Effect of Particle Size on Pore Structure and Fractal Characteristics of Deep Siliceous Shales in Southern Sichuan, China, Measured Using Small-Angle Neutron Scattering and Low-Pressure Nitrogen Adsorption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Shale Samples and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. SANS Experiment
2.2.2. LP-N2GA Experiment
2.2.3. LP-CO2GA Experiment
3. Results
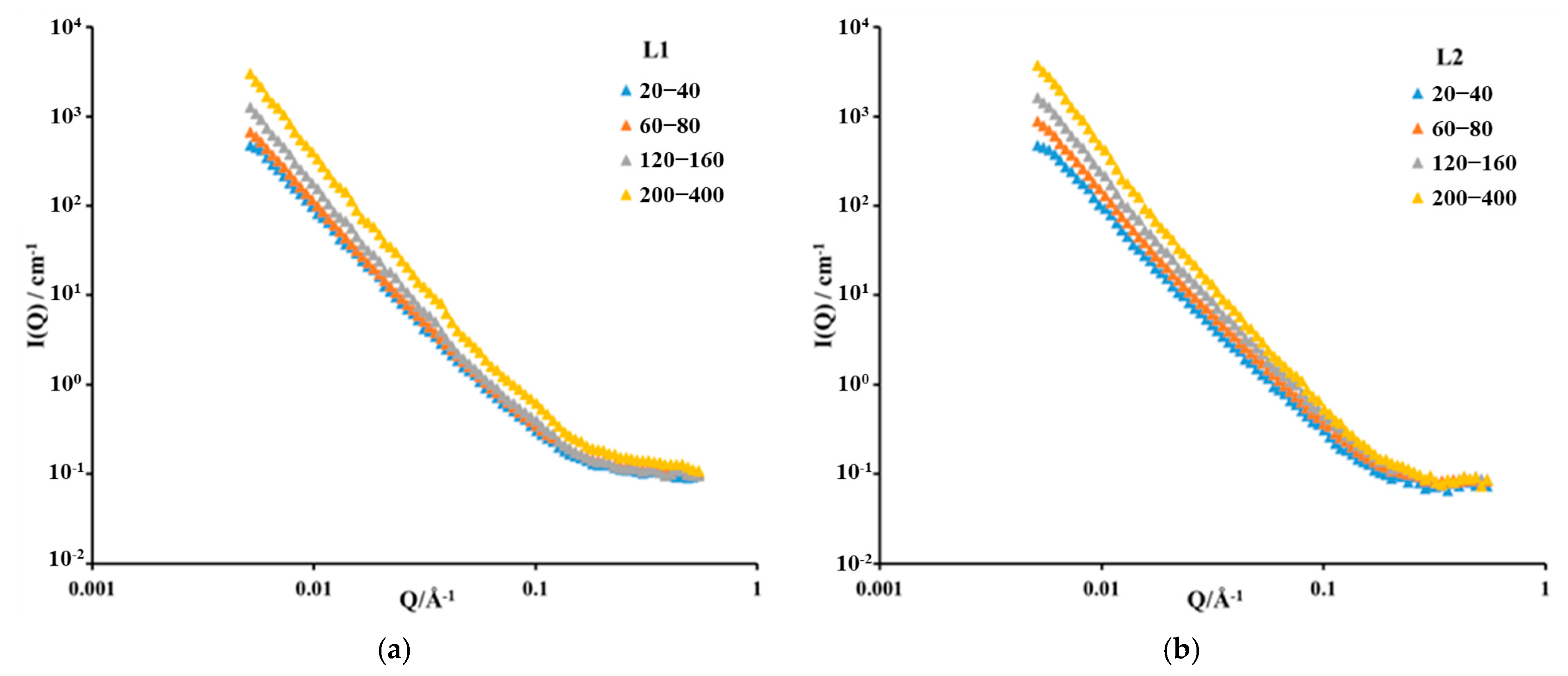
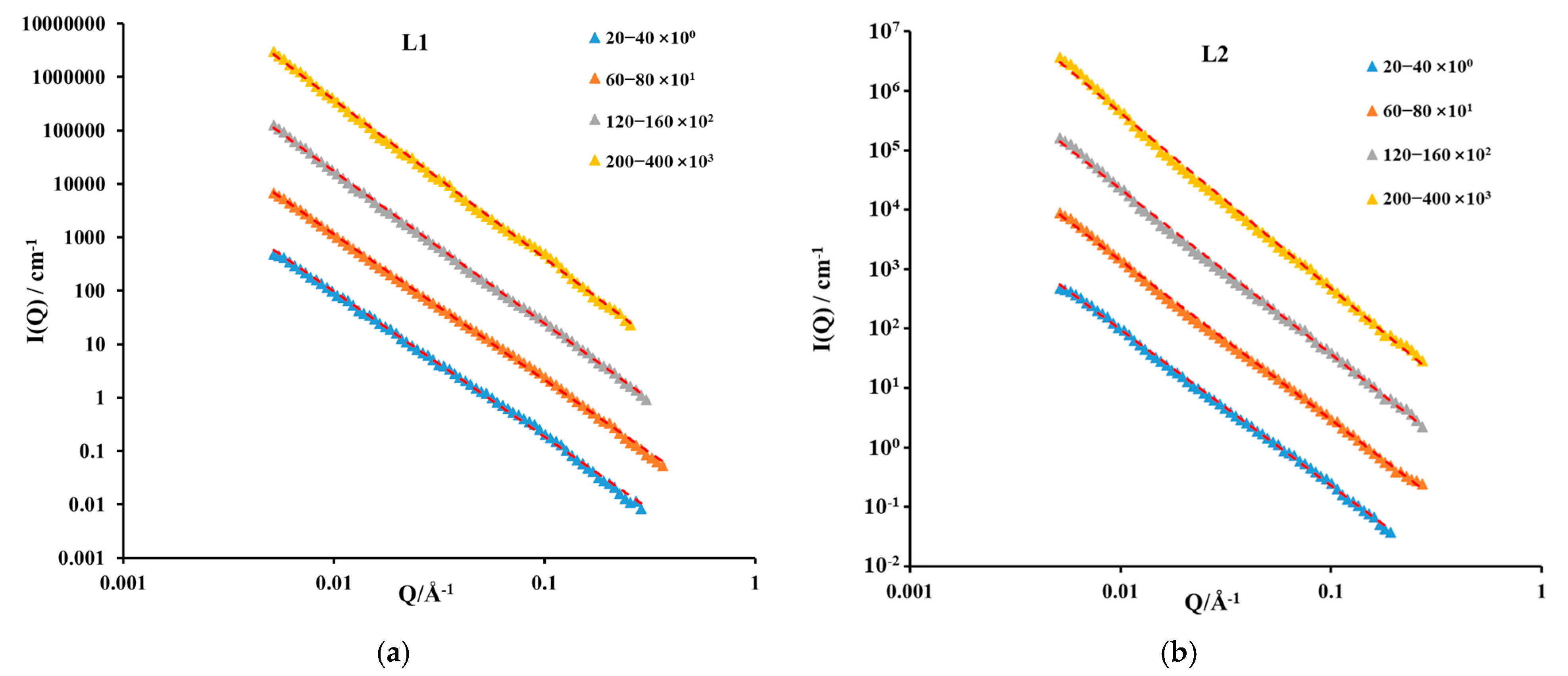
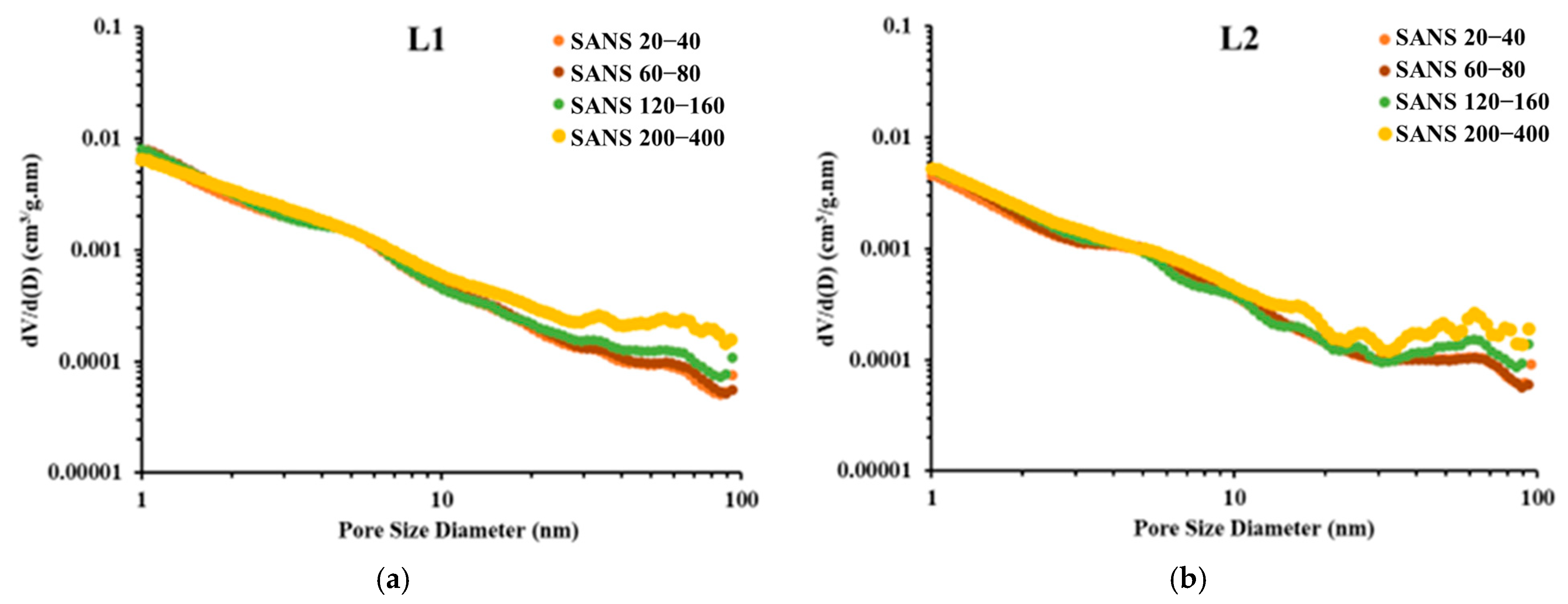
3.1. Experimental Results of SANS
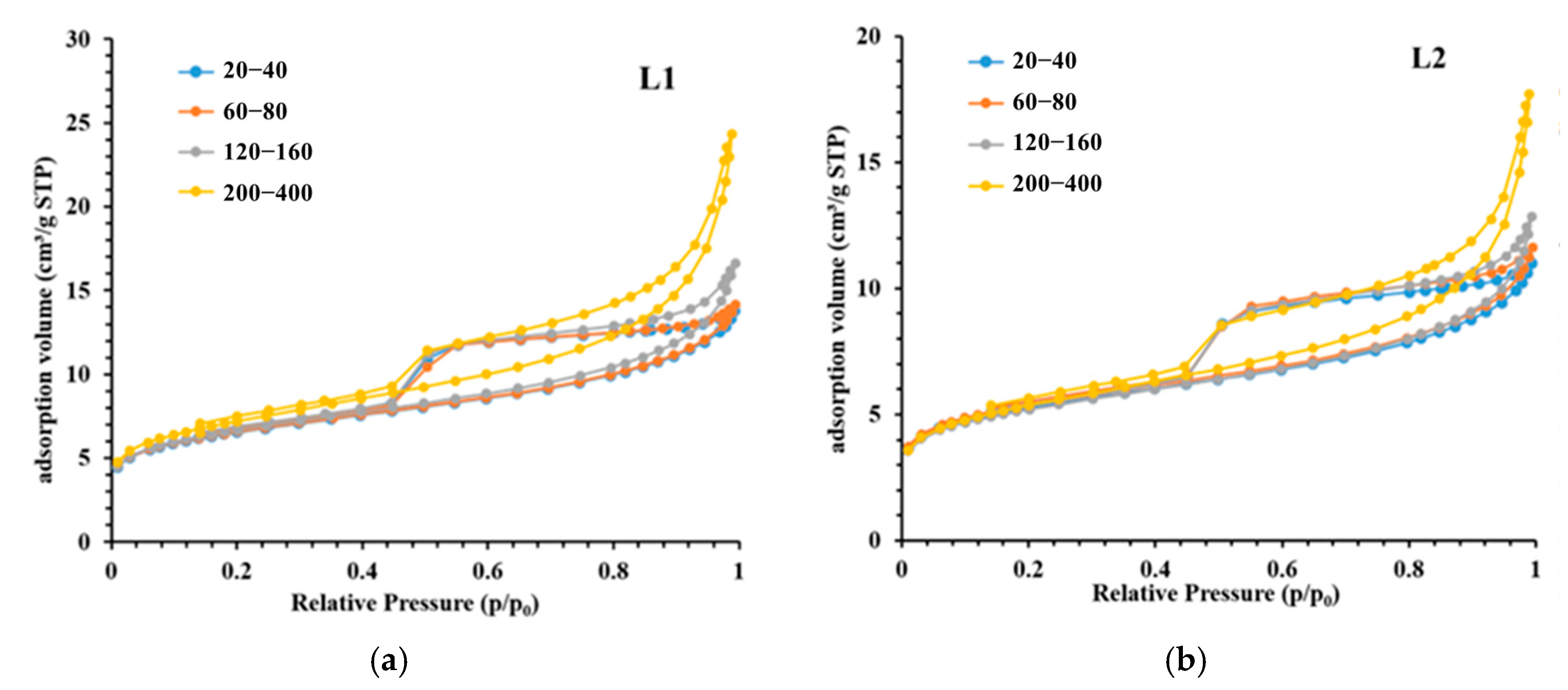
