Numerical Modelling of Soil Erosion on Cephalonia Island, Greece Using Geographical Information Systems and the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- A, soil loss per unit area (t/ha),
- R, rainfall erosivity factor (MJ mm/ha h),
- Κ, soil erodibility factor (t h M/J mm),
- LS, topographic factor that constitute of the slope length factor (L) and slope steepness factor (S) (-),
- C, vegetation management factor (-), and
- Ρ, erosion control practice factor (-).
3. Results
3.1. Rainfall Erosivity Factor (R)
3.2. Soil Erodibility Factor (K)
3.3. Topographical Factor LS
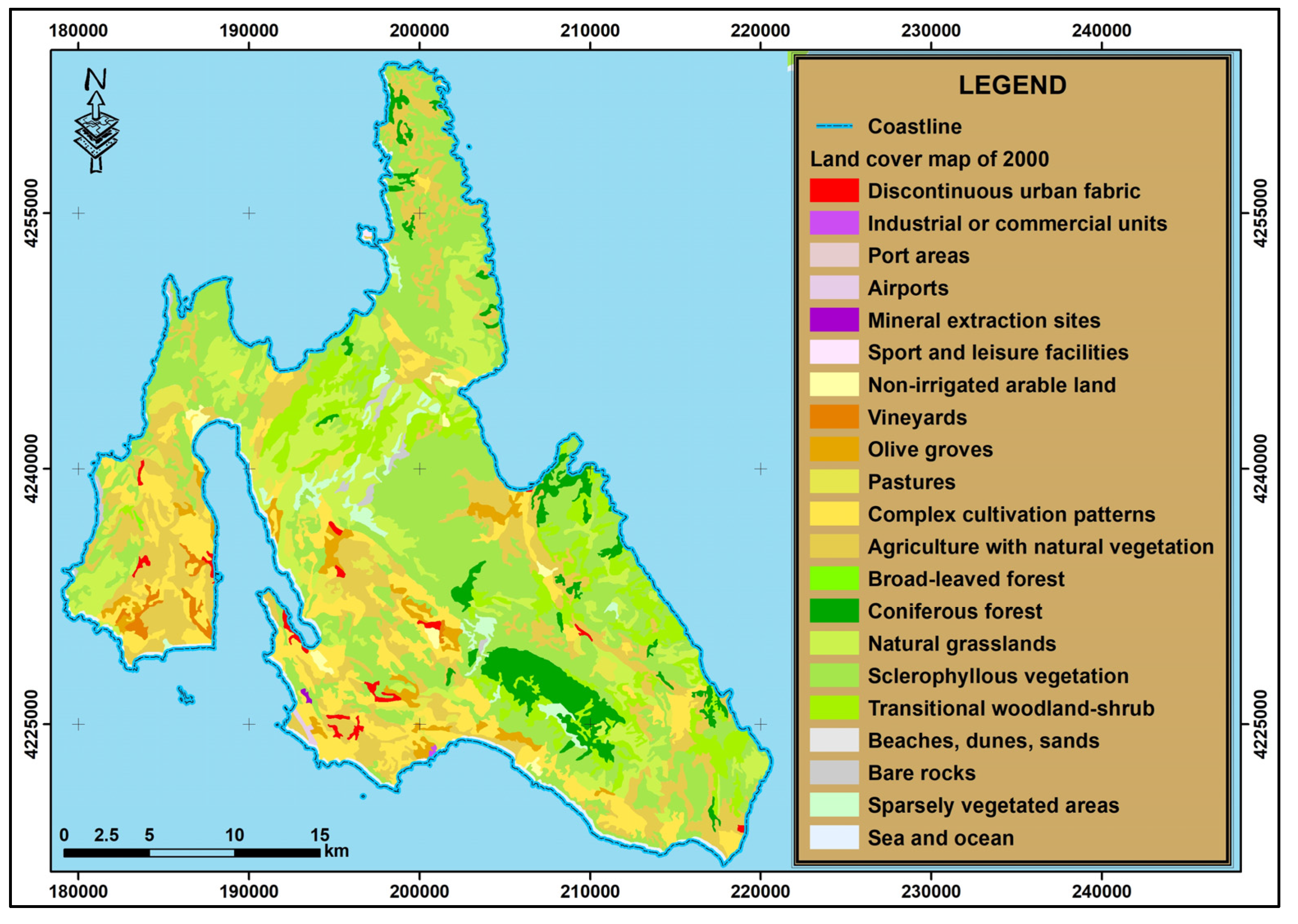
3.4. Vegetation Management Cover Factor (C)
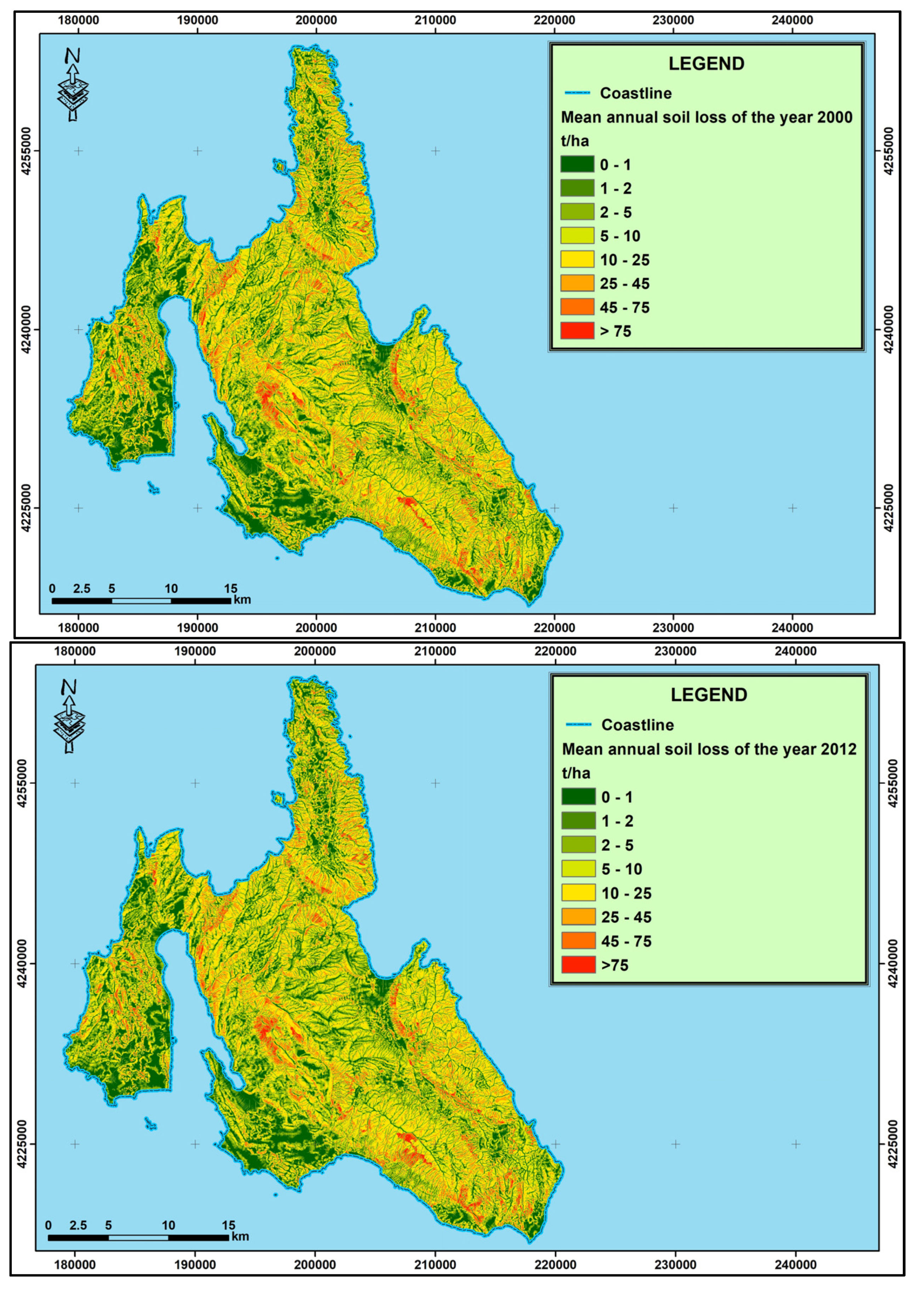
3.5. Mean Annual Soil Loss Rates (A)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Renschler, C.S.; Mannaerts, C.; Diekkruger, B. Evaluating spatial and temporal variability in soil erosion risk—Rainfall erosivity and soil loss ratios in Andalusia, Spain. Catena 1999, 34, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobin, A.; Jones, R.; Kirkby, M.; Campling, P.; Govers, G.; Kosmas, C.; Gentile, A.R. Indicators for pan-European assessment and monitoring of soil erosion by water. Environ. Sci. Policy 2004, 7, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldeman, L.R.; Hakkeling, R.A.; Sombroek, G.W. World Map of the Status of Human-Induced Soil Degradation: An Explanatory Note, 2nd ed.; International Soil Reference and Information Centre: