Influence of Nitrogen Fertilization Rate on Soil Respiration: A Study Using a Rapid Soil Respiration Assay
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
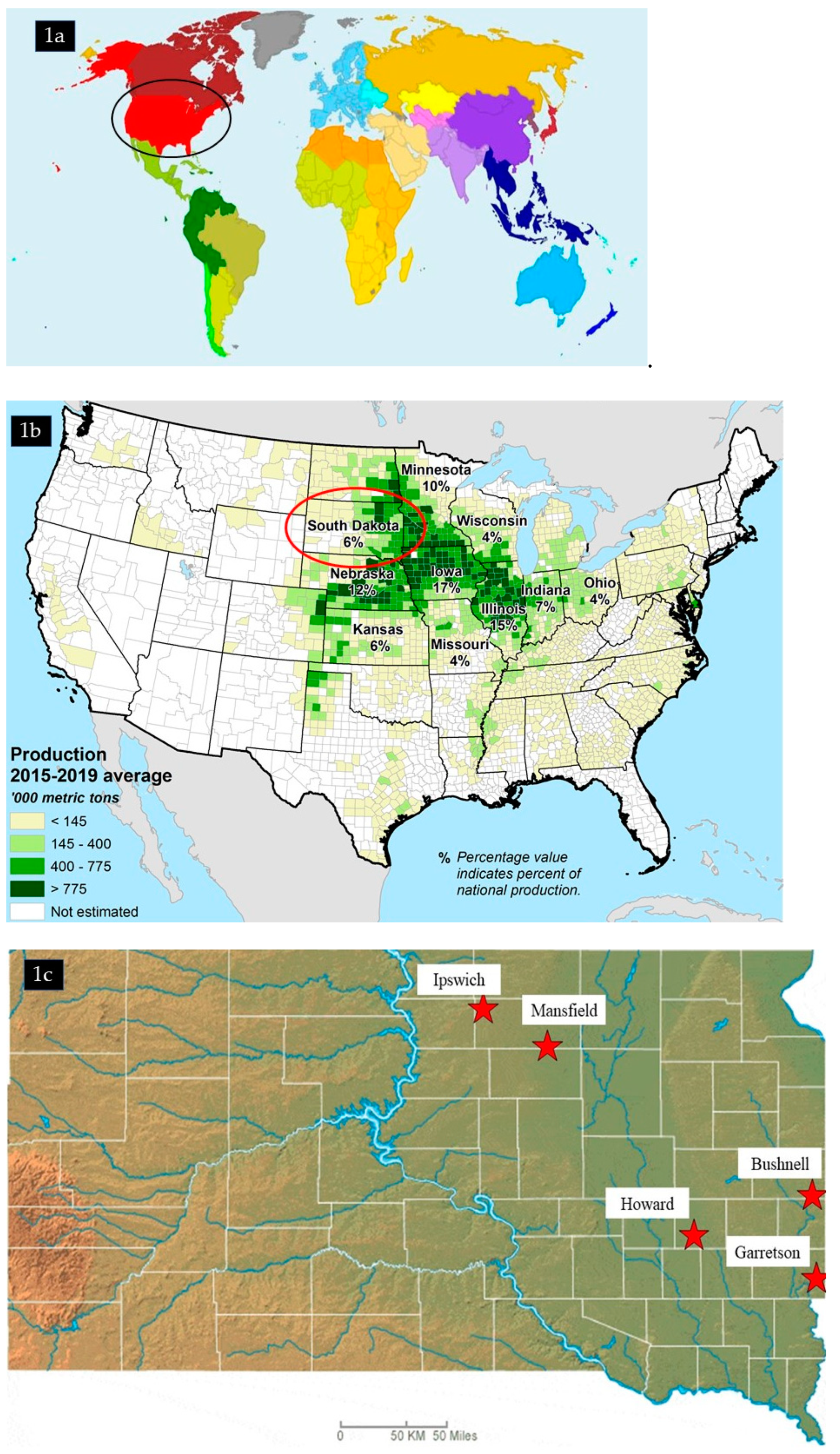
2.1. Study Sites and Experimental Design
2.2. Incubation Study and Measuring Soil Respiration
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparison between CASH Protocol and Haney Method
3.2. Impact of Nitrogen Fertilizer Application Rates on Soil Respiration
3.3. Corn Grain yield and Nitrogen Application Rate
3.4. Soil Respiration Rate and Corn Grain yield
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, X.-B.; Li, Y.-N.; Du, Y.-D. Optimized nitrogen fertilizer application improves yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies of winter rapeseed cultivated under continuous ridges with film mulching. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 109, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhen, X.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Qian, B.; et al. Timing and splitting of nitrogen fertilizer supply to increase crop yield and efficiency of nitrogen utilization in a wheat–peanut relay intercropping system in China. Crop. J. 2019, 7, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, P.; Ding, W.; Ullah, S.; Abbas, T.; Li, M.; Ai, C.; Zhou, W. Identifying the critical nitrogen fertilizer rate for optimum yield and minimum nitrate leaching in a typical field radish cropping system in China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baethgen, W.E.; Alley, M.M. Optimizing Soil and Fertilizer Nitrogen Use by Intensively Managed Winter Wheat. II. Critical Levels and Optimum Rates of Nitrogen Fertilizer. Agron. J. 1989, 81, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miner, G.; Delgado, J.; Ippolito, J.; Stewart, C.; Manter, D.; Del Grosso, S.; Floyd, B.; D’Adamo, R. Assessing manure and inorganic nitrogen fertilization impacts on soil health, crop productivity, and crop quality in a continuous maize agroecosystem. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 75, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, P.; Aula, L.; Oyebiyi, F.; Raun, W.R. World Cereal Nitrogen Use Efficiency Trends: Review and Current Knowledge. age 2019, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Searchinger, T.D.; Zhou, M.; Pan, D.; Yang, J.; Wu, L.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F.; et al. Air quality, nitrogen use efficiency and food security in China are improved by cost-effective agricultural nitrogen management. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassman, K.G.; Dobermann, A.; Walters, D.T. Agroecosystems, Nitrogen-Use Efficiency, and Nitrogen Management. Ambio 2002, 31, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Swaney, D.P.; Hong, B.; Howarth, R.W.; Li, X. Influence of rapid rural-urban population migration on riverine nitrogen pollution: perspective from ammonia-nitrogen. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 27201–27214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piikki, K.; Stenberg, B. A modified delta yield approach for estimation of economic optimal nitrogen rate (EONR) for wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Agric. Food Sci. 2017, 26, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Miao, Y.; Dong, R.; Chen, Z.; Kusnierek, K.; Mi, G.; Mulla, D.J. Economic Optimal Nitrogen Rate Variability of Maize in Response to Soil and Weather Conditions: Implications for Site-Specific Nitrogen Management. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.K.; Bali, S.K. A Review of Methods to Improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Agriculture. Sustainability 2017, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, G.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Zhao, S.; Wang, C.; Kuypers, M.M.M.