Winter Malting Barley Growth, Yield, and Quality following Leguminous Cover Crops in the Northeast United States
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
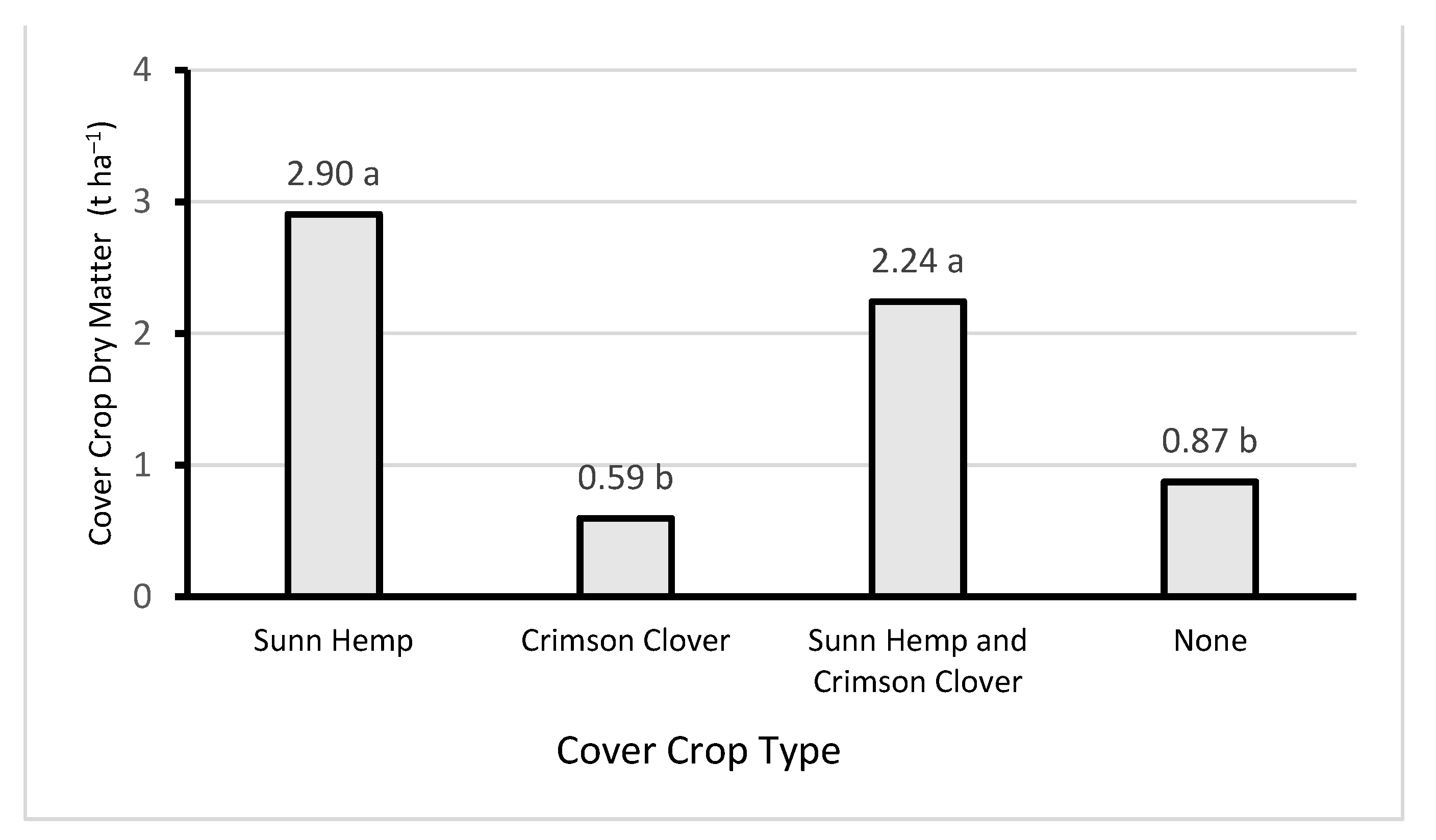
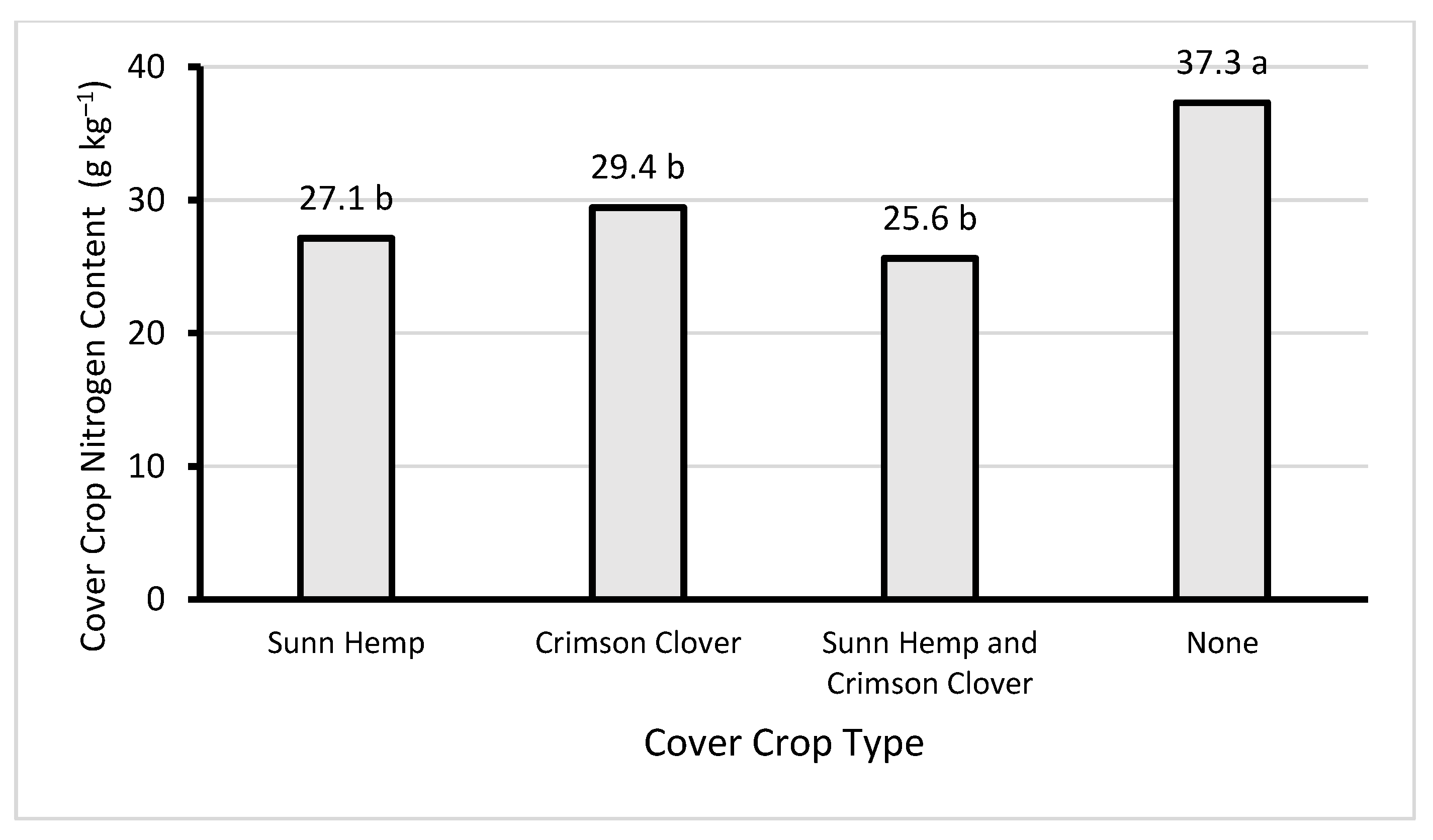
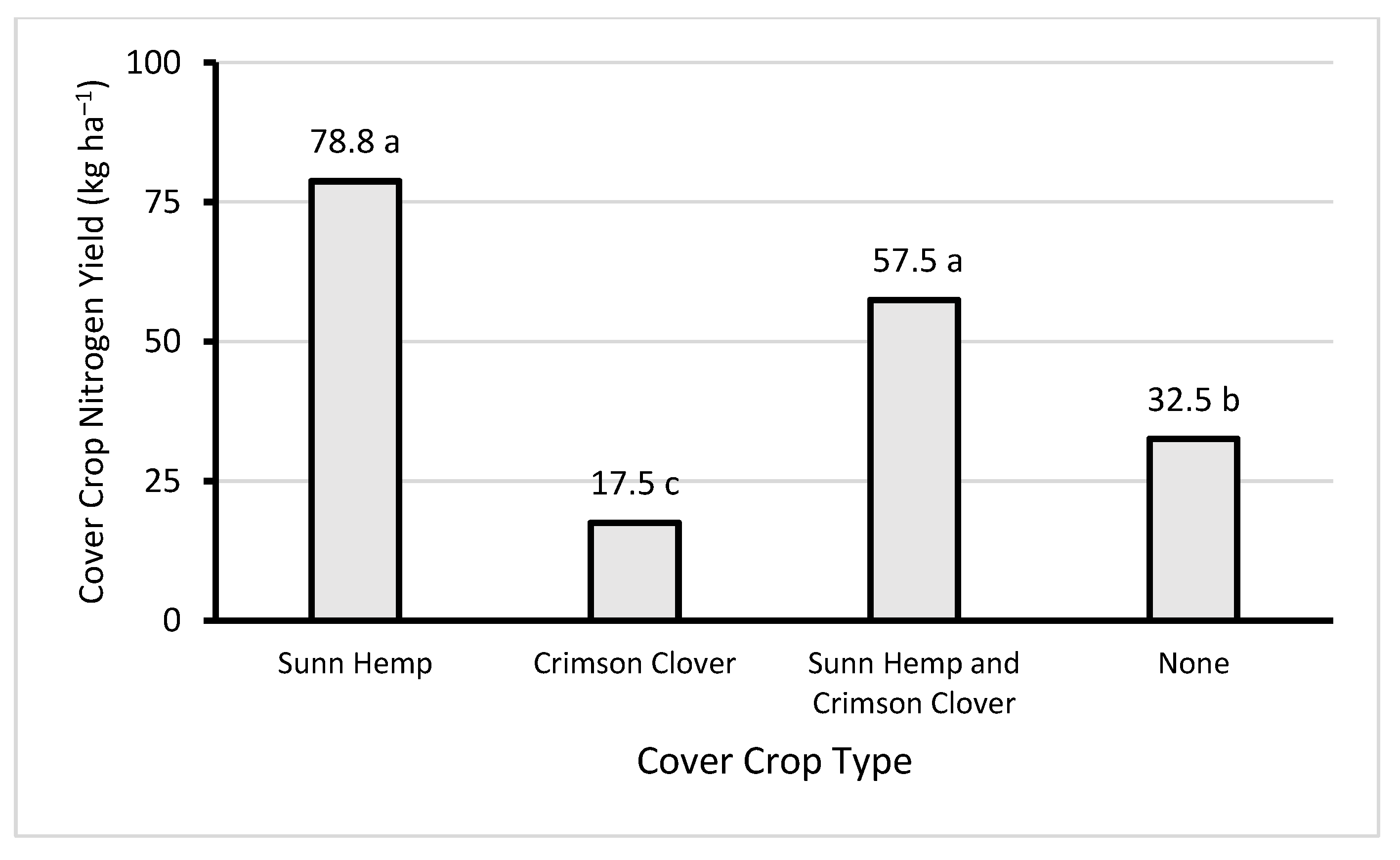
3.1. Cover Crop Biomass and Nitrogen Content
3.2. Soil Nitrate in the Fall and Spring
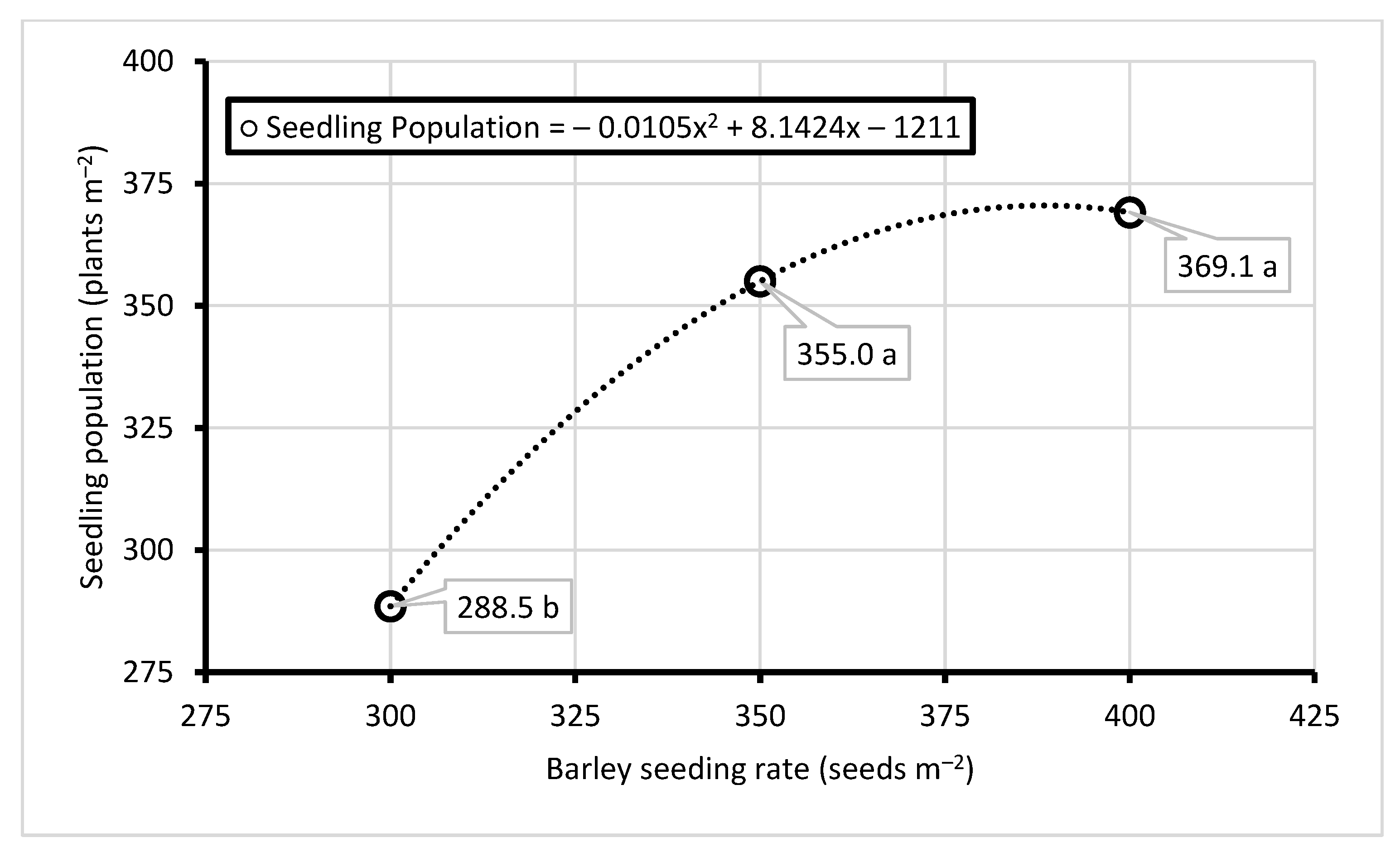
3.3. Barley Seeding Rate Impact on Stand Establishment, Winter Survival, and Growth of Barley
3.4. Influence of Cover Crop Species and Barley Seeding Rate on Barley Yield and Malting Quality Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shrestha, R.K.; Lindsey, L.E. Agronomic Management of Malting Barley and Research Needs to Meet Demand by the Craft Brew Industry. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 1570–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazor, J. The Organic Grain Grower: Small-Scale, Holistic Grain Production for the Home and Market Producer; Chelsea Green Publishing: White River Junction, VT, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Surjawan, I.; Dougherty, M.P.; Camire, M.E.; Jemison, J.J. Malting Quality of Maine-Grown Barley; MR433: Onono, ME, USA, 2004; p. 433. Available online: https://digitalcommons.library.umaine.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1009&context=aes_miscreports (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Robertson, L.D.; Wesenberg, D.M. Major uses of barley. In Idaho Spring Barley Production Guide; Bull 742; Robertson, L.D., Stark, J.C., Eds.; Ag Publications: Moscow, ID, USA, 2003; Available online: http://www.extension.uidaho.edu/publishing/pdf/BUL/BUL0742.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Brewers Association. Malting Barley Characteristics for Craft Brewers; Brewers Publications: Boulder, CO, USA, 2020; Available online: https://cdn.brewersassociation.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/Malting_Barley_Characteristics_For_Craft_Brewers.