2.1. Definition
In practical studies, one is not so much interested in the dependence of the pair distribution on the particle azimuths , . Instead, the pair is characterized by a relative angle and a characteristic pair angle , which can be for instance the azimuth of the leading particle with highest transverse momentum (in jet-like correlation studies) or that of the total momentum of the pair (in femtoscopy studies). The two-particle distribution is then studied as a function of and—if one is interested in azimuthally sensitive correlations—, resulting in a probability density .
As was argued in Ref. [
1], a set of robust observables to characterize the dependence on the azimuthal angle
consists of Fourier “pair flow” coefficients, similar to those used in Equation (
1), namely such that
with coefficients
which depend on the relative angle
. As discussed in Ref. [
1], even for a non-fluctuating geometry of the initial state there is no
symmetry in the system, so that the sine coefficients
are in general different from zero. In addition, every method used to measure the single-particle flow harmonics
is automatically applicable to the pair flow coefficients
,
.
To fix ideas, we consider in the following and , such that and .
2.2. Pair Flow Coefficients for Uncorrelated Particles
When particles
a and
b are uncorrelated, so that
, one can readily compute the resulting pair flow coefficients and express them in terms of the single-particle harmonics
,
, where for the sake of generality we allow different coefficients for the two particles (The symmetry planes associated with the two particles are still supposed to coincide,
). After some straightforward but lengthy algebra, one finds for instance
where we use the convention
for negative values of
q. This result illustrates explicitly that the pair flow coefficients still depend on the relative angle
. An additional dependence on
is contained in the global denominator entering the calculation of
, which was omitted from Equation (
5).
Considering an idealized simple example for which only
is non-zero at the single-particle level, Equation (
5) shows that this gives rise to both a second harmonic
and a fourth harmonic
modulation of the two-particle distribution, with
(This term should not be confused with the similar-looking term
which is the second harmonic of the dependence on
of the
-averaged two-particle distribution).
2.3. Fluctuations of Single-Particle and Pair Flow
In
Section 2.2 we assumed fixed values of the single-flow coefficients
and of the orientations
of the symmetry planes, which is not what one finds in a typical set of experimental events. The remainder of these proceedings is devoted to a preliminary investigation of the effect of event-by-event fluctuations.
Let us first discuss fluctuations of the symmetry plane angles. Obviously, they can only affect the terms of the sum on the right hand side of Equation (
5). For unpolarized colliding nuclei, each
should be arbitrarily, equally distributed, yet there can still be correlations between the orientations of different symmetry planes in a given event—in particular between
and
, while
and
seem rather uncorrelated at LHC energies—such that the cosine factor does not vanish on average (Measurements of suitable multiparticle observables have been proposed to access those average cosine terms [
2]). Nonetheless, we neglect those nonlinear terms in the following and focus on the first contribution on the right hand side of Equation (
5), i.e., we approximate
.
We now focus on the fluctuations of the single-particle flow coefficients
. These reflect fluctuations in the eccentricities
of the initial-state geometry. When the latter remain small, i.e., for not too peripheral collisions,
and
for
are almost linearly related
, as found both in fluid-dynamical [
3,
4,
5] and in far-from-equilibrium transport [
6] calculations. Accordingly, the fluctuations in
are linearly transferred into fluctuations of the final-state
. The probability distribution of the fluctuations of
for arbitrary
n resp.
for
is to a very good approximation a power law distribution [
7,
8]
with
resp.
. Note that the fluctuations of
may also be describable by a power law [
9], although both
and
contribute. The only parameter in these distributions is the number
, which depends on
n. In general the power law distribution becomes sharper for higher values of
. In order to pin down the value of this parameter, we performed Glauber Monte Carlo initial stage studies and fitted the power law distribution to the gained histograms for the values of the realized eccentricities
.
Using Equation (
5), without the terms from the sum—which is a reasonable assumption if we choose
as we do now—and the probability distribution (
6) for the single-particle triangular flow
, we can deduce the probability distribution for the pair flow coefficient
. In the above sketched scenario—no two-particle correlation at play, power law distributions for
and
—the fluctuations of
are governed by the distribution
where the integrals run over the whole set of realizations of
for particle
a and particle
b—here assumed to be totally independent. The delta distribution guarantees the functional dependence of the pair flow coefficient
on
and
. As one can see, the probability distribution of the pair flow coefficients depends on the relative angle
(The sine pair flow coefficient
shows a similar behaviour. Further details will be included in a forthcoming paper).
