Mitigation of Salt Stress in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Through Sulphur, Calcium, and Nitric Oxide: Impacts on Ionic Balance, Nitrogen-Sulphur Metabolism, and Oxidative Stress
Abstract
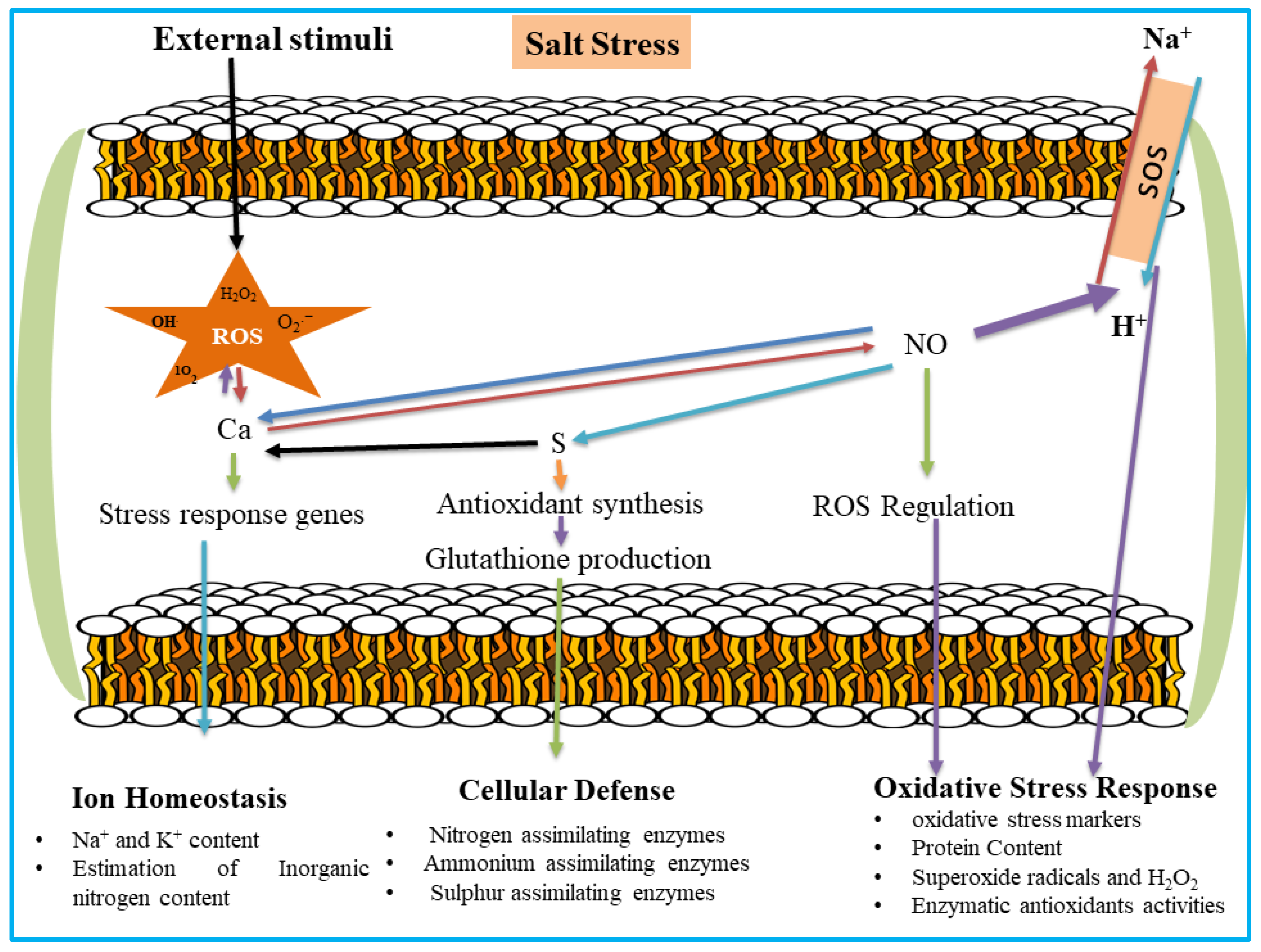
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Calculation of Na+ and K+ Content
2.3. Estimation of Inorganic Nitrogen Content (Nitrate, Nitrite, Ammonia)
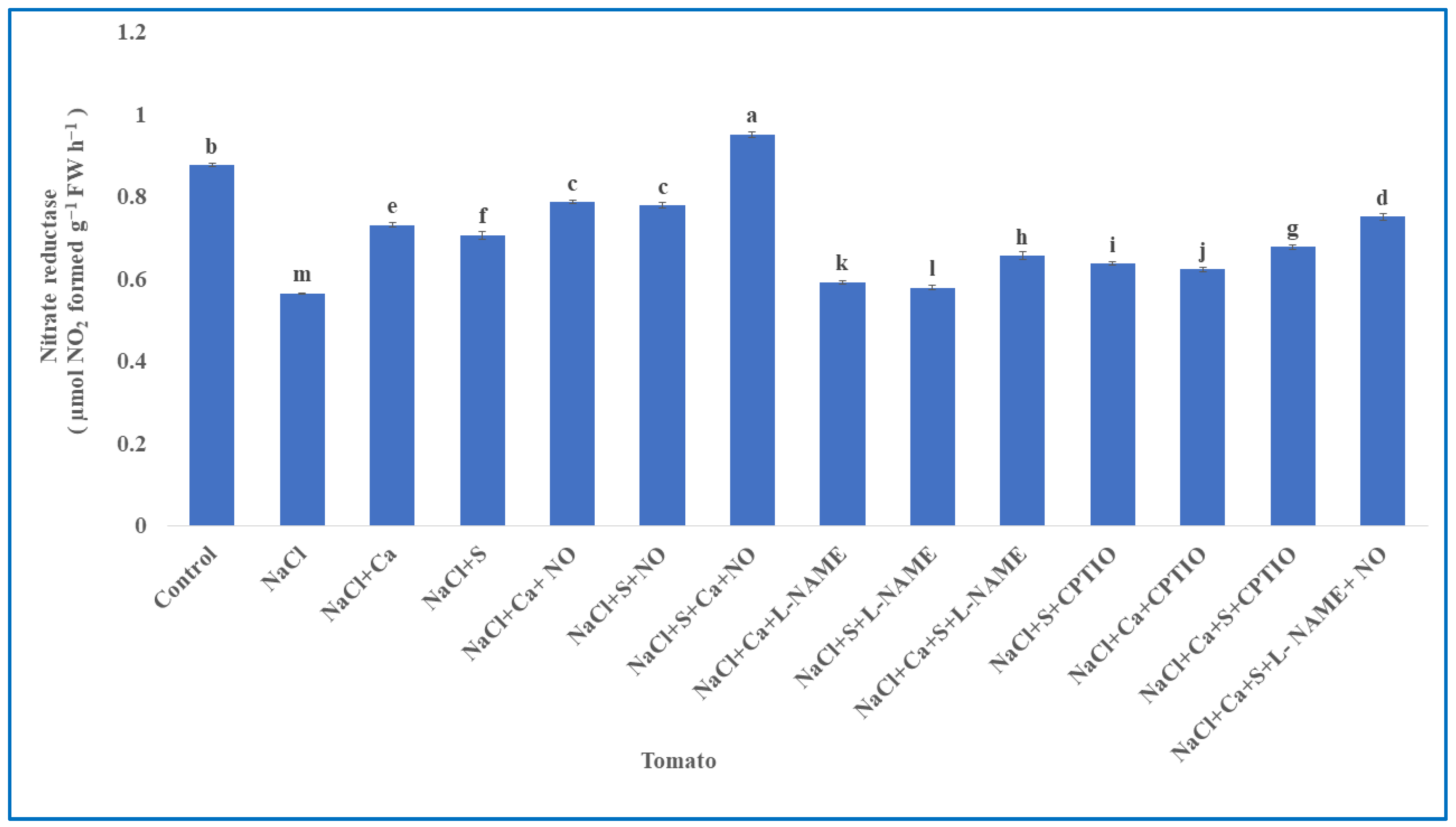
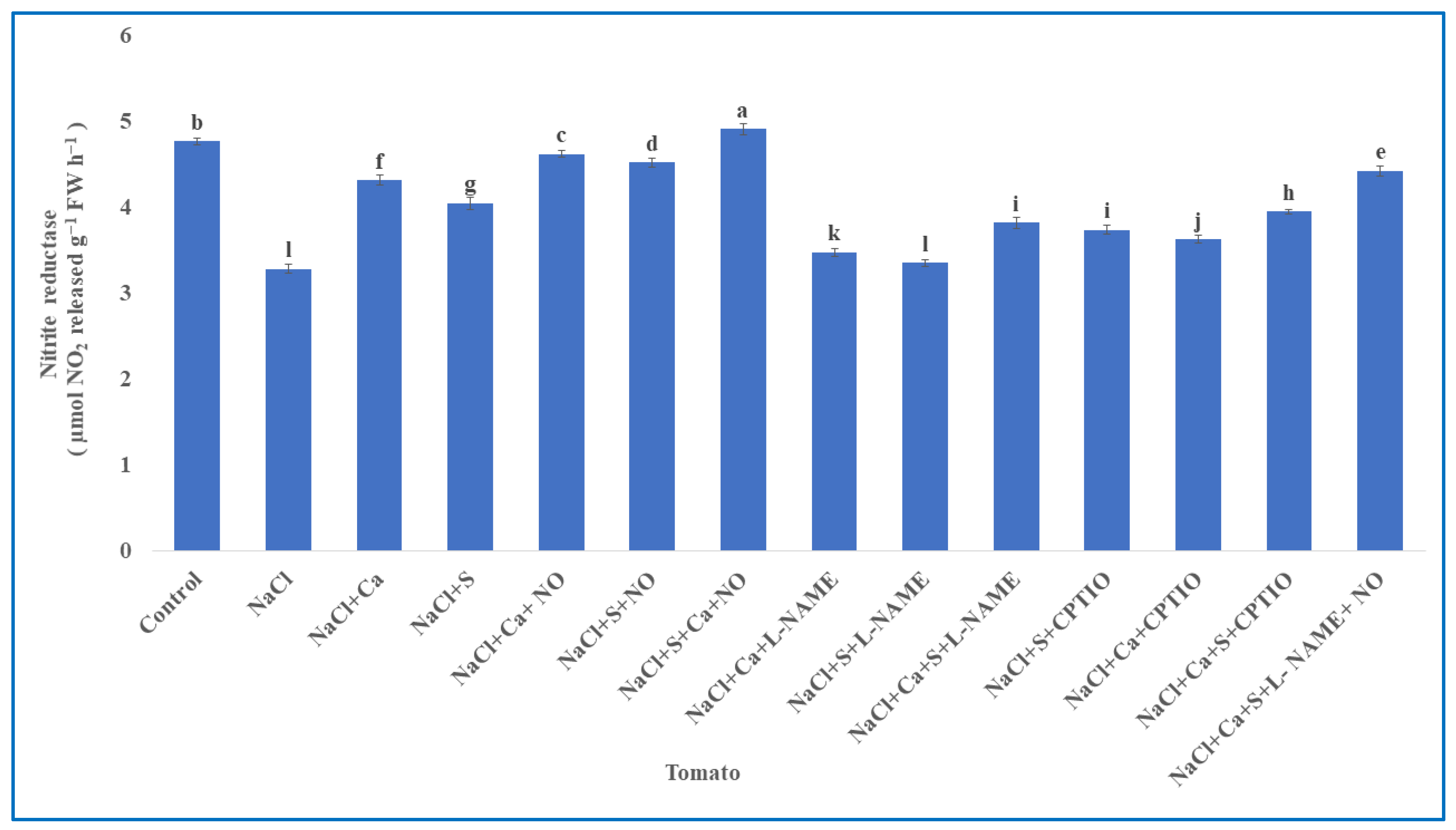
2.4. Estimation of Nitrogen Assimilating Enzymes (Nitrate Reductase, Nitrite Reductase) Activities
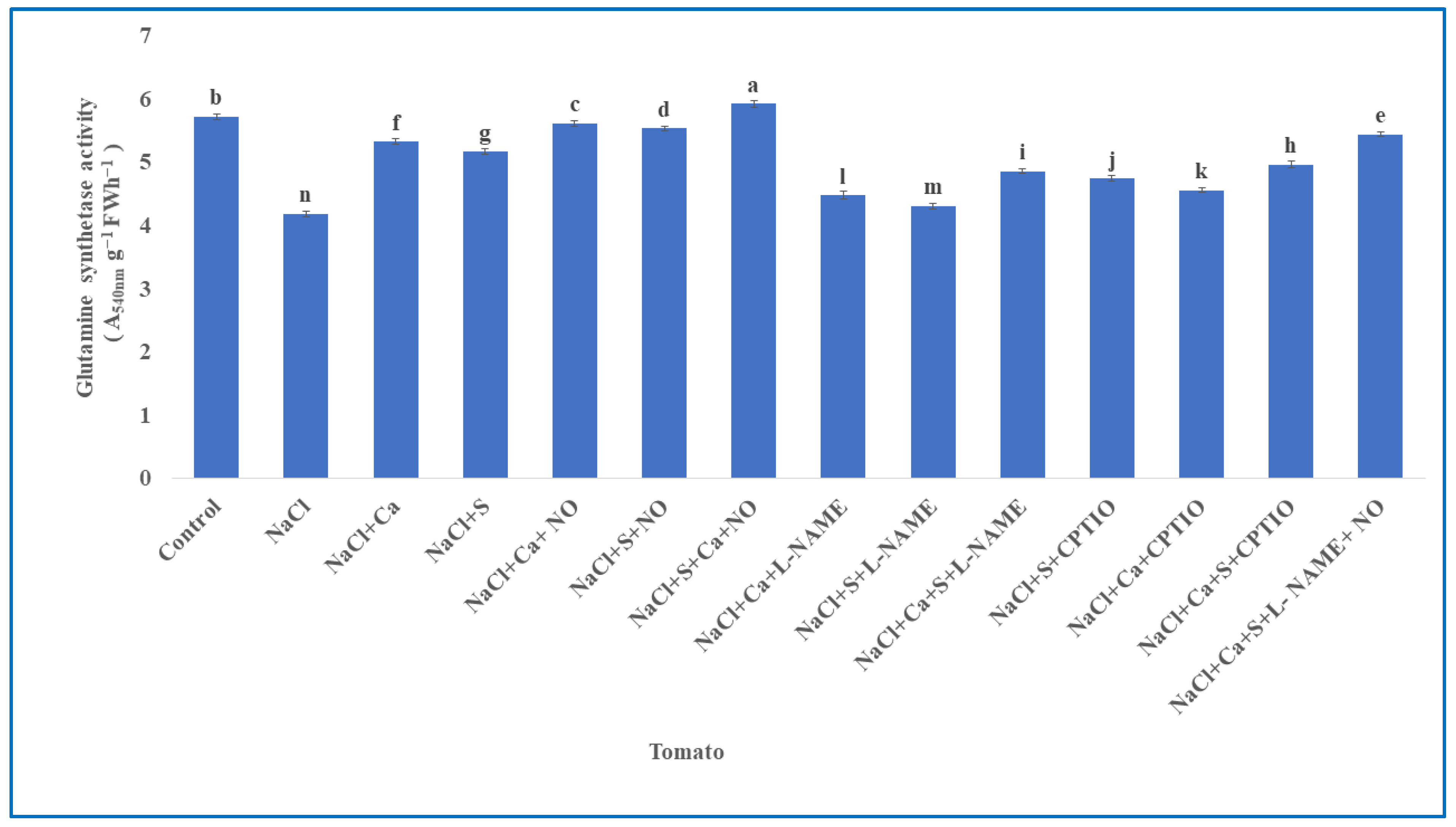
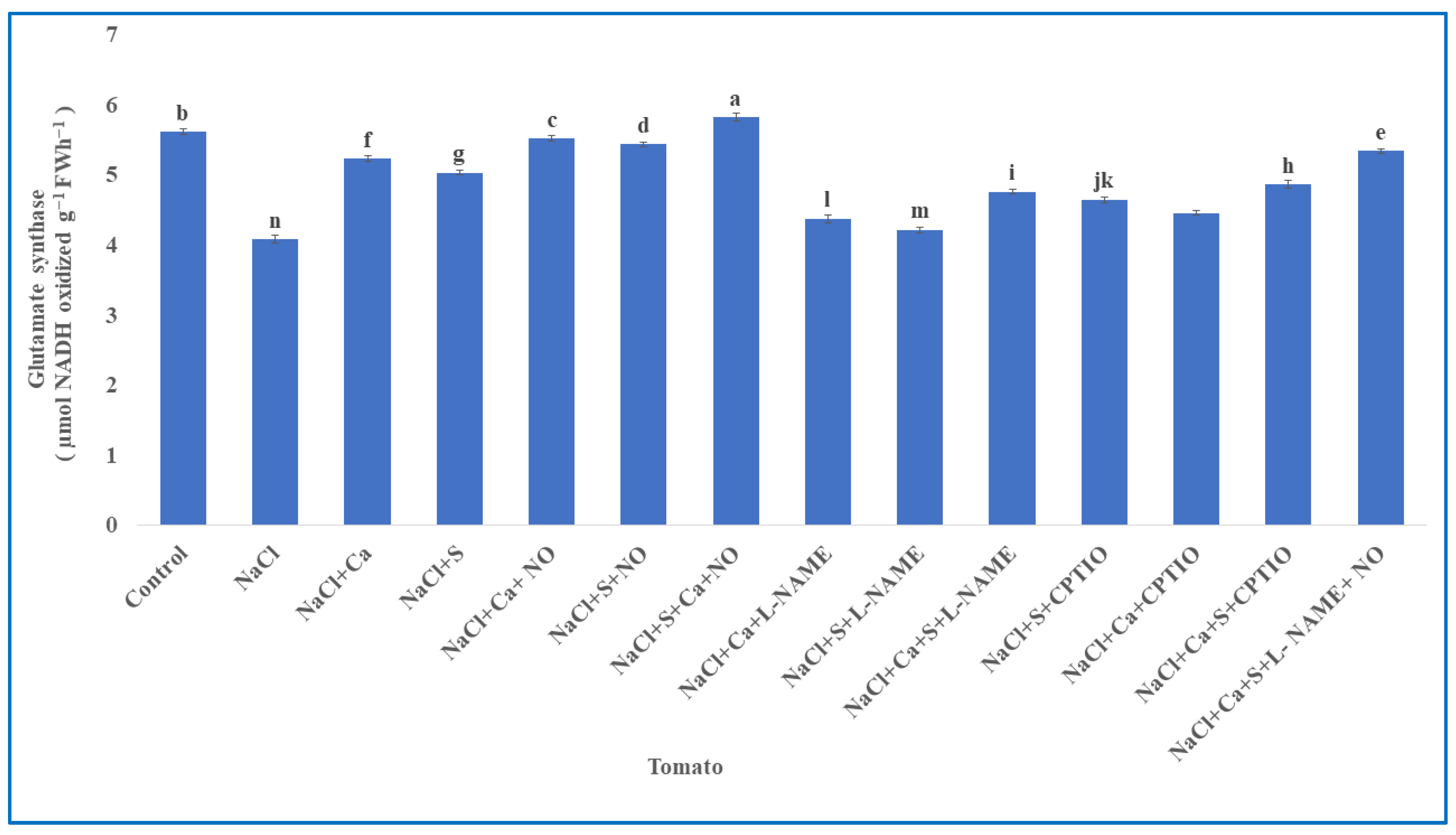
2.5. Estimation of Ammonium Assimilating Enzymes (Glutamine Synthetase and Glutamate Synthase) Activities
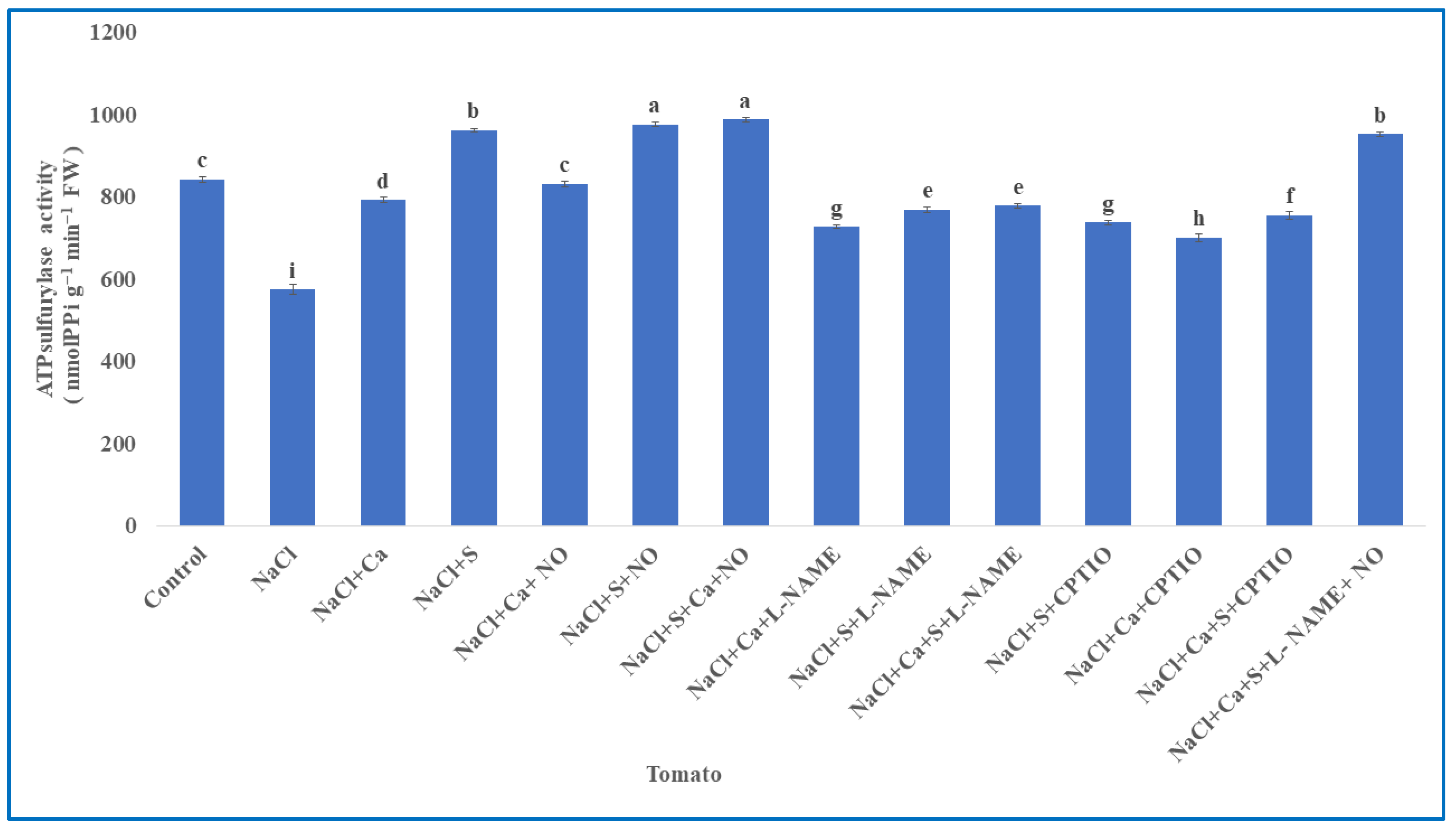
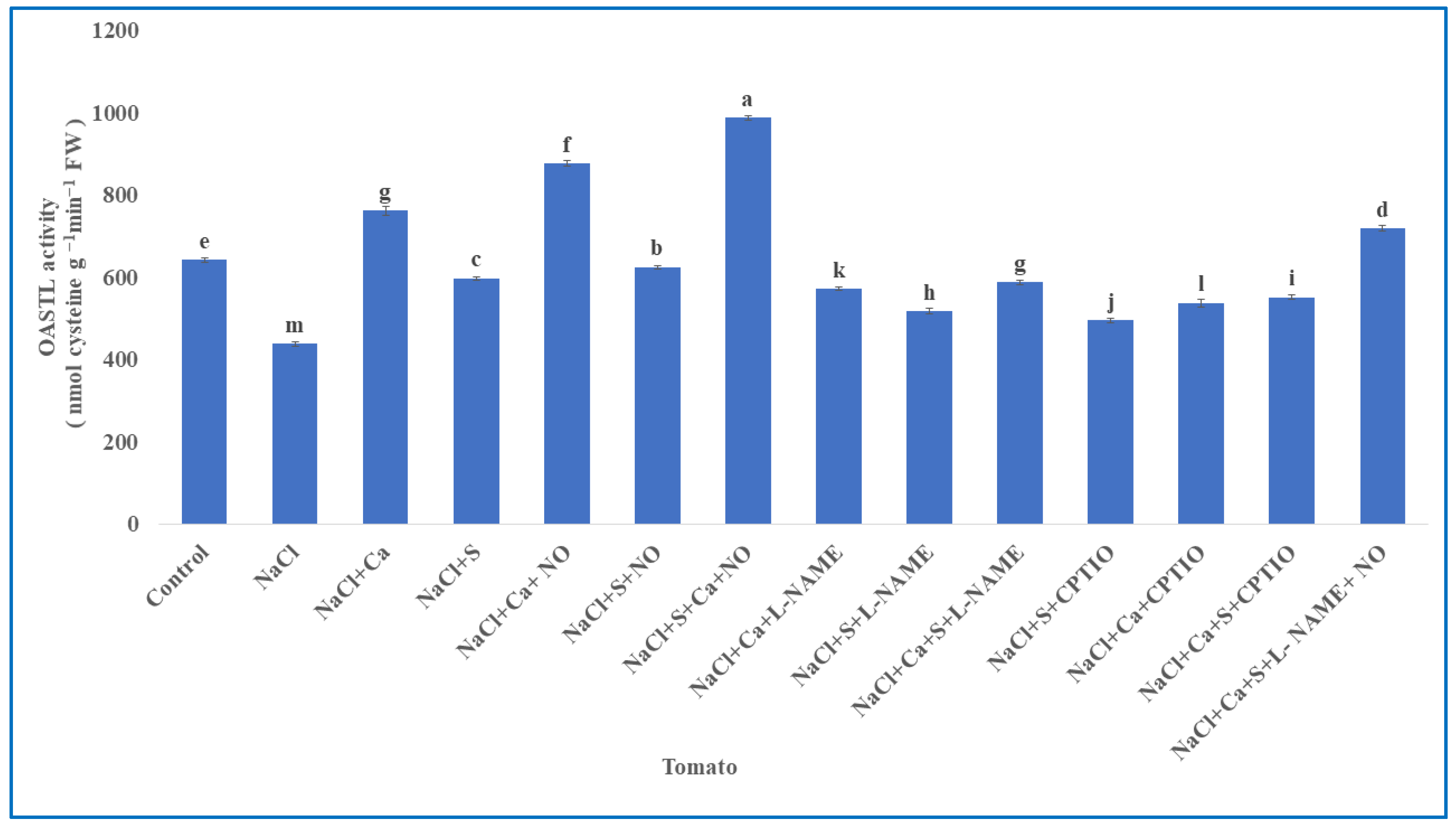
2.6. Estimation of Sulphur Assimilating Enzymes
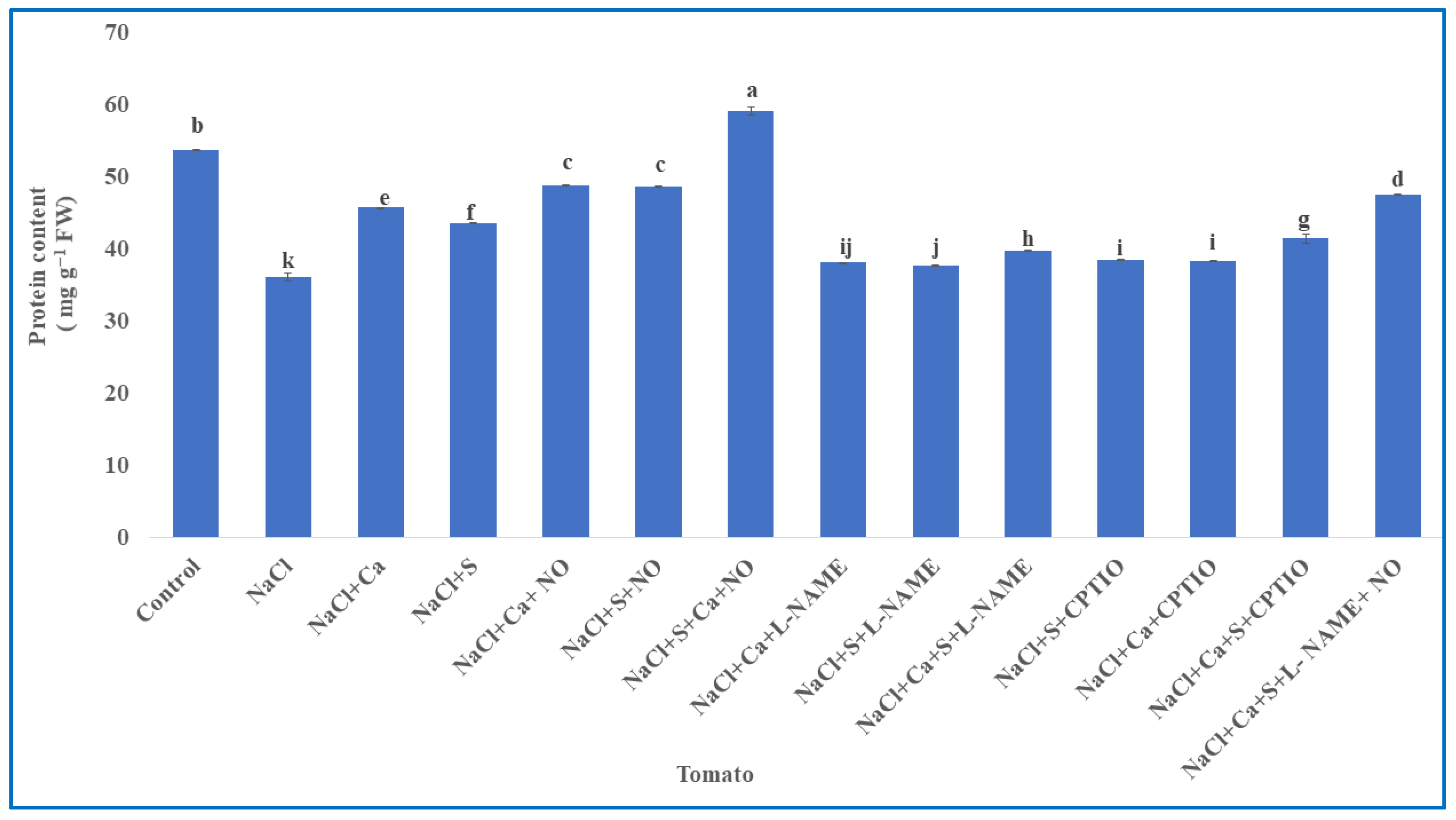
2.7. Estimation of Protein Content
2.8. Histochemical Detections of Superoxide and H2O2
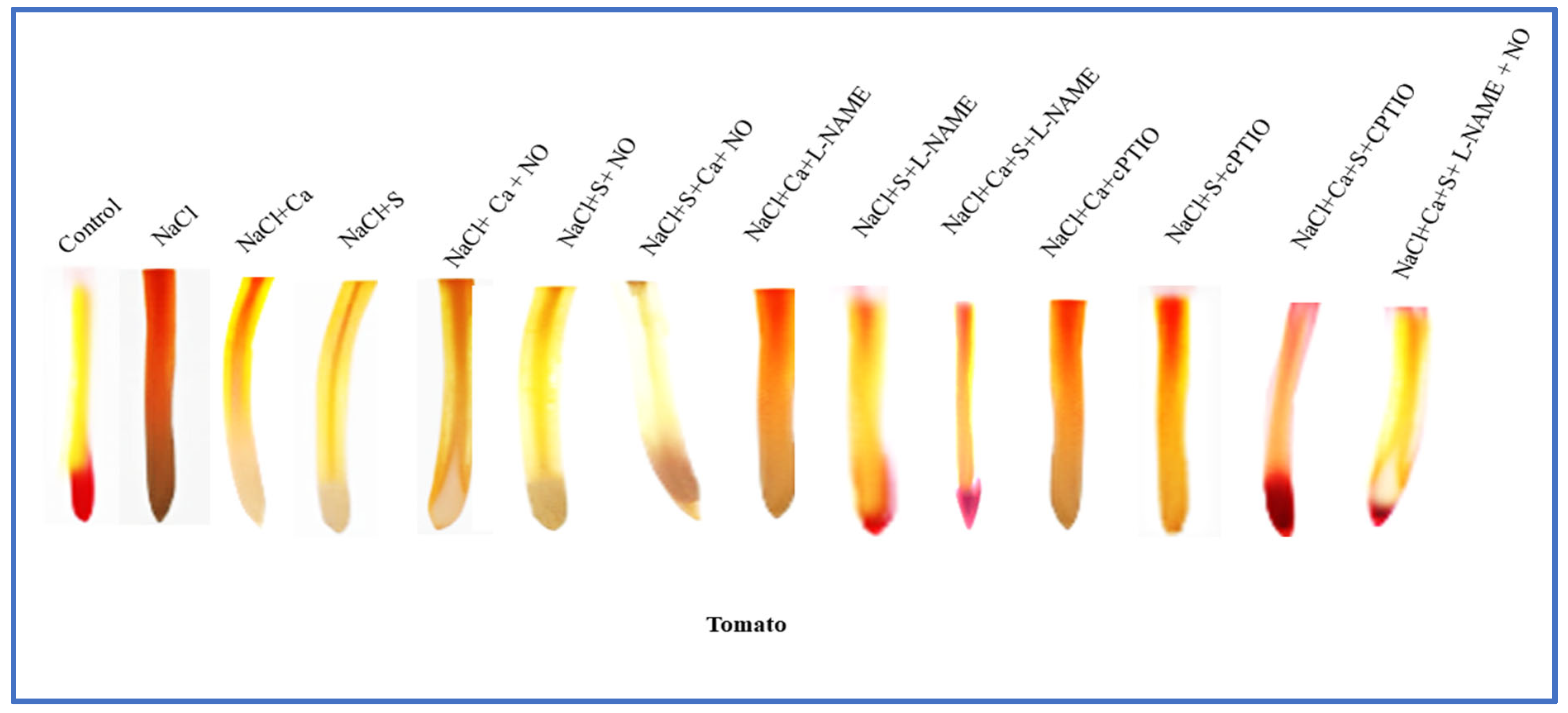
2.9. In Vivo Visualization of Nitric Oxide in Roots by Fluorescence
2.10. Estimation of Nitric Oxide Content
2.11. In Vivo Visualization of ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) in Leaf and Roots
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Estimation Na+ and K+ Content in Tomato
3.2. Estimation of Inorganic Nitrogen Contents in Tomato
3.3. Enzymes Involved in Nitrogen Assimilation in Tomato
3.4. Ammonium Assimilation Enzymes in Tomato
3.5. Enzymes Involved in Sulphur Assimilation in Tomato
3.6. Protein Content Estimation in Tomato
3.7. Visualization of ROS in Tomato: Histochemical Detection of Superoxide and Hydrogen Peroxide
3.8. In Vivo Visualization of Nitric Oxide in Roots by Fluorescence in Tomato
3.9. Elucidation of Crosstalk Mechanism with Nitric Oxide
4. Acknowledging Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zargar, M.; Bodner, G.; Tumanyan, A.; Tyutyuma, N.; Plushikov, V.; Pakina, E.; Shcherbakova, N.; Bayat, M. Productivity of various barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cultivars under semi-arid conditions in southern Russia. Agron. Res. 2018, 16, 2242–2253. [Google Scholar]
- Roșca, M.; Mihalache, G.; Stoleru, V. Tomato responses to salinity stress: From morphological traits to genetic changes. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1118383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Huang, Z.; Li, M.; Hou, Z. Growth, ionic homeostasis, and physiological responses of cotton under different salt and alkali stresses. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Usman, K.; Alsafran, M.; Jabri, H.A.; Samreen, T.; Saleem, M.H.; Tu, S. Nickel toxicity interferes with NO3−/NH4+ uptake and nitrogen metabolic enzyme activity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plants 2022, 11, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manne, H.; Kumari, N.; Yashveer, S.; Nain, S.; Duhan, J.; Avtar, R.; Sushil; Jattan, M.; Rani, B.; Alsahli, A.A.; et al. Mitigation of lead toxicity in Brassica juncea L. by sulphur application—Via various biochemical and transcriptomic strategies. J. King Saud Univ.