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Zhu, Y. Microbial pathways for nitrogen loss in an upland soil. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 1723–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietema, A. Microbial carbon and nitrogen dynamics in coniferous forest floor material collected along a European nitrogen deposition gradient. For. Ecol. Manag. 1998, 101, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Lin, G. Differential responses of auto- and heterotrophic soil respiration to water and nitrogen addition in a semiarid temperate steppe. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 16, 2345–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Dong, Y.; Qi, Y.; Xiao, S.; He, Y.; Ma, T. Effects of nitrogen fertilization on soil respiration in temperate grassland in Inner Mongolia, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 62, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Niu, D.; Hall, S.J.; Wen, H.; Li, X.; Fu, H.; Wan, C.; Elser, J.J. Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on soil respiration components and their temperature sensitivities in a semiarid grassland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Gong, J.; Zhai, Z.; Pan, Y.; Liu, M.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Baoyin, T.-T. The responses of soil respiration to nitrogen addition in a temperate grassland in northern China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1466–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aber, J.D.; Nadelhoffer, K.J.; Steudler, P.; Melillo, J.M. Nitrogen Saturation in Northern Forest Ecosystems. BioScience 1989, 39, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culman, S.W.; Snapp, S.S.; Freeman, M.A.; Schipanski, M.E.; Beniston, J.; Lal, R.; Drinkwater, L.E.; Franzluebbers, A.J.; Glover, J.D.; Grandy, A.S.; et al. Permanganate Oxidizable Carbon Reflects a Processed Soil Fraction that is Sensitive to Management. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurisso, T.T.; Culman, S.W.; Horwath, W.R.; Wade, J.; Cass, D.; Beniston, J.W.; Bowles, T.M.; Grandy, A.S.; Franzluebbers, A.J.; Schipanski, M.E.; et al. Comparison of Permanganate-Oxidizable Carbon and Mineralizable Carbon for Assessment of Organic Matter Stabilization and Mineralization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2016, 80, 1352–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.R.; Stine, M.A.; Gruver, J.B.; Samson-Liebig, S.E.; Weil, R.R. Estimating active carbon for soil quality assessment: A simplified method for laboratory and field use. Am. J. Altern. Agric. 2003, 18, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Bean, G.; Kitchen, N.R.; Veum, K.S.; Camberato, J.J.; Ferguson, R.B.; Fernandez, F.G.; Franzen, D.W.; Laboski, C.A.; Nafziger, E.D.; Sawyer, J.E.; et al. Relating four-day soil respiration to corn nitrogen fertilizer needs across 49 U.S. Midwest fields. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 1195–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R. Soil Organic Matter Pools and Their Associations with Carbon Mineralization Kinetics. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H.; Andrews, J.A. Soil respiration and the global carbon cycle. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micks, P.; Aber, J.D.; Boone, R.D.; A Davidson, E. Short-term soil respiration and nitrogen immobilization response to nitrogen applications in control and nitrogen-enriched temperate forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 196, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS). United Sates Acreage. 2020. Available online: https://www.fsa.usda.gov/news-room/efoia/electronic-reading-room/frequently-requested-information/crop-acreage-data/index (accessed on 26 April 2021).
