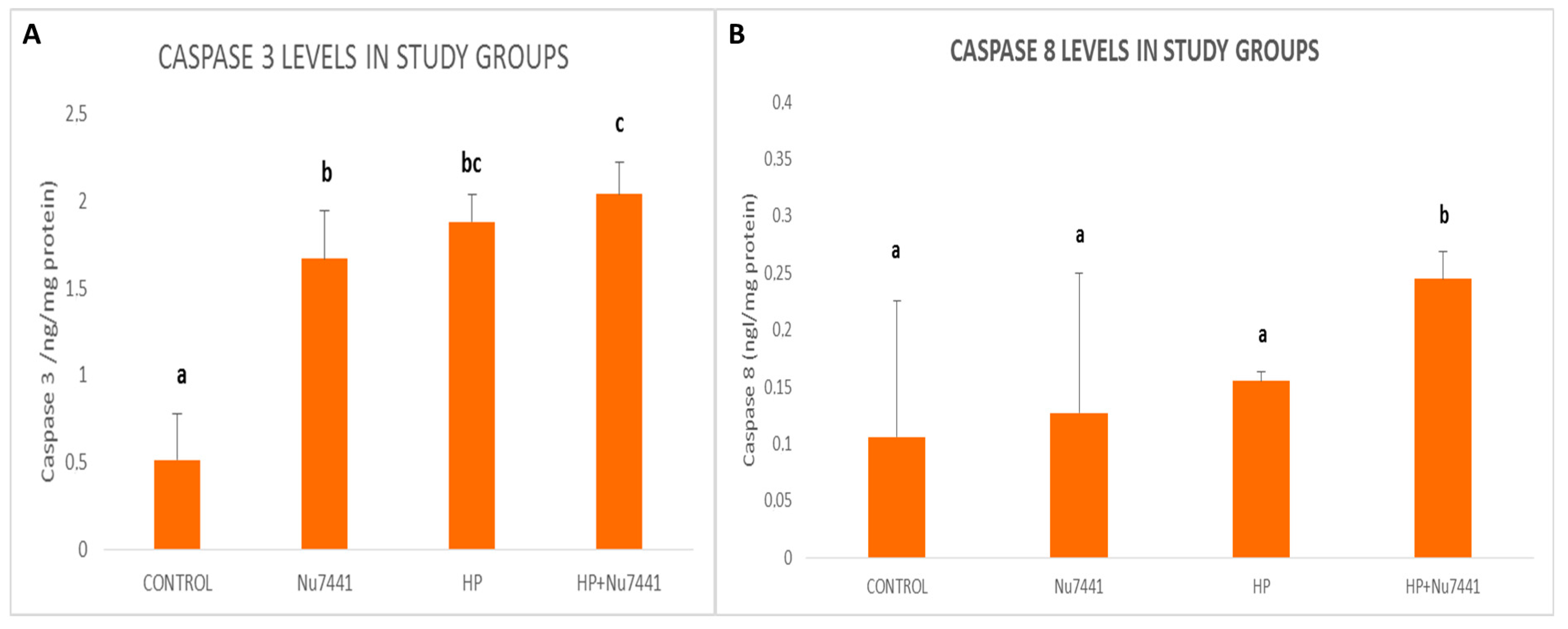
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Martel, C.; Ferlay, J.; Franceschi, S.; Vignat, J.; Bray, F.; Forman, D.; Plummer, M. Global burden of cancers attributable to infections in 2008: A review and synthetic analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, N.R.R.; Nammi, D.; Pasupuleti, A.C.M.; Surekha, C. Helicobacter pylori ınduced gastric ınflammation, ulcer, and cancer: A pathogenesis perspective. Int. J. Inflamm. Cancer Integ. Ther. 2014, 1, 1000113. [Google Scholar]
- Toller, I.M.; Neelsen, K.J.; Steger, M.; Hartung, M.L.; Hottiger, M.O.; Stucki, M.; Kalali, B.; Gerhard, M.; Sartori, A.A.; Lopes, M.; et al. Carcinogenic bacterial pathogen Helicobacter pylori triggers DNA double-strand breaks and a DNA damage response in its host cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14944–14949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paniagua, G.L.; Monroy, E.; Rodríguez, R.; Arroniz, S.; Rodríguez, C.; Cortés, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Negrete, E.; Vaca, S. Frequency of vacA, cagA and babA2 virulence markers in Helicobacter pylori strains isolated from Mexican patients with chronic gastritis. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2009, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, N.R. DNA damage by reactive species: Mechanisms, mutation and repair. J. Biosci. 2012, 37, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkekoglu, P.; Oral, D.; Kocer-Gumusel, B.; Chao, M.W. DNA Double-Strand Breaks Caused by Different Microorganisms: A Special Focus on Helicobacter pylori. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2017, 36, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.P.; Bartek, J. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 2009, 461, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oral, D.; Sur, Ü.; Özkemahlı, G.; Akyön, Y.; Koçer-Gümüşel, B.; Erkekoğlu, P. Helicobacter Pylori Causes Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in DNA Double Strand Break Repair Inhibited Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells. Proceedings 2018, 2, 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2251544
Oral D, Sur Ü, Özkemahlı G, Akyön Y, Koçer-Gümüşel B, Erkekoğlu P. Helicobacter Pylori Causes Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in DNA Double Strand Break Repair Inhibited Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells. Proceedings. 2018; 2(25):1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2251544
Chicago/Turabian StyleOral, Didem, Ünzile Sur, Gizem Özkemahlı, Yakut Akyön, Belma Koçer-Gümüşel, and Pınar Erkekoğlu. 2018. "Helicobacter Pylori Causes Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in DNA Double Strand Break Repair Inhibited Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells" Proceedings 2, no. 25: 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2251544
APA StyleOral, D., Sur, Ü., Özkemahlı, G., Akyön, Y., Koçer-Gümüşel, B., & Erkekoğlu, P. (2018). Helicobacter Pylori Causes Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in DNA Double Strand Break Repair Inhibited Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma Cells. Proceedings, 2(25), 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2251544




