Abstract
Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.), renowned for its applications in environmental, industrial, and medicinal fields, is critically evaluated in this comprehensive review focusing on the impacts of chemical and organic fertilizers on its cultivation. As hemp re-emerges as a crop of economic significance, the choice between chemical and organic fertilization methods plays a crucial role in determining not only yield but also the quality and sustainability of production. This article examines the botanical characteristics of hemp, optimal growth conditions, and the essential biochemical processes for its cultivation. A detailed comparative analysis is provided, revealing that chemical fertilizers, while increasing yield by up to 20% compared to organic options, may compromise the concentration of key phytochemicals such as cannabidiol by approximately 10%, highlighting a trade-off between yield and product quality. The review presents quantitative assessments of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) from both fertilizer types, noting that K significantly influences the synthesis of terpenes and cannabinoids, making it the most impactful element in the context of medicinal and aromatic hemp varieties. Optimal rates and timing of application for these nutrients are discussed, with a focus on maximizing efficiency during the flowering stage, where nutrient uptake directly correlates with cannabinoid production. Furthermore, the challenges associated with the U.S. industrial hemp market are addressed, noting that reducing production costs and improving processing infrastructure is essential for sustaining industry growth, especially given the slow expansion in fiber and cannabidiol markets due to processing bottlenecks. The review concludes that while chemical fertilizers may offer immediate agronomic benefits, transitioning towards organic practices is essential for long-term environmental sustainability and market viability. The future of the hemp industry, while promising, will depend heavily on advancements in genetic engineering, crop management strategies, and regulatory frameworks that better support sustainable cultivation practices. This nuanced approach is vital for the industry to navigate the complex trade-offs between productivity, environmental health, and economic viability in the global market.
1. Introduction
The resurgence of interest in hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) cultivation for industrial purposes is not without its challenges [1]. Despite its numerous benefits, hemp cultivation requires careful attention to regulatory frameworks, particularly regarding ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) levels and genetic purity [2]. Strains with higher THC content pose legal and logistical challenges, necessitating strict oversight to ensure compliance with regulations [3]. Moreover, concerns over cross-pollination with THC-rich varieties necessitate rigorous testing and monitoring protocols to maintain the integrity of industrial hemp crops [4]. Furthermore, the industrialization of hemp production presents logistical hurdles, particularly in developing infrastructure for processing and distribution [5]. Establishing efficient supply chains for hemp-derived products requires investments in processing facilities, transportation networks, and market development initiatives [6].
Collaborative efforts between government agencies, industry stakeholders, and research institutions are essential to address these challenges and unlock the full potential of hemp as a sustainable industrial crop [7]. In addition to regulatory and logistical challenges, hemp cultivation also faces agronomic obstacles related to soil fertility, pest management, and climate adaptation [8]. Implementing sustainable agricultural practices such as crop rotation, integrated pest management, and soil conservation measures is crucial to optimizing yields and minimizing environmental impacts [9]. Research into hemp genetics and breeding programs aimed at developing cultivars tailored to specific agroecological conditions can enhance resilience and productivity [10]. Moreover, the socio-economic implications of hemp cultivation must be carefully considered to ensure equitable distribution of benefits across communities [11]. Smallholder farmers and rural communities stand to benefit from the economic opportunities offered by hemp production, but adequate support mechanisms and capacity-building initiatives are needed to empower local stakeholders [12]. Inclusive policies that prioritize sustainable development, social equity, and cultural preservation can foster a thriving hemp industry that benefits society as a whole [13].
The growing demand for sustainable alternatives to traditional commodities presents a unique opportunity for hemp to emerge as a cornerstone of the bio-based economy [14]. By leveraging its diverse applications and environmental advantages, hemp has the potential to revolutionize industries ranging from textiles and construction to healthcare and renewable energy [15]. However, realizing this potential requires coordinated efforts to overcome regulatory, logistical, agronomic, and socio-economic barriers to hemp cultivation and utilization [16]. The industrial significance of hemp extends far beyond its traditional associations with fiber production and medicinal use [17]. As a versatile and sustainable crop, hemp offers a multitude of economic, environmental, and social benefits that warrant attention from researchers, policymakers, and entrepreneurs alike. By addressing the challenges and seizing the opportunities presented [18]. Furthermore, the global shift towards sustainability and environmental stewardship underscores the importance of incorporating hemp into sustainable development agendas [19,20]. By integrating hemp cultivation into agroforestry systems, carbon sequestration initiatives, and waste valorization strategies, we can harness its potential to mitigate climate change, promote biodiversity, and foster resilience in the face of environmental challenges [21]. Embracing hemp as a catalyst for sustainable development offers a pathway towards achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and building a more inclusive, regenerative, and prosperous future for all [22]. Through hemp cultivation, we can pave the way for a more resilient, equitable, and sustainable future [23].
Moreover, the resurgence of interest in hemp cultivation presents an opportunity for innovation and collaboration across diverse sectors [24]. As researchers explore novel applications and processing techniques, partnerships between academia, industry, and government can drive technological advancements and market expansion [25]. Investments in research and development initiatives focused on improving hemp genetics, refining extraction methods, and scaling up production capabilities can unlock new possibilities for value-added products and market diversification [26]. By fostering a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship, we can unleash the full potential of hemp as a sustainable solution to global challenges, from climate change to economic inequality [27,28]. The manifold application of the hemp is shown in Figure 1.
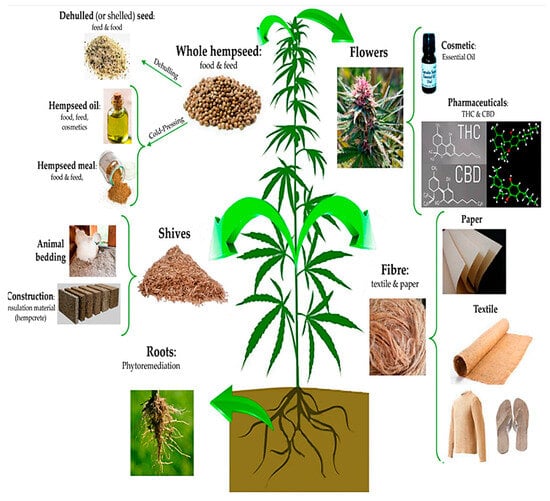
Figure 1.
The manifold applications of the hemp plant: virtually, each part of this plant can be used in a specific industrial field [29].
This comprehensive review aims to assess hemp cultivation practices by comparing the effectiveness and sustainability of chemical versus organic fertilization methods. The study delves into the plant’s agronomy context to better understand its unique cultivation requirements and potential under different nutrient regimes. The objectives include a detailed examination of how various fertilization types (chemical and organic) impact plant growth, yield, and quality, with a focus on identifying optimal practices for different growth stages. Additionally, the review explores broader themes such as the technologies used in organic cultivation, the environmental impacts of these practices, and the economic challenges and opportunities facing hemp farmers. This investigation aims to offer insights that can inform both current agricultural practices and future policy-making in the hemp industry.
2. Methodology
A thorough literature search was conducted across multiple academic databases, including Web of Knowledge, Scopus, ScienceDirect, Google Scholar, Web of Science Core Collection by Clarivate Analytics, and ResearchGate, focusing on publications up to 2024. We employed a diverse set of keywords to capture various aspects relevant to the cultivation of hemp and its response to different fertilization methods. These keywords included “hemp cultivation”, “chemical fertilizers”, “organic fertilizers”, “nutrient effects on hemp”, “organic cultivation technologies”, “hemp growth conditions”, “economic impact of hemp farming”, and “global hemp production trends”. To ensure a broad and relevant range of search results, keywords were combined using logical operators such as “OR” and “AND”. Including quotation marks around specific terms, such as “organic hemp cultivation”, helped in accurately retrieving pertinent records. All keywords were consistently used across all selected databases to maximize search coverage and gather a comprehensive collection of literature (Figure 2).
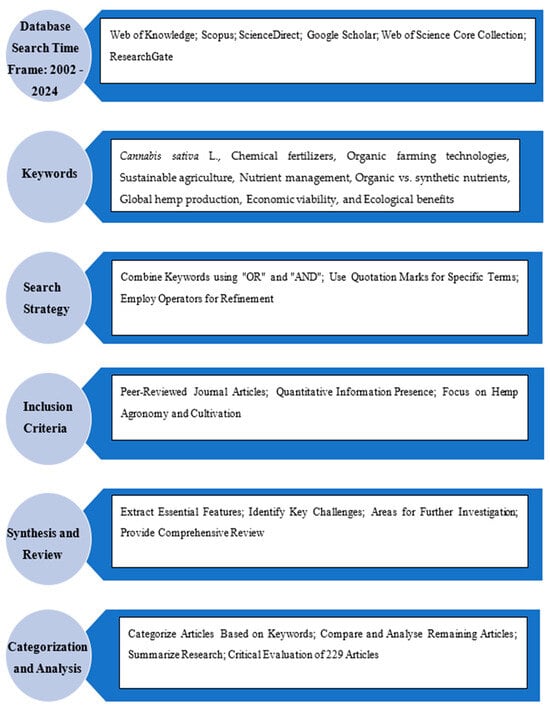
Figure 2.
Diagrammatic view of the organization of the paper.
3. Biochemistry of Hemp
Cannabis plants produce unique specialized metabolites called cannabinoids, which consist of polyketide and monoterpene substructures (Figure 3). Hitherto, more than 100 cannabinoids have been isolated from marijuana and hemp, and their chemical and pharmacological properties have been intensively investigated [30]. Among these metabolites, ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), identified as the psychoactive cannabinoid [31], has engaged considerable attention because this cannabinoid has valuable therapeutic potentials, including analgesic, anticonvulsant, antiemetic, and appetite-stimulating properties [32]. It is reported that in recent years, cannabidiol (CBD), an isomer of THC with a distinct molecular structure, has garnered significant attention as a potent antiseizure medication for treating intractable childhood epilepsy [33]. Notably, CBD is recognized for its ability to mitigate the adverse psychotropic effects of THC. This recognition has led to the approval of Nabiximols (Sativex®), an oral spray derived from cannabis containing THC and CBD in a 1:1 (w/w) ratio, in Canada and several European countries for alleviating symptoms associated with multiple sclerosis, such as pain and spasms [34]. Furthermore, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recently approved Epidiolex®, a CBD-based medication, for treating rare and severe childhood epilepsy disorders such as Dravet and Lennox–Gastaut syndromes [35]. Recent research has suggested that structural differences in cannabinoids, like ∆9-THC and CBD, and variations in alkyl chain structures may significantly impact their pharmacological effects [36]. For instance, ∆9-tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), with a propyl side chain, acts as a receptor antagonist. Studies show cannabinoid receptor antagonists can influence metabolic parameters linked to diseases like obesity and diabetes, indicating potential therapeutic value for THCV [37]. This resurgence of interest in plant cannabinoids underscores the importance of cannabinoid biochemistry in research, particularly in biotechnological production. Initially stored as cannabinoid acids, such as THCA and CBDA, cannabinoids undergo nonenzymatic decarboxylation into their active forms during storage and consumption [38].
The process of cannabinoid biosynthesis involves three main steps: polyketide formation, prenylation, and oxidative cyclization, as depicted in Figure 2. Research on this topic began around twenty-five years ago with the discovery of THCA synthase in young C. sativa leaves [18]. While early studies progressed slowly, recent omics-based approaches have rapidly advanced, nearly identifying all specialized enzymes in this pathway [39]. This progress has prompted further exploration of cannabinoid biotechnology [40]. This review outlines the unique characteristics of these biosynthetic enzymes and discusses their potential and challenges in biotechnological applications for producing active cannabinoid metabolites [41]. Although all Cannabis sativa plants share commonalities, differences in appearance, chemical composition, production methods, and usage are detailed in the literature. The main characteristics that distinguish hemp from marijuana are shown in Table 1 [42,43].

Table 1.
The main characteristics that distinguish hemp from marijuana.
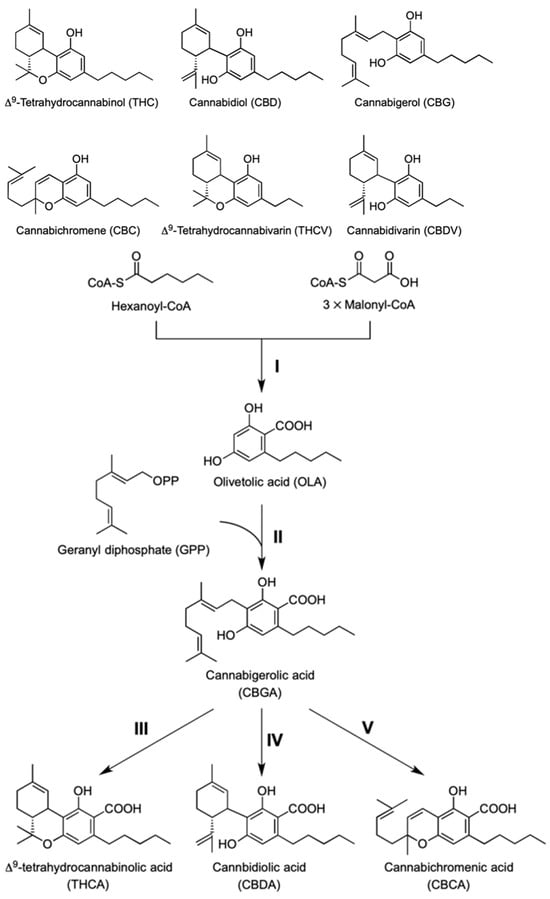
Figure 3.
Structures of representative cannabinoids. Their generally accepted abbreviations are presented in parentheses. Biosynthetic pathway of cannabinoids. The biosynthetic enzymes catalyzing respective steps are as follows. I, tetraketide synthase and olivetolic acid cyclase; II, CsPT4, a prenyltransferase; III, THCA synthase; IV, CBDA synthase; V, CBCA synthase [44].