- Sanyal, D.; Wolthuizen, J.; Karl, D.; Bly, A. Cover Crops Influence Soil Health, Nutrient Cycling, and Crop Yield in South Dakota. In Embracing the Digital Environment 2019 ASA-CSSA-SSSA International Annual Meeting, San Antonio, TX, USA, 10–13 November 2019; ASA-CSSA-SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Moebius-Clune, D. Cornell Soil Health Assessment for Quantification of Soil Respiration. 2016. p CSH 06. Available online: https://cpb-us-e1.wpmucdn.com/blogs.cornell.edu/dist/f/5772/files/2015/03/CASH-Standard-Operating-Procedures-030217final-u8hmwf.pdf (accessed on 26 April 2021).
- Wang, J.; Sainju, U.M. Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Fractions and Crop Yields Affected by Residue Placement and Crop Types. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; 2020; Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/indicators/oxygen-consuming-substances-in-rivers/r-development-core-team-2006 (accessed on 26 April 2021).
- Royston, P. Remark AS R94: A Remark on Algorithm AS 181: The W-test for Normality. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Applied Stat.) 1995, 44, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. lmerTest Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pregitzer, K.S.; Zak, D.R.; Maziasz, J.; Deforest, J.; Curtis, P.S.; Lussenhop, J. Interactive Effects of Atmospheric CO2 and Soil-N Availability on Fine Roots of Populus tremuloides. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, A.J.; Pregitzer, K.S.; Ruess, R.W.; Hendrick, R.L.; Allen, M.F. Root respiration in North American forests: Effects of nitrogen concentration and temperature across biomes. Oecologia 2002, 131, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, R.D.; Davidson, E.; Savage, K.; Arabia, C.; Steudler, P. Chronic nitrogen additions reduce total soil respiration and microbial respiration in temperate forest soils at the Harvard Forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 196, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-H.; Jose, S. Soil respiration, fine root production, and microbial biomass in cottonwood and loblolly pine plantations along a nitrogen fertilization gradient. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 185, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, W.; Gundersen, P.; Fang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, H. Nitrogen addition reduces soil respiration in a mature tropical forest in southern China. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2007, 14, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, K.S.; Craine, J.M.; Fierer, N. Nitrogen fertilization inhibits soil microbial respiration regardless of the form of nitrogen applied. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 2336–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Liu, L.; Ma, Y.; Yin, G.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Piao, S. The effect of nitrogen addition on soil respiration from a nitrogen-limited forest soil. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 197, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, P.; Han, C.-R.; Groffman, P. Soil respiration in conventional and no-tillage agroecosystems under different winter cover crop rotations. Soil Tillage Res. 1988, 12, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokela, W.E.; Randall, G.W. Corn Yield and Residual Soil Nitrate as Affected by Time and Rate of Nitrogen Application. Agron. J. 1989, 81, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamhoseini, M.; Aghaalikhani, M.; Sanavy, S.M.; Mirlatifi, S. Interactions of irrigation, weed and nitrogen on corn yield, nitrogen use efficiency and nitrate leaching. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 126, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Bushnell | Garretson | Howard | Ipswich | Mansfield |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tillage practice | Conventional | No-till | No-till | No-till | No-till |