Nairobi, Kenya, 1991; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- European Environment Agency. Environment in the European Union at the Turn of the Century; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 1999; p. 44. ISBN 92-828-6775-7. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/92-9157-202-0-sum/eu_98_uk.pdf (accessed on 6 December 2017).
- Fistikoglu, O.; Harmancioglu, Ν.Β. Integration of GIS with USLE in Assessment of Soil Erosion. Water Res. Manag. 2002, 16, 447–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykoudi, E.; Zarris, D. Identification of regions with high risk of soil erosion in the island Cephalonia using the universal soil loss equation. In Proceedings of the 6th Panhellenic Geographical Conference, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2–6 October 2002; pp. 412–419. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; Mc-Cool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; p. 384. [Google Scholar]
- Novotny, V.; Olem, H. Water Quality: Prevention, Identification, and Management of Diffuse Pollution; Wiley: New York, NY, USA; Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994; p. 1072. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkby, M.J. Modelling water erosion processes. In Soil Erosion; Kirkby, M.J., Morgan, R.C., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1980; pp. 183–216. [Google Scholar]
- Zarris, D.; Lykoudi, E.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Appraisal of River Sediment Deposits in Reservoirs of Hydropower Dams; National Technical University: Athens, Greece, 2001; p. 243. [Google Scholar]
- Schwertmann, U.; Vogl, W.; Kainz, M. Bodenerosion Durch Wasser: Vorhersage des Abtrags und Bewertung von Gegenmassnahmen, 2nd ed.; Ulmer: Stuttgart, Germany, 1990; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Knijff, J.M.; Jones, R.A.; Montanarella, L. Soil Risk Assessment in Italy; European Soil Bureau: Brussels, Belgium, 2000; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann, B. Die Boden den Insel Kefallinia. Ph.D. Thesis, Justus-Liebig University, Giessen, Germany, 2 March 1964. [Google Scholar]
- MALta Soil Information System (MALSIS). A Soil Information System for The Maltese Islands LIFE 00/TCY/MT/000036 Report; Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries: Valetta, Malta, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Stefano, C.; Ferro, V.; Porto, P. Length Slope Factors for applying the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation at Basin Scale in Southern Italy. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 2000, 75, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Corine Land Cover 2000 Seamless Vector Data. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/clc-2000-vector-6 (accessed on 15 December 2017).
- Corine Land Cover 2012 Seamless Vector Data. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/clc-2012-vector (accessed on 15 December 2017).