—Sci. 2024, 36, 103175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Wang, D.; Xie, K.; Lu, Y.; Shi, C.; EL Sabagh, A.; Gu, W.; Xu, P. Pre-sowing seed treatment with kinetin and calcium mitigates salt induced inhibition of seed germination and seedling growth of choysum (Brassica rapa var. parachinensis). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 227, 112921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, B.A.; John, A.; Rahayu, F.; Martasari, C.; Husni, A.; Sukmadjaja, D.; Prahardini, P.E.R.; Kosmiatin, M.; Supriadi, K.; Purwati, R.D.; et al. Potato stress resilience: Unraveling the role of signalling molecules and phytohormones. Plant Gene 2024, 38, 100456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, A.F.; Iqbal, N.; Albaqami, M.; Khan, N.A. The emerging key role of reactive sulfur species in abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Physiol. Plant. 2023, 175, e13945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, B.A.; Kumari, R.; Rakhra, G.; Parihar, P.; Singh, R.; Raju, A.D.; Srivastava, P.K.; Prasad, S.M.; Singh, R.; Gulliya, S. Sulfur assimilation and regulation of abiotic stress via OMICS. Plant Stress 2024, 14, 100630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Kapoor, P.; Mir, B.A.; Singh, M.; Parrey, Z.A.; Rakhra, G.; Parihar, P.; Khan, M.N.; Rakhra, G. Unlocking the versatility of nitric oxide in plants and insights into its molecular interplays under biotic and abiotic stress. Nitric Oxide 2024, 150, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, B.A.; Taziun, T.; Mir, M.R.; Mir, T.u.G.; Kumari, R.; Wani, A.K.; Akhtar, N. Reactive Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Sulfur Species Under Abiotic Stress in Plants. In Plant Secondary Metabolites and Abiotic Stress; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 213–242. ISBN 978-1-394-18645-7. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, R.; Zhuang, Y.; Lali, M.N.; Zhao, L.; Xie, J.; Xiong, H.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y. Root reduction caused directly or indirectly by high application of nitrogen fertilizer was the main cause of the decline in biomass and nitrogen accumulation in citrus seedlings. Plants 2024, 13, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, A.; Pandey, A.; Gupta, M. Protective role of nitric oxide on nitrogen-thiol metabolism and amino acids profiling during arsenic exposure in Oryza sativa L. Ecotoxicology 2020, 29, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Prasad, S.M. Regulation of chromium toxicity tolerance in tomato and brinjal by calcium and sulfur through nitric oxide: Involvement of enzymes of sulfur assimilation and the ascorbate-glutathione cycle. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 166, 103789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hou, H.; Li, J. Frontiers in fluorescence imaging: Tools for the in situ sensing of disease biomarkers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2025, 13, 1133–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoagland, D.R.; Arnon, D.I. The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif. Agric. Exp. Stn. 1950, 347, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, R.; Khan, M.N.; Parrey, Z.A.; Kapoor, P.; Mir, B.A.; Taziun, T.; Parihar, P.; Rakhra, G. Synergistic effects of hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide in enhancing salt stress tolerance in cucumber seedlings. Physiol. Plant. 