Abstract
The realistic representation of deformations is still an active area of research, especially for soft objects whose behavior cannot be simply described in terms of elasticity parameters. Most of existing techniques assume that the parameters describing the object behavior are known a priori based on assumptions on the object material, such as its isotropy or linearity, or values for these parameters are chosen by manual tuning until the results seem plausible. This is a subjective process and cannot be employed where accuracy is expected. This paper proposes a data-driven neural-network-based model for capturing implicitly deformations of a soft object, without requiring any knowledge on the object material. Visual data, in form of 3D point clouds gathered by a Kinect sensor, is collected over an object while forces are exerted by means of the probing tip of a force-torque sensor. A novel approach advantageously combining distance-based clustering, stratified sampling and neural gas-tuned mesh simplification is then proposed to describe the particularities of the deformation. The representation is denser in the region of the deformation (an average of 97% perceptual similarity with the collected data in the deformed area), while still preserving the object overall shape (74% similarity over the entire surface) and only using on average 30% of the number of vertices in the mesh.
1. Introduction
The acquisition and realistic representation of soft objects deformations is still an active area of research. Realistic, plausible models require the acquisition of experimental measurements using physical interaction with the object in order to capture its complex behavior when subject to various forces. This acquisition can be carried out based on instrumented indentation and usually involves the monitoring of the evolution of the force (e.g., its magnitude, direction, and location) applied by a force sensor accompanied by a visual capture of the deformed object surface to collect geometry data. In order to collect 3D geometry data, a classical solution offering high precision are laser scanners. They are however expensive and the acquisition is often lengthy. Kinect proves to be a simple, fast and cost-effective alternative that offers enough precision for this purpose. Data provided by this sensor, has been successfully used for the reconstruction of 3D pointclouds of objects by merging data from multiple viewpoints for rigid [1] and non-rigid objects [2,3] as well. A few open-source [4] and commercial solutions [5] are also available. Once 3D data is collected, various approaches can be used for representing a deformable object such as: mass-spring models [6], finite element method (FEM), Green functions [7], and Non-uniform rational basis spline (NURBS) [8], just to mention a few. Most of these assume that the parameters describing the object behavior are known a priori or values are chosen by manual tuning until the results seem plausible. This is a subjective process and cannot be employed where accuracy is expected. Researchers tried to overcome this problem by recuperating parameters based on a comparison between the real and simulated object. Zaidi et al. [6] model an object in interaction with a robot hand as a non-linear isotropic mass-spring system. In [9], the stiffness properties of mass-spring models are estimated by applying force constraints, recording the displacements and comparing them between the reference and the estimated model using particle filters. The authors of [10] present a genetic solution to identify the stiffness of mass-spring-systems by using a linear FEM model as reference. In order to compute the elasticity parameters, Frank et al. [11] minimize the difference between the real object in interaction with a force-torque sensor and the simulated object (homogeneous and isotropic) in form of a linear FEM model.
In this context, the objective of this work is to propose an original solution for the representation of the deformation of soft objects based on force-torque and 3D vision measurements. The solution does not make assumptions on the material of the object, such as its isotropy or homogeneity, and capitalizes on an advantageous combination of distance-based clustering, stratified sampling and neural gas-tuned mesh simplification. The paper discusses the data acquisition process, its preparation, the deformation characterization and quality estimation issues.
2. Proposed Framework for Soft Object Deformation Representation
2.1. Data Acquisition
In order to collect data on soft object deformation, forces are exerted by physical interaction with the probing tip of an ATI force-torque sensor, as illustrated in Figure 1a. The Kinect sensor is employed to collect 3D pointclouds representing the object by turning the sensor around the object of interest following the trajectory marked by blue arrows in Figure 1a and integrating the partial collected pointclouds using a commercially-available solution [5]. An example of resulting object mesh is shown in Figure 1b.
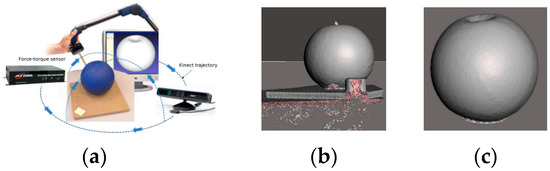
Figure 1.
(a) Acquisition of soft object deformation behavior; (b) raw data; and (c) cleaned model.
