Sensorized Insole for Diabetic Foot Monitoring †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
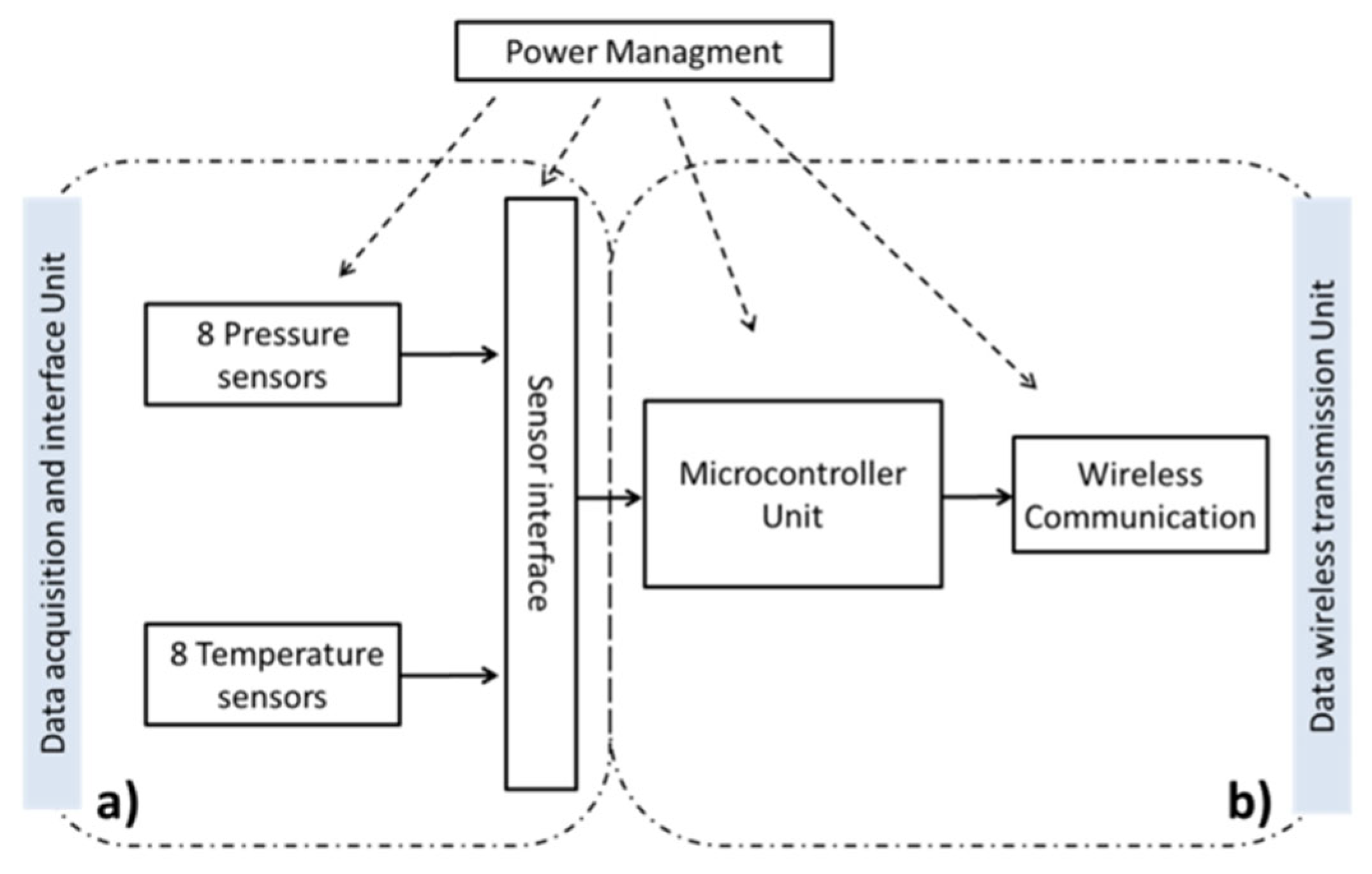
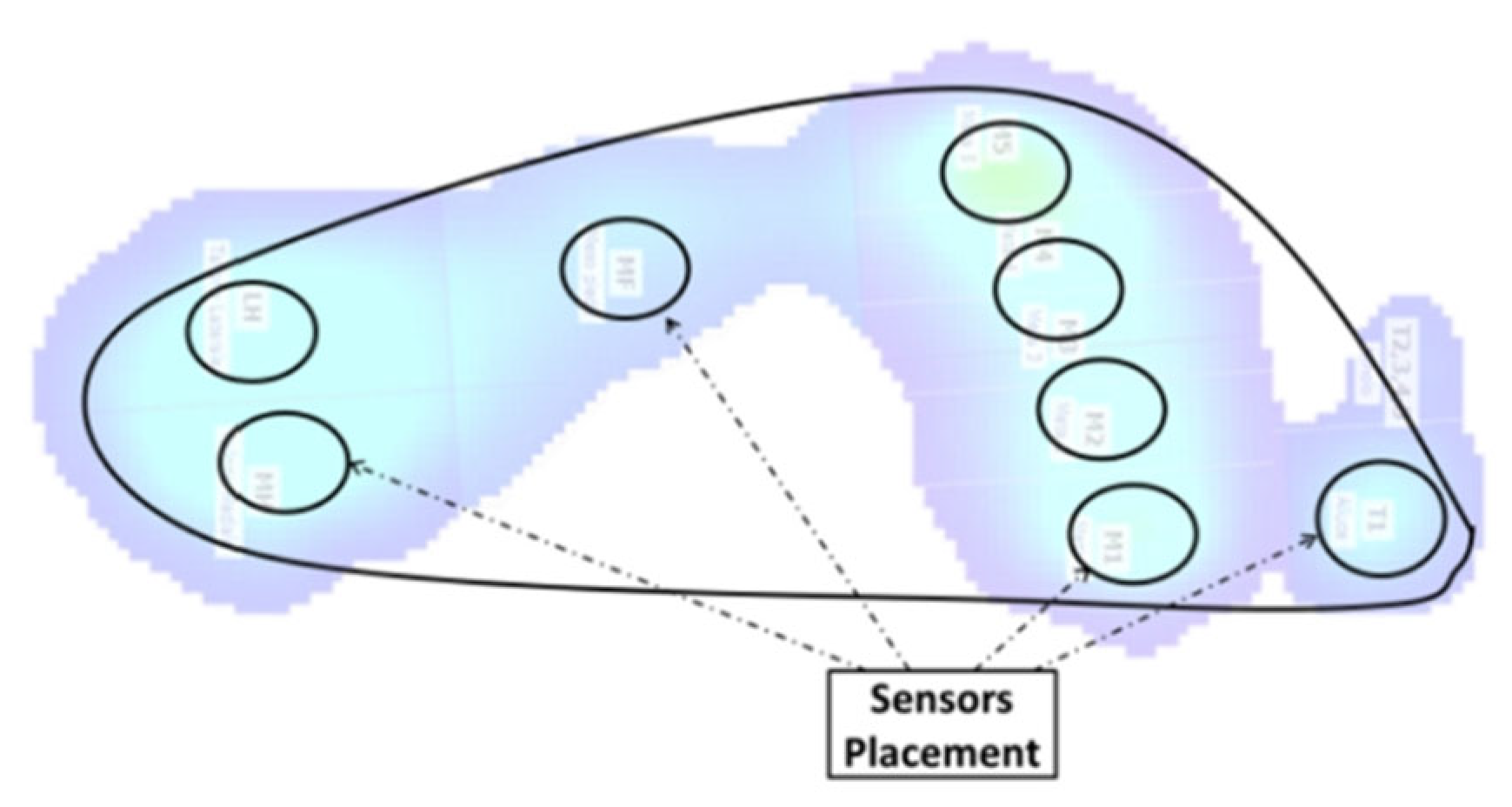
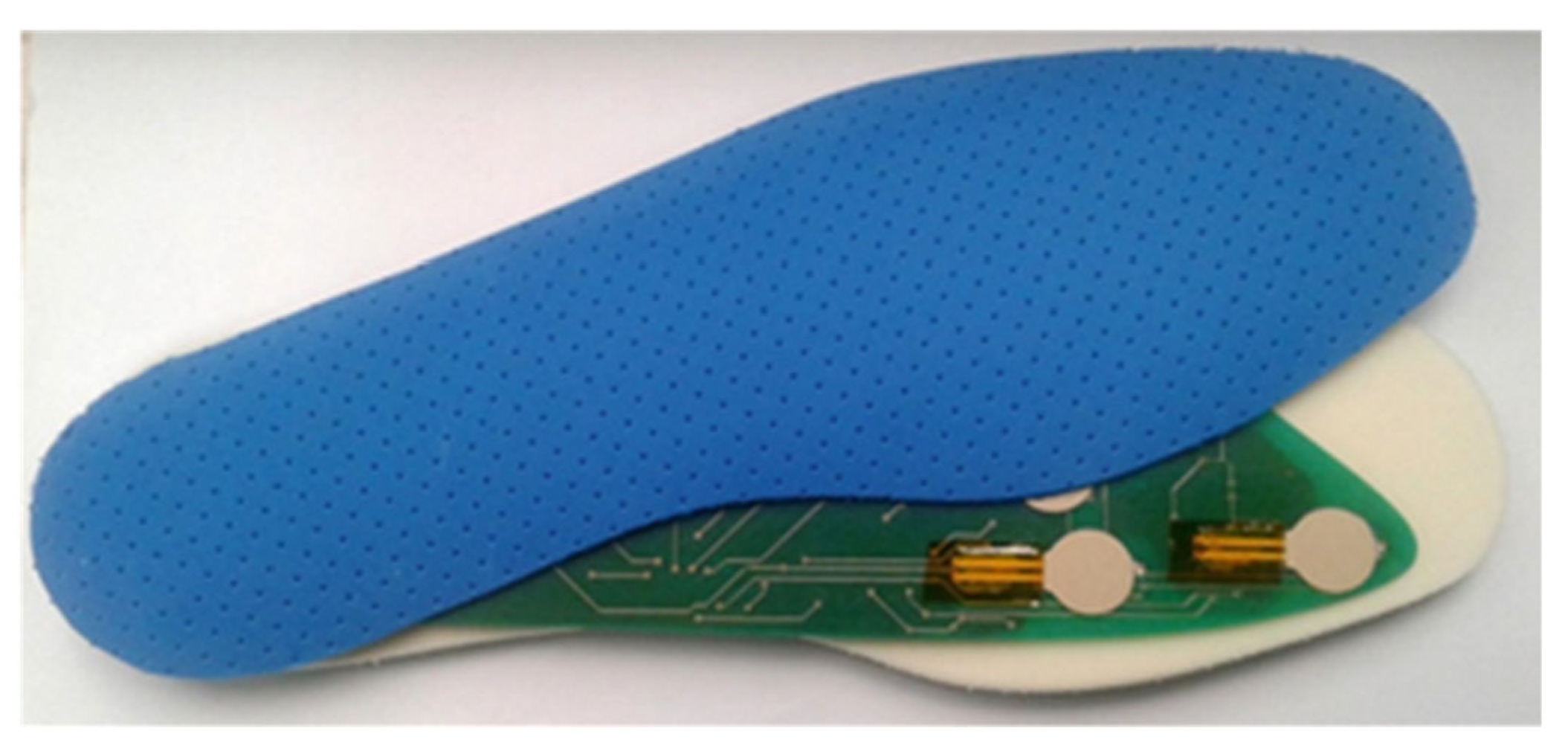
2. Materials and Methods
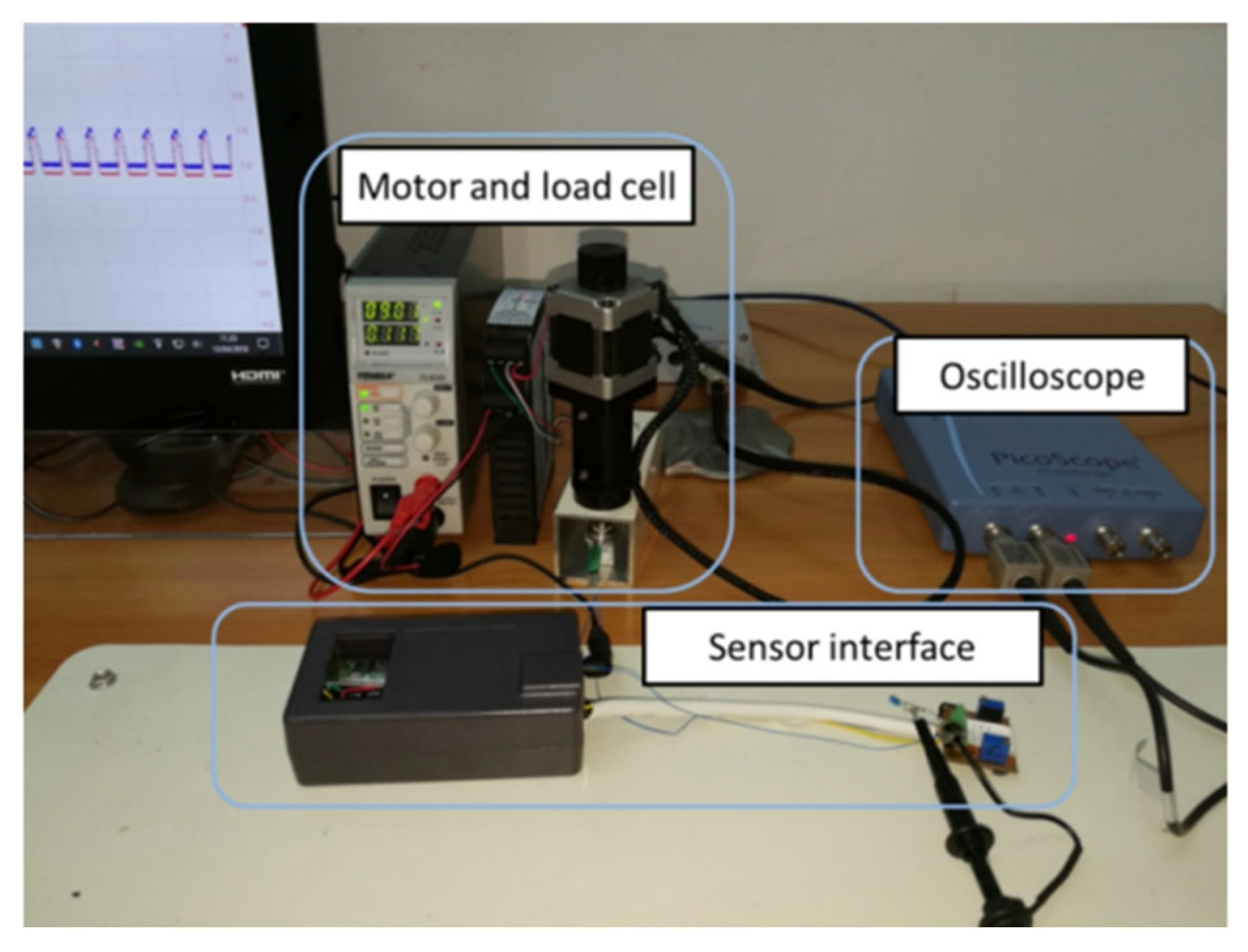
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Iraj, B.; Khorvash, F.; Ebneshahidi, A.; Askari, G. Prevention of diabetic foot ulcer. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ogurtsova, K.; Da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Huang, Y.; Linnenkamp, U.; Guariguata, L.; Cho, N.H.; Cavan, D.; Shaw, J.E.; Makaroff, L.E. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 128, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdanpanah, L.; Nasiri, M.; Adarvishi, S. Literature review on the management of diabetic foot ulcer. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, N.; Bries, M.; Sazonov, E. A Comparative Review of Footwear-Based Wearable nSystems. Electronics 2016, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etehadtavakol, M.; Ng, E.Y.K. Assessment of Foot Complications in Diabetic Patients Using Thermography: A Review. In Application of Infrared to Biomedical Sciences; Series in BioEngineering; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 33–43. ISBN 978-981-10-3147-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ferber, R.; Webber, T.; Everett, B.; Groenland, M. Validation of plantar pressure measurements for a novel in-shoe plantar sensory replacement unit. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2013, 7, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Btsbioengineering. Available online: http://www.btsbioengineering.com/it/prodotti/p-walk/ (accessed on 15 June 2018).
- IEE. Available online: https://www.iee.lu/en/technologies/force-sensing-resistor (accessed on 15 June 2018).
- Maximintegrated. Available online: https://www.maximintegrated.com/en/products/sensors-and-sensor-interface/MAX30205.html (accessed on 15 June 2018).
| Features | Smart Insole System |
|---|---|
| Temperature accuracy | 0.21 °C (range 25–40 °C) |
| Pressure accuracy | 8% (range 40 to 298 kPa) |
| Power consumption | Max 46.3 mW (Data transmission mode) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rescio, G.; Leone, A.; Francioso, L.; Siciliano, P. Sensorized Insole for Diabetic Foot Monitoring. Proceedings 2018, 2, 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130860
Rescio G, Leone A, Francioso L, Siciliano P. Sensorized Insole for Diabetic Foot Monitoring. Proceedings. 2018; 2(13):860. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130860
Chicago/Turabian StyleRescio, Gabriele, Alessandro Leone, Luca Francioso, and Pietro Siciliano. 2018. "Sensorized Insole for Diabetic Foot Monitoring" Proceedings 2, no. 13: 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130860
APA StyleRescio, G., Leone, A., Francioso, L., & Siciliano, P. (2018). Sensorized Insole for Diabetic Foot Monitoring. Proceedings, 2(13), 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2130860