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Hmielowski, T. From Field to Pint: Malting Barley in the Eastern U.S. Crop. Soils 2017, 50, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrigley, C.; Batey, I.; Miskelly, D. Cereal Grains: Assessing and Managing Quality; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- BMBRI (Brewing and Malting Barley Research Institute). Quality Factors in Malting Barley. 2010. Available online: http://bmbri.ca/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Quality-Factors-in-Malting-Barley-May-2010.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- ASBC (American Society of Brewing Chemists). Methods of Analysis, 14th ed.; The Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Darby, H.; Cummings, E.; Emick, H. Organic Winter Malt Barley Variety Trial; UVM Extension: Burlington, VT, USA, 2017; Available online: https://scholarworks.uvm.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1055&context=nwcsp (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Hashemi, M.; Zandvakili, O.R.; Shureshjani, R.A.; Etemadi, F.; Darby, H. Evaluating Winter Barley Cultivar Using Data Envelopment Analysis Models. J. Autom. Sin. 2019, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallett, J. Malt: A Practical Guide from Field to Brewhouse; Brewers Publications: Boulder, CO, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Siller, A.; Hashemi, M.; Wise, C.; Smychkovich, A.; Darby, H. Date of Planting and Nitrogen Management for Winter Malt Barley Production in the Northeast, USA. Agronomy 2021, 11, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.H.W.; Wiersma, J.J.; Sheaffer, C.C.; Steffenson, B.J.; Smith, K.P. Assessment of Winter Barley in Minnesota: Relationships among Cultivar, Fall Seeding Date, Winter Survival, and Grain Yield. Crop. Forage Turfgrass Manag. 2019, 5, 190055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA NASS (National Agricultural Statistics Service). Small Grains 2020 Summary 09/30/2020. 