During the interaction, the force magnitude is monitored as well as the angle of the probing tip with respect to the object’s surface. The interaction parameters with the force-torque sensor are recuperated via a serial port. A script is used to recuperate in real-time the measured force magnitude over the x, y and z axes sent by the sensor. The force magnitude F at point P at the moment t is then computed as the norm of the three orthogonal force components along the x-, y- and z-axes as . At the same time, images of the setup are collected using a camera during each measurement step, each 10 s, in order to recuperate with the help of image processing software, the angle of the probing tip with respect to the surface of the object.
2.2. Data Preparation
Because of the different sampling rates of the force-torque sensor, of the angle information collection and of 3D data acquisition, a synchronization process is required to associate the correct surface deformation with the corresponding angle and force magnitude measurements. This is achieved by calculating a mean of all measurements gathered over the time it takes for the 3D model to be collected (e.g., in the interval t1 – t2), namely: (1) the mean of the measured force magnitude values returned by the force-torque sensor: , where n is the number of readings returned by the sensor in the interval t1 – t2 and (2) the mean of the angle values computed over the series of images: , where m is the number of images captured in the interval t1 – t2. The deformed object model is therefore considered to be the result of the application of a force with a magnitude equal to the computed average magnitude and applied at an angle equal to the calculated average angle value,
The 3D data collected contains undesired elements, such as the table on which the object is placed, the fixed landmarks required by the software to merge data from multiple viewpoints and the probing tip, as it can be noticed in Figure 1b. These are eliminated in part automatically (e.g., table and landmarks), in part manually (e.g., probing tip). The holes around the probing tip are filled using Meshmixer [12], in order to obtain clean meshes of the deformable object (Figure 1c).
2.3. Deformation Characterization
Starting from the cleaned mesh, in order to better characterize the deformation around the probing point, instead of using the entire collected pointcloud (Figure 2a) we first construct a selectively-densified mesh (Figure 2b), in which the area around the point of interaction between the probing tip and object surface is preserved at higher resolution, while the other areas are simplified. This ensures the deformed area around the probing tip has a higher density than the rest of the object’s surface. In order to achieve this, similar to the approach proposed in [13], the QSlim [14] algorithm is adapted to only simplify points that are not the interaction point with the probing tip and its 12-degree immediate neighbors. The value of 12 is chosen by trial and error, as it allows to correctly capture the entire deformed area over the 3D point clouds collected. This process ensures a uniform representation of the object by defining an equal number of faces, representing 30% of the faces in the initial model for all the instances of a deformed object. The 30% is obtained by monitoring the evolution of the errors and of the computation time for an increasing percentage and finding the best compromise between the two. The results are shown for three test objects in Figure 2b and Figure 3b.
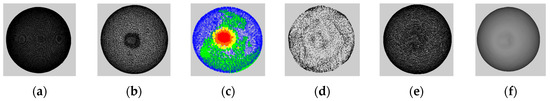
Figure 2.
Steps of the proposed method: (a) initial object mesh; (b) mesh with higher density in the deformed area; (c) stratified sampled data for neural-gas mapping; (d) neural-gas fitting; (e) neural-gas-tuned simplification; (f) neural-gas-tuned simplified object mesh.
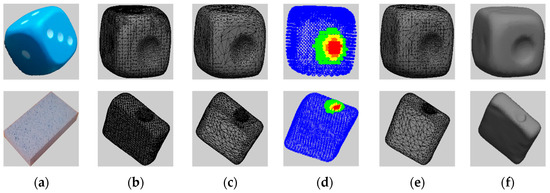
Figure 3.
Results for the cube and sponge model: (a) initial object; (b) initial object mesh; (c) mesh with higher density in the deformed area; (d) stratified sampled data for neural-gas mapping; (e) neural-gas-tuned simplified object mesh and (f) final object model.
Once this selectively-densified mesh is obtained, a stratified sampling technique is employed to only retain a subset of data for neural-gas tuning. Stratified sampling is a technique that generates samples by subdividing the sampling domain into non-overlapping partitions (clusters) and by sampling independently from each partition. In particular, the mesh is initially clustered according to the distance with respect to the initial non-deformed mesh. To detect the number of cluster to use, the normalized interval between 0 and the maximum distance between the non-deformed mesh and each instance of the deformed object under the study is gradually split in an increasing number of equal intervals (=number of clusters) and the points in the deformed area around the probing tip (12 immediate neighbors) are compared with the cluster situated at the largest distance (red in Figure 2c). It is desired that the highest possible number of points from the deformed zone is situated in this cluster. During testing, the number of points of the deformed zone in this cluster is monitored, and the process is stopped once the largest number of points in the deformed zone are found in this cluster. A number of 5 clusters was identified to ensure the best results.
