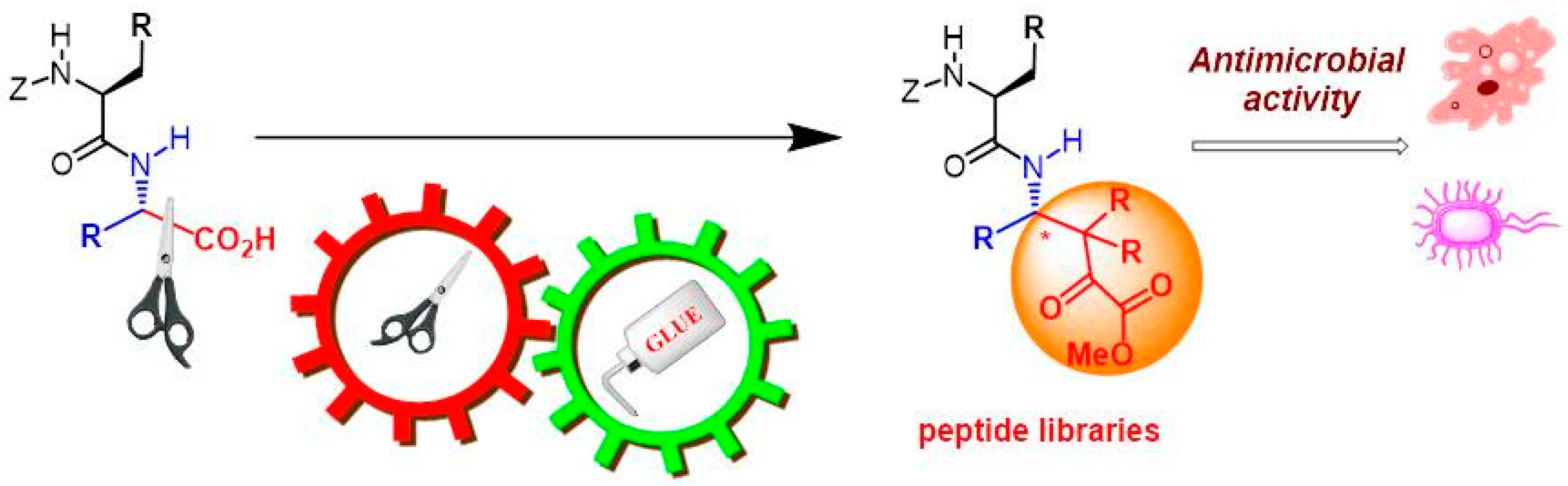
The Search for New Antimicrobial Agents, by Site-Selective Peptide Modification †
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kastin, A.J. Handbook of Biologically Active Peptides; Chapters 10 (systemins), 11 (defensins), 12 (cathelicidins), 45 (dermaseptins), 46 (temporins); Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Estudillo, I.; Boto, A. Domino Process Achieves Site-Selective Peptide Modification with High Optical Purity. Applications to Chain Diversification and Peptide Ligation. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 9379–9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boto, A.; González, C.; Hernández, D.; Romero-Estudillo, I.; Rodriguez-Paz, N.; Lastra, J.M.P.d.l. The Search for New Antimicrobial Agents, by Site-Selective Peptide Modification. Proceedings 2017, 1, 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1060673
Boto A, González C, Hernández D, Romero-Estudillo I, Rodriguez-Paz N, Lastra JMPdl. The Search for New Antimicrobial Agents, by Site-Selective Peptide Modification. Proceedings. 2017; 1(6):673. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1060673
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoto, Alicia, C. González, D. Hernández, I. Romero-Estudillo, N. Rodriguez-Paz, and J. M. Pérez de la Lastra. 2017. "The Search for New Antimicrobial Agents, by Site-Selective Peptide Modification" Proceedings 1, no. 6: 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1060673
APA StyleBoto, A., González, C., Hernández, D., Romero-Estudillo, I., Rodriguez-Paz, N., & Lastra, J. M. P. d. l. (2017). The Search for New Antimicrobial Agents, by Site-Selective Peptide Modification. Proceedings, 1(6), 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1060673