2020. Available online: https://downloads.usda.library.cornell.edu/usda-esmis/files/5t34sj573/7p88d6171/bn999x131/smgr0920.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Turkington, T.K.; O’Donovan, J.T.; Edney, M.J.; Juskiw, P.E.; McKenzie, R.H.; Harker, K.N.; Clayton, G.W.; Xi, K.; Lafond, G.P.; Irvine, R.B.; et al. Effect of Crop Residue, Nitrogen Rate and Fungicide Application on Malting Barley Productivity, Quality, and Foliar Disease Severity. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 92, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sainju, U.M. Tillage, Cropping Sequence, and Nitrogen Fertilization Influence Dryland Soil Nitrogen. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.; Petrie, S.; Budde, A.; Corey, A.; Hayes, P.; Kling, J.; Rhinhart, K. Variety and N Management Effects on Grain Yield and Quality of Winter Barley. Crop Manag. 2008, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, W.B.; Sainju, U.M.; Caesar-TonThat, T.; Iversen, W.M. Malt Barley Yield and Quality Affected by Irrigation, Tillage, Crop Rotation, and Nitrogen Fertilization. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edney, M.J.; O’Donovan, J.T.; Turkington, T.K.; Clayton, G.W.; McKenzie, R.; Juskiw, P.; Lafond, G.P.; Brandt, S.; Grant, C.A.; Harker, K.N.; et al. Effects of Seeding Rate, Nitrogen Rate and Cultivar on Barley Malt Quality: Effects of Seeding Rate, Nitrogen Rate and Cultivar on Barley Malt Quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 2672–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delogu, G.; Cattivelli, L.; Pecchioni, N.; De Falcis, D.; Maggiore, T.; Stanca, A.M. Uptake and Agronomic Efficiency of Nitrogen in Winter Barley and Winter Wheat. Eur. J. Agron. 1998, 9, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, R.H.; Middleton, A.B.; Bremer, E. Fertilization, Seeding Date, and Seeding Rate for Malting Barley Yield and Quality in Southern Alberta. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2005, 85, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darby, D.H.; Emick, H.; Cummings, E. Winter Barley Seeding Rate, Cover Crop and Variety Trial; UVM Extension: Burlington, VT, USA, 2016; Available online: https://scholarworks.uvm.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1113&context=nwcsp (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- O’Donovan, J.T.; Turkington, T.K.; Edney, M.J.; Clayton, G.W.; McKenzie, R.H.; Juskiw, P.E.; Lafond, G.P.; Grant, C.A.; Brandt, S.; Harker, K.N.; et al. Seeding Rate, Nitrogen Rate, and Cultivar Effects on Malting Barley Production. Agron. J. 2011, 103, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, S. Seeding Rates and Harvest Dates on Productivity of ‘Tropic Sun’ Sunn Hemp in South-Central New York; Final Study Report: USDA-NRCS, Big Flats Plant Materials Center: Corning, NY, USA, 2016. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_PLANTMATERIALS/publications/nypmcsr12923.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Clark, A. Managing Cover Crops Profitably, 3rd ed.; Sustainable Agriculture Network: Beltsville, MD, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mansoer, Z.; Reeves, D.W.; Wood, C.W. Suitability of Sunn Hemp as an Alternative Late-Summer Legume Cover Crop. Soil Sci. Soc. of Am. J. 1997, 61, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hinds, J.; Hooks, C.R.R. Population Dynamics of Arthropods in a Sunn-Hemp Zucchini Interplanting System. Crop Prot. 2013, 53, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooks, C.R.R.; Hinds, J.; Zobel, E.; Patton, T. Impact of Crimson Clover Dying Mulch on Two Eggplant Insect Herbivores: Impact of Crimson Clover on Insects in Eggplant. J. Appl. Entomol. 2013, 137, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.M.; Drury, C.F.; Reynolds, W.D.; Phillips, L.A. Nitrogen Release from Shoots and Roots of Crimson Clover, Hairy Vetch, and Red Clover. Can. J. Soil. Sci. 2020, 100, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechtig, A. QuickChem Method 