4. Hemp Agronomy
4.1. Hemp in Crop Rotations
Hemp fits best in a crop rotation with cereals or, preferably, a legume, as an oilseed crop, but it can be grown as a fiber crop after any other crop [45]. Monoculture hemp ought to be avoided for a variety of reasons, such as pathogen build-up, reduced fertility, and risks of reduced quality. Hemp plants have been shown to reduce the quantity of a limited number of nematode species and certain fungi in soils, and hemp may be grown without chemical pesticides [46]. Hemp was found to suppress three infectious agents (Verticillium dahlia and the root-knot nematodes, Meloidogyne Chitwood, and Meloidogyne hapla), suggesting that incorporating hemp into a cycle of crops could improve soil health properties [47]. However, research into nematodes and plant pathogens is relatively limited at this point compared to other crops, and the understanding of hemp’s suppressiveness may evolve as additional research is conducted and published. Hemp grown at dense plant populations can quickly cover the soil surface as plants can rapidly develop following emergence, particularly fiber-yielding types, making it a strong competitor against weeds.
This is possibly among the most significant impacts of rotating hemp with other crops [48]. The production of hemp is frequently followed by the planting of winter cereals, and for this reason, harvesting must be completed as soon as possible, especially on heavy soil that is high in clay content, since these become quickly unworkable with late summer or fall rains. This is following some authors’ recommendations that early sowing times and early harvests can be used to optimize fiber output to prevent unfavorable retting (post-harvest fiber handling) and stem-drying conditions [49].
4.2. Seed Bed Preparation and Sowing
Traditionally, hemp has been planted in the same way as other break crops in terms of soil preparation. Tillage techniques for hemp, especially on soils rich in clay, include plowing at a 30–40 cm depth in fall or winter. Final preparation is performed in the spring as a shallow cultivation for creating a thin seedbed [50]. The most significant consideration when growing hemp in a new area is determining the ideal planting date that will enable optimum stand establishment and high yields of grain and/or fiber. For hemp, sufficient moisture is crucial during key stages of crop development, such as germination and emergence. Young, freshly germinated hemp plants are vulnerable to a variety of biotic, physical, and environmental stresses. Therefore, hemp sowing time and seed layer preparations are significant in terms of stand establishment.
It is also important to consider thinking about the expected weather forecast soon after planting in case of low seedling vigor. This is particularly important when using traditional tillage methods with direct seeding [51].
Seeding dates are mostly determined by climatic factors. Hemp germinates at temperatures as low as 1–2 °C; however, it should not be planted early in the season. Sowing should be delayed until the soil temperature reaches 10–12 °C to ensure the hemp’s quick development, as this enhances its capacity to surpass weeds [52]. Most hemp types will sprout in 3 to 5 days when sown in warm soils (>10 °C) with sufficient soil moisture. To ensure rapid germination and plant development, seeding dates are typically determined by soil temperature and moisture accessibility, as well as the photoperiod, which determines the duration of the vegetative process and, eventually, stalk and grain yield [50].
Plant spacing in hemp is determined by the type of hemp grown, such as fiber, seed, or cannabinoids. In general, densely planted hemp encourages greater plant height and restricts flowering. Hemp grown primarily for fiber is planted closely together to promote stalk elongation while reducing branching and yielding longer and stronger fibers. Particularly when it is produced for fiber or seed products, hemp is frequently planted using seed drills with row spacing ranging from 7.6 to 17.8 cm. However, the recommended seeding rates differ significantly, with the ideal sowing depth varying from 1.9 to 3.2 cm depending on soil type, soil preparation, available water, and seeding date [53]. According to another study, the spacing between hemp plants grown for fiber ranges from 20 to 40 cm [44,54]. It was suggested that similar planting densities would be necessary for the best hemp oil output for varieties produced for seed. Research has shown that 120 plants per square meter with an interrow spacing of 0.5 m produced high yields of the stem, seed, and inflorescence combined [53]. Another study suggested hemp seed drills for sowing at depths of 2–3 cm and row spacing of 9–17 cm [45,55]. The quantity of seed for sowing varies and ranges from 40 to 150 kg ha−1 [56]. According to other authors, seeding rate recommendations vary from 40 to 65 kg ha−1 for fiber hemp to reach 200–300 plant m−2 and 20 kg ha−1 for seed hemp [57,58].
4.3. Factors Influencing Growth, Development, and Yield of Hemp
The amount of light, nutrients, and water received, groundwater availability, photoperiod, and day/night temperatures are crucial factors that influence the growth, development, and yield of different hemp genotypes. Studies have revealed that variation in environmental factors can affect the flowering time and sex characteristics, resulting in changes in the cannabinoids and seed oil content, and composition, yield, biomass, and fiber quality [59,60,61]. Flowering time influences biomass and seed yield. Moreover, flowering is considered a reference growth stage for harvesting floral and fiber hemp [62]. In North Carolina, USA, researchers observed that bast fiber harvest should occur no later than the initial appearance of male reproductive growth. For hurd-oriented fiber, it is an arbitrary decision, but if a variety is prone to developing THC, then it may be harvested by initial female reproductive growth (personal communication with farmers and scientists). Hemp is a short-day plant sensitive to photoperiods. Studies report that hemp requires a photoperiod of 12–14 daylight hours. For most hemp genotypes, a more extended photoperiod (longer days and shorter nights or longer exposure to light) increases plant height, delays flowering, and prolongs the vegetative stage, which is suitable for fiber and biomass production. Meanwhile, a longer dark period causes early flowering and restricted yield [63,64,65]. Previous research [66] reported that 11–12 h of photoperiod are required to induce flowering in Thai hemp. The study [67] revealed that even a minor change of 15 min in the photoperiod can affect floral initiation in some cultivars. In contrast, some genotypes among tested hemp cultivars (15 cannabinoids and 12 fiber/grain) are less affected by photoperiodicity [59].
An aeroponic study [68] with 25-day-old seedlings exposed to ten different LED light spectra and a photoperiod of 16 h indicated that the light spectrum of red, blue, and green in the ratio of 7:2:1 increased all the tested cannabinoids (CBD, delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid [THCA] and cannabidiolic acid [CBDA]). The magnitude of changes in cannabinoids varied with different spectra and light treatments. Contrasting findings about photoperiod sensitivity, insensitivity, and diverse responses to varied light spectrums in different genotypes require further research. The temperature for the optimum development of hemp varies with genotypes and their origin. For instance, 30 °C is the maximum cardinal temperature (T Max) for six hemp varieties with different origins such as Poland, Netherlands, Italy, France, and Ukraine [69]. Previous research [70] noted that wild hemp from three agroclimatic regions of Pakistan grew suitably in a mild, humid climate at 16–27 °C. Seasonal changes in daily mean temperature can affect seed production and quality, biomass accumulation, and seed oil [57]. Identifying cultivars with local adaptation is an important strategy to improve hemp’s vegetative and flowering performance [58]. Hemp cultivation is challenging in tropical and subtropical regions compared to those in high latitudes due to high temperature, humidity, and greater pest pressure. Moreover, longer dark periods in these areas cause early season transition from vegetative to the flowering stage, limiting stem elongation and biomass accumulation and adversely affecting the successful commercial cultivation of hemp [71].
Hemp is commonly reported as a low-water use crop [72]. This claim needs further evaluation in warmer regions relative to the more northerly latitudes where hemp is grown. Yet, even in the high latitude region, water deficit stress is considered a main factor limiting hemp biomass yield [73]. A common reference crop for hemp water requirements is cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). In the southern U.S. (latitudes south of 37° N) hemp does best where annual rainfall (plus irrigation) is 750 mm or more. Early claims of drought tolerance and low water requirement for all hemp types (cannabinoid, grain, and especially fiber) in Texas, USA appear unfounded. Some Texas production regions and the Southwestern U.S., where precipitation is less than 500 mm annually and evaporative demand is higher, require substantial irrigation to achieve good yields. Cotton farmers in this region who grow fiber hemp report that hemp requires about 20% more irrigation than cotton for optimal economic yield. Little to no hemp is grown in the Southwestern U.S. and much of the lower Western U.S. without supplemental irrigation (personal communication with farmers).
Hemp requires high soil water during the initial stage of root establishment. After that, a well-developed root system may allow hemp to withstand moderately drier conditions [74,75]. Several studies have been conducted to understand the water requirements of hemp in different agroclimatic zones. For instance, studies conducted in Europe revealed that hemp needs 500–700 mm of water for growth and development. Meanwhile, in the vegetative stage, a minimum of 250–300 mm of water is needed for optimum growth [76,77]. It is reported in [78] that 250 mm of water was required for monoecious early fiber genotypes and 450 mm for dioecious late genotypes grown in a semi-arid Mediterranean environment (Southern Italy). Another study conducted in Southern Italy over two years with diverse genotypes showed that the replenishment of 66% of the water lost through evapotranspiration is required for excellent hemp production. Furthermore, the water requirement of hemp (435 mm) is higher than soybean and sunflower, but lower than sorghum [79]. However, these studies were conducted at northerly latitudes at mild temperatures where evapotranspiration is lower than southern latitudes. However, the amount of water required for hemp cultivation depends on the agroclimatic region, genotype, soil characteristics, weather conditions, and evapotranspiration. Hemp is susceptible to waterlogging. Thus, well-drained loam soils rich in organic matter are best suited for hemp cultivation [80]. Sandy loam soil, followed by clay loam soil, was reported to be suitable for hemp cultivation. Heavy clay soil and sandy soil are not well suited. The optimal soil pH for hemp cultivation is 6.0–7.5. Preferably, the optimal soil for hemp should have good drainage and adequate water-holding capacity, good aeration, and residual nutrients. These conditions are best met in sandy loam soil [81].
Interaction of hemp cultivars with the environment in response or adaptation to abiotic stress factors may be more important than cultivar traits associated with high yield [82]. Changes in environmental factors can adversely affect yields. Several abiotic stress factors affect hemp cultivation, particularly, high temperatures, drought, salinity, flood, or excess soil moisture. However, limited studies have been conducted to understand the effect of abiotic stress factors on hemp and its cultivation.
4.4. Water Deficit Stress
A field investigation to understand the interaction of hemp genotype and the environment was carried out at Fort Collins and Yellow Jacket, Colorado, USA [83]. Thirteen cultivars from a diverse set of germplasm from breeding programs (European project Multi Hemp) across Europe and Asia were used to study the environmental effects, and genotype and environment interactions (GEI) [83]. Two irrigation treatments were applied in Fort Collins (limited irrigation [147 mm] and fully irrigated [398 mm]) and a single sprinkler irrigation treatment (fully irrigated; 203 mm) was applied in Yellow Jacket. The yield in Fort Collins was 1123 kg ha−1 under full irrigation, but lower under limited irrigation (404 kg ha−1). Total plant biomass (2482 kg ha−1), plant height (135 cm), basal stem diameter (5.77 mm), and stand establishment (14%) were reduced under limited irrigation. A lower CBD content (1.43%) and a slightly higher cannabichromene (CBC) content (0.0052%) were detected in plants under limited irrigation. Notably, genotypic differences were found between treatments in both locations. Overall results imply the strong interaction between genotype and environment. At the same time, a study performed in Southern Italy using high-throughput techniques (Ground Penetrating Radar [GPR] and Sentinel-2 multispectral satellite [S2-MSI]) reported that hemp can draw soil moisture in the absence of precipitation and/or irrigation. The results show that the water deficit stress resistance of hemp, however, depends on crop vigor [83]. Previous research [84] compared controlled environment versus in-field screening to identify the traits responsible for drought tolerance in hemp. Twelve diverse genotypes were grown in a growth chamber. The magnitude of water deficit stress was calculated by measuring the net transpiration rate (NTR) and the fraction of transpirable soil water (FTSW). Three experiments were conducted with different objectives such as (1) understanding the transpiration rate (TR) response to soil drying, (2) the sensitivity of TR to high vapor pressure deficit (VPD), and (3) field evaluation of the expression of traits related to CBD. The range of threshold of FTSW across genotypes was 0.16 to 0.81. Five cultivars closed stomata when the FTSW threshold was reduced to 0.55 and four cultivars reduced transpiration only when VPD increased (>2.5 kPa). However, other genotypes showed transpiration-limiting traits when VPD increased to a range of 1.5–2.5 kPa. Cultivar Ha3ze showed a quick response to drought by reducing TR and showed a higher CBD as well.
4.5. Heat Stress
Abiotic stress triggered by changes in day and night temperatures is equally crucial to the effect of drought on hemp production. Previous research [76] performed a two-year field suitability assessment of six hemp varieties with different origins, sexual types, and maturity to monitor the dual-purpose production (seed and stem) capabilities. During the grain-filling stage, a daily maximum temperature above 30 °C reduced seed quality (seed weight, oil content, protein content, crude fiber, and ash). The previous study [70] conducted four experiments to understand the effect of temperature (45–50 °C) in different sowing times, and drought on different cannabinoids using a local hemp variety. Exposure of plants to high temperatures for 7 days significantly reduced CBGA and CBG, however, CBDA, THCA, CBD, and THC did not change. Again, in this study, yield per unit area of production is not shown. It is reported [49] that a field experiment in Potsdam, Germany used two multipurpose industrial cultivars during drought-prone and high-temperature seasons (early May to the end of October). During the experimental period, the maximum solar radiation was 1200 J m−2 s −1, the temperature was 35 °C, and the precipitation was 16 mm (56 mm was the total precipitation during the entire growth period). Both cultivars adjusted to the harsh temperature and dry conditions, but the response magnitude differed between them. In both cultivars, leaf area, plant density, leaf area index, and photosynthesis were reduced with the early onset of senescence as the season progressed.