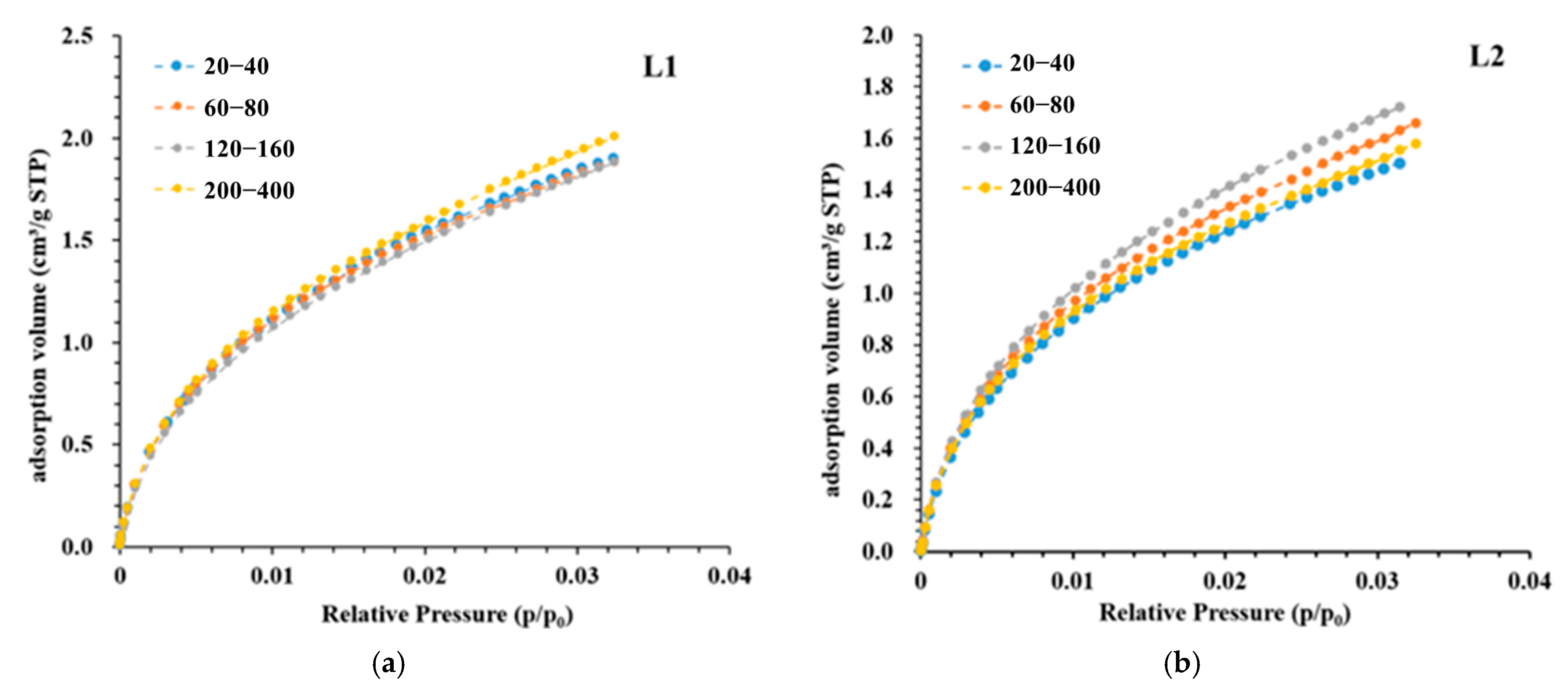
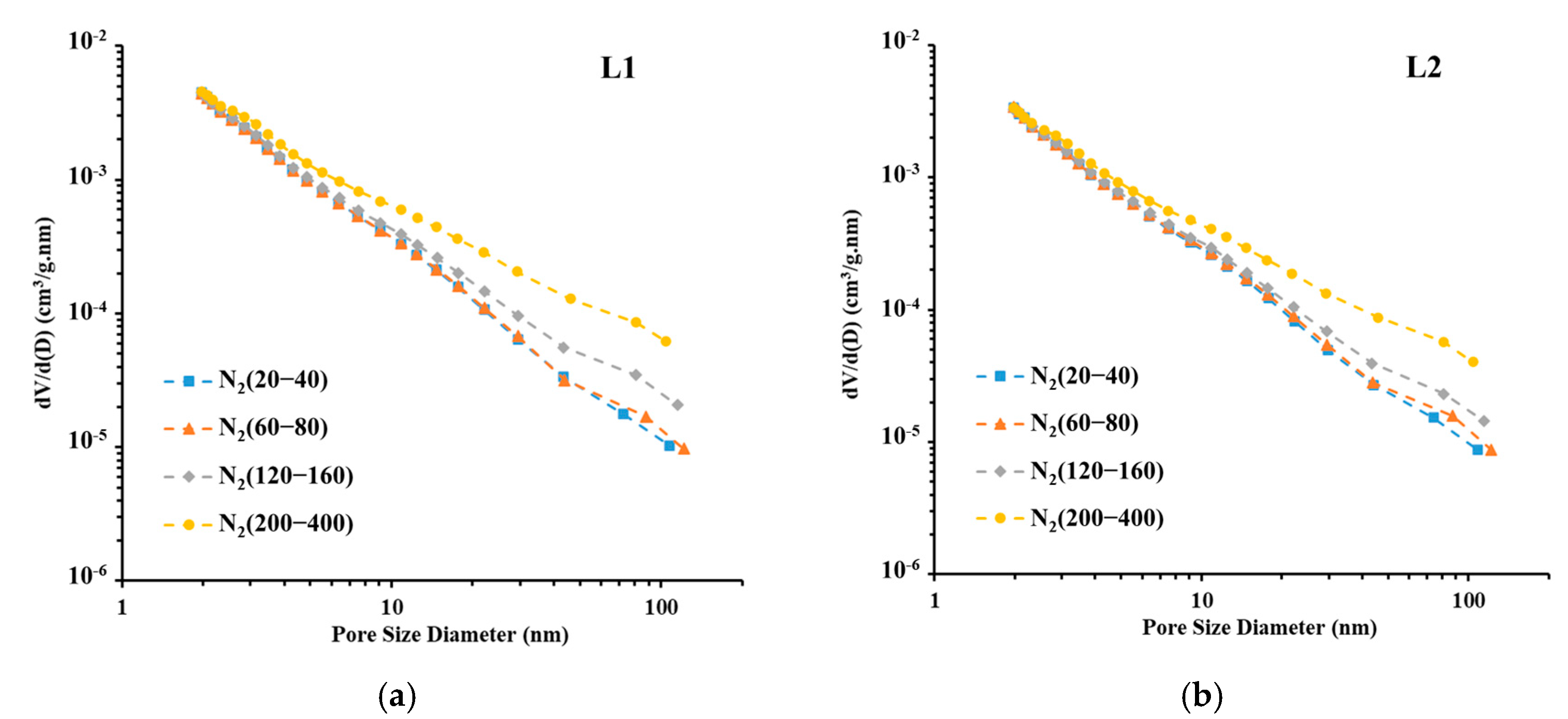
3.2. Experimental Results of LPGA
4. Discussion
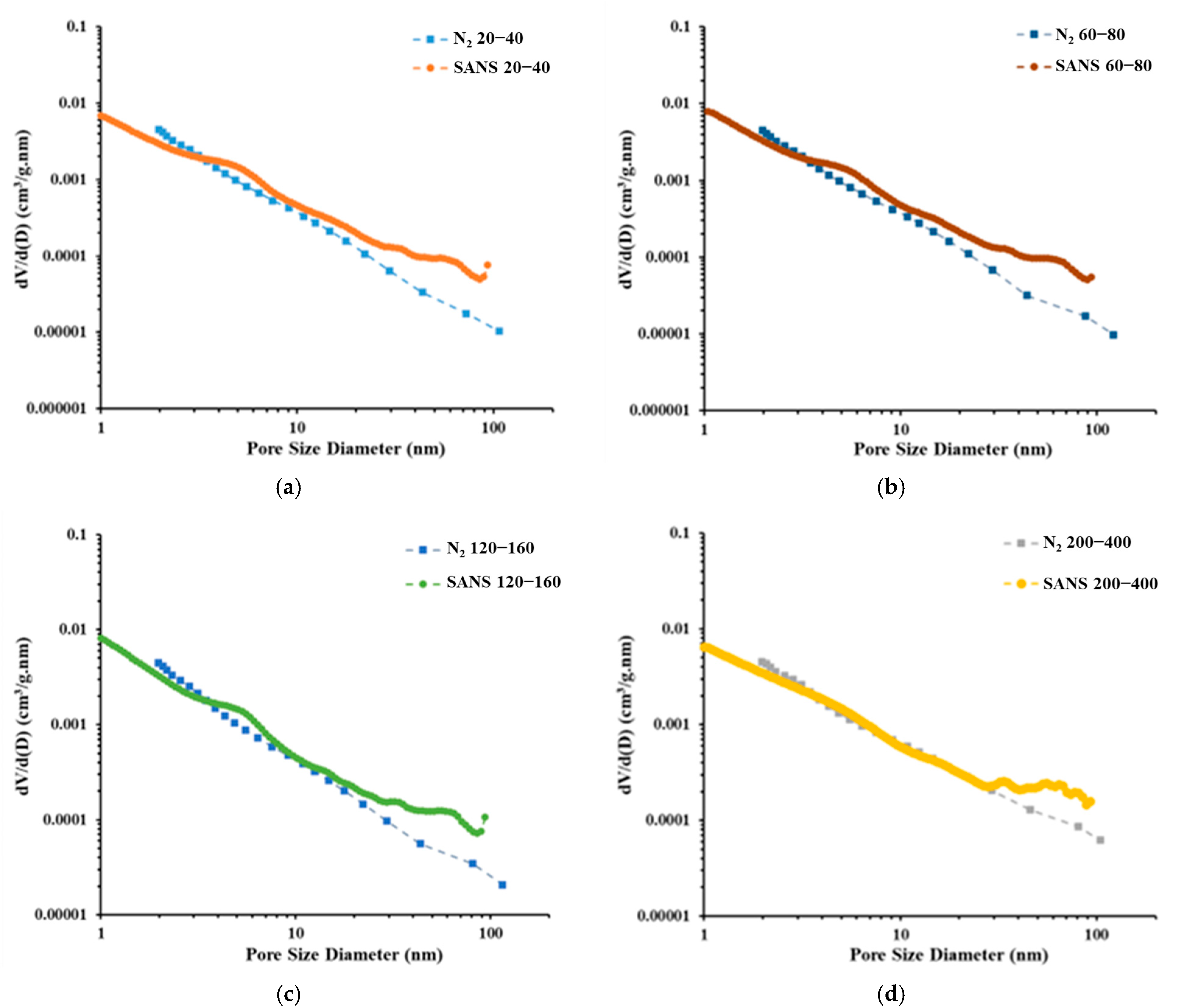
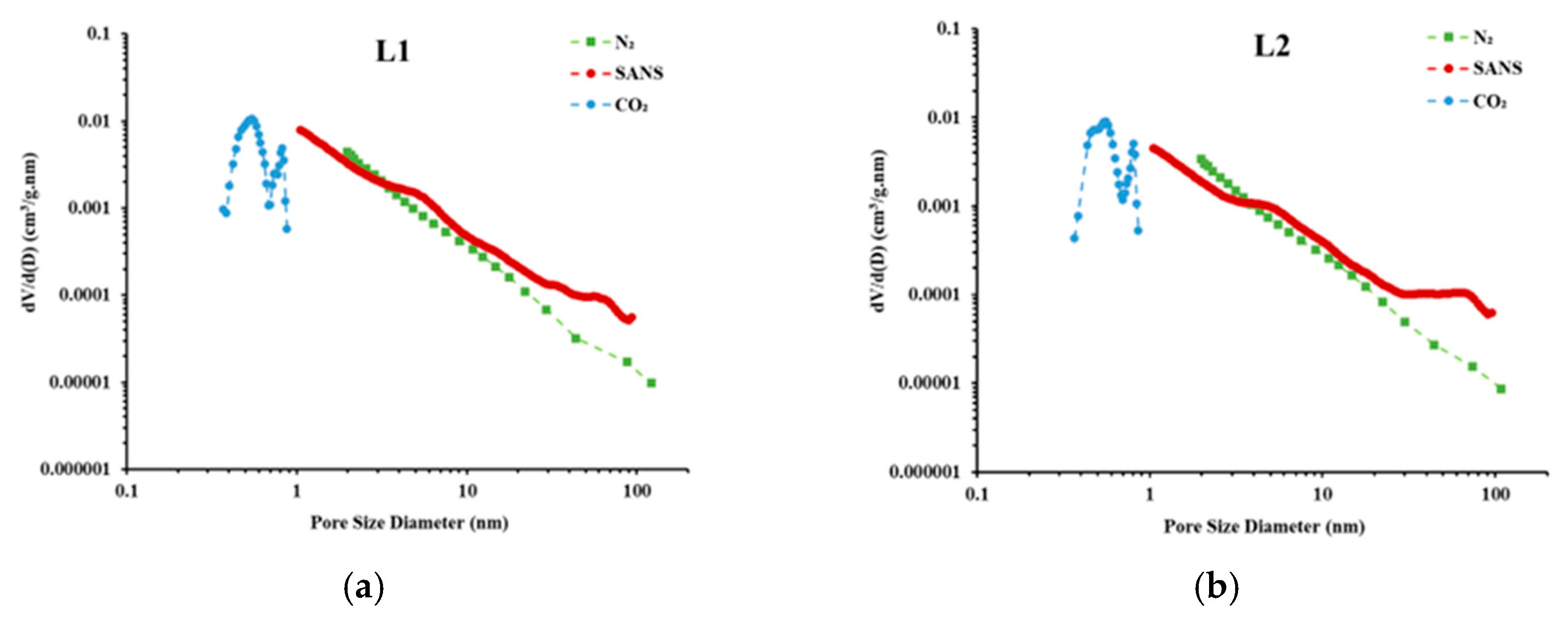