Once the number of clusters identified, points are sampled randomly but in various proportions from each cluster to identify the adequate amount of data to be used by monitoring the evolution of errors described Section 2.4. The proportions are varied by taking into consideration the fact that a good representation is desired specifically in the deformed area and therefore more samples are desired for regions in which the deformation is larger. The adequate amount of data is identified by trial and error, by varying iteratively the percentage of data randomly extracted from each cluster from 25% to 90%, as further detailed in the experimental section. Figure 2c and Figure 3d show points sampled from the 5 clusters, with blue points belonging to the closer cluster to initial object and green, yellow, orange and red points are increasingly more distant with respect to the initial mesh (the deformed zone is shown in red). This stratified sampling is not sufficient, as the fine differences around the deformed zone and over the object surface might not be appropriately represented, which is the reason why a tuning of the selectively densified mesh is also executed using a neural gas network. The choice of a neural gas network [15] is justified by the fact that it converges quickly, reaches a low distortion error and it can capture fine details [16]. A neural gas network is fitted over the sampled points and takes the form of the object, while preserving more details in the regions where the local geometry changes [16]. This property allows to ensure that fine differences around the deformed zone and over the surface of the object can be captured accurately in the model. Using again the QSlim algorithm, the areas identified by neural gas are kept at higher resolution in the simplification, by rearranging the triangles of the selectively-densified mesh.
2.4. Quality Evaluation
The quality of the resulting representation is evaluated from quantitative and qualitative point of view. A first measure is computed using Metro [17] that allows comparing two meshes (e.g., the full-resolution mesh of an object and its simplified version) based on the computation of the Hausdorff distance. It returns the maximum (max) and mean distance (mean) as well as the variance (rms). The second category of errors considered takes into account human perceptual quality judgments. The normalized Laplacian pyramid-based image quality assessment error [18] is chosen for this purpose. As this error is meant to be used on images, images are collected over the simplified models of objects from 25 viewpoints and are compared with the images of the full-resolution object from the same viewpoints. The error measures for each instance of an object are reported as an average over these viewpoints. A qualitative evaluation of the results is obtained using Cloud Compare [19] that allows visualizing the regions most affected by error in the simplified object.
3. Experimental Results
The proposed framework is tested on three objects with different materials, a rubber ball (Figure 1a), a foam cube and a sponge (Figure 3a). Following the explanations in Section 2, and in particular in Section 2.3, we have identified initially the number of clusters to be used. Figure 2c and Figure 3d show the points sampled from these clusters, with red points belonging to the farthest cluster to initial object (deformed zone) and with orange, yellow, green and blue points being increasingly closer with respect to the initial mesh (blue = perfect match), for the combination of 87% from the closest (red) cluster, 77%, 67%, 57%, respectively from the 2nd, 3rd and 4th cluster, and 47% from the farthest distanced cluster points. Our tests revealed that overall, this is the best combination of percentages for our dataset. To validate the proposed approach, Figure 4 shows the color-coded comparison using Cloud Compare, between the measured object and its proposed representation where the blue means perfect match and green, yellow, orange an increasing error and red, the largest error (there is no link between these results and the colored clusters, even though the representation is interpreted in the same way). Figure 4a,c,e show the results after the selectively-densified simplification around the probing point. It can be noticed that the error is almost 0 (blue) in the deformed zone, as expected.
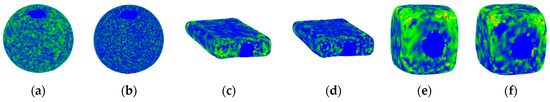
Figure 4.
Color-coded results for the ball, sponge and cube with respect to initial full-resolution model: (a) selectively-densified mesh around probing point for ball for = 4.5 N, = 10°; (b) final mesh for ball = 4.5 N, = 10°; (c) selectively-densified mesh around probing point for sponge for = 3.7 N, = 49°; (d) final mesh for sponge for = 3.7 N, = 49° (e) selectively-densified mesh around probing point for cube for = 5 N, = 85°; and (f) final mesh for cube for = 5 N, = 85°.
Once the neural gas is applied (Figure 4b,d,e respectively), the error decreases slightly over all the objects due to a better disposition of triangles in the mesh, but stays very low in the deformed zone. To validate quantitatively these results, we have computed the Metro and perceptual errors, as an average over the top 5 best sampling percentages and over the instances of each object, as shown in Table 1. It can be noticed that the overall perceptual similarity achieved is on average of 74% over the entire surface of the object and of 91% over the deformed area, with an average computing time per object of 0.43 s on a Pentium III, 2 GHz CPU, 64 bit operating system, 4 GHz memory machine.