4.6. Salinity Stress
Limited information is available on the impact of flooding and salinity on hemp. Previous research [85,86] studied the effect of five stress factors on cannabinoids of three chemotype III hemp cultivars (CBD dominant with less than 0.3% THC). The flooding was induced by increasing the soil volumetric water content to field capacity (0.35–0.4 m3 m−3) using trickle irrigation. This was repeated two to three times per week throughout the sampling period (a total of four samplings with one-week intervals, September to October 2019) to maintain a soil volumetric water content > 0.32 m3 m−3. There were no significant changes in cannabinoids and the CBD/THC ratio after exposure to flooding. These researchers explained that flooding was induced by increasing the soil volumetric water content to field capacity. However, achieving field capacity cannot be considered as flooding and this study was conducted in well-drained Ontario soil. As discussed, well-drained soils are best for hemp cultivation. These factors may be the reason for the nonsignificant effect on cannabinoids and the CBD/THC ratio in this study. Studies on the effect of salinity on seed germination and seedling growth/physiology were conducted in China using seeds of two fiber hemp cultivars [86,87]. Neutral salt (NaCl, Na2SO4) and alkaline salt (Na2CO3, NaHCO3) produced several salinity levels up to 300 mM. The germination rate decreased linearly with increasing salt concentration. Higher Na2CO3 had a more adverse effect on germination. Seed germination and length of radicles and hypocotyls increased at a low concentration of neutral salt. Hemp seedlings were more sensitive to Na2CO3 than to NaCl stress. Previous research [88] used four genotypes to study the effect of salinity up to 200 mM on seed germination and root morphology (root length and fresh weight). Additionally studied were the oxidative stress indices (hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and lipid peroxidation) and the enzymatic antioxidant quenching system (activities of superoxide dismutase [SOD], catalase [CAT], guaiacol peroxidase [GPOD], ascorbate peroxidase [APOD] and glutathione reductase [GR]). Seed germination percentage, root length, and fresh weight decreased linearly with increasing salinity levels. At the same time, oxidative stress indices and antioxidant enzyme activity increased in roots with distinct genotypic variation.
5. Growth Conditions for the Cultivation of Hemp
Hemp, originating in the Central and South Asian regions over 5000 years ago, including areas like China, India, Iran, and Pakistan, has now spread globally, particularly thriving in moderate climates [89]. It grows best in temperatures ranging from 13 to 22 °C and adapts well to various soil types, preferring deep, well-aerated soil with a pH of around 6 and good moisture retention [90]. However, it is susceptible to soil compaction and flooding, which can lead to lodging during heavy rain. To ensure consistent seed germination, a finely prepared seedbed is necessary, with conventional methods being preferred. Seed depth is crucial, with depths over 2 inches potentially affecting uniformity [91]. While “no-till systems” can work, they may result in uneven emergence depending on the season. Adequate nutrient supply is vital, as hemp depletes soil nutrients at harvest [92]. Hemp cultivation primarily focuses on bast fiber production, with factors like plant density, irrigation, and weather significantly influencing yield and quality, especially in Mediterranean semi-arid areas [93]. Challenges such as low plant density, lodging, and fungal infections can decrease fiber quality and yield. Stem growth and diameter are heavily influenced by plant density and weather conditions [94]. Hemp thrives in mild climates with a humid atmosphere and 25–30 inches of rainfall annually [95]. Ensuring adequate soil moisture is crucial for seed germination and the growth of young plants. During the vegetative growth phase, hemp responds positively to high daytime temperatures, ideally ranging from 28 to 30 °C in regions such as the Northern US, China, and Europe. This temperature range supports rapid growth and increases water needs [96]. However, it is important to note that in hotter regions where temperatures can reach around 40 °C, hemp may not perform as well compared to other crops that are better adapted to such extreme conditions. Hemp can tolerate brief periods of lower temperatures, down to −0.5 °C, for 4 to 5 days after the development of the third pair of leaves [97].
6. Fertilization of Hemp
Fertility studies on hemp in the United States were initiated during World War II, primarily aimed at determining the most effective fertilization rates to enhance fiber hemp production [98]. This was crucial as hemp fibers were extensively used domestically for the production of ropes and textiles [99]. However, it is acknowledged that each production system has its specific requirements for nutrient application and management [100]. For instance, the methods used for fertility in raised-bed plasticulture with soluble fertilizer applied via drip irrigation would differ significantly from those used in row-crop production [101]. This differentiation is further compounded by the introduction of newer hemp cultivars, each with their unique characteristics [102]. Research, such as that conducted by previous research [103], has indicated differences in nitrogen requirements between fiber, grain, and dual-crop cultivars, as well as disparities between fiber and dual-purpose hemp varieties [104]. Additionally, numerous studies have highlighted cultivar differences and interactions with environmental factors for each type of hemp. Despite these advancements, the lack of consistent seed certification programs in the United States has resulted in inefficiencies regarding the identification and purity of hemp cultivars [105].
7. Chemical Fertilizers
7.1. Sources of Chemical Fertilizers Used for Hemp Production
Whether small-scale or industrial, hemp cultivation relies on specific chemical fertilizers to boost plant growth and yield [106]. While the choice of fertilizer may vary, some are universally preferred for their effectiveness. For instance, Ammonium Nitrate (NH4NO3) stimulates robust vegetative growth, while Urea (CO(NH2)2) is known for its high nitrogen content, promoting vigorous growth during the vegetative stage [107]. Superphosphate (Ca(H2PO4)2) enhances root development, flowering, and seed formation, crucial for overall crop productivity. Potassium Chloride (KCl) aids water uptake, photosynthesis, and disease resistance [108]. Magnesium Sulfate (MgSO4) promotes chlorophyll synthesis and nutrient uptake, while Calcium Nitrate (Ca (NO3)2) supports cell wall formation and structural integrity [109]. Monoammonium Phosphate (NH4H2PO4) supports early root development, flowering, and seed production. Micronutrient blends address deficiencies for optimal plant performance [110]. Chemical fertilizers play a vital role in cannabis cultivation, providing essential nutrients for growth, flowering, and seed production, essential for optimizing yields and quality while maintaining sustainable practices.
7.2. Effect of Nitrogen (N)
For fiber hemp varieties, biomass is crucial, while seed-yielding varieties focus on grain and protein content [111]. Nitrogen (N) is particularly essential during the initial month of hemp growth, with most field experiments applying it at sowing. Studies show that about 79% of total N uptake occurs within the first month, with a daily uptake of 3–4 kg ha−1 [112]. However, applying N after sowing or using a split method does not increase stem yield compared to N distribution at sowing. While an increase in stem biomass is noticed with N fertilization up to 120 kg N ha−1, further increases do not lead to yield improvements [113]. Excessive N application can cause rapid stem elongation, making hemp more prone to lodging, while insufficient N results in yield loss and excess affects fiber quality [114]. Adjusting N fertilizer application based on initial soil fertility is crucial, as hemp growth response to fertilizer N varies depending on soil nitrogen levels [115]. Greenhouse-grown hemp for CBD showed N deficiency symptoms when leaf tissue analysis indicated 1.62% N content, indicating the need for further research on N application effects in field conditions for both seed and CBD hemp varieties [116]. Research indicates that higher levels of nitrogen (N) fertilization can lead to the production of stems with weaker, coarser fiber or lower fiber content, as well as stems with diameters exceeding the optimal range, resulting in decreased fiber strength [117]. Furthermore, elevated N fertilization rates have been observed to increase the protein content in fiber, which negatively affects fiber strength [118]. However, some studies suggest that excessive N fertilization may not necessarily negatively impact fiber production beyond increasing leaf growth, which could complicate crop processing [119]. The timing and method of N application also vary in their effects on fiber hemp production, with certain studies showing no significant effects while others demonstrate increased yields with specific application methods [120].
Planting density is another critical factor for fiber hemp, with high-density planting potentially enhancing the quality of bast fiber if self-thinning is minimized [121]. Nevertheless, research findings on the effects of planting density and N fertilization rates on self-thinning and total yield have been inconsistent [122]. Further exploration is needed to understand the interplay between excessive N fertilization, planting density, and the timing of N application in hemp production systems [123]. Efficient nutrient management is pivotal for maximizing plant productivity and minimizing environmental impacts, underscoring the importance of research to determine the optimal nutrient quantities and application timings for different hemp cultivars and environmental conditions across various production regions [124]. The visual appearance of hemp under increasing N supply is shown in Figure 4. The effect of nitrogen fertilizers on hemp growth properties is summarized in Table 2.
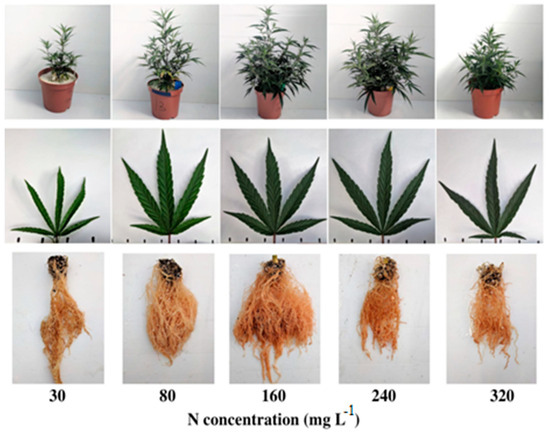
Figure 4.
Visual appearance of the plants (top row), leaves (middle row), and roots (bottom row) under increasing N supply. From left to right: 30, 80, 160, 240, 320 mg L−1 N. Leaf images are of the youngest, fully developed leaf on the main stem, taken 31 days after initiating the fertigation treatments [125].

Table 2.
Effect of nitrogen fertilizers on hemp growth properties.
Table 2.
Effect of nitrogen fertilizers on hemp growth properties.
| Fertilizer Type | Parameter | Growing Conditions | Impact of N Application | Growing Media | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonium nitrate (surface broadcast) | Plant height, seed yield, seed protein content, biomass | Field | Increase | Silty loam-type soil | [126] |
| Liquid N by fertigation (80% N–NO3−, 20% N–NH4+) | Photosynthetic pigments, osmotic potential, total N and N–NO3, water use efficiency | Growth chamber | Increase | Soilless, perlite 2-1-2 cultivation media | [127] |
| Liquid N by fertigation (80% N–NO3−, 20% N–NH4+) | Nitrogen use efficiency; Ca, Mn, and Zn uptake | Growth chamber | Decrease | Soilless, perlite | [127] |
| Urea (46% N) | Fiber yield | Field | Increase | NR | [128] |
| Liquid N–NO3− | Chlorophyll, malondialdehyde, N accumulation in the plant, soluble protein | Greenhouse | Increase | Peat | [129] |
| Liquid N–NO3− | Stem mass density, root/shoot ratio | Greenhouse | Decrease | Peat | [129] |
| Liquid N–NO3− | Antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase and peroxidase) | Greenhouse | First, increase then decrease after 6.0 mmol N L−1 | Peat | [129] |
| Urea | Lead accumulation in leaves | Greenhouse | Increase | Soil spiked with lead in pots | [128] |
| Calcium ammonium nitrate | Seed crude protein content | Field | Increase | Loam to sandy | [130] |
| Calcium ammonium nitrate | Biomass cellulose and hemicellulose | Field | Nonsignificant increase | Loam to sandy | [118] |
| Ammonium phosphate | Sex ratio | Field | Not affected | NR | [131] |
| Peters Professional 20-20-20 (N-P-K) | CBD, CBG yield (g plant−1) | Growth chamber | Decrease after 50 mg L−1 N | Pro-mix HP mycorrhizae | [132] |
CBD, cannabidiol; CBG, cannabigerol; NR (not reported).
7.3. Effect of Phosphorus (P)
Previous studies have noted that phosphorus (P) is crucial for the growth and development of hemp, particularly in its early stages [133]. However, research on the specific effects of phosphorus on hemp production remains limited. While phosphorus application has been linked to increased plant height, its impact on hemp biomass and seed yields appears to be inconsistent and minimal, yielding negligible effects [134]. Studies suggest that hemp’s response to phosphorus may vary depending on growing conditions, with phosphorus availability significantly affecting the elasticity and tensile strength of hemp fibers [135]. Furthermore, phosphorus deficiency can disrupt nutrient uptake, leading to symptoms like stunted growth and the reddish-purple discoloration of leaves due to anthocyanin pigment formation [136].
During the vegetative and flowering stages, phosphorus is absorbed gradually, primarily accumulating in the leaves [137]. By the end of the flowering stage, over 70% of the phosphorus in the plant is typically found in the seeds. Similar to other crops, when soil phosphorus levels are adequate, additional phosphorus fertilizer may not significantly improve hemp yield [138]. However, studies have shown that additional phosphorus can enhance yield under conditions of low initial soil fertility [139]. Varieties of hemp intended for grain production may require higher phosphorus levels, as preliminary data indicate phosphorus accumulation in hemp seeds [140]. While phosphorus fertilization can affect hemp height and cellulose concentration, its effects on biomass, seed yield, protein content, and oil content vary across studies and hemp cultivars. Further research is needed to understand phosphorus requirements in hemp cultivation and their implications for different varieties and environmental conditions [141].
A phosphorus deficiency (Figure 5) tends to be more common after plants start making buds in the flowering stage. Cannabis plants tend to love phosphorus in the flowering/budding stage, and it is unlikely for a cannabis plant to receive too much phosphorus using standard nutrients formulated for a flowering plant like cannabis. Nearly all flowering nutrients will come with an abundance of phosphorus for the plants. So, if there is a cannabis phosphorus deficiency while using standard cannabis nutrients, this is related to a root pH problem. The effect of phosphorus fertilizers on hemp growth properties is summarized in Table 3.

Figure 5.
The progression of a cannabis phosphorus deficiency (https://www.growweedeasy.com/cannabis-plant-problems/phosphorus-deficiency, accessed on 14 January 2024).

Table 3.
Effect of phosphorus fertilizers on hemp growth properties.
Table 3.