2025, 177, e70109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Hong, Y.; Zhu, G.; Li, Y.; Niu, Q.; Yao, J.; Hua, K.; Bai, J.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, H. Loss of salt tolerance during tomato domestication conferred by variation in a Na+/K+ transporter. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e103256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhel, M.; Husain, T.; Prasad, S.M.; Singh, V.P. GABA requires nitric oxide for alleviating arsenate stress in tomato and brinjal seedlings. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 42, 670–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Prasad, S.M. Management of chromium (VI) toxicity by calcium and sulfur in tomato and brinjal: Implication of nitric oxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, S.E.; Grimshaw, H.M.; Parkinson, J.A.; Quarmby, C. Chemical Analysis of Ecological Materials; Blackwell Scientific: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1974; ISBN 0-632-00321-9. [Google Scholar]
- Cataldo, D.A.; Maroon, M.; Schrader, L.E.; Youngs, V.L. Rapid colorimetric determination of nitrate in plant tissue by nitration of salicylic acid. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1975, 6, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snell, F.; Snell, C. Nitrite by sulphanilamide and N-(1-naphthyl) ethylenediamine hydrochloride. In Colorimetric Methods of Analysis; Van Nostrand Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1949; pp. 804–805. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Mohan Prasad, S.; Pratap Singh, V. Additional calcium and sulfur manages hexavalent chromium toxicity in Solanum lycopersicum L. and Solanum melongena L. seedlings by involving nitric oxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debouba, M.; Gouia, H.; Suzuki, A.; Ghorbel, M.H. NaCl stress effects on enzymes involved in nitrogen assimilation pathway in tomato “Lycopersicon esculentum” seedlings. J. Plant Physiol. 2006, 163, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillo, C. Diurnal variations of nitrite reductase, glutamine synthetase, glutamate synthase, alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase in barley leaves. Physiol. Plant. 1984, 61, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Srivastava, H.S. Increase in glutamate synthase (NADH) activity in maize seedlings in response to nitrate and ammonium nitrogen. Physiol. Plant. 1986, 66, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappartient, A.G.; Touraine, B. Demand-driven control of root ATP sulfurylase activity and SO42-uptake in intact canola (the role of phloem-translocated glutathione). Plant Physiol. 1996, 111, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemenschneider, A.; Riedel, K.; Hoefgen, R.; Papenbrock, J.; Hesse, H. Impact of reduced O-acetylserine(thiol)lyase isoform contents on potato plant metabolism. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 892–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostofa, M.G.; Fujita, M. Salicylic acid alleviates copper toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings by up-regulating antioxidative and glyoxalase systems. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 959–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Ahammed, G.J.; Li, Z.-X.; Wei, J.-P.; Shen, C.; Yan, P.; Zhang, L.-P.; Han, W.-Y. Nitric oxide mediates brassinosteroid-induced flavonoid biosynthesis in Camellia sinensis L. J. Plant Physiol. 2017, 214, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Indoliya, Y.; Chauhan, A.S.; Singh, S.P.; Singh, A.P.; Dwivedi, S.; Tripathi, R.D.; Chakrabarty, D. Nitric oxide mediated transcriptional modulation enhances plant adaptive responses to arsenic stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frahry, G.; Schopfer, P. NADH-stimulated, cyanide-resistant superoxide production in maize coleoptiles analyzed with a tetrazolium-based assay. Planta 2001, 212, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Cao, X.; Du, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F. Canola (Brassica napus) enhances sodium chloride and sodium ion tolerance by maintaining ion homeostasis, higher antioxidant enzyme activity and photosynthetic capacity fluorescence parameters. Funct. Plant Biol. 2024, 51, FP23089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Wei, H.; Ding, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, L.; Ding, C.; Tang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, G. Melatonin enhances Na+/K+ homeostasis in rice seedlings under salt stress through increasing the root H+-pump activity and Na+/K+ transporters sensitivity to ROS/RNS. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 182, 104328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J.; Agathokleous, E. Nitric oxide, hormesis and plant biology. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidana, S. Physiological Mechanisms Conferring Ameliorative Effects of Nitric Oxide and Cytokinin on Salinity Stress Tolerance in Pea and Barley. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Tasmania, Hobart, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Raju, A.D.; Prasad, S.M. Hydrogen sulfide regulates NaCl tolerance in brinjal and tomato seedlings by Na+/K+ homeostasis and nitrogen metabolism. Plant Stress 2023, 7, 100129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwan, S.E.M.; Dahdouh, S.M.M.; Abu-hashim, M.; Merwad, A.-R.M. The role of organic amendments combined with nitrogen fertilizers in enhancing nitrogen use efficiency for wheat in saline calcareous soil. J. Plant Nutr. 2025, 48, 839–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, B.; Tanwir, S.; Ahmad, F.; Ahmad, J.N. Jasmonic Acid and Salicylic Acid improved resistance against Spodoptera frugiperda Infestation in maize by modulating growth and regulating redox homeostasis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameel, J.; Anwar, T.; Majeed, S.; Qureshi, H.; Siddiqi, E.H.; Sana, S.; Zaman, W.; Ali, H.M. Effect of salinity on growth and biochemical responses of brinjal varieties: Implications for salt tolerance and antioxidant mechanisms. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Alvi, A.F.; Fatma, M.; Al-Hashimi, A.; Sofo, A.; Khan, N.A. Relative effects of melatonin and hydrogen sulfide treatments in mitigating salt damage in wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1406092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, R.; Theivanayagam, M.; Lee, I.