12-107-04-1-A. Determination of Nitrate/Nitrite by Flow Injection Analysis; Lachat Instruments 6645 West Mill Road: Milwaukee WI, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- James, C. A Manual of Assessment Keys for Plant Diseases; American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- AACC. AACC Approved Methods of Analysis, 11th ed.; Method 56-81.04 Determination of Falling Number; Cereals & Grains Association: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, D.; Ganesh, S.; Koolaard, J. Predictmeans: Calculate Predicted Means for Linear Models. R Package Version 1.0.6. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=predictmeans (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Jiwan, S.R.; Singh, W.S. Weed composition and nutrient uptake by weeds in sole and intercrops during rabi season. Indian J. Ecol. 2021, 48, 300–303. [Google Scholar]
- da Conceição de Matos, C.; da Silva Teixeira, R.; da Silva, I.R.; Costa, M.D.; da Silva, A.A. Interspecific competition changes nutrient: Nutrient ratios of weeds and maize. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2019, 182, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainju, U.M.; Lenssen, A.W.; Barsotti, J.L. Dryland Malt Barley Yield and Quality Affected by Tillage, Cropping Sequence, and Nitrogen Fertilization. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Year | Month | Avg Temp (°C) | Departure from Avg. * | Max Temp (°C) | Departure from Avg. | Min Temp (°C) | Departure from Avg. | Total Precipitation (cm) | Departure from Avg. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | July | 21.1 | −1.3 | 32.7 | 4.0 | 11.3 | −4.8 | 8.4 | −2.1 |
| August | 21.1 | −0.3 | 32.5 | 4.6 | 11.3 | −3.7 | 6.4 | −3.9 | |
| September | 18.3 | 0.9 | 33.0 | 8.8 | 4.9 | −5.7 | 16.3 | 4.9 | |
| October | 9.2 | −1.4 | 23.3 | 6.3 | −7.4 | −11.8 | 5.6 | −7.4 | |
| November | 6.2 | 1.7 | 23.1 | 12.7 | −8.9 | −7.5 | 5.1 | −3 | |
| December | 4.0 | 4.8 | 16.4 | 12.2 | −5.5 | 0.4 | 11.9 | 1.3 | |