Effect of phosphorus fertilizers on hemp growth properties.
| Property | P Effect | Explanation | Recommended Dosage (kg P2O5/ha) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root development | Enhancement | Enhanced root systems support better water and nutrient uptake. | 20–50 | [142] |
| Energy storage and transfer | Increased efficiency | Phosphorus plays a key role in the process of energy transfer within plants, helping convert nutrients into usable energy. | 20–50 | [143] |
| Flowering and seed production | Potential improvement | Adequate phosphorus can improve the quality and quantity of flowering, subsequently affecting seed production. | 50–100 | [133] |
| Disease resistance | Improved resistance | Phosphorus can help enhance the plant’s resistance to various diseases, particularly root rot and other soil-borne pathogens. | 20–50 | [138] |
| Overall plant health | Overall improvement | Sufficient phosphorus contributes to the general health and vigor of the plant, potentially leading to higher yields. | 20–50 | [140] |
| Nutrient uptake efficiency | Improvement | Phosphorus improves the plant’s ability to uptake other essential nutrients from the soil, particularly micronutrients. | 20–50 | [141] |
| Stress tolerance | Increased tolerance | Phosphorus can enhance the plant’s ability to withstand abiotic stresses such as drought and salinity. | 20–50 | [144] |
| Photosynthetic efficiency | Enhancement | Phosphorus is involved in the synthesis of ATP during photosynthesis, which may increase the overall efficiency of this process. | 20–50 | [145] |
7.4. Effect of Potassium (K)
Potassium (K) is a key nutrient for hemp cultivation, although its specific effects have been less extensively studied compared to nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) [146]. Research indicates that K may not significantly affect hemp biomass and seed yield, but it remains essential for the plant’s growth and development [147]. As hemp matures, its demand for K increases, particularly during fiber development stages, emphasizing its role in ensuring fiber quality. However, determining optimal K fertilization rates for hemp production is still a subject of ongoing research, with some trials suggesting a recommendation of 175 kg K ha−1 [148]. Despite its importance, the impact of K fertilization on seed and CBD yields in hemp varieties under field conditions remains largely unexplored. Previous studies have shown varied responses to K fertilization, with some reporting slight increases in stem or hurd yield, especially in adverse weather conditions [149]. Nevertheless, further research is needed to fully understand the effects of K fertilization on hemp production and to develop tailored fertilization practices for maximizing both the yield and quality of hemp crops [150]. The visual appearance of the leaves of medical cannabis cultivar, developed on plants receiving increasing K supply is shown in Figure 6. The effect of potassium fertilizers on hemp growth properties is summarized in Table 4.
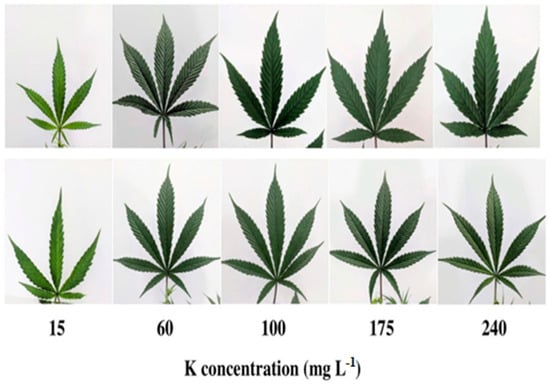
Figure 6.
The visual appearance of leaves of cannabis developed on plants receiving increasing K supply. From left to right: 15, 60, 100, 175, and 240 ppm K. Images of the youngest fully developed leaf on the main stem, taken 26 days after the initiation of the fertigation regime [151].

Table 4.
Effect of potassium fertilizers on hemp growth properties.
Table 4.
Effect of potassium fertilizers on hemp growth properties.
| Property | K Effect | K Rate Application (kg K2O/ha) | Time of Application | Growing Culture Media | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stem strength | Enhancement | 80–120 | Pre-planting | Soil-based | [152] |
| Disease resistance | Improvement | 80–120 | At planting | Soil-based | [147] |
| Water efficiency | Increases | 80–120 | Pre-planting | Soil-based | [153] |
| Nutrient uptake | Improvement | 80–120 | At planting and mid-season | Soil and hydroponic | [154] |
| Yield and quality | Increase | 100–150 | Split application at planting and flowering | Soil-based and hydroponic | [155] |
| Photosynthesis | Improvement | 80–120 | At planting | Soil-based | [151] |
| Root development | Enhancement | 80–120 | Pre-planting | Soil-based | [148] |
| Stress tolerance | Increases | 80–120 | Pre-planting | Soil-based | [149] |
| Fiber quality | Improvement | 80–120 | Pre-planting | Soil-based | [149] |
| Seed oil content | Enhancement | 100–150 | At planting and mid-season | Soil-based | [151] |
7.5. N, P, K Timing Application for Hemp
Effective fertilization of hemp requires not only the right amounts of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) but also the precise timing of these applications to maximize crop health and productivity [100]. Understanding the specific growth stages of hemp and the nutrient uptake at each phase is critical for optimizing the timing of fertilizer applications [102].
Nitrogen is vital for the early growth stages of hemp, promoting vigorous vegetative growth and the development of a robust plant structure. The optimal timing for nitrogen application is during the initial 6 to 8 weeks post-planting when hemp plants are rapidly expanding their leaf and stem mass [125]. This early application helps establish a strong foundation for subsequent flowering and seed formation stages. It is important to balance nitrogen levels to avoid excessive vegetative growth at the expense of flowering, which is crucial for hemp varieties cultivated for their seeds or CBD content [121].
Phosphorus plays a critical role in root development and the overall energy transfer within the hemp plant, which is essential for the health and growth of the plant throughout its lifecycle. The most beneficial time to apply phosphorus is right at planting or just before, to ensure that the developing roots can access it. This early-stage application supports a strong root system which is essential for efficient water and nutrient uptake throughout the plant’s growth cycle [134,135]. Additional phosphorus may also be applied during the flowering stage to support the development of seeds [137].
Potassium is crucial for the overall resilience of the plant, aiding in water regulation, disease resistance, and the synthesis of proteins and starches. For hemp, potassium should be applied before the onset of flowering and again as the plants enter the seed production or cannabinoid synthesis phase [151]. This ensures that hemp has sufficient potassium to support these critical processes, which directly impact yield quality and quantity, especially in plants cultivated for CBD production [147,151].
Together, these strategic applications of N, P, and K not only enhance the growth and productivity of hemp but also contribute to a more sustainable cultivation practice by reducing the likelihood of nutrient runoff and ensuring that the plants receive nutrients at times when they are most effective. This approach, tailored to the specific needs and growth stages of hemp, is essential for maximizing both the yield and the quality of the harvested product [104].
7.6. Effect of Other Nutrients
Previous studies have underscored the importance of magnesium (Mg) in hemp farming, as its deficiency can lead to leaf discoloration and stunted growth [156]. Additionally, hemp may suffer from deficiencies in micronutrients like copper (Cu), manganese (Mn), and boron (B), potentially weakening the plant’s stems [107]. To address these deficiencies, supplementing with micronutrients alongside sufficient phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) fertilization has been proposed to improve fiber and seed hemp yield and quality, especially when soil P and K levels are adequate [157]. However, further research is required to fully grasp how micronutrient supplementation impacts cannabinoid composition across different hemp cultivars [158].
Research on Romanian hemp grain varieties has revealed high concentrations of calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and potassium (K), with P and K supplementation resulting in increased calcium levels in seeds [159]. While fiber hemp generally requires less calcium compared to grain hemp, opinions vary regarding hemp’s overall nutrient requirements [160]. Calcium uptake typically increases during the vegetative phase, primarily accumulating in hemp fiber, hurd, and leaves [161]. Similarly, magnesium application during planting has been found to boost seed and hurd yield, albeit potentially reducing fiber content. Conversely, sulfur (S) supplementation has yielded mixed results, with minimal effects observed in grain and dual-purpose hemp strains despite existing soil deficiencies [162]. Although certain nutrient deficiencies may not immediately impede hemp growth, prolonged shortages in boron (B) and copper (Cu) have been associated with significantly reduced biomass [163]. Nonetheless, the precise impact of nutrient deficits on phytochemical concentrations requires further investigation, particularly across various growth stages and hemp varieties [164].
7.7. Organic Fertilizers
While chemical fertilizers have traditionally been relied upon to provide plants with essential nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, concerns over soil and water pollution have spurred a growing interest in organic alternatives, particularly animal manures [165]. These organic fertilizers, rich in organic matter, offer a valuable source of nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium [166]. However, a complete transition away from chemical fertilizers in agriculture is not immediately feasible, as agricultural sustainability hinges on maintaining adequate income and food security [167]. Instead, a balanced approach that integrates renewable, natural materials with organic sources, while judiciously utilizing chemical fertilizers, is essential for preserving soil fertility, enhancing biological activity and improving soil structure [168]. Numerous studies have explored the combined application of organic and chemical fertilizers across various crops, showing promising results, particularly in increasing oil yield [169]. For instance, combining cow manure with nitrogen application has proven effective in boosting both oil yield and content in sunflower cultivation [170]. Likewise, incorporating organic fertilizers like vermicompost with nitrogen supplementation has demonstrated significant potential in increasing seed yield and oil content in rapeseed [171]. However, the impact of nitrogen fertilization on oil content may vary depending on the plant species. While it may decrease oil content in juniper, it can enhance oil yield in medicinal plants like thyme [172]. This underscores the importance of tailored fertilizer strategies customized to the specific requirements and growth characteristics of each crop [173].
Optimal Rate of Organic Fertilizer during the Flowering Stage for Hemp
Fertilization is one of the most important factors for indoor cannabis production. Overfertilization can lead to salt accumulation in the root zone, whereas under fertilization can cause nutrient deficiency and lower yields [125]. The suggested fertilization rate for hemp ranges from 50 to 200 kg N ha−1 [126] which is similar to other high-yielding field crops such as wheat [127]. It is difficult, however, to base fertilizer rates for cannabis on suggestions for hemp or other crops because of the differences in species and growing conditions [128]. Furthermore, it is common for nutrient requirements to vary based on the growth stage in flowering plants. A recent evaluation of the effects of organic fertilization during the vegetative stage for cannabis suggests that overfertilization during the vegetative stage may decrease both THC concentration in floral material and floral dry weight on the harvest [129]. An optimal fertilizer rate of 389 mgL−1 was proposed using a liquid organic fertilizer (4.0 N–1.3 P–1.7 K) in two coir-based organic substrates. To our knowledge, there is no research on the flowering-stage fertilizer rates for cannabis [130].
Appropriate choice of a growing substrate is also important for indoor cannabis production. Substrates vary in physical and chemical properties; therefore, to ensure a suitable root zone environment it is important for fertigation to be tailored to the growing substrate [131,132]. Although there is scant research on growing substrates for cannabis, the information we collected from the industry indicates that many North American cannabis producers are using either coir- or peat-based substrates, or inert substrates such as stone wool. Previous research evaluated two coir-based substrates for vegetative-stage cannabis production. At the end of the vegetative stage, plants were transferred into a growth chamber for the flowering stage under similar conditions to determine if treatment effects carried forward to harvest. The substrates differed in CC by 11% but no differences in growth, yield, or cannabinoid content were reported between the two. Vegetative-stage cannabis may grow well in substrates within a certain range; however, there are no similar evaluations for flowering-stage cannabis production [129,130,131,132].
7.8. Organic Cultivation Technologies
Organic farming, which prohibits synthetic chemicals, presents an appealing option for hemp cultivation due to its lower reliance on such inputs compared to crops like corn and soybeans [174]. Hemp’s rapid growth and dense canopy naturally suppress weeds, reducing the need for expensive herbicides and weed control measures [175]. This makes hemp an excellent fit for organic production, where key factors include selecting the appropriate cultivar, planting method, and strategies for fertilizer and pest management. Integrating hemp into organic crop rotations encourages the development of beneficial mycorrhizae, enhancing the plant’s ability to compete with weeds and supporting soil biota [176]. Despite their vital role in soil health, earthworms, particularly Lumbricus terrestris, are not extensively studied in hemp agroecosystems [177]. Hemp’s ability to deter harmful soil organisms like nematodes further underscores its value in crop rotation [178]. Organic hemp farming promotes biodiversity by providing habitats and food sources for beneficial organisms such as pollinators and predatory insects [179]. This contributes to ecosystem resilience and reduces the reliance on chemical interventions. Organic practices prioritize natural fertilizers, cover crops, and crop rotations to enhance soil health and fertility, promoting the long-term sustainability of farms [180]. Strict adherence to organic certification standards ensures that hemp products meet consumer demand for environmentally friendly and socially responsible agricultural practices [181]. In contrast, conventional cultivation relies on synthetic chemicals for crop management, highlighting the distinct approaches and trade-offs between organic and conventional agriculture [182]. Organic farming prioritizes soil vitality and biodiversity, fostering beneficial soil life like earthworms and mycorrhizae to enrich nutrient cycling and enhance soil structure [183]. It employs methods like cover cropping and reduced tillage to minimize erosion and conserve water [184]. Conversely, chemical fertilizers in hemp farming offer precise and rapid nutrient delivery tailored to crop needs, potentially resulting in faster growth and higher yields [185]. However, their excessive use can lead to nutrient runoff, water pollution, and soil degradation, impacting long-term soil health and microbial activity [186]. Furthermore, organic hemp products are esteemed for their environmental and social responsibility, appealing to sustainability-conscious consumers and commanding premium prices due to organic certification [187]. Ultimately, the choice between organic and chemical fertilizers depends on environmental impact, product quality, market demand, and grower preferences [132].