-B.; Yi, P.-H.; Jeong, S.T. Uncovering Biochar Role in Enhancing Nutrient Uptake, Plant Defense, Yield, and Nhx Gene Expression to Mitigate Salinity Stress in Chinese Cabbage. SSRN 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Jin, S. Nitric oxide improves salt tolerance of Cyclocarya paliurus by regulating endogenous glutathione level and antioxidant capacity. Plants 2022, 11, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishnav, A.; Kumari, S.; Jain, S.; Varma, A.; Tuteja, N.; Choudhary, D.K. PGPR-mediated expression of salt tolerance gene in soybean through volatiles under sodium nitroprusside. J. Basic Microbiol. 2016, 56, 1274–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feezan, A.; Afzal, S.; Shoaib, S.M.; Rehman, K.; Hussain, A.; Akash, M.S.H.; Shahid, M.; Sadaf, B. Biochemical Impact of Nickel-Induced Metabolic Impairment and the Protective Effects of Resveratrol and Ascorbic Acid. J. Food Biochem. 2024, 2024, 8607956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, F.; Bhat, J.A.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Shah, T.; Ahmad, P. Nitric oxide mitigates vanadium toxicity in soybean (Glycine max L.) by modulating reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidant system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 451, 131085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.; Jin, X.; Fang, J.; Wei, S.; Ma, J.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Exploring the molecular landscape of nitrogen use efficiency in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) under low nitrogen stress: A transcriptomic and metabolomic approach. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhalipour, M.; Kulak, M.; Mohammadi, S.A.; Esmaielpour, B.; Nouraein, M.; Kocak, M.Z.; Farajzadeh, S.M.; Gohari, G.; Fotopoulos, V.; Vita, F. Foliar application of either melatonin or sodium nitpoprusside regulates the antioxidant status, and the morpho-physiological attributes and essential oil production in sage (Salvia officinalis L.) under salinity stress. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 323, 112526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, N.B.; Shawky, B.T. Synergistic effects of salicylic acid and melatonin on modulating ion homeostasis in salt-stressed wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) plants by enhancing root H+-pump activity. Plants 2022, 11, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.-X.; Tian, P.; Li, C.-Z.; Hu, X.-D.; Lin, Y.-J. Elucidating the intricacies of the H2S signaling pathway in gasotransmitters: Highlighting the regulation of plant thiocyanate detoxification pathways. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 276, 116307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, G.; Khan, A.; Khare, R.; Pathak, P.K.; Trivedi, P.K. Galactinol synthase 4 requires sulfur assimilation pathway to provide tolerance towards arsenic stress under limiting sulphur condition in Arabidopsis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 486, 137060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Pan, X.; Deng, Y.; Ge, Z.; Li, S.; Su, D.; Zhao, G.; Tang, H.; Wang, X. Combined transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses reveal the mechanisms by which the interaction between sulfur and nitrogen affects garlic yield and quality. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, M.S.; Li, G.; Xie, D.; Farag, R.; Hasan, M.M.; Alabdallah, N.M.; Al-Harbi, N.A.; Al-Qahtani, S.M.; Zeeshan, M.; Nasar, J.; et al. Melatonin mitigates salt-induced growth inhibition through the regulation of carbohydrate and nitrogen metabolism in tomato seedlings. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 4290–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Lan, Y.; Gong, F.; Li, C.; Xia, F.; Li, Y.; Fang, C. Comparative physiology and transcriptome response patterns in cold-tolerant and cold-sensitive varieties of Solanum melongena. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uğurlar, F.; Kaya, C. Synergistic mitigation of nickel toxicity in pepper (Capsicum annuum) by nitric oxide and thiourea via regulation of nitrogen metabolism and subcellular nickel distribution. Funct. Plant Biol. 2023, 50, 1099–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Waraich, E.A.; Shahid, H.; Ahmad, Z.; Zulfiqar, U.; Mahmood, N.; Al-Ashkar, I.; Ditta, A.; El Sabagh, A. Exogenously Applied Potassium Enhanced Morpho-Physiological Growth and Drought Tolerance of Wheat by Alleviating Osmotic Imbalance and Oxidative Damage. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 32, 4447–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, S.A.; Abdelhameed, R.E.; Metwally, R.A. In vivo and In vitro evaluation of the antifungal activity of the PGPR Bacillus amyloliquefaciens RaSh1 (MZ945930) against Alternaria alternata with growth promotion influences on Capsicum annuum L. plants. Microb. Cell Fact. 2023, 22, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, F.; Ortega, A.; Espinosa-Vellarino, F.L.; Garrido, I. Effect of thallium(I) on growth, nutrient absorption, photosynthetic pigments, and antioxidant response of Dittrichia plants. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yengkokpam, P.; Mazumder, P.B. Antioxidant enzymatic activities and profiling of gene expression associated with organophosphate stress tolerance in Solanum melongena L.cv. Longai. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Patel, A.; Tiwari, S.; Pandey, A.; Kumar, S.; Prasad, S.M. Nitric oxide and 5-aminolevulinic acid up-regulate growth, PS II photochemistry and antioxidant activity in UV-B stressed cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum. Plant Stress 2024, 11, 100332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Prasad, S.M. Interplay mechanism of exogenous hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide in modulating ascorbate–glutathione cycle under nickel-induced oxidative stress in two paddy field cyanobacteria. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 33, 674–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.K.; Rajalekshmi, R. Effect of hydro-, halo- and osmopriming on seed germination and seedling performance of Psophocarpus tetragonolobus (L.) DC. (winged bean). J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 24, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz-Gokdogan, E.; Burun, B. Effects of 24-Epibrassinolide on Shoot Tip Cultures Under NaCl Stress in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). J. Agric. Sci./Tarim Bilim. Derg. 2024, 30, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.; Ahanger, M.A.