4.1. Porosity and PSD Analysis
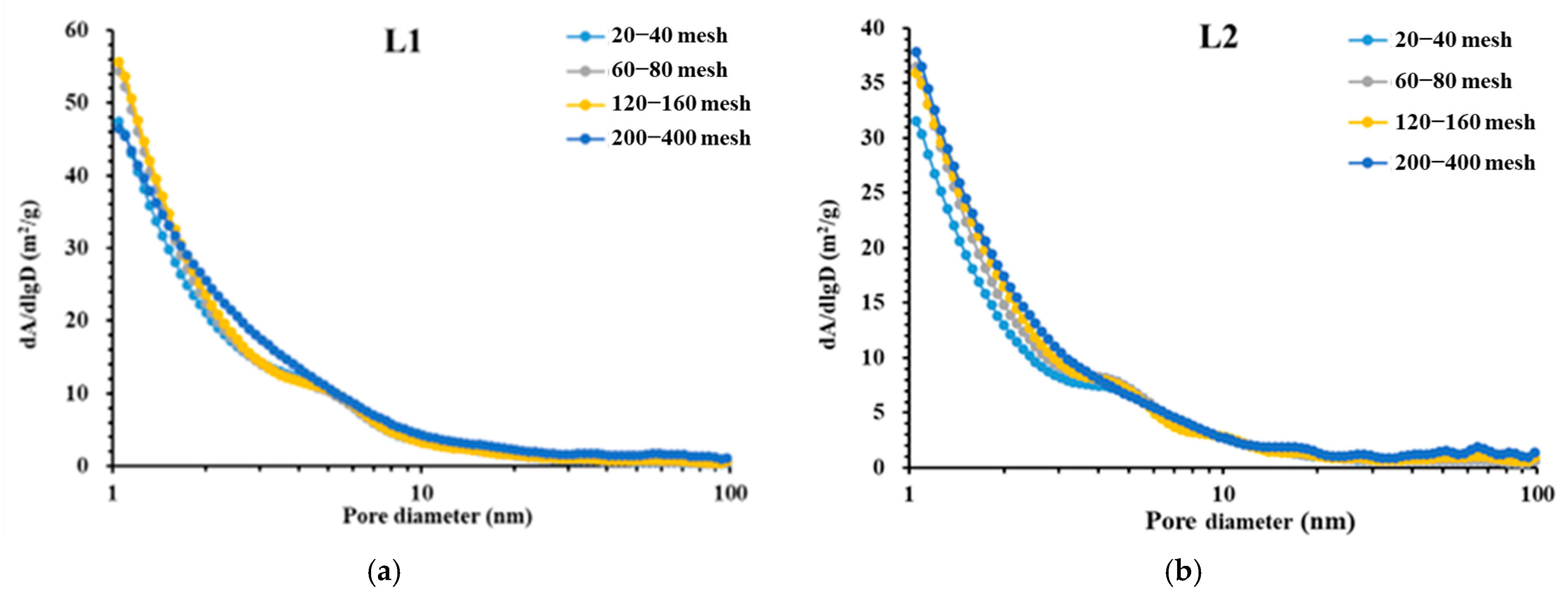
4.2. Specific Surface Area Analysis
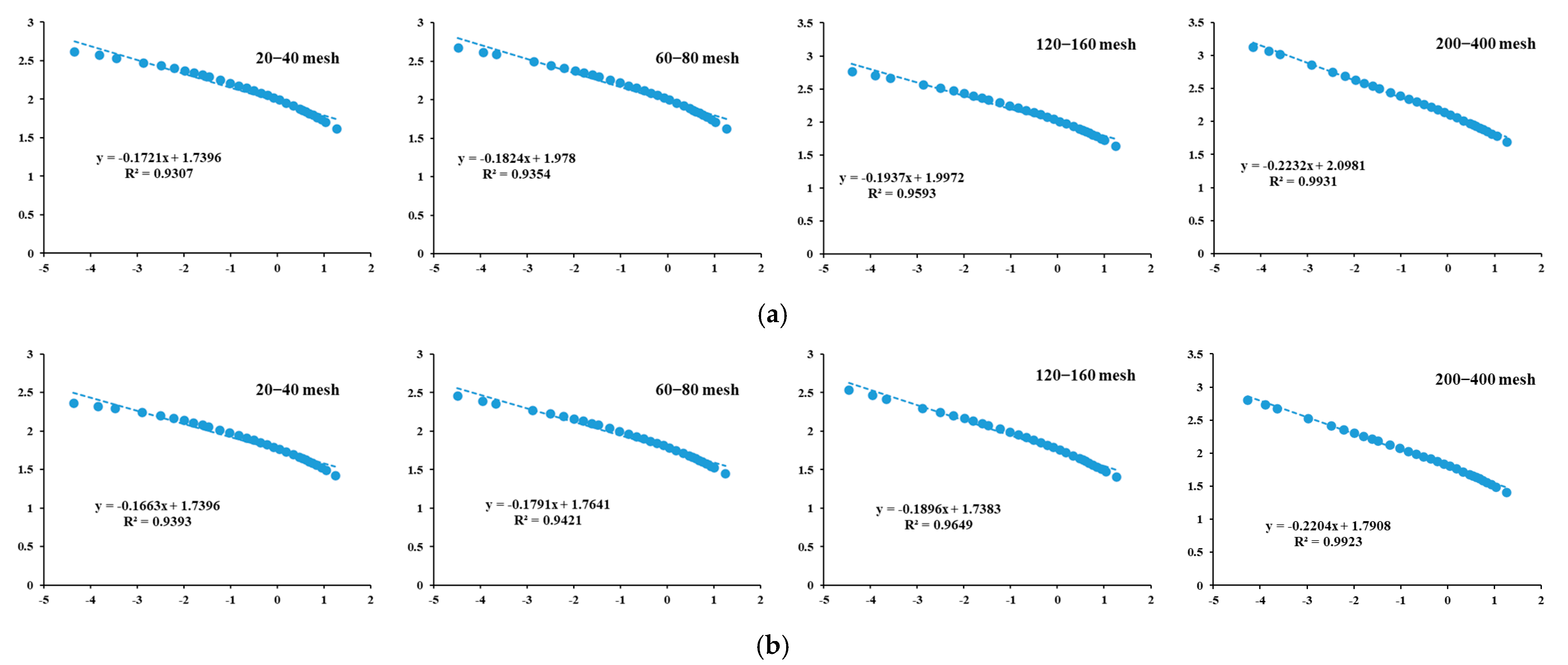
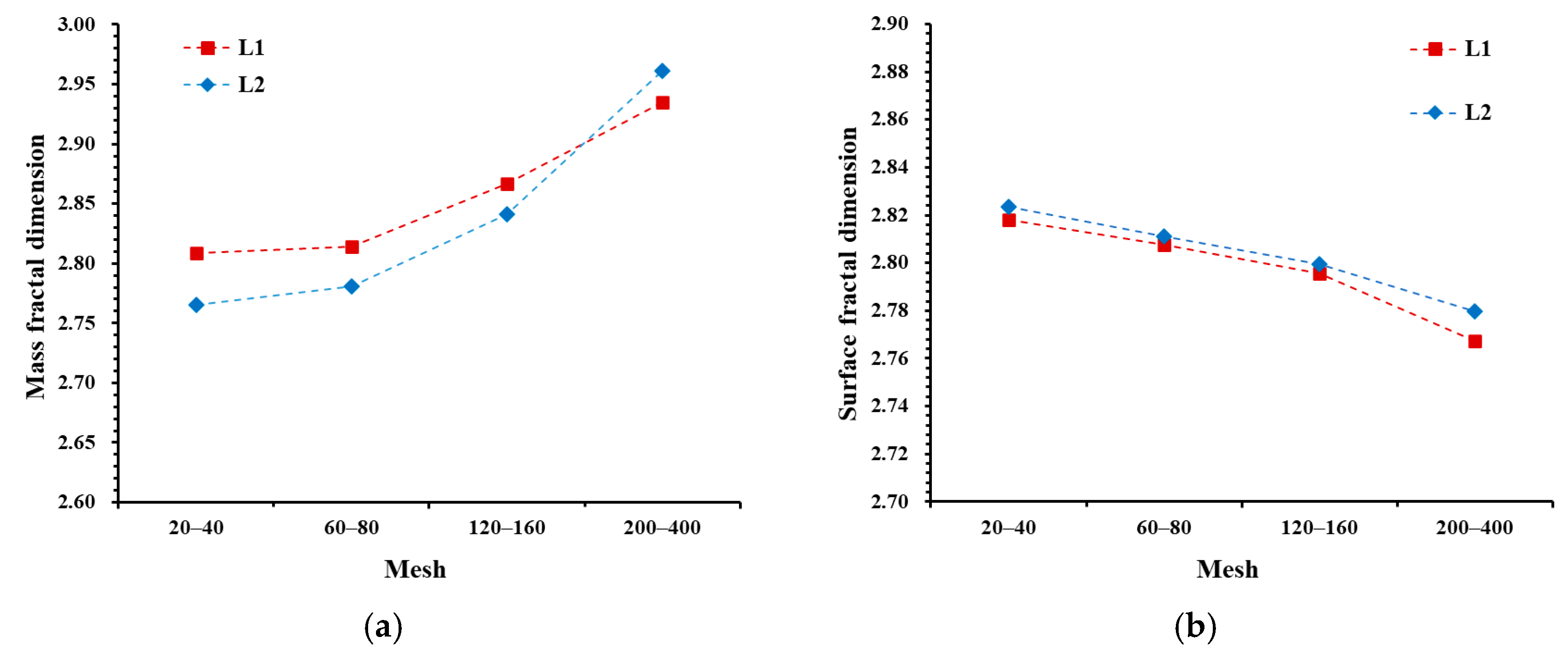