The comparative study on the effects of organic versus mineral (chemical) fertilizers on hemp, specifically during the flowering stage, sheds light on several crucial aspects of agricultural practices for medicinal cannabis (Figure 7). Previous research [188] focused on assessing the impact of these fertilizer types on biomass, cannabidiol (CBD) yield, and nutrient use efficiency, under conditions of nutrient stress [189]. Organic fertilizers demonstrated a lower acquisition and utilization efficiency compared to mineral fertilizers. Although the yield of inflorescences was reduced under nutrient-stress conditions, there was a compensatory increase in CBD concentration in plants fertilized with fewer nutrients [190]. This suggests that a reduction in fertilizer input does not necessarily decrease CBD yield, thanks to increased cannabinoid concentration [191]. Interestingly, the study found that mineral fertilizers, when applied at reduced concentrations, significantly increased the agronomic nutrient use efficiency for N and K by 72%, compared to higher nutrient concentrations. This indicates that mineral fertilizers might be more effective in terms of nutrient utilization efficiency under controlled nutrient stress scenarios [192].
Furthermore, the results indicated that while organic fertilizers are considered more environmentally friendly, they may require optimization in terms of nutrient bioavailability and timing of application to match the effectiveness of mineral fertilizers. This study underscores the necessity of fine-tuning fertilizer regimes to achieve optimal growth and cannabinoid production in medicinal cannabis, highlighting the trade-offs and potentials of both organic and mineral fertilizers under nutrient-limited conditions [193]. While chemical fertilizers may offer higher efficiency and possibly more predictable results under certain conditions, the choice between organic and chemical depends on various factors including the specific crop needs, environmental considerations, cost, and the goals of the cultivation operation. Each type of fertilizer has its advantages and potential drawbacks, and the best choice often involves a balance of these factors alongside sustainable practices [194].
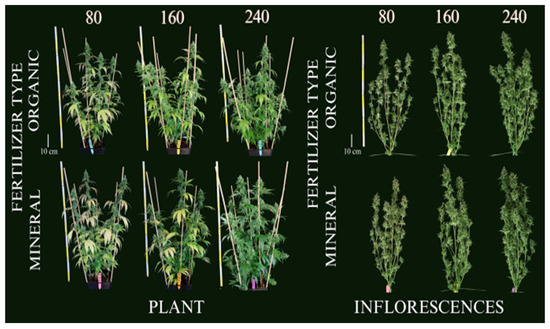
Figure 7.
Cannabis plants at the final harvest date (99 days after planting) for the three organic and mineral fertilizer concentrations. Left: entire plants, right: defoliated plants [194]. Numbers are fertilizer concentration (mg L−1).
8. Economic Issues and Perspectives for Industrial Hemp
The hemp industry is experiencing remarkable growth, with U.S. retail sales soaring to at least USD 820 million in 2017, reflecting a 16% surge from the previous year [195]. This upward trajectory has been consistent since 2012, with the CBD product market leading the charge, followed closely by personal care products, food items, industrial applications, and textiles [196]. Before the passage of the 2014 Farm Bill, restrictions on hemp production fueled a surge in hemp-related imports into the United States [17]. Imports exceeded USD 78 million, nearly doubling from levels seen in 2013 and 2014. However, in recent years, there has been a decline in imports, dropping to USD 67 million in 2017 [197]. It is important to note that these figures underestimate total imports as they do not include finished products such as clothing, construction materials, and hemp-based paper [198]. Currently, Canada serves as the primary supplier of hemp seeds, while China dominates the market for raw and processed hemp fiber [199].
9. Chemical and Organic Fertilizer Effect on Implications for Global Hemp and Economic Issues
The industrial hemp market has experienced exponential growth, projected to reach USD 1.9 billion by 2022, with significant contributions from CBD products and industrial applications such as textiles and personal care products [200]. This rapid expansion is influenced by legislative milestones like the 2014 Farm Bill, which liberalized hemp cultivation, shifting the industry from heavy reliance on imports to bolstering domestic production capabilities [201]. Within this burgeoning framework, the strategic use of fertilizers—both organic and chemical—becomes pivotal, influencing not only agricultural yields but also the broader economic landscape and environmental sustainability of hemp production [202]. Organic fertilizers are championed for their environmental benefits, enhancing soil health, and reducing chemical runoff, thus aligning with global shifts towards sustainable and eco-friendly agricultural practices [203]. Their use in hemp cultivation can potentially command premium market prices due to the growing consumer demand for organically produced goods. However, the higher initial costs and longer periods required to realize yield benefits from organic inputs pose economic challenges, particularly for small-scale producers or those new to hemp cultivation [204].
Conversely, chemical fertilizers offer the advantage of immediate nutrient availability, which can lead to enhanced plant growth and a quicker return on investment. This aspect is crucial in regions competing in the global market, where efficiency and output volume are often prioritized [205]. The predictability and cost-effectiveness of chemical fertilizers can make them attractive, especially in large-scale operations aiming to capitalize on the expanding hemp market rapidly [206]. Despite these benefits, the use of chemical fertilizers raises concerns about long-term soil degradation and environmental harm, which could potentially lead to regulatory repercussions and shifts in consumer preferences away from non-organically produced hemp [207]. This dynamic necessitates a balanced approach to fertilizer use, one that considers not only economic and production efficiencies but also long-term sustainability and market perceptions [208].
For American hemp farmers, navigating these choices involves understanding the complex interplay between market demands, regulatory environments, and agronomic practices [209]. The economic viability of integrating hemp into crop rotations hinges on effectively managing these factors to enhance both short- and long-term profitability [210]. The evolving landscape of the hemp market, characterized by fluctuating prices, regulatory challenges, and intense international competition, especially from established producers like Canada and emerging players like Uruguay, demands strategic foresight and adaptability [211].
The importance of targeted research and development cannot be overstated, as it underpins the capacity to make informed decisions regarding fertilizer use and its implications for market competitiveness and environmental stewardship. Federal initiatives, such as those enabled by the 2018 Farm Bill, which includes provisions for crop insurance and research funding, are crucial in supporting hemp producers in this volatile market [212]. Exploring alternative market structures and vertically integrated production models may also provide valuable risk management strategies, ensuring that U.S. hemp producers can navigate both current challenges and future opportunities in the global arena [213]. This comprehensive approach to understanding the implications of fertilizer use in hemp cultivation reveals the intricate balance required between achieving immediate economic benefits and ensuring long-term sustainability and competitiveness in the global market [214].
Moreover, as the global landscape for hemp continues to evolve, the strategic utilization of both chemical and organic fertilizers must be adapted to meet the changing regulatory standards and consumer expectations [215]. For instance, as environmental awareness increases, the demand for sustainably grown products could shift market dynamics significantly, making organic practices more appealing despite their higher initial costs and slower returns [202]. To capitalize on this trend, producers may need to innovate in organic fertilization techniques to enhance efficiency and reduce costs, potentially leveraging new technologies or bio-engineered solutions [208].
On the international stage, the competitiveness of hemp products is closely tied to the perceived quality and sustainability of their production processes. Countries with strict environmental regulations may favor imports of organically fertilized hemp, presenting an opportunity for producers who prioritize green farming practices [210]. Conversely, regions with less stringent standards may continue to see robust demand for products grown with chemical fertilizers, highlighting the need for a diversified approach to cultivation strategies to cater to various markets [212].
The introduction of advanced analytical tools and precision agriculture technologies can also play a crucial role in optimizing fertilizer usage. These technologies allow farmers to apply the exact amount of nutrients needed at the right time and place, minimizing waste and environmental impact [206]. For organic producers, such innovations could bridge the gap between the traditional inefficiencies associated with organic farming and the need for competitive yields. For chemical fertilizer users, these tools can help mitigate the adverse environmental effects associated with overfertilization, aligning more closely with global sustainability goals [212].
Furthermore, the economic implications of fertilizer use in hemp cultivation extend beyond the immediate agricultural sector to influence ancillary industries such as manufacturing, retail, and export [205]. The quality of hemp fiber and extracts, which is highly dependent on cultivation practices, including fertilization, directly impacts the downstream products’ marketability and success. As such, the choice of fertilizer not only affects crop yield but also the overall quality and consumer acceptance of hemp-derived products [211].
In conclusion, the decision between chemical and organic fertilizers in hemp production involves a complex array of factors, including but not limited to cost, efficiency, market demands, and environmental impact. As the industry matures, ongoing research and stakeholder engagement will be essential in developing best practices that satisfy both economic objectives and sustainability criteria [210]. This holistic approach will ensure that the hemp industry remains robust and capable of adapting to future challenges and opportunities in the global marketplace [207].
10. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Hemp’s resurgence is not merely a trend, but a renaissance driven by its multifaceted benefits, captivating attention across diverse spheres ranging from media to scientific communities [216]. Its versatility, from industrial applications to health and wellness products, underscores its potential to revolutionize various industries [217]. However, to harness this potential effectively, it is imperative to acknowledge the unique cultivation requirements of hemp. Unlike traditional crops, hemp possesses distinctive characteristics that necessitate tailored cultivation approaches. Its robust nature and fast growth make it a resilient crop, yet its sensitivity to environmental conditions demands careful management [218]. The burgeoning hemp market has spurred a wave of innovation in cultivation and fertilization techniques, prompting a revaluation of conventional agricultural practices. Research indicates that organic fertilizers, such as compost and manure, play a pivotal role in fostering soil health and enhancing nutrient absorption in hemp plants. In contrast, the indiscriminate use of chemical fertilizers poses risks of soil degradation and environmental contamination over time [219]. Thus, a paradigm shift towards a holistic cultivation strategy that integrates both organic and chemical fertilizers emerge as a pragmatic approach for sustainable hemp cultivation. This hybrid approach not only promotes robust growth and yield but also mitigates the environmental footprint by reducing chemical dependency and enriching soil vitality [220]. By adopting such a balanced methodology, stakeholders can uphold the principles of ecological sustainability while fostering economic prosperity within the burgeoning hemp industry [221]. Moreover, unlocking the full potential of hemp requires concerted efforts to expand its applications beyond traditional uses [222]. Recent strides in genetic research and regulated production have facilitated the development of specialized hemp cultivars tailored for specific purposes, from fiber and grain production to cannabinoid extraction for medicinal and recreational purposes [223]. However, achieving a harmonious balance between economic prosperity and ecological integrity is paramount for the long-term viability of hemp cultivation [224]. Embracing a holistic approach that melds traditional wisdom with contemporary scientific insights can pave the way for sustainable agricultural practices that nurture both human prosperity and planetary well-being [225]. In essence, hemp epitomizes the ethos of sustainable agriculture, offering a beacon of hope for a future where prosperity is intricately intertwined with environmental stewardship [226]. By embracing innovative cultivation methods and expanding the horizons of hemp’s applications, we can forge a path towards a more resilient and regenerative agricultural landscape, where hemp stands as a symbol of progress towards a sustainable future.
