Surface Acoustic Wave Sensors for the Detection of Hazardous Compounds in Indoor Air †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Formaldehyde Sensor
2.2. Carbon Monoxide Sensor
3. Results
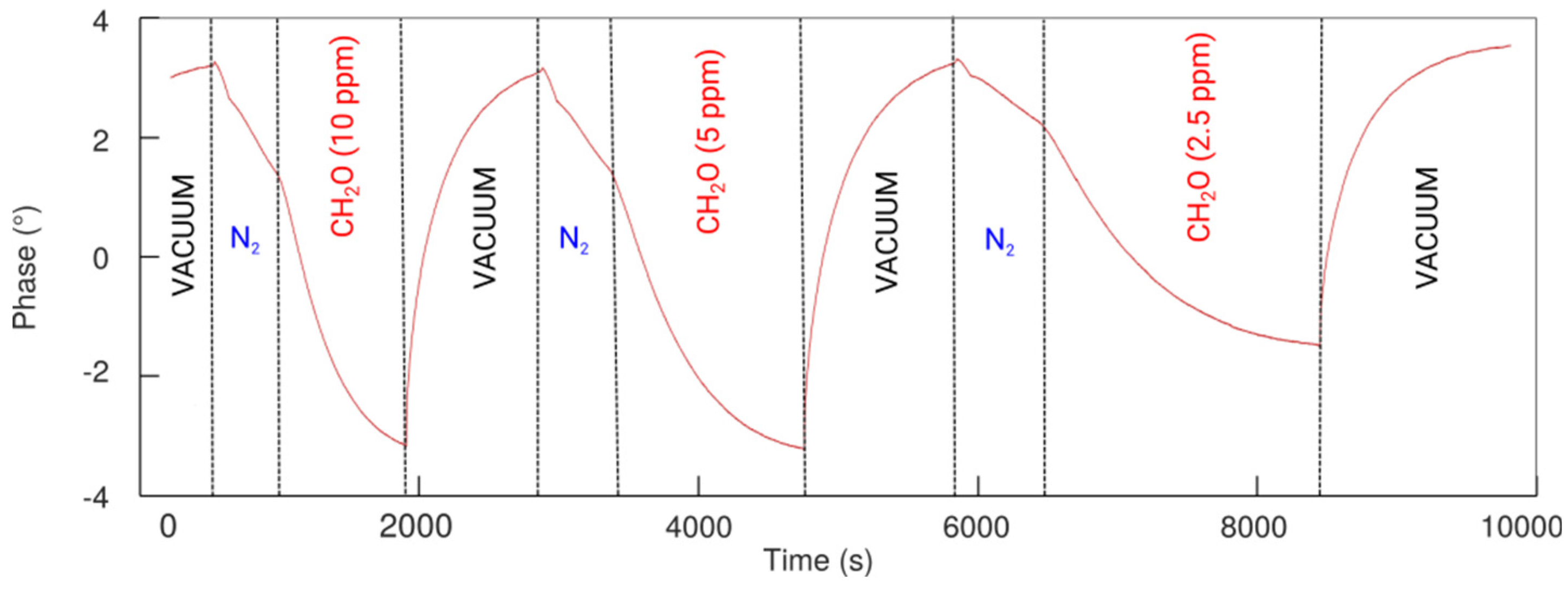
3.1. Formaldehyde Measurements
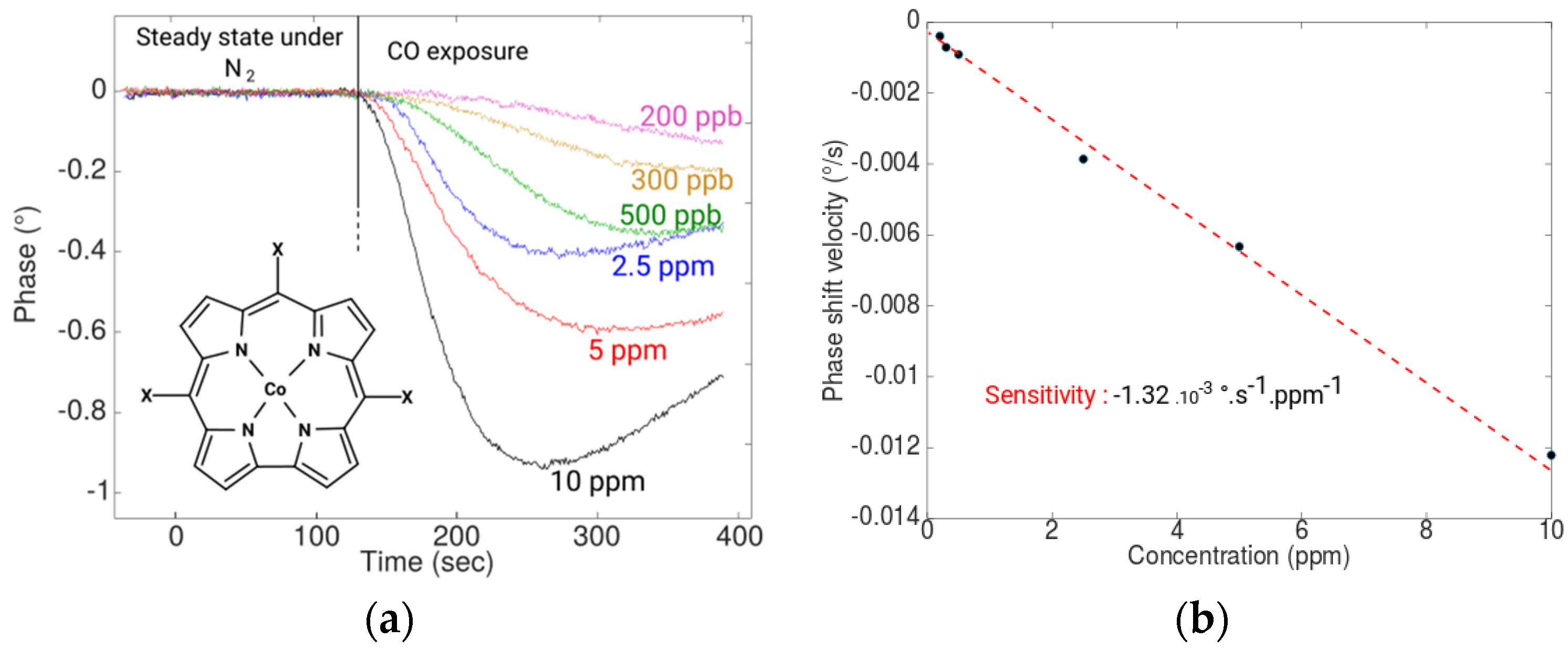
3.2. Carbon Monoxide Measurements
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, W.J.; Terada, N.; Nomura, T.; Takahashi, R.; Lee, S.D.; Park, J.H.; Konno, A. Effect on formaldehyde on the expression of adhesion molecule in nasal microvascular endothelial cells: The role of formaldehyde in the pathogenesis of sick building syndrome. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2002, 32, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raub, J.A.; Mathieu-Nolf, M.; Hampson, N.B.; Thom, S.R. Carbon monoxide poisoning—A public health perspective. Toxicology 2000, 145, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyzanowski, M.; World Health Organization—Regional Office for Europe. New guidelines for selected indoor chemicals establish targets at which health risks are significantly reduced, Fact sheet, 15 December 2010. 15 December.
- Christophe, L.; Ménard, C.; Verrier, A.; Arwidson, P.; du Roscoät, E. Carbon monoxide: Analysis of perceptions, knowledge and behaviors of intoxicated household referents during the heating season 2013–2014 in France. Bull. Epidémiol. Hebd. 2015, 2016, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Guilard, R.; Gros, C.P.; Bolze, F.; Jérôme, F.; Ou, Z.; Shao, J.; Fischer, J.; Weiss, R.; Kadish, K.M. Alkyl and Aryl Substituted Corroles. 1. Synthesis and Characterization of Free Base and Cobalt Containing Derivatives. X-ray Structure of (Me4Ph5Cor) Co (py)2. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 4845–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbe, J.-M.; Canard, G.; Brandès, S.; Jerôme, F.; Dubois, G.; Guilard, R. Metallocorroles as sensing components for gas sensors: Remarkable affinity and selectivity of cobalt(III) corroles for CO vs. O2 and N2. Dalton Trans. 2004, 8, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vanotti, M.; Theron, C.; Poisson, S.; Quesneau, V.; Naitana, M.; Soumann, V.; Brandès, S.; Desbois, N.; Gros, C.; Tran-Thi, T.-H.; et al. Surface Acoustic Wave Sensors for the Detection of Hazardous Compounds in Indoor Air. Proceedings 2017, 1, 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040444
Vanotti M, Theron C, Poisson S, Quesneau V, Naitana M, Soumann V, Brandès S, Desbois N, Gros C, Tran-Thi T-H, et al. Surface Acoustic Wave Sensors for the Detection of Hazardous Compounds in Indoor Air. Proceedings. 2017; 1(4):444. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040444
Chicago/Turabian StyleVanotti, Meddy, Christophe Theron, Sacha Poisson, Valentin Quesneau, Mario Naitana, Valérie Soumann, Stéphane Brandès, Nicolas Desbois, Claude Gros, Thu-Hoa Tran-Thi, and et al. 2017. "Surface Acoustic Wave Sensors for the Detection of Hazardous Compounds in Indoor Air" Proceedings 1, no. 4: 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040444
APA StyleVanotti, M., Theron, C., Poisson, S., Quesneau, V., Naitana, M., Soumann, V., Brandès, S., Desbois, N., Gros, C., Tran-Thi, T.-H., & Blondeau-Patissier, V. (2017). Surface Acoustic Wave Sensors for the Detection of Hazardous Compounds in Indoor Air. Proceedings, 1(4), 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings1040444