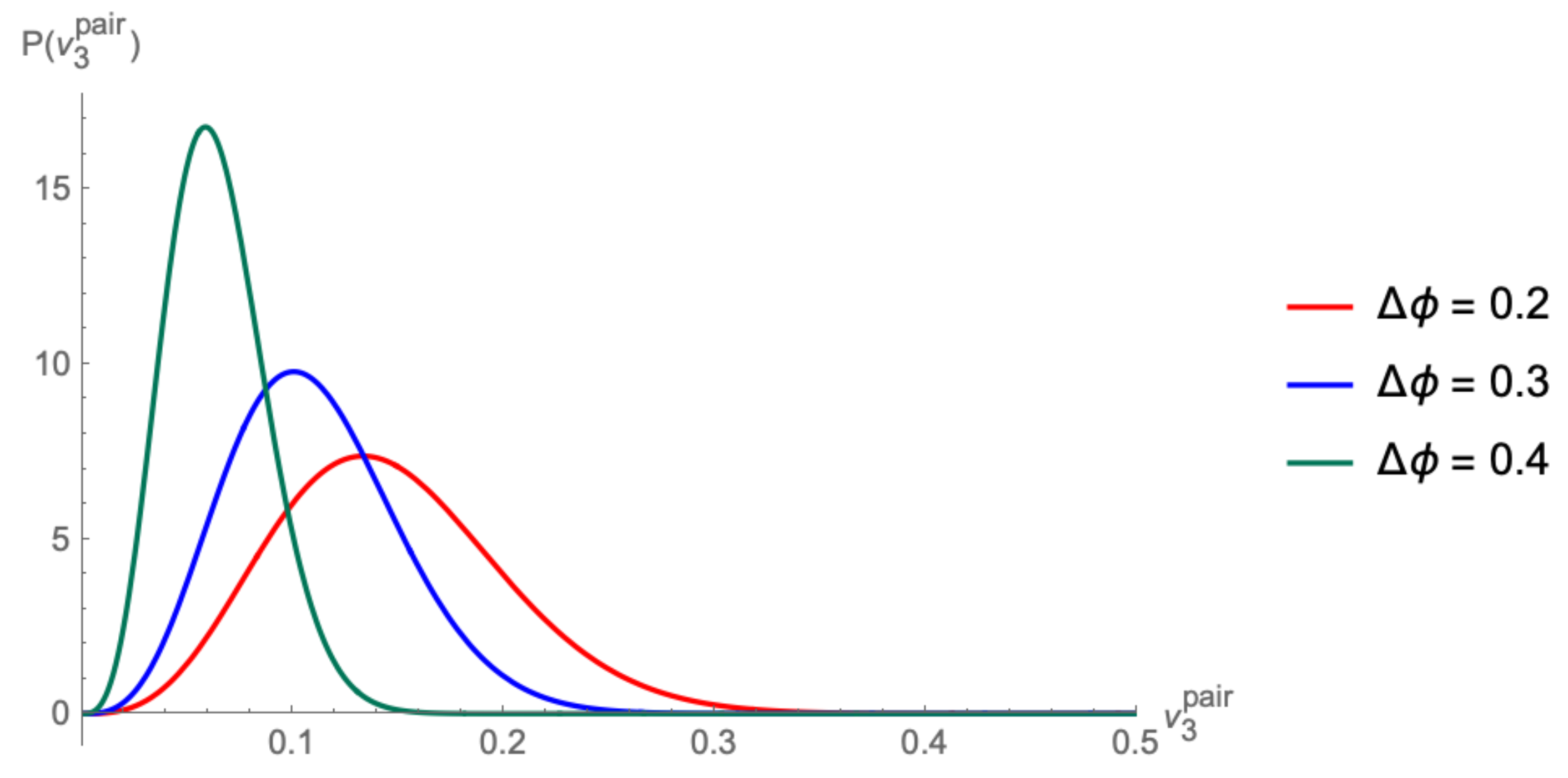
In
Figure 1, we display the distribution (
7) for different values of the relative angle
, using fitted values of
.
One observes that the distributions are more peaked for larger values of the relative angle, whereas for small relative angles—when the cosine inside the delta distribution in Equation (
7) approaches 1—the fluctuations in
are strongly affecting the distribution of the pair flow coefficient.