Author Contributions
Investigation, resources, writing—original draft preparation, F.A.; writing—review and editing, D.K. and A.S.; supervisor, re-writing, and review, M.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding or grants.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author D.K. was employed by the company BGT GmbH (founder). Author A.S. was employed by the company Canngoo GmbH (founder). The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationship that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Cerino, P.; Buonerba, C.; Cannazza, G.; D’Auria, J.; Ottoni, E.; Fulgione, A.; Gallo, A. A review of hemp as food and nutritional supplement. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2021, 6, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, J.P.; Stjepanović, D.; Le Foll, B.; Hoch, E.; Budney, A.J.; Hall, W.D. Cannabis use and cannabis use disorder. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocq, M.A. History of cannabis and the endocannabinoid system. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci 2020, 22, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElSohly, M.A.; Chandra, S.; Radwan, M.; Majumdar, C.G.; Church, J.C. A comprehensive review of cannabis potency in the United States in the last decade. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2021, 6, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fordjour, E.; Manful, C.F.; Sey, A.A.; Javed, R.; Pham, T.H.; Thomas, R.; Cheema, M. Cannabis: A multifaceted plant with endless potentials. Front. Pharmacol 2024, 14, 1200269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levinsohn, E.A.; Hill, K.P. Clinical uses of cannabis and cannabinoids in the United States. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 411, 116717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E.; Chanet, G.; Morin-Crini, N. Traditional and new applications of hemp. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 42: Hemp Production and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 37–87. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.F.; Islam, M.Z.; Mahmud, M.S.; Sarker, M.E.; Islam, M.R. Hemp as a potential raw material toward a sustainable world: A review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visković, J.; Zheljazkov, V.D.; Sikora, V.; Noller, J.; Latković, D.; Ocamb, C.M.; Koren, A. Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) agronomy and utilization: A review. Agronomy 2023, 13, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, S. Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) research priorities: Opinions from United States hemp stakeholders. GCB Bioenergy 2021, 13, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, G.; Storz, M.A.; Calapai, G. The role of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) as a functional food in vegetarian nutrition. Foods 2023, 12, 3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Fahad, S.; Du, G.; Cheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Tang, K.; Deng, G. Evaluation of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) as an industrial crop: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 52832–52843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, J.A.; Smart, L.B.; Smart, C.D.; Stack, G.M.; Carlson, C.H.; Philippe, G.; Rose, J.K. Limited effect of environmental stress on cannabinoid profiles in high-cannabidiol hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). GCB Bioenergy 2021, 13, 1666–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiker, E.E.; Uslu, N.; Al Juhaimi, F.; Ahmed, I.A.M.; Ghafoor, K.; Özcan, M.M.; Almusallam, I.A. Effect of roasting on antioxidative properties, polyphenol profile and fatty acids composition of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seeds. LWT 2021, 139, 110537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, G. Introduction to emerging industrial applications of cannabis (Cannabis sativa L.). Rendiconti Lincei Sci. Fis. e Nat. 2021, 32, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E.; Chanet, G.; Morin-Crini, N. Applications of hemp in textiles, paper industry, insulation and building materials, horticulture, animal nutrition, food and beverages, nutraceuticals, cosmetics and hygiene, medicine, agrochemistry, energy production and environment: A review. Environ. Chem. Let. 2020, 18, 1451–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fike, J.H.; Darby, H.; Johnson, B.L.; Smart, L.; Williams, D.W. Industrial hemp in the USA: A brief synopsis. Sustainable agriculture reviews. Hemp Prod. Apply 2020, 42, 89–109. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Bai, M.; Song, H.; Yang, L.; Zhu, D.; Liu, H. Hemp (Cannabis sativa subsp. sativa) Chemical composition and the application of hempseeds in food formulations. Plant Food Hum. Nut. 2022, 77, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wei, X.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, C.; Long, S.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, H. Industrial hemp—An old but versatile bast fiber crop. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 6269–6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, R.G.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Crippa, J.A.S.; Hallak, J.E.; Rossi, G.N.; Rocha, J.M.; Zuardi, A.W. Serious adverse effects of cannabidiol (CBD): A review of randomized controlled trials. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2020, 16, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzara, E.; Torresi, J.; Fico, G.; Papini, A.; Kulbaka, N.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Petrelli, R. A comprehensive phytochemical analysis of terpenes, polyphenols and cannabinoids, and micromorphological characterization of 9 commercial varieties of Cannabis sativa L. Plants 2022, 11, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellati, F.; Brighenti, V.; Sperlea, J.; Marchetti, L.; Bertelli, D.; Benvenuti, S. New methods for the comprehensive analysis of bioactive compounds in Cannabis sativa L.(hemp). Molecules 2018, 23, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, R.; Panseri, S.; Giupponi, L.; Leoni, V.; Citti, C.; Cattaneo, C.; Giorgi, A. Phytochemical and ecological analysis of two varieties of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) grown in a mountain environment of Italian Alps. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzimas, P.S.; Beteinakis, S.; Petrakis, E.A.; Papastylianou, P.T.; Kakabouki, I.; Small-Howard, A.L.; Halabalaki, M. Uncovering the metabolite complexity and variability of cultivated hemp (Cannabis sativa L.): A first phytochemical diversity mapping in Greece. Phytochemistry 2024, 222, 114076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Sotto, A.; Gullì, M.; Acquaviva, A.; Tacchini, M.; Di Simone, S.C.; Chiavaroli, A.; Ferrante, C. Phytochemical and pharmacological profiles of the essential oil from the inflorescences of the Cannabis sativa L. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 183, 114980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judžentienė, A.; Garjonytė, R.; Būdienė, J. Phytochemical composition and antioxidant activity of various extracts of fibre hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) cultivated in lithuania. Molecules 2023, 28, 4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ubeed, H.M.S.; Bhuyan, D.J.; Alsherbiny, M.A.; Basu, A.; Vuong, Q.V. A comprehensive review on the techniques for extraction of bioactive compounds from medicinal cannabis. Molecules 2022, 27, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AL Ubeed, H.M.; Brennan, C.S.; Schanknecht, E.; Alsherbiny, M.A.; Saifullah, M.; Nguyen, K.; Vuong, Q.V. Potential applications of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) extracts and their phytochemicals as functional ingredients in food and medicinal supplements: A narrative review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 7542–7555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinon, B.; Molinari, R.; Costantini, L.; Merendino, N. The seed of industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.): Nutritional quality and potential functionality for human health and nutrition. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siano, F.; Moccia, S.; Picariello, G.; Russo, G.L.; Sorrentino, G.; Di Stasio, M.; Volpe, M.G. Comparative study of chemical, biochemical characteristic and ATR-FTIR analysis of seeds, oil and flour of the edible Fedora cultivar hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Molecules 2018, 24, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banskota, A.H.; Tibbetts, S.M.; Jones, A.; Stefanova, R.; Behnke, J. Biochemical characterization and in vitro digestibility of protein isolates from hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) by-products for salmonid feed applications. Molecules 2022, 27, 4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, C.; Givonetti, A.; Leoni, V.; Guerrieri, N.; Manfredi, M.; Giorgi, A.; Cavaletto, M. Biochemical aspects of seeds from Cannabis sativa L. plants grown in a mountain environment. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keiller, B.G.; Potter, M.; Burton, R.A.; van Eyk, P.J. Elucidating the degradation reaction pathways for the hydrothermal carbonisation of hemp via biochemical compositional analysis. Fuel 2021, 294, 120450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, P.; Campbell, B.J.; Nicodemus, T.J.; Cahoon, E.B.; Mullen, J.L.; McKay, J.K. Quantitative trait loci controlling agronomic and biochemical traits in Cannabis sativa. Genetics 2021, 219, iyab099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taura, F.; Tanaya, R.; Sirikantaramas, S. Recent advances in cannabinoid biochemistry and biotechnology. Sci. Asia 2019, 45, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merenkova, S.; Fatkullin, R.; Kalinina, I. Effect of fermentation on the biochemical parameters antioxidant capacity and dispersed composition of plant beverages based on barley and hemp seeds. Fermentation 2022, 8, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguchi, M.; Kane, S.; Potlakayala, S.; George, H.; Proano, R.; Sheri, V.; Rudrabhatla, S. Metabolic engineering strategies of industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.): A brief review of the advances and challenges. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 580621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karche, T. The application of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) for a green economy: A review. Turk. J. Bot. 2019, 43, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boleti, A.P.D.A.; Frihling, B.E.F.; e Silva, P.S.; Cardoso, P.H.D.O.; de Moraes, L.F.R.; Rodrigues, T.A.A.; Migliolo, L. Biochemical aspects and therapeutic mechanisms of cannabidiol in epilepsy. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 132, 1214–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folina, A.; Kakabouki, I.; Tourkochoriti, E.; Roussis, I.; Pateroulakis, H.; Bilalis, D. Evaluation of the effect of topping on cannabidiol (CBD) content in two industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) cultivars. Bull. Hortic. 2020, 3, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, J.D.; Neufeld, J.; Leson, G. Evaluating the quality of protein from hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) products through the use of the protein digestibility-corrected amino acid score method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11801–11807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Cunha Leme Filho, J.F.; Thomason, W.E.; Evanylo, G.K.; Zhang, X.; Strickland, M.S.; Chim, B.K.; Diatta, A.A. Biochemical and physiological responses of Cannabis sativa to an integrated plant nutrition system. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 5237–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroto Fernandez, E.; Peterseil, V.; Hackl, G.; Menges, S.; de Meijer, E.; Staginnus, C. Distribution of chemical phenotypes (chemotypes) in European agricultural hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) cultivars. J. Forensic Sci. 2020, 65, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, M.N.; Shahbazi, F.; Rondeau-Gagné, S.; Trant, J.F. The biosynthesis of the cannabinoids. J. Cannabis Res. 2021, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostuik, J.; Williams, D.W. Hemp agronomy–Grain and Fiber Production. In Industrial Hemp as a Modern Commodity Crop; Fike, J., Riddle, T., Nelson, J., Flaherty, P., Williams, D.W., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society: Madison, WI, USA, 2019; pp. 59–72. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Werf, H.M.G.; van Geel, W.C.A.; Wijlhuizen, M. Agronomic research on hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) in the Netherlands, 1987–1993. J. Int. Hemp Assoc. 1995, 2, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Kok, C.J.; Coenen, G.C.M.; de Heij, A. The effect of fibre hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) on selected soil-borne pathogens. J. Int. Hemp Assoc. 1994, 1, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Adesina, I.; Bhowmik, A.; Sharma, H.; Shahbazi, A. A review on the current state of knowledge of growing conditions, agronomic soil health practices and utilities of hemp in the United States. Agriculture 2020, 10, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaducci, S.; Scordia, D.; Liu, F.H.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, H.; Testa, G.; Cosentino, S.L. Key cultivation techniques for hemp in Europe and China. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 68, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desanlis, F.; Cerruti, N.; Warner, P. Hemp agronomics and cultivation. In Hemp: Industrial Production and Uses; Bouloc, P., Allegret, S., Arnaud, L., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 98–124. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, C.; Cassady, C.; Ernst, M. Industrial hemp production. Cent. Crop. Diversif. Univ. Ky 2015, 27, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Ale, M.T.; Kołaczkowski, B.; Fernando, D.; Daniel, G.; Meyer, A.S.; Thygesen, A. Comparison of traditional field retting and Phlebia radiata Cel 26 retting of hemp fibres for fibre-reinforced composites. AMB Express 2017, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, M.; van Eeden, T.; Beswa, D. Cannabis sativa Cannabinoids as Functional Ingredients in Snack Foods—Historical and Developmental Aspects. Plants 2022, 11, 3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bócsa, I.; Karus, M. The Cultivation of Hemp: Botany, Varieties, Cultivation and Harvesting; Hemptech: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 1998; Volume 184. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, M.P.; Clarke, R.C. Physical evidence for the antiquity of Cannabis sativa L. J. Int. Hemp Assoc. 1998, 5, 80–92. [Google Scholar]
- Le, C. Industrial. Guide Technique; Institut Technique du Chanvre; Technopole de l’Aube en Champagne: Troyes, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Benelli, G.; Pavela, R.; Petrelli, R.; Cappellacci, L.; Santini, G.; Fiorinin, D.; Sut, S.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Canale, A.; Maggi, F. The essential oil from industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) by-products as an effective tool for insect pest management in organic crops. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 122, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouloc, P.; Allegret, S.; Arnaud, L. (Eds.) Hemp: Industrial Production and Uses; CABI: Delémont, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 5, pp. 53–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Anderson, S.L.; Brym, Z.T.; Pearson, B.J. Photoperiodic Flowering Response of Essential Oil, Grain, and Fiber Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, J.; Salentijn, E.M.; Paulo, M.-J.; Thouminot, C.; van Dinter, B.J.; Magagnini, G.; Gusovius, H.-J.; Tang, K.; Amaducci, S.; Wang, S. Genetic Variability of Morphological, Flowering, and Biomass Quality Traits in Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, T.; Honermeier, B. Effect of sowing date and plant density on the cell morphology of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2006, 23, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaducci, S.; Colauzzi, M.; Zatta, A.; Venturi, G. Flowering Dynamics in Monoecious and Dioecious Hemp Genotypes. J. Ind. Hemp 2008, 13, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salentijn, E.M.; Petit, J.; Trindade, L.M. The Complex Interactions Between Flowering Behavior and Fiber Quality in Hemp. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.; Bhattarai, S.P.; Midmore, D.J. Review of Flowering Control in Industrial Hemp. J. Nat. Fibers 2012, 9, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.; Bhattarai, S.P.; Midmore, D.J. The Effects of Photoperiod on Phenological Development and Yields of Industrial Hemp. J. Nat. Fibers 2014, 11, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengloung, T.; Kaveeta, L.; Nanakorn, W. Effect of Sowing Date on Growth and Development of Thai Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Agric. Nat. Resour. 2009, 43, 423–431. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.J.; Ryu, B.R.; Azad, M.O.; Rahman, M.H.; Cheong, E.J.; Lim, J.-D.; Lim, Y.-S. Cannabinoids Accumulation in Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Plants under LED Light Spectra and Their Discrete Role as a Stress Marker. Biology 2021, 10, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldini, M.; Ferfuia, C.; Zuliani, F.; Danuso, F. Suitability Assessment of Different Hemp (Cannabis Sativa L.) Varieties to the Cultivation Environment. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 143, 111860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, F.; Latif, S.; Ashraf, M. Analytical Characterization of Hemp (Cannabis sativa) Seed Oil from Different Agro-Ecological Zones of Pakistan. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2006, 83, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.; Bhattarai, S.P.; Midmore, D.J. The Effects of Different Sowing Times on Maturity Rates, Biomass, and Plant Growth of Industrial Fiber Hemp. J. Nat. Fibers 2013, 10, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.R.; Loveys, B.R.; Cowley, J.M.; Hall, T.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Burton, R.A. Physiological and morphological responses of industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) to water deficit. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 187, 115331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žydelis, R.; Herbst, M.; Weihermüller, L.; Ruzgas, R.; Volungevičius, J.; Barčauskaitė, K.; Tilvikienė, V. Yield potential and factor influencing yield gap in industrial hemp cultivation under nemoral climate conditions. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 139, 126576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Tejero, I.F.; Durán Zuazo, V.H.; Sánchez-Carnenero, C.; Hernández, A.; Ferreiro-Vera, C.; Casano, S. Seeking Suitable Agronomical Practices for Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Cultivation for Biomedical Applications. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 139, 111524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salentijn, E.M.; Zhang, Q.; Amaducci, S.; Yang, M.; Trindade, L.M. New developments in fiber hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) breeding. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 68, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, W.D.; Van der Werf, H.M.G.; Mathijssen, E.W.J.M.; Van den Brink, P.W.M. Constraints to dry matter production in fibre hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Eur. J. Agron. 1995, 4, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herppich, W.B.; Gusovius, H.-J.; Flemming, I.; Drastig, K. Effects of Drought and Heat on Photosynthetic Performance, Water Use and Yield of Two Selected Fiber Hemp Cultivars at a Poor-Soil Site in Brandenburg (Germany). Agronomy 2020, 10, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, S.; Riggi, E.; Giorgio, T.; Scordia, D.; Venera, C. Evaluation of European Developed Fibre Hemp Genotypes (Cannabis sativa L.) in Semi-Arid Mediterranean Environment. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 50, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bari, V.; Campi, P.; Colucci, R.; Mastrorilli, M. Potential Productivity of Fibre Hemp in Southern Europe. Euphytica 2004, 140, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Werf, H.M.G. Agronomy and Crop Physiology of Fibre Hemp: A Literature Review. Cent. Agrobiol. Res. (CABO-DLO) Rep. 1991, 142, 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Zheljazkov, V.D.; Maggi, F. Valorization of CBD-hemp through distillation to provide essential oil and improved cannabinoids profile. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.J.; Berrada, A.F.; Hudalla, C.; Amaducci, S.; McKay, J.K. Genotype × Environment Interactions of Industrial Hemp Cultivars Highlight Diverse Responses to Environmental Factors. Agrosystems Geosci. Environ. 2019, 2, 180057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satriani, A.; Loperte, A.; Pascucci, S. The Cultivation of Industrial Hemp as Alternative Crop in a Less-Favoured Agricultural Area in Southern Italy: The Pignola Case Study. Pollutants 2021, 1, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, K.; Shekoofa, A.; Walker, E.; Kelly, H. Physiological Screening for Drought-Tolerance Traits Among Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Cultivars in Controlled Environments and in Field. J. Crop Improv. 2021, 35, 816–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Pauli, C.S.; Gostin, E.L.; Staples, S.K.; Seifried, D.; Kinney, C.; Vanden Heuvel, B.D. Effects of Short-Term Environmental Stresses on the Onset of Cannabinoid Production in Young Immature Flowers of Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). J. Cannabis Res. 2022, 4, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stack, G.M.; Toth, J.A.; Carlson, C.H.; Cala, A.R.; Marrero-González, M.I.; Wilk, R.L.; Smart, L.B. Season-long characterization of high-cannabinoid hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) reveals variation in cannabinoid accumulation, flowering time, and disease resistance. GCB Bioenergy 2021, 13, 546–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, F. Seed Germination of Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Cultivars Responds Differently to the Stress of Salt Type and Concentration. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 123, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Liu, H.; Du, G.; Yang, F.; Deng, G.; Yang, Y.; Liu, F. Fiber and seed type of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) responded differently to salt-alkali stress in seedling growth and physiological indices. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 129, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, N. Salinity Induced Antioxidant Defense in Roots of Industrial Hemp (IH: Cannabis sativa L.) for Fiber during Seed Germination. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struik, P.C.; Amaducci, S.; Bullard, M.J.; Stutterheim, N.C.; Venturi, G.; Cromack, H.T.H. Agronomy of fibre hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) in Europe. Ind. Crops Prod. 2000, 11, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Prato, L.; Ansari, O.; Hardy, G.E.S.J.; Howieson, J.; O’Hara, G.; Ruthrof, K.X. The cannabinoid profile and growth of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) is influenced by tropical daylengths and temperatures, genotype and nitrogen nutrition. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 178, 114605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żuk-Gołaszewska, K.; Gołaszewski, J. Hemp production. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 42: Hemp Production and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 4, pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, W.G.; Behe, B. A national survey to characterize industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) production challenges under protected cultivation. J. Agric. Hemp Res. 2020, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, N.; Privé, J.P.; Joly, D.L.; Moreau, G. Associations between cannabinoids and growth stages of twelve industrial hemp cultivars grown outdoors in Atlantic Canada. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 172, 113997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandinières, H.; Amaducci, S. Agronomy and ecophysiology of hemp cultivation. In Cannabis/Hemp for Sustainable Agriculture and Materials; Springer: Singapore, 2022; Volume 8, pp. 89–125. [Google Scholar]
- Poniatowska, J.; Panasiewicz, K.; Wielgus, K.; Szalata, M.; Jaśkiewicz, B. Influence of agroclimatic conditions on active substances content in hemp cultivated in the South-East Baltic region. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 6119–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Tejero, I.F.; Hernández, A.; Ferreiro-Vera, C.; Zuazo, V.H.D.; García, J.H.; Sánchez-Carnerero, C.; Casano, S. Yield of new hemp varieties for medical purposes under semi-arid Mediterranean environment conditions. Commun. Sci. 2020, 11, e3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, N.; Privé, J.P.; Moreau, G. Spatiotemporal variability and sensitivity of industrial hemp cultivars under variable field conditions. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 138, 126549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Deng, G.; Yu, J.; Hu, W.; Liu, F. Fiber hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) yield and its response to fertilization and planting density in China. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 177, 114542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakabouki, I.; Kousta, A.; Folina, A.; Karydogianni, S.; Zisi, C.; Kouneli, V.; Papastylianou, P. Effect of fertilization with urea and inhibitors on growth, yield and cbd concentration of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Sustainability 2021, 13, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, A.; Volpe, M.G.; Polimeno, F.; Siano, F.; Maglione, G.; Di Tommasi, P.; Vitale, L. Soil fertilization with urea has little effect on seed quality but reduces soil N2O emissions from a hemp cultivation. Agriculture 2020, 10, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.S.; Vann, M.C.; Suchoff, D.H.; McGinnis, M.; Whipker, B.E.; Edmisten, K.L.; Gatiboni, L.C. Hemp yield and cannabinoid concentrations under variable nitrogen and potassium fertilizer rates. Crop Sci. 2023, 63, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankowski, J.; Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Graczyk, M.; Niedziela, G.; Sieracka, D.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. The Effect of Mineral Fertilization on the Content of Bioactive Compounds in Hemp Seeds and Oil. Molecules 2023, 28, 4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atoloye, I.A.; Adesina, I.; Shahbazi, A.; Bhowmik, A. Response of cannabidiol hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) varieties grown in the southeastern United States to nitrogen fertilization. Open Agric. 2022, 7, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laleh, S.; Al-Ahmadi, M.J.; Parsa, S. Response of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) to integrated application of chemical and manure fertilizers. Acta Agric. Slov. 2021, 117, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowski, J.; Edmisten, K.; Davis, J.; McGinnis, M.; Hicks, K.; Cockson, P.; Whipker, B.E. Augmenting nutrient acquisition ranges of greenhouse grown CBD (Cannabidiol) hemp (Cannabis sativa) cultivars. Horticulturae 2020, 6, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheay, H.T.; Omondi, E.C.; Brewer, C.E. Potential of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) for paired phytoremediation and bioenergy production. GCB Bioenergy 2021, 13, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prade, T.; Svensson, S.E.; Andersson, A.; Mattsson, J.E. Biomass and energy yield of industrial hemp grown for biogas and solid fuel. Biomater. Bioeng. 2011, 35, 3040–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrow, G.A.; Pawar, R.S.; Srigley, C.; Sam, J.F.; Talavera, C.; Parker, C.H.; Noonan, G.O. A survey of cannabinoids and toxic elements in hemp-derived products from the United States marketplace. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 97, 103800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, M.R. Bast fibres: Hemp cultivation and production. In Handbook of Natural Fibres; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2020; Volume 4, pp. 163–196. [Google Scholar]
- Kousta, A.; Papastylianou, P.; Travlos, I.; Mavroeidis, A.; Kakabouki, I. Effect of Fertilization and Weed Management Practices on Weed Diversity and Hemp Agronomic Performance. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poniatowska, J.; Panasiewicz, K.; Szalata, M.; Zarina, L.; Zute, S.; Wielgus, K. Variability of cannabinoid yields of fibre hemp cultivars depending on the sowing density and nitrogen fertilisation. Plant Soil Environ. 2022, 68, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevan, L.; Jones, M.; Zheng, Y. Optimisation of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium for soilless production of Cannabis sativa in the flowering stage using response surface analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 764103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podder, S.; Shafian, S.; Thomason, W.E.; Wilson, T.B.; Fike, J.H. Hemp Seed Yield Responses to Nitrogen Fertility Rates. Crops 2024, 4, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandinières, H.; Croci, M.; Impollonia, G.; Marcone, A.; Gay, A.; Winters, A.; Amaducci, S. Multi-environment assessment of a yellow hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) cultivar’s eco-physiology and productivity under varying levels of nitrogen fertilisation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 195, 116360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zha, W.; Tang, K.; Deng, G.; Du, G.; Liu, F. Effect of nitrogen supply on growth and nitrogen utilization in hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Agronomy 2021, 11, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelliffe, J.; Lopez, R.A.; Ghimire, S. CBD hemp production costs and returns for Connecticut farmers in 2020. Zwick Cent. Outreach Rep. 2020, 66, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, N.; Brym, Z.; Oyola, L.A.M.; Sharma, L.K. Nitrogen fertilization impact on hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) crop production: A review. Agron. J. 2023, 115, 1557–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubin, M.P.; Seguin, P.; Vanasse, A.; Tremblay, G.F.; Mustafa, A.F.; Charron, J.B. Industrial hemp response to nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilization. Crop Forage Turfgrass Manag. 2015, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, C.L.; Malhi, S.S.; Raney, J.P.; Wang, Z.H. The effect of N and P fertilization on growth, seed yield and quality of industrial hemp in the Parkland region of Saskatchewan. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2004, 84, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sausserde, R.; Adamovičs, A. Impact of nitrogen fertilizer rates on industrial hemp growth and development. PLoS ONE 2013, 3, e4561208. [Google Scholar]
- Campiglia, E.; Radicetti, E.; Mancinelli, R. Plant density and nitrogen fertilization affect agronomic performance of industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) in Mediterranean environment. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 100, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.L.; Pearson, B.; Kjelgren, R.; Brym, Z. Response of essential oil hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) growth, biomass, and cannabinoid profiles to varying fertigation rates. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sausserde, R.; Adamovics, A. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer rates on industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Biomass production. In Proceedings of the International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference: SGEM, Albena, Bulgaria, 16–22 June 2013; Volume 1, pp. 339–351. [Google Scholar]
- Vági, E.; Balázs, M.; Komóczi, A.; Kiss, I.; Mihalovits, M.; Székely, E. Cannabinoids enriched extracts from industrial hemp residues. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 2019, 63, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saloner, A.; Bernstein, N. Response of medical cannabis (Cannabis sativa L.) to nitrogen supply under long photoperiod. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 572293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentino, N.; Formisano, C.; Delfine, S.; Chianese, G. Environmental and agronomic factors affecting the chemical composition and biological activity of cannabis extracts. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1407262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, K.P.; Hoeng, J.; Goffman, F.; Schlage, W.K.; Latino, D. Opportunities, Challenges, and Scientific Progress in Hemp Crops. Molecules 2024, 29, 2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, G.; Du, G.; Yang, Y.; Bao, Y.; Liu, F. Planting density and fertilization evidently influence the fiber yield of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Agronomy 2019, 9, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalata, M.; Dreger, M.; Zielińska, A.; Banach, J.; Szalata, M.; Wielgus, K. Simple extraction of cannabinoids from female inflorescences of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Molecules 2022, 27, 5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malík, M.; Velechovský, J.; Tlustoš, P. The overview of existing knowledge on medical cannabis plants growing. Plant Soil Environ. 2021, 67, 425–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, C.A. Effect of commercial fertilizers on the sex expression of hemp. Bot. Gaz. 1945, 107, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glivar, T.; Eržen, J.; Kreft, S.; Zagožen, M.; Čerenak, A.; Čeh, B.; Benković, E.T. Cannabinoid content in industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) varieties grown in Slovenia. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 145, 112082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, M.S.; Arsenault, T.; Bui, T.H.; Zuverza-Mena, N.; Bharadwaj, A.; Prapayotin-Riveros, K.; Dimkpa, C.O. Copper Stimulation of Tetrahydrocannabinol and Cannabidiol Production in Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Is Copper-Type, Dose, and Cultivar Dependent. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 6921–6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Deng, H.; Heise, J.A.; Puthoff, D.P.; Bou-Abboud, N.; Yu, H.; Peng, J. Contents of cannabinoids in hemp varieties grown in Maryland. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 32186–32197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Zhou, W.; Long, S.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, C.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y. Effects of Different N, P, and K Rates on the Growth and Cannabinoid Content of Industrial Hemp. J. Nat. Fibers 2023, 20, 2159605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, D.; Connelly, G.; Ellison, S. Different fertility approaches in organic hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) production alter floral biomass yield but not CBD: THC ratio. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.C.D.; Muraoka, T.; Franzini, V.I.; Villanueva, F.C.A.; Buzetti, S.; Moreti, D. Phosphorus utilization by corn as affected by green manure, nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2012, 47, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifico, D.; Miselli, F.; Carboni, A.; Moschella, A.; Mandolino, G. Time course of cannabinoid accumulation and chemotype development during the growth of Cannabis sativa L. Euphytica 2008, 160, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, N.; Gorelick, J.; Zerahia, R.; Koch, S. Impact of N, P, K, and humic acid supplementation on the chemical profile of medical cannabis (Cannabis sativa L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iványi, I.; Izsáki, Z. Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilization on nutrional status of fiber hemp. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2009, 40, 974–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffman, C.B.; Gentner, W.A. Responses of Greenhouse-grown Cannabis sativa L. to Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium 1. Agron. J. 1977, 69, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, C.L.; Malhi, S.S.; Moskal, G.J.; Leach, D.W. How hungry is hemp for fertilizers? In Soils and Crops Workshop; The University of Saskatchewan: Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rosas, J.M.; Bedia, J.R.M.J.; Rodríguez-Mirasol, J.; Cordero, T. HEMP-derived activated carbon fibers by chemical activation with phosphoric acid. Fuel 2009, 88, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iványi, I. Hemp resilience within agro-ecosystem. Növénytermelés 2010, 59 (Suppl. 8), 409–412. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, A.R. Growth Studies with Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Ph.D. Thesis, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Finnan, J.; Burke, B. Potassium fertilization of hemp (Cannabis sativa). Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 41, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscariello, C.; Matassa, S.; Esposito, G.; Papirio, S. From residue to resource: The multifaceted environmental and bioeconomy potential of industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 175, 105864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffman, C.B.; Gentner, W.A. Greenhouse propagation of Cannabis sativa L. by vegetative cuttings. Econ. Bot. 1979, 33, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saloner, A.; Bernstein, N. Effect of potassium (K) supply on cannabinoids, terpenoids and plant function in medical cannabis. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, E.R.; Young, S.; Li, X.; Henriquez Inoa, S.; Suchoff, D.H. The effect of transplant date and plant spacing on biomass production for floral hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Agronomy 2022, 12, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saloner, A.; Sacks, M.M.; Bernstein, N. Response of medical cannabis (Cannabis sativa L.) genotypes to K supply under long photoperiod. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treadwell, D.; Chase, C.; Cho, A.; Alligood, M.; Elsakr, J. Potential for sunn hemp (Crotalaria juncea) to utilize soil potassium. Proc. Fla. State Hortic. Soc. 2009, 122, 243–246. [Google Scholar]