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Wijaya, L.; Alam, P. Exogenous application of nitric oxide modulates osmolyte metabolism, antioxidants, enzymes of ascorbate-glutathione cycle and promotes growth under cadmium stress in tomato. Protoplasma 2018, 255, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Sahu, P.; Kumari, A.; Luthra, S. Advances in Production Technology of Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Agric. Food E-Newsl. 2023, 5, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gatasheh, M.K.; Shah, A.A.; Noreen, Z.; Usman, S.; Shaffique, S. FeONPs alleviate cadmium toxicity in Solanum melongena through improved morpho-anatomical and physiological attributes, along with oxidative stress and antioxidant defense regulations. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghani, M.I.; Ali, A.; Atif, M.J.; Ali, M.; Ahanger, M.A.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Z. Different leafy vegetable cropping systems regulate growth, photosynthesis, and PSII functioning in mono-cropped eggplant by altering chemical properties and upregulating the antioxidant system. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1132861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.; Alhaithloul, H.A.; Hakeem, K.R.; Alharbi, B.M.; El-Esawi, M.; Elkelish, A. Exogenous nitric oxide mitigates nickel-induced oxidative damage in eggplant by upregulating antioxidants, osmolyte metabolism, and glyoxalase systems. Plants 2019, 8, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Garg, N. Nitric oxide and AMF-mediated regulation of soil enzymes activities, cysteine-H2S system and thiol metabolites in mitigating chromium (Cr (VI)) toxicity in pigeonpea genotypes. Biometals 2024, 37, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, M.Z.U.; Sarker, U.; Roy, S.K.; Alam, M.S.; Azam, M.G.; Miah, M.Y.; Hossain, N.; Ercisli, S.; Alamri, S. Manure-biochar compost mitigates the soil salinity stress in tomato plants by modulating the osmoregulatory mechanism, photosynthetic pigments, and ionic homeostasis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhao, Y.; Lou, W.; Abdalmegeed, D.; Guan, R.; Shen, W. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes can promote Brassica napus L. and Arabidopsis thaliana L. root hair development through nitric oxide and ethylene pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| S.No | Treatments | Tomato | Units (Both Parameters) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ Content | K+ Content | |||
| 1 | Control | 4.45 ± 0.08 k | 50.68 ± 0.06 b | mg g−1 DW |
| 2 | NaCl | 6.49 ± 0.06 a | 30.47 ± 0.09 i | mg g−1 DW |
| 3 | NaCl + Ca | 5.11 ± 0.06 h | 40.92 ± 0.04 e | mg g−1 DW |
| 4 | NaCl + S | 5.32 ± 0.05 g | 40.81 ± 0.06 e | mg g−1 DW |
| 5 | NaCl + Ca + NO | 4.73 ± 0.07 j | 50.48 ± 0.05 bc | mg g−1 DW |
| 6 | NaCl + S + NO | 4.83 ± 0.06 i | 50.28 ± 0.06 cd | mg g−1 DW |
| 7 | NaCl + Ca + S + NO | 4.40 ± 0.06 k | 60.49 ± 0.41 a | mg g−1 DW |
| 8 | NaCl + Ca + L- NAME | 6.09 ± 0.03 c | 30.83 ± 0.05 h | mg g−1 DW |
| 9 | NaCl + S + L- NAME | 6.25 ± 0.05 b | 30.73 ± 0.06 h | mg g−1 DW |