| 2016 | January | −2.7 | 1.6 | 11.0 | 9.7 | −15.5 | −5.5 | 3.8 | −3.7 |
| February | −1.9 | 1.3 | 14.9 | 12.0 | −26.1 | −16.8 | 10.4 | 2.4 | |
| March | 4.7 | 3.2 | 25.5 | 18.0 | −8 | −3.5 | 8.4 | 0.1 | |
| April | 7.4 | −0.8 | 26.2 | 11.2 | −11 | −12.5 | 5.3 | −4.5 | |
| May | 14.2 | −0.2 | 32.6 | 11.6 | −1.7 | −9.5 | 6.6 | −2.7 | |
| June | 19.1 | −0.2 | 30.9 | 5.5 | 5.3 | −7.7 | 3.6 | −8.7 | |
| July | 22.3 | −0.1 | 34.4 | 5.7 | 9.9 | −6.1 | 4.3 | −6.2 | |
| August | 22.2 | 0.8 | 33.6 | 5.7 | 8.9 | −6.1 | 4.6 | −5.6 | |
| September | 17.7 | 0.3 | 30.6 | 6.4 | 2.7 | −8 | 9.3 | −2 | |
| October | 10.3 | −0.4 | 23.8 | 6.9 | −4 | −8.4 | 5.4 | −7.6 | |
| November | 4.2 | −0.3 | 19.0 | 8.6 | −6.5 | −5.1 | 8.2 | 0.1 | |
| December | −1.6 | −0.7 | 11.4 | 7.2 | −19.2 | −13.3 | 7.7 | −2.9 | |
| 2017 | January | −1.3 | 3.0 | 13.6 | 12.2 | −18.7 | −8.7 | 7.0 | −0.5 |
| February | −0.3 | 2.8 | 20.8 | 17.8 | −18.6 | −9.2 | 3.8 | −4.2 | |
| March | −0.8 | −2.4 | 15.4 | 7.9 | −14.4 | −10 | 4.0 | −4.3 | |
| April | 10.2 | 2.0 | 29.0 | 14.0 | −3.7 | −5.2 | 11.1 | 1.3 | |
| May | 13.0 | −1.4 | 33.3 | 12.3 | 0.2 | −7.6 | 8.2 | −1.1 | |
| June | 18.8 | −0.4 | 34.4 | 9.0 | 4.7 | −8.3 | 11.8 | −0.5 | |
| July | 20.6 | −1.8 | 32.3 | 3.6 | 10.7 | −5.4 | 5.7 | −4.8 |
| Cover Crop Type | Cover Crop Dry Matter Yield | Cover Crop Nitrogen Content | Cover Crop Nitrogen Yield | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (t ha−1) | (g kg−1) | (kg ha−1) | ||||
| Sunn Hemp | 2.90 | a | 27.1 | b | 78.7 | a |
| Crimson Clover | 0.59 | b | 29.4 | b | 17.5 | c |
| Sunn Hemp and Crimson Clover | 2.24 | a | 25.6 | b | 57.4 | a |
| No Cover Crop | 0.87 | b | 37.3 | a | 32.5 | b |
| Overall Experiment Mean | ||||||
| 1.82 | 27.3 | 49.6 | ||||
| Effect Significance | ||||||
| Cover Crop Type | *** | * | *** | |||
| Cover Crop Type | Fall Soil Nitrate (mg kg−1) | Spring Soil Nitrate (mg kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sunn Hemp | 3.3 | a | 7.2 |
| Crimson Clover | 2.0 | b | 6.7 |
| Sunn Hemp and Crimson Clover | 2.8 | ab | 6.3 |