- McPartland, J.M.; Cutler, S.; McIntosh, D.J. Hemp production in Aotearoa. J. Ind. Hemp 2004, 9, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iványi, I. Relationship between leaf nutrient concentrations and yield of fibre hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Cereal Res. Commun. 2005, 33, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedan, D.; Pagnoux, C.; Chotard, T.; Smith, A.; Lejolly, D.; Gloaguen, V.; Krausz, P. Effect of calcium rich and alkaline solutions on the chemical behaviour of hemp fibres. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 9336–9342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrado, G.; Pannico, A.; Zarrelli, A.; Kyriacou, M.C.; De Pascale, S.; Rouphael, Y. Macro and trace element mineral composition of six hemp varieties grown as microgreens. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Esteban, J.I.; Torija-Isasa, M.E.; de Cortes Sánchez-Mata, M. Mineral elements and related antinutrients, in whole and hulled hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seeds. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 109, 104516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schayot, C.T. Hemp Microgreen Mineral Content, Cannabinoids, Total Phenolics, and Antioxidants. Ph.D. Thesis, Louisiana State University and Agricultural & Mechanical College, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yep, B.; Zheng, Y. Potassium and micronutrient fertilizer addition in a mock aquaponic system for drug-type Cannabis sativa L. cultivation. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2020, 101, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, K.; Kara, S.M.; Ozkutlu, F.; Gul, V. Monitoring of heavy metals and selected micronutrients in hempseeds from North-western Turkey. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 5, 463–467. [Google Scholar]
- Mihoc, M.; Pop, G.; Alexa, E.; Dem, D.; Militaru, A. Microelements distribution in whole hempseeds (Cannabis sativa L.) and in their fractions. Rev. De. Chim. 2013, 64, 776–780. [Google Scholar]
- Morad, D.; Bernstein, N. Response of medical cannabis to magnesium (Mg) supply at the vegetative growth phase. Plants 2023, 12, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, I.M.; Nascimento, P.D.A.; Yamamoto, C.I.; Oliveira, A. Evaluation of trace elements in cannabis products. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 113, 104721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalousek, P.; Holátko, J.; Schreiber, P.; Pluháček, T.; Širůčková Lónová, K.; Radziemska, M.; Brtnický, M. The effect of chelating agents on the Zn-phytoextraction potential of hemp and soil microbial activity. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łochyńska, M.; Frankowski, J. Impact of silkworm excrement organic fertilizer on hemp biomass yield and composition. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łochyńska, M.; Frankowski, J. The effects of silkworm excrement organic fertilizer on the hemp yield. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds, J.; Wang, K.H.; Marahatta, S.P.; Meyer, S.L.; Hooks, C.R. Sunn hemp cover cropping and organic fertilizer effects on the nematode community under temperate growing conditions. J. Nematol. 2013, 45, 265. [Google Scholar]
- Caplan, D.; Dixon, M.; Zheng, Y. Optimal rate of organic fertilizer during the flowering stage for cannabis grown in two coir-based substrates. HortScience 2017, 52, 1796–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, C.; Young, J.P. The effects of organic and inorganic nitrogen fertilizer on the morphology and anatomy of Cannabis sativa “Fédrina” (industrial fibre hemp) grown in Northern British Columbia, Canada. J. Ind. Hemp 2006, 11, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, D.; Dixon, M.; Zheng, Y. Optimal rate of organic fertilizer during the vegetative-stage for cannabis grown in two coir-based substrates. HortScience 2017, 52, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliana, A.I.; Sumarni, T.; Islami, T. Application of bokashi and sunn hemp (Crotalaria juncea L.) to improve inorganic fertilizer efficiency on maize (Zea mays L.). J. Degrad. Min. Lands Manag. 2015, 3, 433. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ahmadi, S.L.M.J.; Parsa, S. Effect of Different Levels of Organic and Chemical Fertilizers on Yield, Harvest Index and Extract Percentage of Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Iran. J. Field Crops Res. 2017, 15, 823–837. [Google Scholar]
- Wylie, S.E.; Ristvey, A.G.; Fiorellino, N.M. Fertility management for industrial hemp production: Current knowledge and future research needs. GCB Bioenergy 2021, 13, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pylypchenko, A.; Marenych, M.; Hanhur, V.; Semenov, A.; Korotkova, I.; Rozhkov, A.; Ponomarenko, S. Impact of Organic Cultivation Technology of Fiber Hemp (Cannabis Sativa L.) on Soil Agrochemical and Bioecological Properties. J. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 24, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pylypchenko, A.; Marenych, M.; Hanhur, V.; Tymoshchuk, T.; Malynka, L. Features of forming the productivity of modern hemp varieties using organic cultivation technology. Sci. Horizons 2023, 26, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pylypchenko, A.; Marenych, M.; Hanhur, V.; Semenov, A.; Sakhno, T.; Ponomarenko, S.; Rozhkov, A. Formation of the Quality Indicators of Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Seeds Sown under Organic Growing Technology. J. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 24, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingha, B.; Sandler, L.; Bhowmik, A.; Akotsen-Mensah, C.; Jackai, L.; Gibson, K.; Turco, R. Industrial hemp knowledge and interest among North Carolina organic farmers in the United States. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höppner, F.; Menge-Hartmann, U. Cultivation experiments with two fibre hemp varieties. J. Intern. Hemp. Assoc. 1995, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Jonaitienė, V.; Jankauskienė, Z.; Stuogė, I. Hemp cultivation opportunities and perspectives in Lithuania. In Natural Fibres: Advances in Science and Technology towards Industrial Applications: From Science to Market; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 4, pp. 407–414. [Google Scholar]
- Puiu, I.; Popa, L.D.; Robu, T.; Țibulcă Ghițău, C.S.; Țopa, D.C.; Lipșa, F.D.; Teliban, G.C. Research on the Optimization of the Industrial Hemp Cultivation Technology for the Full Use of Biomass. 2022. Available online: https://repository.iuls.ro/xmlui/handle/20.500.12811/3438 (accessed on 19 January 2024).
- Cherney, J.H.; Small, E. Industrial hemp in North America: Production, politics and potential. Agronomy 2016, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngobeni, N.D.; Mokoena, M.L.; Funnah, S.M. Growth and yield response of fibre hemp cultivars (Cannabis sativa L.) under different N-levels in Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 11, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, M.K. Benefits of cultivating industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa ssp. sativa)—A versatile plant for a sustainable future. Chem. Proc. 2022, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttharak, P.; Wangnai, P.; Puttharak, J.; Baisaeng, N. Optimizing medicinal hemp production with synergistic light-enhanced technologies and organic biorefinery approaches. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2024, 254, 112890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhondt, F.; Muthu, S.S. Hemp and Sustainability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zaica, A.; Anghelache, D.; Zaica, A.; Popa, D.; Teliban, G. Technologies and technical equipment for farmers in the field of hemp cultivation. Natl. Inst. Res.-Dev. Mach. Install. Des. Agric. Food Ind.-INMA Buchar. 2022, 8, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Malabadi, R.B.; Kolkar, K.P.; Chalannavar, R.K.; Acharya, M.; Mudigoudra, B.S. Industrial Cannabis sativa: Hemp-Biochar-Applications and Disadvantages. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2023, 20, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massuela, D.C.; Munz, S.; Hartung, J.; Nkebiwe, P.M.; Graeff-Hönninger, S. Cannabis Hunger Games: Nutrient stress induction in flowering stage–impact of organic and mineral fertilizer levels on biomass, cannabidiol (CBD) yield and nutrient use efficiency. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1233232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhuis, W.; van Delden, S.H.; van Dam JE, G.; Marinho, J.P.; Struik, P.C.; Stomph, T.J. Plant weight determines secondary fibre development in fibre hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 139, 111493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Santanen, A.; Jaakkola, S.; Ekholm, P.; Hartikainen, H.; Stoddard, F.L.; Mäkelä, P.S. Biomass yield and quality of bioenergy crops grown with synthetic and organic fertilizers. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 59, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, C. The Effects of Organic and Inorganic Nitrogen Fertilizer on the Morphology and Anatomy of Industrial Fibre Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Grown in Northern British Columbia, Canada. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Northern British Columbia, Prince George, BC, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Werf, H.M.L. life cycle analysis of field production of fibre hemp, the effect of production practices on environmental impacts. Euphytica 2004, 140, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaducci, S.; Zatta, A.; Raffanini, M.; Venturi, G. Characterisation of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) roots under different growing conditions. Plant Soil 2008, 313, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golia, E.E.; Bethanis, J.; Ntinopoulos, N.; Kaffe, G.G.; Komnou, A.A.; Vasilou, C. Investigating the potential of heavy metal accumulation from hemp. The use of industrial hemp (Cannabis Sativa L.) for phytoremediation of heavily and moderated polluted soils. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 31, 100961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, T.B.; Will, S. Economic issues and perspectives for industrial hemp. Industrial Hemp as a Modern Commodity Crop; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; Volume 4, pp. 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- Fortenbery, T.R.; Bennett, M. Opportunities for commercial hemp production. Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 2004, 26, 97–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawro, A.; Batog, J.; Gieparda, W. Chemical and enzymatic treatment of hemp biomass for bioethanol production. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, T.; Shepherd, J.; Olson, D.; Snell, W.; Proper, S.; Thornsbury, S. Economic Viability of Industrial Hemp in the United States: A Review of State Pilot Programs. 2020. Available online: https://www.ers.usda.gov/webdocs/publications/95930/eib-217.pdf (accessed on 8 January 2024).
- Thompson, E.C.; Berger, M.C.; Allen, S.N. Economic Impact of Industrial Hemp in Kentucky. Ph.D. Thesis, Center for Business and Economic Research, Carol Martin Gatton College of Business and Economics, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, A.; Jia, L.; Kumar, D.; Yoo, C.G. Recent advancements in biological conversion of industrial hemp for biofuel and value-added products. Fermentation 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, H.; Fu, W. Hemp: A sustainable plant with high industrial value in food processing. Foods 2023, 12, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carus, M.; Sarmento, L. The European Hemp Industry: Cultivation, processing and applications for fibres, shivs, seeds and flowers. Eur. Ind. Hemp. Assoc. 2016, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, R. The Great Book of Hemp: The Complete Guide to the Environmental, Commercial, and Medicinal Uses of the World’s Most Extraordinary Plant; Inner Traditions/Bear Co.: Rochester, VT, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Vantreese, V.L. Industrial Hemp: Global Operations, Local Implications. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Agricultural Economics, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Vantreese, V.L. Industrial Hemp: Global Markets and Prices. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Agricultural Economics, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ranalli, P. Advances in Hemp Research; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Muttil, N.; Sadath, S.; Coughlan, D.; Paresi, P.; Singh, S.K. Hemp as A Sustainable Carbon Negative Plant: A Review of Its Properties, Applications, Challenges and Future Directions. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2024, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ely, K.; Podder, S.; Reiss, M.; Fike, J. Industrial hemp as a crop for a sustainable agriculture. In Cannabis/Hemp for Sustainable Agriculture and Materials; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Negoiţa, C. A critical analysis of hemp (Cannabis Sativa L.) use: Scientific, legislative and socio-economic aspects. J. Soc. Sci. 2024, 7, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dölle, K.; Kurzmann, D.E. Cannabis, the plant of the unlimited possibilities. Adv. Res 2019, 20, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fike, J. Industrial hemp: Renewed opportunities for an ancient crop. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2016, 35, 406–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R. Hemp as an Agricultural Commodity; Congressional Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; Volume 4, pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Fortenbery, T.R.; Mick, T.B. Industrial Hemp: Opportunities and Challenges for Washington. Available online: https://wpcdn.web.wsu.edu/cahnrs/uploads/sites/6/2021/09/WP2014-10.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2024).
- Sandberg, S. The importance of culture for cannabis markets: Towards an economic sociology of illegal drug markets. Br. J. Criminol. 2012, 52, 1133–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Heisters, S. Environmental costs of hemp prohibition in the United States. J. Ind. Hemp 2008, 13, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Pan, Z. Cannabidiol and terpenes from hemp–ingredients for future foods and processing technologies. J. Future Foods 2021, 1, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranalli, P. Current status and future scenarios of hemp breeding. Euphytica 2004, 140, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimalasiri, E.M.; Jahanshiri, E.; Chimonyo, V.G.; Kuruppuarachchi, N.; Suhairi, T.A.S.T.M.; Azam-Ali, S.N.; Gregory, P.J. A framework for the development of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) as a crop for the future in tropical environments. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 172, 113999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, A.M.; Lewis, J.D.; Afzal, M.T. Potential of industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) for bioenergy production in Canada: Status, challenges and outlook. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 141, 110784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranalli, P.; Venturi, G. Hemp as a raw material for industrial applications. Euphytica 2004, 140, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, E.; Marcus, D. Hemp: A new crop with new uses for North America. Trends New Crops New Uses 2002, 24, 284–326. [Google Scholar]
- Amaducci, S.; Gusevas, H.J. Hemp–cultivation, extraction and processing. In Industrial Applications of Natural Fibres: Structure, Properties and Technical Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 3, pp. 109–134. [Google Scholar]
- Komahan, D.H.S.; Swanepoel, Q.M.; Nicholls, I.; Sofkova-Bobcheva, S.; Barge, R.; Kerckhoffs, L.H.J. Future Scenario of Better New Zealand Adapted Industrial Hemp Varieties. 2019. Available online: https://www.agronomysociety.org.nz/files/ASNZ_2019_07._Future_NZ_adapted_hemp_varieties.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- Sieracka, D.; Frankowski, J.; Wacławek, S.; Czekała, W. Hemp Biomass as a Raw Material for Sustainable Development. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryz, N.R.; Remillard, D.J.; Russo, E.B. Cannabis roots: A traditional therapy with future potential for treating inflammation and pain. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2017, 2, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.S.U.; Rashid, N.; Saif, A.; Mahmood, T.; Han, J.I. Potential of bioenergy production from industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa): Pakistan perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 18, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).