Impedimetric IgG-Biosensor with In-Situ Generation of the Redox-Probe †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. EIS Measurement
2.3. Gold Surface Functionalization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Functionalization Steps
3.2. EIS Response to IgG Binding
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matos-Gomes, N.; Katsurayama, M.; Makimoto, F.H.; Santana, L.L.O.; Paredes-Garcia, E.; Becker, M.A.d.; Dos-Santos, M.C. Psychological stress and its influence on salivary flow rate, total protein concentration and IgA, IgG and IgM titers. Neuroimmunomodulation 2010, 17, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randviir, E.P.; Banks, C.E. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy: An overview of bioanalytical applications. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 1098–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogomolova, A.; Komarova, E.; Reber, K.; Gerasimov, T.; Yavuz, O.; Bhatt, S.; Aldissi, M. Challenges of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in protein biosensing. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 3944–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijksma, M.; Boukamp, B.A.; Kamp, B.; van Bennekom, W.P. Effect of Hexacyanoferrate(II/III) on Self-Assembled Monolayers of Thioctic Acid and 11-Mercaptoundecanoic Acid on Gold. Langmuir 2002, 18, 3105–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, J.; Schnelting, C.; Slavcheva, E.; Schnakenberg, U. Hampering of the Stability of Gold Electrodes by Ferri-/Ferrocyanide Redox Couple Electrolytes during Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doubova, L.M.; Fabrizio, M.; Daolio, S.; Forlini, A.; Rondinini, S.; Vertova, A. Electron transfer across the interface gold/self-assembled organic monolayer. Comparison of single- and two-component systems. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2012, 48, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
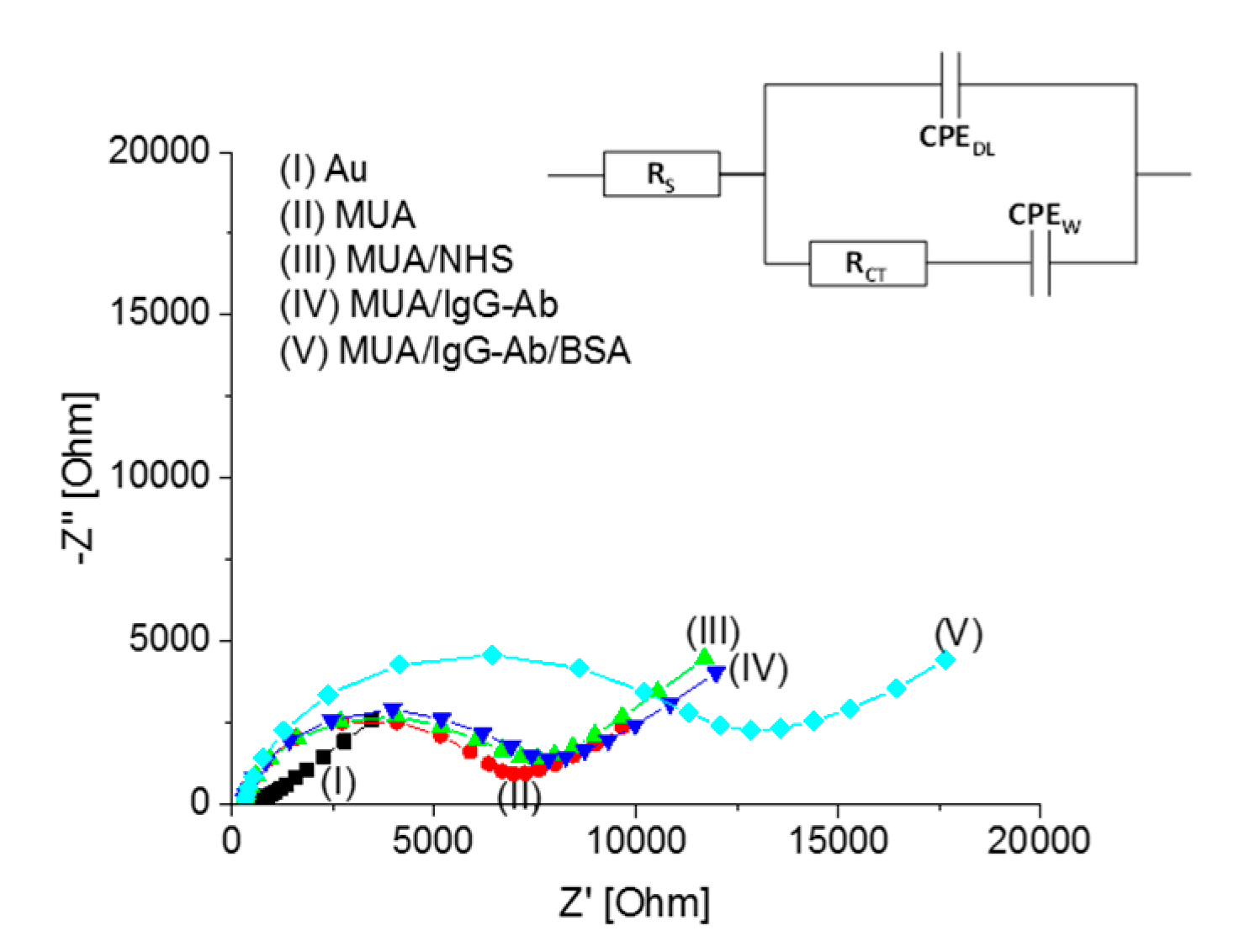
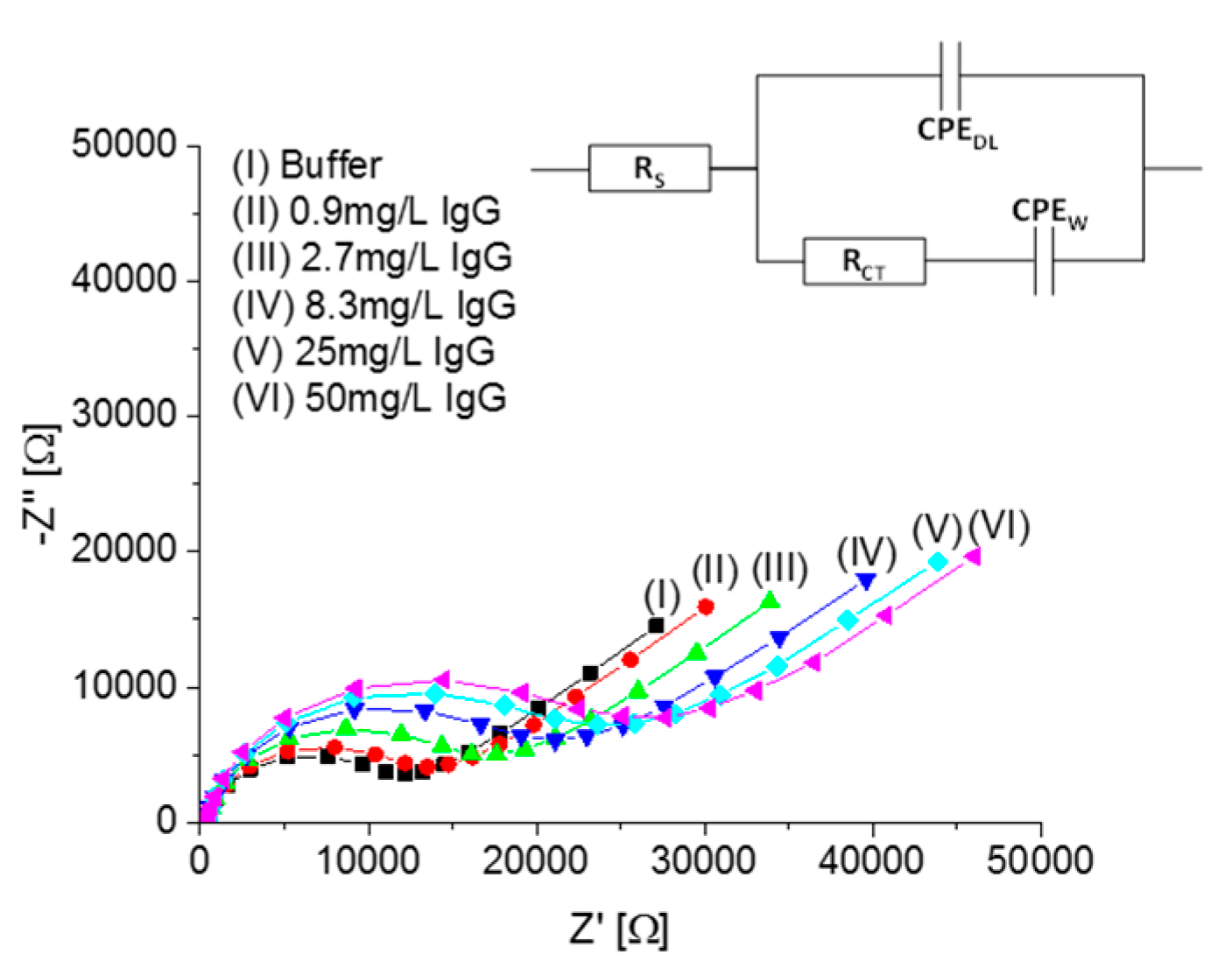

| Concentration | Average RCT | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| Blank | 11.0 kΩ | 0.75 kΩ |
| 0.9 mg/L IgG | 12.3 kΩ | 0.36 kΩ |
| 2.7 mg/L IgG | 15.7 kΩ | 0.90 kΩ |
| 8.3 mg/L IgG | 18.6 kΩ | 0.46 kΩ |
| 25 mg/L IgG | 21.2 kΩ | 0.42 kΩ |
| 50 mg/L IgG | 23.4 kΩ | 0.55 kΩ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schrattenecker, J.D.; Heer, R.; Hainberger, R.; Fafilek, G. Impedimetric IgG-Biosensor with In-Situ Generation of the Redox-Probe. Proceedings 2017, 1, 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040534
Schrattenecker JD, Heer R, Hainberger R, Fafilek G. Impedimetric IgG-Biosensor with In-Situ Generation of the Redox-Probe. Proceedings. 2017; 1(4):534. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040534
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchrattenecker, Julian D., Rudolf Heer, Rainer Hainberger, and Günter Fafilek. 2017. "Impedimetric IgG-Biosensor with In-Situ Generation of the Redox-Probe" Proceedings 1, no. 4: 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040534
APA StyleSchrattenecker, J. D., Heer, R., Hainberger, R., & Fafilek, G. (2017). Impedimetric IgG-Biosensor with In-Situ Generation of the Redox-Probe. Proceedings, 1(4), 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040534