Table 1.
Error measures and computing time.
4. Conclusions
The paper proposed an innovative data-driven representation of soft objects based on selectively-densified simplification, stratified sampling and neural gas tuning. The proposed solution avoids recuperating elasticity parameters which cannot be precisely and accurately identified for certain materials such as foam or rubber, as those used in the context of this work therefore eliminating the need to make assumptions on the material, such as its homogeneity or isotropy, assumptions that are often encountered in the literature.
Author Contributions
Bilal Tawbe and Ana-Maria Cretu conceived and designed the experiments; Bilal Tawbe performed the experiments; Bilal Tawbe and Ana-Maria Cretu analyzed the data; Ana-Maria Cretu wrote the paper.
Acknowledgments
This work supported in part by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and the Fonds de recherche du Québec—Nature et Technologies (FRQNT) New University Researchers Start-up Program. The authors would like to thank François Audet and Alain Huot for their help with the data collection for the ball model.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Krainin, M.; Henry, P.; Ren, X.; Fox, D. Manipulator and object tracking for in-hand 3D object modeling. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2011, 30, 1311–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollhofer, M.; Nießner, M.; Izadi, S.; Rhemann, C.; Zach, C.; Fisher, M.; Wu, C.; Fitzgibbon, A.; Loop, C.; Theobalt, C.; et al. Real-time non-rigid reconstruction using an RGB-D camera. ACM Trans. Graph. 2014, 33, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, M.; Taylor, J.; Fuchs, H.; Fitzgibbon, A.; Izadi, S. 3D Scanning deformable objects with a single RGBD sensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 493–501. [Google Scholar]
- Microsoft Kinect Fusion. Available online: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn188670.aspx (accessed on 1 August 2016).
- Skanect. Available online: http://skanect.occipital.com/ (accessed on 1 August 2016).
- Zaidi, L.; Bouzgarrou, B.; Sabourin, L.; Menzouar, Y. Interaction modeling in the grasping and manipulation of 3D deformable objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Robotics, Istanbul, Turkey, 27–31 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, J.; Pai, D.K.; Woodham, R.J. Acquisition of elastic models for interactive simulation. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2002, 21, 713–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordt, A.; Koch, R. Fast tracking of deformable objects in depth and colour video. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, Dundee, Scotland, UK, 30 August–1 September 2011; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Burion, S.; Conti, F.; Petrovskaya, A.; Baur, C.; Khatib, O. Identifying physical properties of deformable objects by using particle filters. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Robotics and Automation, Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2008; pp. 1112–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, G.; Solenthaler, B.; Szekely, G.; Harders, M. Simultaneous topology and stiffness identification for mass-spring models based on FEM reference deformations. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2004, LNCS 3217, Saint-Malo, France, 26–29 September 2004; pp. 293–301. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, B.; Schmedding, R.; Stachniss, C.; Teschner, M.; Burgard, W. Learning the Elasticity Parameters of Deformable Objects with a Manipulation Robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 1877–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Meshmixer. Available online: http://www.meshmixer.com/ (accessed on 1 August 2016).
- Monette-Thériault, H.; Cretu, A.-M.; Payeur, P. 3D Object modeling with neural gas based selective densification of surface meshes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference Systems, Man and Cybernetics, San Diego, CA, USA, 5–8 October 2014; pp. 1373–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Garland, M.; Heckbert, P.S. Surface simplification using quadric error meshes. In Proceedings of the T Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) Siggraph, New York, NY, USA, 3–8 August 1997; pp. 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Martinetz, M.; Berkovich, S.G.; Schulten, K.J. Neural-gas network for vector quantization and its application to time-series prediction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1993, 4, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cretu, A.-M.; Payeur, P.; Petriu, E.M. Selective range data acquisition driven by neural gas networks. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2009, 58, 2634–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cignoni, P.; Rocchini, C.; Scopigno, R. Metro: Measuring error on simplified surfaces. Comp. Graph. Forum 1998, 17, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laparra, V.; Balle, J.; Berardino, A.; Simoncelli, E.P. Perceptual image quality assessment using a normalized Laplacian pyramid. In Proceedings of the Human Vision and Electronic Imaging, Fargo, ND, USA, 15–18 February 2016; Volume 16. [Google Scholar]
- CloudCompare—3D Point Cloud and Mesh Processing Software. Available online: http://www.danielgm.net/cc/ (accessed on 1 August 2016).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).