Bootstrapping Enhanced Model for Improving Soil Nitrogen Prediction Accuracy in Arid Wheat Fields
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
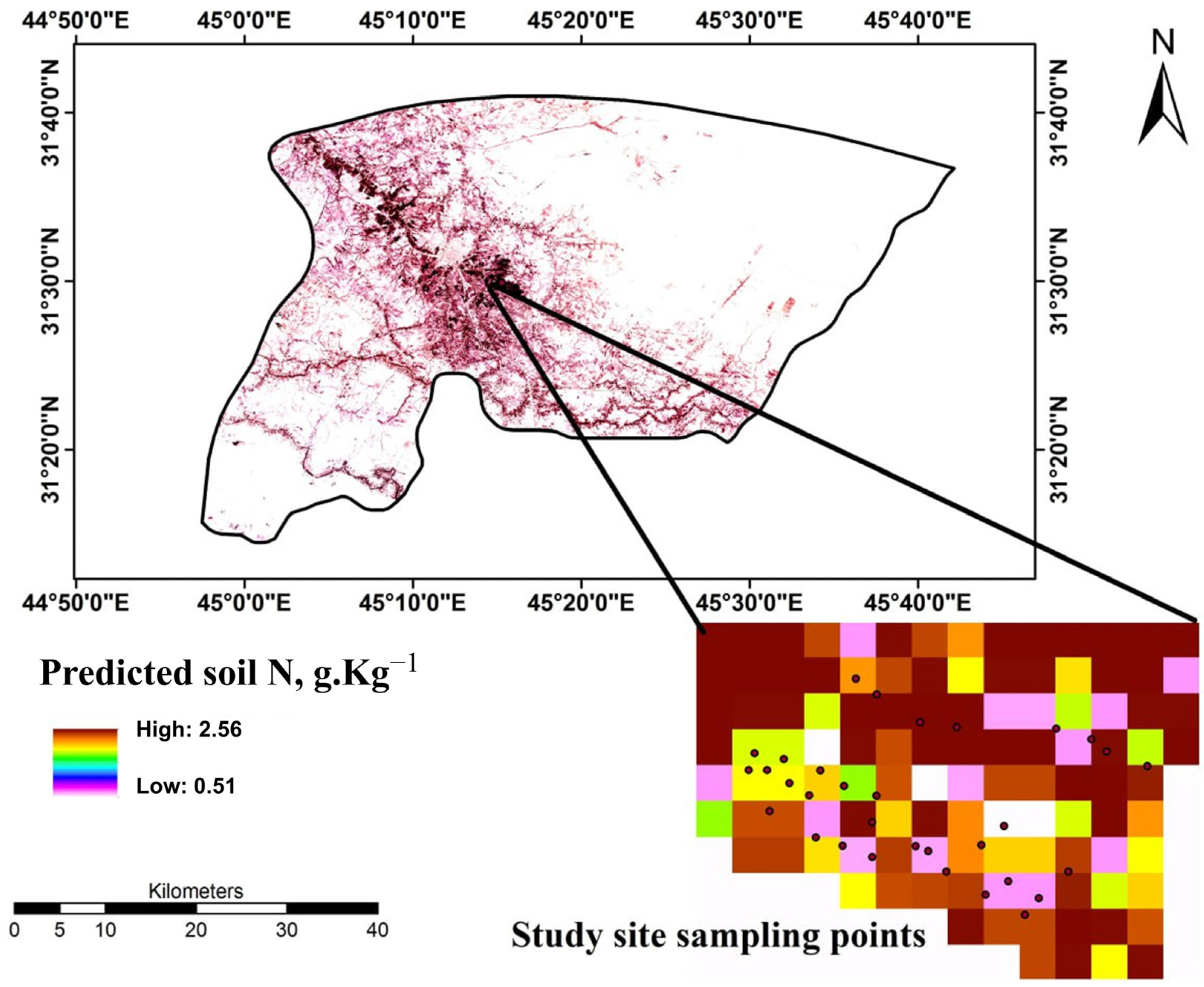
2.1. Study Area and Soil Sampling
2.2. Image Capture and Processing
2.3. Identifying Key Reflectance Bands
2.4. Model Selection and Validation
2.5. Bootstrapping Implementation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Features Derivation
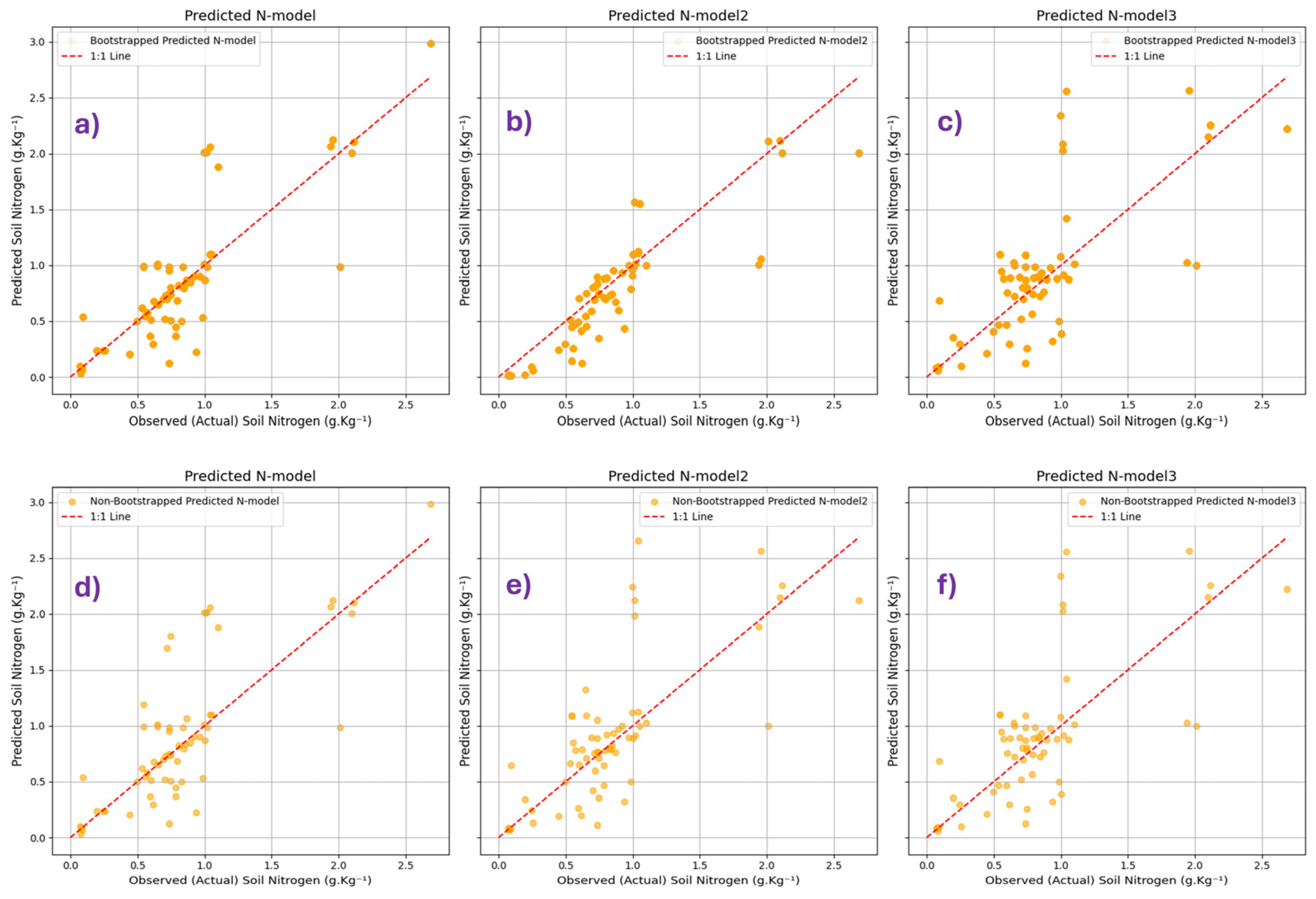
3.2. Bootstrapping vs. Non-Bootstrapping Models
3.3. Spatial Characteristics of Soil N Prediction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mueller, N.D.; Gerber, J.S.; Johnston, M.; Ray, D.K.; Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J.A. Closing Yield Gaps through Nutrient and Water Management. Nature 2012, 490, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Schulte-Uebbing, L.; De Vries, W.; Zou, T.; Davidson, E.A. Sustainable Nitrogen Management Index: Definition, Global Assessment, and Potential Improvements. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, S.; Lam, S.K.; Yu, Y.; van Grinsven, H.J.M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Bodirsky, B.L.; Wang, S.; Duan, J.; et al. Cost-Effective Mitigation of Nitrogen Pollution from Global Croplands. Nature 2023, 613, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.R.; Clark, M.; Buchanan, G.M.; Ficetola, G.F.; Rondinini, C.; Tilman, D. Proactive Conservation to Prevent Habitat Losses to Agricultural Expansion. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, A.M.; Khosla, R.; Longchamps, L.; Dahal, S. Characterizing Variation in Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Wheat Genotypes Using Proximal Canopy Sensing for Sustainable Wheat Production. Agronomy 2020, 10, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing Nitrogen for Sustainable Development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; Masek, J.G.; Cohen, W.B.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E. Opening the Archive: How Free Data Has Enabled the Science and Monitoring Promise of Landsat. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 2–10. [Google Scholar]
- Forkuor, G.; Hounkpatin, O.K.L.; Welp, G.; Thiel, M. High-Resolution Mapping of Soil Properties Using Remote Sensing Variables in Southwestern Burkina Faso: A Comparison of Machine Learning and Multiple Linear Regression Models. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, M.A.; Khosla, R.; Longchamps, L.; Dahal, S. Using NDVI to Differentiate Wheat Genotypes Productivity under Dryland and Irrigated Conditions. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, H.; Song, H.Y.; Garcia Pereira, A.; Hernandez Gomez, A. Measurement and analysis of soil nitrogen and organic matter content using near-infrared spectroscopy techniques. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2005, 6, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Morgan, C.L.S.; Grunwald, S.; Brown, D.J.; Sarkhot, D.V. Comparison of soil reflectance spectra and calibration models obtained using multiple spectrometers. Geoderma 2011, 161, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Li, M.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H. A portable soil nitrogen detector based on NIRS. Precis. Agric. 