| No Cover Crop | 2.1 | b | 5.9 |
| Overall Experiment Mean | |||
| 2.5 | 6.5 | ||
| Effect Significance | |||
| Cover Crop Type | ** | ns | |
| Barley Seeding Rate | Barley Population (Plants m−2) | Winter Survival (Percent) | Heading Date (Julian Day) | Height (cm) | Foliar Disease | Lodging | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Percent of Plants Affected) | ||||||||
| 300 seeds m−2 | 288.5 | b | 95.3 | b | 139.9 | 54.1 | 52.5 | 10.4 |
| 350 seeds m−2 | 355.0 | a | 97.8 | ab | 139.0 | 56.6 | 47.5 | 11.8 |
| 400 seeds m−2 | 369.1 | a | 98.4 | a | 139.6 | 54.9 | 47.5 | 10.5 |
| Overall Experiment Mean | ||||||||
| 337.5 | 97.2 | 139.5 | 55.2 | 49.2 | 10.9 | |||
| Effect Significance | ||||||||
| Barley Seeding Rate | *** | ** | ns | ns | ns | ns | ||
| Cover Crop Type | Barley Seeding Rate | Grain Yield (13.5% Moisture) | Protein (0% Moisture) | Test Weight | 1000 Kernel Weight | Germinative Energy | Falling Number | DON |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (seeds m−2) | (t ha−1) | (g kg−1) | (kg hl−1) | (g) | (percent) | (seconds) | (mg kg−1) | |
| Sunn Hemp | 300 | 3.53 | 118.4 | 58.68 | 46.40 | 80.38 | 233.9 | 0.20 |
| 350 | 3.95 | 107.7 | 58.15 | 45.89 | 84.38 | 231.0 | 0.18 | |
| 400 | 3.75 | 110.0 | 58.06 | 45.55 | 79.75 | 234.4 | 0.10 | |
| Crimson Clover | 300 | 3.15 | 114.8 | 58.66 | 47.00 | 85.00 | 237.3 | 0.17 |
| 350 | 3.24 | 106.9 | 58.60 | 46.14 | 84.00 | 221.8 | 0.10 | |
| 400 | 3.77 | 114.3 | 57.90 | 46.70 | 80.00 | 227.0 | 0.20 | |
| Sunn Hemp and Crimson Clover | 300 | 3.62 | 108.5 | 59.15 | 45.73 | 81.63 | 221.5 | 0.18 |
| 350 | 3.85 | 111.0 | 58.28 | 47.13 | 89.13 | 212.1 | 0.15 | |
| 400 | 3.54 | 109.0 | 58.58 | 45.70 | 81.38 | 214.9 | 0.19 | |
| No Cover Crop | 300 | 3.25 | 112.3 | 56.57 | 46.54 | 82.00 | 230.5 | 0.05 |
| 350 | 3.23 | 111.1 | 58.85 | 46.43 | 79.38 | 211.5 | 0.15 | |
| 400 | 3.48 | 110.9 | 57.50 | 45.36 | 77.00 | 221.4 | 0.25 | |
| Cover Crop Type | ||||||||
| Sunn Hemp | 3.74 | 112.0 | 58.30 | 45.95 | 81.50 | 233.1 | 0.16 | |