| Grazing history | No | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Total precipitation (mm, May–Sep) | 608 | 538 | 567 | 484 | 484 |
| Soil pH | 5.5 | 5.3 | 5.7 | 6.4 | 6.1 |
| Electrical conductivity (mS cm−1) | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Soil organic matter (%) | 3.3 | 3.7 | 5.5 | 5.3 | 4.0 |
| Soil nitrate (kg ha−1, 0–60 cm) | 29 | 28 | 117 | 61 | 68 |
| Available phosphorus (ppm, 0–15 cm) | 13 | 12 | 12 | 24 | 6.3 |
| Available potassium (ppm 0–15 cm) | 94 | 120 | 172 | 273 | 261 |
| Soil sulfate (kg ha−1, 0–60 cm) | 60 | 55 | 19 | 53 | 70 |
| Date of planting | 5/8/2019 | 5/18/2019 | 5/12/2019 | 5/14/2019 | 5/8/2019 |
| Date of fertilization | 5/3/19 | 5/16/2019 | 5/16/2019 | 5/3/2019 | 5/3/2019 |
| Date of soil (Corn V6 stage) sampling | 6/19/2019 | 6/25/2019 | 6/24/2019 | 6/18/2019 | 6/18/2019 |
| Date of harvest | 11/12/2019 | 11/08/2019 | Not harvested | 11/16/2019 | 11/16/2019 |
| Locations | Nitrogen Rates | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 kg N ha−1 | 45 kg N ha−1 | 90 kg N ha−1 | 180 kg N ha−1 | Mean (Location) | ||
| Bushnell | 1.20 (0.17) | 1.52 (0.17) | 1.55 (0.12) | 1.54 (0.13) | 1.45D | |
| Garretson | 1.43 (0.08) | 1.50 (0.08) | 1.58 (0.19) | 1.61 (0.09) | 1.53CD | |
| Howard | 1.85 (0.37) | 1.65 (0.19) | 1.84 (0.16) | 1.85 (0.20) | 1.80B | |
| Ipswich | 1.88 (0.22) | 1.85 (0.11) | 2.03 (0.10) | 1.99 (0.15) | 1.94A | |
| Mansfield | 1.65 (0.14) | 1.49 (0.04) | 1.65 (0.08) | 1.76 (0.18) | 1.64C | |
| Mean (N rate) | 1.60b | 1.60b | 1.73a | 1.75a | ||
| p-values | Nitrogen rate Location Nitrogen rate × Location | 0.01615 1.745 × 10−9 0.55176 | ||||
| Locations | Corn Yield (Mg ha−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 kg N ha−1 | 45 kg N ha−1 | 90 kg N ha−1 | 180 kg N ha−1 | Mean (Location) | ||
| Bushnell | 10.9 (1.4) | 11.3 (2.3) | 11.2 (1.2) | 12.7 (0.7) | 11.5A | |
| Garretson | 9.61 (2.2) | 9.93 (2.2) | 10.1 (0.5) | 10.5 (1.4) | 10.0B | |
| Ipswich | 4.87 (0.7)) | 5.18 (1.4) | 6.43 (0.8) | 6.62 (0.6) | 5.8C | |
| Mansfield | 11.9 (0.8) | 12.2 (0.8) | 12.7 (0.2) | 12.9 (0.3) | 12.4A | |
| Mean (N rate) | 9.31b | 9.67ab | 10.1ab | 10.7a | ||
| p-values | N rate Location N rate × Location | 0.881 1.868 × 10−14 0.991 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanyal, D.; Wolthuizen, J.; Bly, A. Influence of Nitrogen Fertilization Rate on Soil Respiration: A Study Using a Rapid Soil Respiration Assay. Nitrogen 2021, 2, 218-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen2020014
Sanyal D, Wolthuizen J, Bly A. Influence of Nitrogen Fertilization Rate on Soil Respiration: A Study Using a Rapid Soil Respiration Assay. Nitrogen. 2021; 2(2):218-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen2020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanyal, Debankur, Johnathon Wolthuizen, and Anthony Bly. 2021. "Influence of Nitrogen Fertilization Rate on Soil Respiration: A Study Using a Rapid Soil Respiration Assay" Nitrogen 2, no. 2: 218-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen2020014
APA StyleSanyal, D., Wolthuizen, J., & Bly, A. (2021). Influence of Nitrogen Fertilization Rate on Soil Respiration: A Study Using a Rapid Soil Respiration Assay. Nitrogen, 2(2), 218-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nitrogen2020014