2014, 15, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shujairy, Q.A.T.; Ali, N.S. Prediction of soil total nitrogen using spectroradiometer and GIS in southern Iraq. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Res. 2017, 3, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Dewitte, O.; Jones, A.; Elbelrhiti, H.; Horion, S.; Montanarella, L. Satellite Remote Sensing for Soil Mapping in Africa: An Overview. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2012, 36, 514–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, M.; Shi, X.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Z. Integrating Hyperspectral Imaging with Machine Learning Techniques for the High-Resolution Mapping of Soil Nitrogen Fractions in Soil Profiles. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Yuan, L. Predicting the High Heating Value and Nitrogen Content of Torrefied Biomass Using a Support Vector Machine Optimized by a Sparrow Search Algorithm. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jin, X.; Adhikari, K.; Li, W.; Yu, M.; Bian, Z.; Wang, Q. Mapping Total Soil Nitrogen from a Site in Northeastern China. Catena 2018, 166, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Kuang, L.; Han, Y.; Xu, Z.; Guo, X. Predicting Spatial Distribution of Soil Organic Carbon and Total Nitrogen in a Typical Human-Impacted Area. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 4465–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, K.; Tariq, A.; Lu, L.; Soufan, W.; El Sabagh, A. Interaction of climate, topography and soil properties with cropland and cropping pattern using remote sensing data and machine learning methods. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2023, 26, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Ma, Z.; Li, B.; Bartels, R.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Dong, J. Spatially Explicit Model for Statistical Downscaling of Satellite Passive Microwave Soil Moisture. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Wu, T.; Luo, J.; Sun, Y.; Xia, L. Land Parcel-Based Digital Soil Mapping of Soil Nutrient Properties in an Alluvial-Diluvial Plain Agricultural Area in China. Geoderma 2019, 340, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohavi, R. A Study of Cross-Validation and Bootstrap for Accuracy Estimation and Model Selection. In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–25 August 1995; pp. 1137–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Zoubir, A.M.; Iskandler, D.R. Bootstrap Methods and Applications. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2007, 24, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesterberg, T. Bootstrap. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2011, 3, 497–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B.; Tibshirani, R.J. An Introduction to the Bootstrap; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Alesso, C.A.; Masola, M.J.; Carrizo, M.E.; Imhoff, S.D.C. Estimating sample size of soil cone index profiles by bootstrapping. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2017, 41, e0160464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.; Brunsdon, C.; Lu, B.; Nakaya, T.; Charlton, M. Introducing bootstrap methods to investigate coefficient nonstationarity in spatial regression models. Spat. Stat. 2017, 21, 241–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dane, J.H.; Reed, R.B.; Hopmans, J.W. Estimating soil parameters and sample size by bootstrapping. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-Q.; Tang, X.-S.; Phoon, K.-K. Bootstrap method for characterizing the effect of uncertainty in shear strength parameters on slope reliability. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2015, 140, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrba, M.; Maciak, M.; Peštová, B.; Pešta, M. Bootstrapping not independent and not identically distributed data. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omondiagebe, O.P.; Roudier, P.; Liburne, L.; Ma, Y.; McNeill, S. Quantifying uncertainty in the prediction of soil properties using mid-infra spectra. Geoderma 2024, 448, 116954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Domke, G.M.; Russell, M.B.; Walters, B.F. Spatial modeling of litter and soil carbon stocks on forest land in the conterminous United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, S.; Karimi, A.; Mousavi, A.; Kerry, R.; Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R. Delineation of soil management zone maps at the regional scale using machine learning. Agronomy 2023, 13, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estefan, G.; Sommer, R.; Ryan, J. (Eds.) Methods of Soil, Plant, and Water Analysis: A Manual for the West Asia and North Africa Region, 3rd ed.; ICARDA: Beirut, Lebanon, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Samarasinghe, S. Neural Networks for Applied Sciences and Engineering: From Fundamentals to Complex Pattern Recognition; Auerbach: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Efron, B. Better bootstrap confidence intervals. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1987, 82, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasmi, A.; Gomez, C.; Chehbouni, A.; Dhiba, D.; Elfil, H. Satellite Multi-Sensor Data Fusion for Soil Clay Mapping Based on the Spectral Index and Spectral Bands Approaches. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshitha, D.N.; Choudhary, S. A Bootstrap Aggregation Approach for Adequate Crop Fertilizer and Nutrition Recommendation. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2022, 26, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantigeza, M.K.; Tesfay, F.; Terefe, H.; Mezgebo, T. Land Use Land Cover Change and Habitat Vulnerability to Disturbance in Menz-Guassa Community Conservation Area, North Shewa, Ethiopia. Res. Sq. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Ali, T.; Gawai, R.; Dronjak, L.; Elaksher, A. The Analysis of Land Use and Climate Change Impacts on Lake Victoria Basin Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data and Google Earth Engine (GEE). Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablat, X.; Huang, C.; Tang, G.; Erkin, N.; Sawut, R. Modeling Soil CO2 Efflux in a Subtropical Forest by Combining Fused Remote Sensing Images with Linear Mixed Effect Models. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, D.; Xu, K.; Cao, W.; Jiang, X.; Ni, J. Monitoring of Nitrogen Indices in Wheat Leaves Based on the Integration of Spectral and Canopy Structure Information. Agronomy 2022, 12, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Du, Q.; Du, P.; Pan, C. Estimation of the Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils Using Airborne Hyperspectral Imaging and Random Forest. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 120987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, R.; Hall, J.W. A Global Assessment of Nitrogen Concentrations Using Spatiotemporal Random Forests. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2022, 2022, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, J.K.; Panday, D.; Robertson, G.P.; Saha, D. Machine learning reveals dynamic controls of soil nitrous oxide emissions from diverse long-term cropping systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2024, 54, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, H.R.; Ma, T.F.; Ruark, M.D. Toward a standardized statistical methodology comparing optimum nitrogen rates among management practices: A bootstrapping approach. Agric. Environ. Lett. 2021, 6, e20045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y. Data preprocessing and machine learning algorithms for soil nitrogen prediction: A comparative study. Ecol. Inform. 2020, 57, 101066. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, Z.; Sun, X.; Yan, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, P.; Chen, J. Mapping topsoil total nitrogen using random forest and modified regression kriging in agricultural areas of central China. Plants 2023, 12, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Xiong, X.; Adhikari, K.; Knadel, M.; Grunwald, S.; Greve, M.H. Modeling Soil Organic Carbon at Regional Scale by Combining Multi-Spectral Images with Laboratory Spectra. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Shang, K.; Xiao, C.; Wang, C.; Tang, H. Spectral Index for Mapping Topsoil Organic Matter Content Based on ZY1-02D Satellite Hyperspectral Data in Jiangsu Province, China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.J.; Zhu, X.C.; Li, C.; Wei, Y.; Guo, X.Y.; Yu, X.Y. Estimating Total Nitrogen Content in Brown Soil of Orchard Based on Hyperspectrum. Open J. Soil Sci. 2017, 7, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesaignoux, A.; Fabre, S.; Briottet, X. Influence of soil moisture content on spectral reflectance of bare soils in the 0.4–14 µm domain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2268–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, D.; Paul, M.; Murshed, M.; Teng, S.W.; Schmidtke, L. Soil moisture, organic carbon, and nitrogen content prediction with hyperspectral data using regression models. Sensors 2022, 22, 7998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Mu, T.; Liu, G.; Yang, X.; Zhu, G.; Shang, C. A method of soil moisture content estimation at various soil organic matter conditions based on soil reflectance. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peri, P.L.; Rosas, Y.M.; Ladd, B.; Toledo, S.; Lasagno, R.G.; Pastur, G.M. Modeling Soil Nitrogen Content in South Patagonia Across a Climate Gradient, Vegetation Type, and Grazing. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sui, B.; Shen, H.; Ouyang, L. Mapping Stocks of Soil Total Nitrogen Using Remote Sensing Data: A Comparison of Random Forest Models with Different Predictors. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 160, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, L.; Mesfin, B. Performance of Mid-Infrared Spectroscopy to Predict Nutrients for Agricultural Soils in Selected Areas of Ethiopia. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Ge, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, T.; Bolan, N.; Lischeid, G.; Rinklebe, J. Influence of Soil Properties, Topography, and Land Cover on Soil Organic Carbon and Total Nitrogen Concentration: A Case Study in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Based on Random Forest Regression and Structural Equation Modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Yan, C.; Yuan, J. Estimation of Soil Organic Matter Based on Spectral Indices Combined with Water Removal Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auzzas, A.; Capra, G.F.; Jani, A.D.; Ganga, A. An Improved Digital Soil Mapping to Predict Nitrogen by Combining Machine Learning Algorithms and Open Environmental Data. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2024, 10, 6519–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefano, C.D.; Ferro, V.; Porto, P. Applying the Bootstrap Technique for Studying Soil Redistribution by Caesium-137 Measurements at Basin Scale. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2000, 45, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Soil Property | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical conductivity (ECe) | 8.7 | dS.m−1 |
| pH | 7.5 | |
| Soil organic matter (OM) | 8 | g.Kg−1 |
| Soil texture | Sandy clay loam | |
| Soil moisture | 10 | % |
| Principal Component | Band 2 | Band 3 | Band 4 | Band 5 | Band 6 | Band 7 | Eigenvalue | Variance Explained% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 0.38 | 0.09 | −0.57 | −0.58 | 0.46 | 0.42 | 1.20 | 25.12 |
| PC2 | 0.40 | −0.05 | −0.39 | 0.06 | 0.08 | −0.82 | 0.99 | 20.84 |
| PC3 | 0.44 | −0.3 | −0.21 | 0.72 | −0.22 | 0.38 | 1.04 | 21.71 |
| PC5 | 0.52 | 0.15 | 0.39 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.46 | 9.59 |
| PC6 | 0.48 | −0.58 | 0.56 | −0.35 | −0.29 | −0.03 | 1.09 | 22.74 |
| Bootstrapping | Mean | R2 | RMSE | Confidence Intervals * |
| B5/B7 | 0.86 | 0.489 | 0.35 | 0.074–0.2157 |
| Log (B5/B7) | 0.89 | 0.773 | 0.10 | 0.723–1.0263 |
| 1/(Log B5/B7) | −0.15 | 0.191 | 1.07 | −0.6954–0.6225 |
| Non-Bootstrapping | Mean | R2 | RMSE | |
| B5/B7 | 0.87 | 0.401 | 0.69 | |
| Log (B5/B7) | 0.87 | 0.614 | 0.17 | |
| 1/(Log B5/B7) | −0.14 | 0.113 | 1.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Shujairy, Q.A.T.; Al-Hedny, S.M.; Naser, M.A.; Shawkat, S.M.; Ali, A.H.; Panday, D. Bootstrapping Enhanced Model for Improving Soil Nitrogen Prediction Accuracy in Arid Wheat Fields. Nitrogen 2025, 6, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen6020023
Al-Shujairy QAT, Al-Hedny SM, Naser MA, Shawkat SM, Ali AH, Panday D. Bootstrapping Enhanced Model for Improving Soil Nitrogen Prediction Accuracy in Arid Wheat Fields. Nitrogen. 2025; 6(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen6020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Shujairy, Qassim A. Talib, Suhad M. Al-Hedny, Mohammed A. Naser, Sadeq Muneer Shawkat, Ahmed Hatem Ali, and Dinesh Panday. 2025. "Bootstrapping Enhanced Model for Improving Soil Nitrogen Prediction Accuracy in Arid Wheat Fields" Nitrogen 6, no. 2: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen6020023
APA StyleAl-Shujairy, Q. A. T., Al-Hedny, S. M., Naser, M. A., Shawkat, S. M., Ali, A. H., & Panday, D. (2025). Bootstrapping Enhanced Model for Improving Soil Nitrogen Prediction Accuracy in Arid Wheat Fields. Nitrogen, 6(2), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen6020023








