Theoretical Investigation of the Impact of Impurities in Recycled Silicon Used for the Production of Ferrosilicon †
1. Introduction
2. Aim and Approach
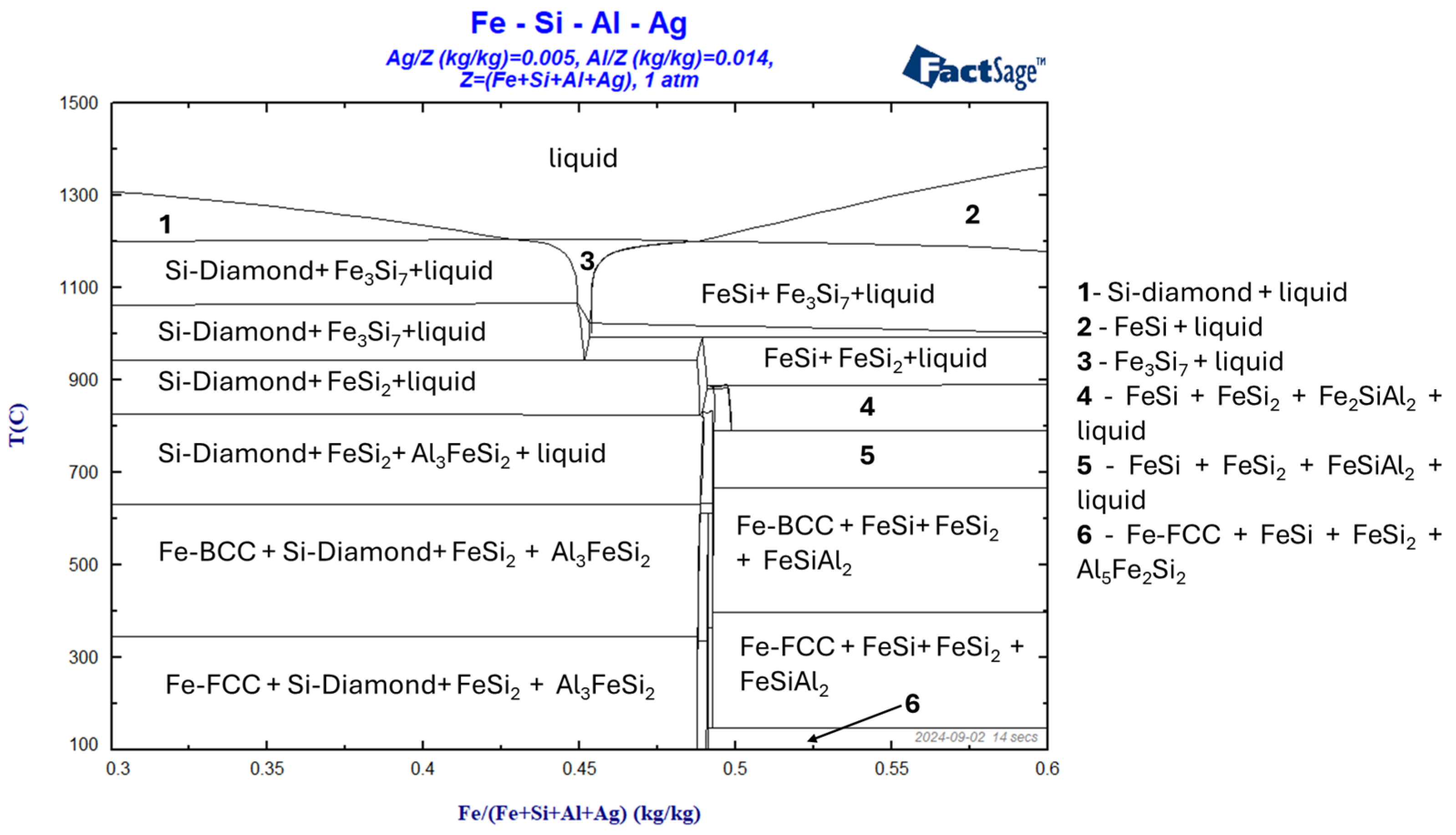
3. Preliminary Results and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riva, L.; Surup, G.R.; Buø, T.V.; Nielsen, H.K. A study of densified biochar as carbon source in the silicon and ferrosilicon production. Energy 2019, 181, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangstad, M.; Beukes, J.P.; Steenkamp, J.; Ringdalen, E. Coal-based reducing agents in ferroalloys and silicon production. In New Trends in Coal Conversion; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 405–438. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, A.N.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Said, R.M.; Somidin, F.; Ismail, S.A. Ismail, Influence of recycled wastes on ferrosilicon production in steel making applications: A short review. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2169, 012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangstad, M. Ferrosilicon and silicon technology. In Handbook of Ferroalloys; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 179–220. [Google Scholar]
- Farzana, R.; Sahajwalla, V. Novel recycling to transform automotive waste glass and plastics into SiC-bearing resource by silica reduction. J. Sustain. Metall. 2015, 1, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzana, R.; Rajarao, R.; Sahajwalla, V. Transforming waste plastic into reductants for synthesis of ferrosilicon alloy. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 19870–19877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzana, R.; Rajarao, R.; Sahajwalla, V. Synthesis of ferrosilicon alloy using waste glass and plastic. Mater. Lett. 2014, 116, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzana, R.; Rajarao, R.; Sahajwalla, V. Characteristics of waste automotive glasses as silica resource in ferrosilicon synthesis. Waste Manag. Res. 2016, 34, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzana, R.; Rajarao, R.; Sahajwalla, V. Reaction mechanism of ferrosilicon synthesis using waste plastic as a reductant. ISIJ Int. 2017, 57, 1780–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajarao, R.; Farzana, R.; Sahajwalla, V. Transforming waste printed circuit boards and compact discs for the synthesis of valuable ferrosilicon alloy. J. Sustain. Metall. 2018, 4, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhamnath, P.; Ślęzak, M.; Karbowniczek, M. Disposing End of Life PV Modules—Reusing, Recycling and Upcycling. In EU PVSEC 2023; EUPVSEC: Lisbon, Portugal, 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Pahari, A.K.; Dubey, B.K. Waste from electrical and electronics equipment. In Plastics to Energy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 443–468. [Google Scholar]