| Crimson Clover | 3.39 | 111.9 | 58.39 | 46.61 | 83.00 | 228.3 | 0.15 | |
| Sunn Hemp and Crimson Clover | 3.67 | 109.5 | 58.67 | 46.18 | 84.04 | 216.2 | 0.17 | |
| No Cover Crop | 3.32 | 111.5 | 57.64 | 46.11 | 79.46 | 221.1 | 0.15 | |
| Barley Seeding Rate | ||||||||
| 300 seeds m−2 | 3.39 | 113.5 | 58.26 | 46.42 | 82.25 | 230.6 | 0.15 | |
| 350 seeds m−2 | 3.57 | 109.2 | 58.47 | 46.39 | 84.22 | 219.1 | 0.14 | |
| 400 seeds m−2 | 3.64 | 111.1 | 58.01 | 45.83 | 79.53 | 224.4 | 0.18 | |
| Overall Experiment Mean | ||||||||
| 3.53 | 111.2 | 58.25 | 46.21 | 82.00 | 224.6 | 0.16 | ||
| Effect Significance | ||||||||
| Cover Crop Type | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | * | ns | |
| Barley Seeding Rate | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Cover Crop Type × Seeding Rate | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siller, A.; Darby, H.; Smychkovich, A.; Hashemi, M. Winter Malting Barley Growth, Yield, and Quality following Leguminous Cover Crops in the Northeast United States. Nitrogen 2021, 2, 415-427. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen2040028
Siller A, Darby H, Smychkovich A, Hashemi M. Winter Malting Barley Growth, Yield, and Quality following Leguminous Cover Crops in the Northeast United States. Nitrogen. 2021; 2(4):415-427. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen2040028
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiller, Arthur, Heather Darby, Alexandra Smychkovich, and Masoud Hashemi. 2021. "Winter Malting Barley Growth, Yield, and Quality following Leguminous Cover Crops in the Northeast United States" Nitrogen 2, no. 4: 415-427. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen2040028
APA StyleSiller, A., Darby, H., Smychkovich, A., & Hashemi, M. (2021). Winter Malting Barley Growth, Yield, and Quality following Leguminous Cover Crops in the Northeast United States. Nitrogen, 2(4), 415-427. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen2040028