- Hrissanthou, V.; Piliotis, A. Estimation of sediment inflow into a reservoir under construction. In Proceedings of the 6th Conference of the Greek Hydrotechnical Union, Thessaloniki, Greece, 22–26 May 1995; pp. 355–362. [Google Scholar]
- Mc Coy, J.; Johnston, K.; Kopp, S.; Borup, B.; Willison, J.; Payne, B. ArcGIS 9 Using ArcGIS Spatial Analyst; ESRI: Redlands, CA, USA, 2002; p. 238. [Google Scholar]
- Iraldo, F.; Meli, A.; Sacco, A.; DeBrincat, R.; Tamburini, F.; Bertoneri, F.; Rocchi, F. Development of Environmental Monitoring Strategy and Environment Monitoring Baseline Surveys; Malta Environmental and Planning Agency: Floriana, Malta, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gitas, I.Z.; Douros, K.; Minakou, C.; Silleos, G.N. Multi-Temporal Soil Erosion Risk Assessment in N. Chalkidiki Using a Modified Usle Raster Model. EARSeL eProceedings 2009, 8, 40–52. Available online: http://www.eproceedings.org/static/vol08_1/08_1_gitas1.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2017).
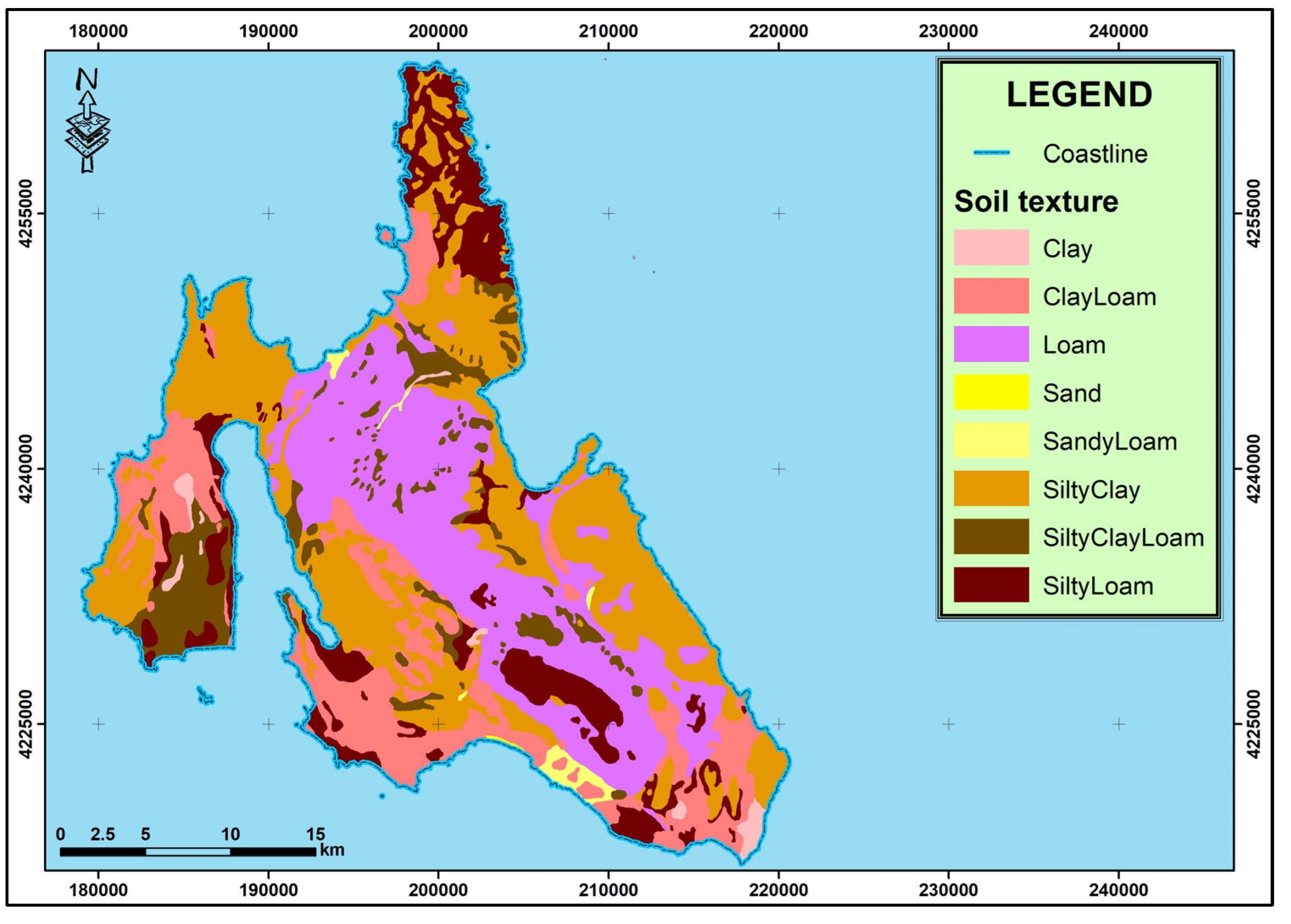

| Soil texture | K Factor | K Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Org. Matter Less than 2% | Org. Matter More than 2% | |
| Clay | 0.24 | 0.21 |
| Clay Loam | 0.33 | 0.28 |
| Loam | 1.50 | 0.26 |
| Sand | 0.03 | 0.01 |
| Sandy Loam | 0.14 | 0.12 |
| Silty Clay | 0.27 | 0.26 |
| Silty Clay Loam | 0.35 | 0.30 |
| Silty Loam | 0.41 | 0.37 |
| Land Cover Type | Land Cover Code | C Factor |
| Continuous urban fabric | 111 | 0.10 |
| Discontinuous urban fabric | 112 | 0.10 |
| Industrial or commercial units | 121 | 0.10 |
| Port areas | 123 | 0.10 |
| Airports | 124 | 0.10 |
| Mineral extraction sites | 131 | 0.15 |
| Sport and leisure facilities | 142 | 0.20 |
| Non-irrigated arable land | 211 | 0.50 |
| Vineyards | 221 | 0.40 |
| Olive groves | 223 | 0.40 |
| Pastures | 231 | 0.25 |
| Complex cultivation patterns | 242 | 0.40 |
| Agriculture with natural vegetation | 243 | 0.80 |
| Broad-leaved forest | 311 | 0.15 |
| Coniferous forest | 312 | 0.10 |