- Ari, V. A review of technology of metal recovery from electronic waste. In E-Waste in Transit-from pollution to resource, 1st ed.; Mihai, F.C., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 122–158. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, S. Sustainable electronic waste management and recycling process. Am. J. Env. Eng. 2012, 2, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latunussa, C.; Mancini, L.; Blengini, G.; Ardente, F.; Pennington, D. Analysis of Material Recovery from Silicon Photovoltaic Panels; JRC Technical Reports- JRC100783; Publications Office of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar]
| FeSi Alloy | FeSi20 | FeSi25 | FeSi45 | FeSi65 | FeSi75Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartzite, kg | 370 | 552 | 931 | 1568 | 1930 |
| Iron chips, kg | 810 | 780 | 658 | 343 | 250 |
| Coke, kg | 200 | 280 | 438 | 720 | 845 |
| Electrode paste, kg | 10 | 8 | 16 | 43.3 | 54 |
| Electricity, MWh/t | 2.1 | 2.7 | 4.8 | 7.4 | 8.8 |
| Silicon yield, % | 94–95 | 97–98.5 | 98–99 | 92–94 | 91–93 |
| No | Material | Percentage in e-Waste [%] |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Copper (Cu) | 1–3% |
| 2 | Aluminum (Al) | 3–5% |
| 3 | Silver (Ag) | 1–3% |
| 4 | Tin (Sn) | 0.5–1% |
| 5 | Lead (Pb) | 0.5–1% |
| 6 | Silicon (Si) | Remaining |
| Alloy Systems | Fe [kg] | Si [kg] | Ag [kg] | Al [kg] | Cu [kg] | Sn [kg] | Pb [kg] | Total [kg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-0 | 55 | 45 | 100 | |||||
| S-1 | 54.7 | 44.8 | 0.5 | 100 | ||||
| S-2 | 53.9 | 44.2 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 100 | |||
| S-3 | 53.6 | 44.0 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 0.5 | 100 | ||
| S-4 | 53.5 | 43.9 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 100 | |
| S-5 | 53.4 | 43.8 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Padhamnath, P.; Migas, P.; Karbowniczek, M. Theoretical Investigation of the Impact of Impurities in Recycled Silicon Used for the Production of Ferrosilicon. Proceedings 2024, 108, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024108018
Padhamnath P, Migas P, Karbowniczek M. Theoretical Investigation of the Impact of Impurities in Recycled Silicon Used for the Production of Ferrosilicon. Proceedings. 2024; 108(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024108018
Chicago/Turabian StylePadhamnath, Pradeep, Piotr Migas, and Mirosław Karbowniczek. 2024. "Theoretical Investigation of the Impact of Impurities in Recycled Silicon Used for the Production of Ferrosilicon" Proceedings 108, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024108018
APA StylePadhamnath, P., Migas, P., & Karbowniczek, M. (2024). Theoretical Investigation of the Impact of Impurities in Recycled Silicon Used for the Production of Ferrosilicon. Proceedings, 108(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024108018