| 10 | NaCl + Ca + cPTIO | 5.69 ± 0.02 e | 40.48 ± 0.05 f | mg g−1 DW |
| 11 | NaCl + S + cPTIO | 5.77 ± 0.04 e | 40.22 ± 0.04 g | mg g−1 DW |
| 12 | NaCl + Ca + S + L-NAME | 5.92 ± 0.05 d | 40.36 ± 0.49 g | mg g−1 DW |
| 13 | NaCl + Ca + S + cPTIO | 5.48 ± 0.04 f | 40.67 ± 0.04 ef | mg g−1 DW |
| 14 | NaCl + Ca + S + L-NAME + NO | 4.91 ± 0.05 i | 50.10 ± 0.07 d | mg g−1 DW |
| S.No | Treatments | Tomato | Units (All Parameters) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrate | Nitrite | Ammonium | |||
| 1 | Control | 0.82 ± 0.004 b | 0.84 ± 0.003 b | 0.63 ± 0.005 h | (µmol g−1 FW) |
| 2 | NaCl | 0.54 ± 0.011 j | 0.54 ± 0.004 n | 0.90 ± 0.010 a | (µmol g−1 FW) |
| 3 | NaCl + Ca | 0.76 ± 0.007 de | 0.74 ± 0.005 f | 0.73 ± 0.006 f | (µmol g−1 FW) |
| 4 | NaCl + S | 0.74 ± 0.004 ef | 0.72 ± 0.005 g | 0.73 ± 0.062 f | (µmol g−1 FW) |
| 5 | NaCl + Ca + NO | 0.80 ± 0.011 bc | 0.82 ± 0.003 c | 0.68 ± 0.008 g | (µmol g−1 FW) |
| 6 | NaCl + S + NO | 0.78 ± 0.004 a | 0.79 ± 0.005 d | 0.71 ± 0.005 f | (µmol g−1 FW) |
| 7 | NaCl + Ca + S + NO | 0.89 ± 0.014 a | 0.86 ± 0.003 a | 0.58 ± 0.006 i | (µmol g−1 FW) |
| 8 | NaCl + Ca + L- NAME | 0.64 ± 0.003 hi | 0.62 ± 0.009 l | 0.83 ± 0.006 bc | (µmol g−1 FW) |
| 9 | NaCl + S + L- NAME | 0.62 ± 0.004 i | 0.56 ± 0.005 m | 0.86 ± 0.005 b | (µmol g−1 FW) |
| 10 | NaCl + Ca + cPTIO | 0.71 ± 0.005 fg | 0.69 ± 0.004 i | 0.78 ± 0.005 de | (µmol g−1 FW) |
| 11 | NaCl + S + cPTIO | 0.75 ± 0.052 g | 0.68 ± 0.004 j | 0.81 ± 0.008 cd | (µmol g−1 FW) |
| 12 | NaCl + Ca + S + L-NAME | 0.67 ± 0.005 h | 0.66 ± 0.005 k | 0.82 ± 0.004 c | (µmol g−1 FW) |
| 13 | NaCl + Ca + S + cPTIO | 0.72 ± 0.005 ef | 0.70 ± 0.004 h | 0.77 ± 0.005 e | (µmol g−1 FW) |
| 14 | NaCl + Ca + S + L-NAME + NO | 0.77 ± 0.006 de | 0.75 ± 0.005 e | 0.72 ± 0.006 f | (µmol g−1 FW) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mir, B.A.; Parrey, Z.A.; Kapoor, P.; Parihar, P.; Rakhra, G. Mitigation of Salt Stress in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Through Sulphur, Calcium, and Nitric Oxide: Impacts on Ionic Balance, Nitrogen-Sulphur Metabolism, and Oxidative Stress. Nitrogen 2025, 6, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen6040093
Mir BA, Parrey ZA, Kapoor P, Parihar P, Rakhra G. Mitigation of Salt Stress in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Through Sulphur, Calcium, and Nitric Oxide: Impacts on Ionic Balance, Nitrogen-Sulphur Metabolism, and Oxidative Stress. Nitrogen. 2025; 6(4):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen6040093
Chicago/Turabian StyleMir, Bilal Ahmad, Zubair Ahmad Parrey, Preedhi Kapoor, Parul Parihar, and Gurmeen Rakhra. 2025. "Mitigation of Salt Stress in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Through Sulphur, Calcium, and Nitric Oxide: Impacts on Ionic Balance, Nitrogen-Sulphur Metabolism, and Oxidative Stress" Nitrogen 6, no. 4: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen6040093
APA StyleMir, B. A., Parrey, Z. A., Kapoor, P., Parihar, P., & Rakhra, G. (2025). Mitigation of Salt Stress in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Through Sulphur, Calcium, and Nitric Oxide: Impacts on Ionic Balance, Nitrogen-Sulphur Metabolism, and Oxidative Stress. Nitrogen, 6(4), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen6040093