| Mixed forest | 313 | 0.15 |
| Natural grasslands | 321 | 0.25 |
| Sclerophyllous vegetation | 323 | 0.20 |
| Transitional woodland-shrub | 324 | 0.15 |
| Beaches, dunes, sands | 331 | 0.80 |
| Bare rocks | 332 | 0.05 |
| Sparsely vegetated areas | 333 | 0.60 |
| Inland marshes | 411 | 0.15 |
| Soil Loss Rate (t/ha) | Category | (Year 2000) Area (%) | (Year 2012) Area (%) | Difference |
| 0–1 | None | 20.04 | 20.49 | 0.45 |
| 1–2 | Very Low | 5.26 | 5.77 | 0.51 |
| 2–5 | 14.41 | 15.40 | 1.00 | |
| 5–10 | Low | 19.74 | 20.10 | 0.36 |
| 10–25 | Moderate | 27.99 | 26.14 | −1.85 |
| 25–45 | High | 7.96 | 7.66 | −0.30 |
| 45–75 | Very High | 3.00 | 2.92 | −0.08 |
| >75 | Severe | 1.60 | 1.52 | −0.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xanthakis, M.; Minetos, P.; Lisitsa, G.; Kamari, G. Numerical Modelling of Soil Erosion on Cephalonia Island, Greece Using Geographical Information Systems and the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). Proceedings 2018, 2, 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2110618
Xanthakis M, Minetos P, Lisitsa G, Kamari G. Numerical Modelling of Soil Erosion on Cephalonia Island, Greece Using Geographical Information Systems and the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). Proceedings. 2018; 2(11):618. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2110618
Chicago/Turabian StyleXanthakis, Michail, Panagiotis Minetos, Georgia Lisitsa, and Georgia Kamari. 2018. "Numerical Modelling of Soil Erosion on Cephalonia Island, Greece Using Geographical Information Systems and the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE)" Proceedings 2, no. 11: 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2110618
APA StyleXanthakis, M., Minetos, P., Lisitsa, G., & Kamari, G. (2018). Numerical Modelling of Soil Erosion on Cephalonia Island, Greece Using Geographical Information Systems and the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). Proceedings, 2(11), 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2110618