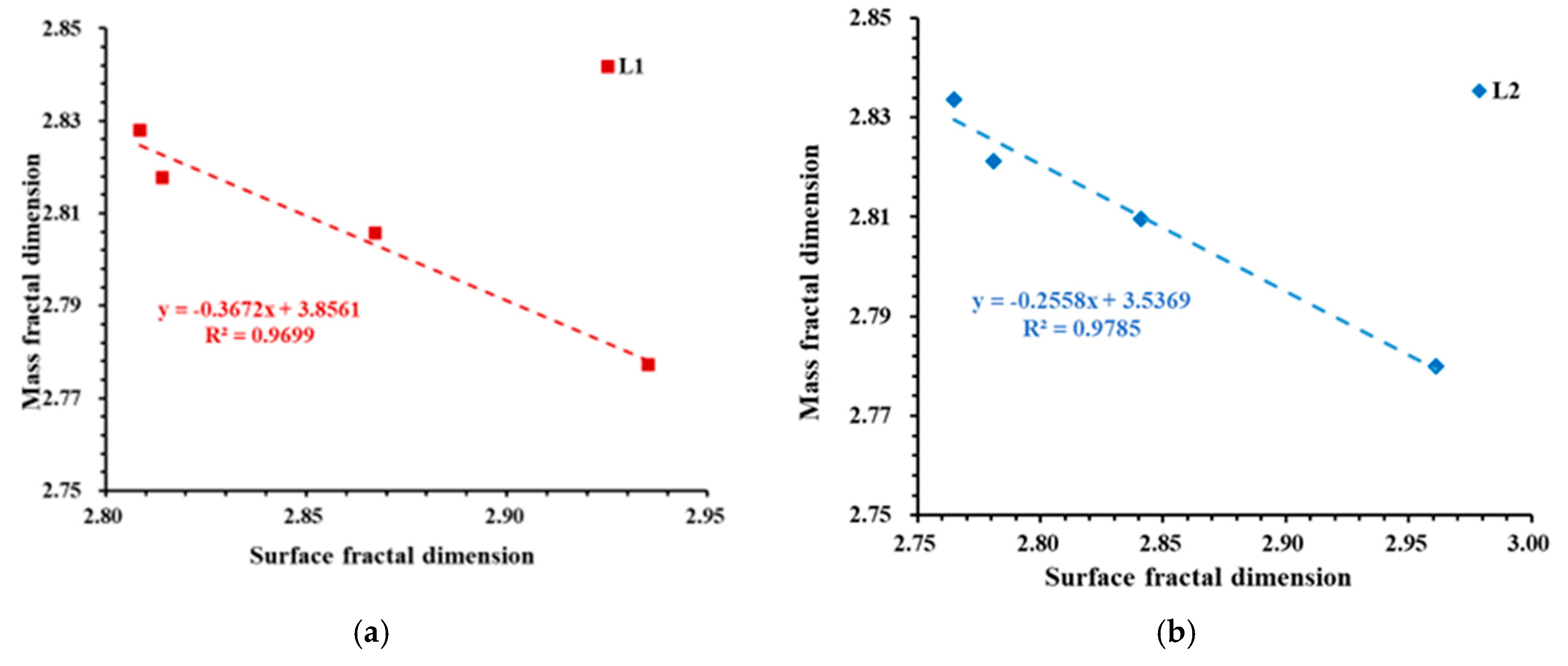
4.3. Fractal Dimension Analysis
4.4. Experimental Errors and Prospects
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Particle size significantly influences the pore volume measured using LP-N2GA. The pore volume of the 200–400-mesh shale samples is 1.86 times that of the 20–40-mesh samples, primarily due to the increase in mesopores and macropores. However, particle size has no significant effect on the pore volume measured using LP-CO2GA. This indicates that when the sample is crushed to 400 mesh, the crushing process does not alter the micropore structure.
- (2)
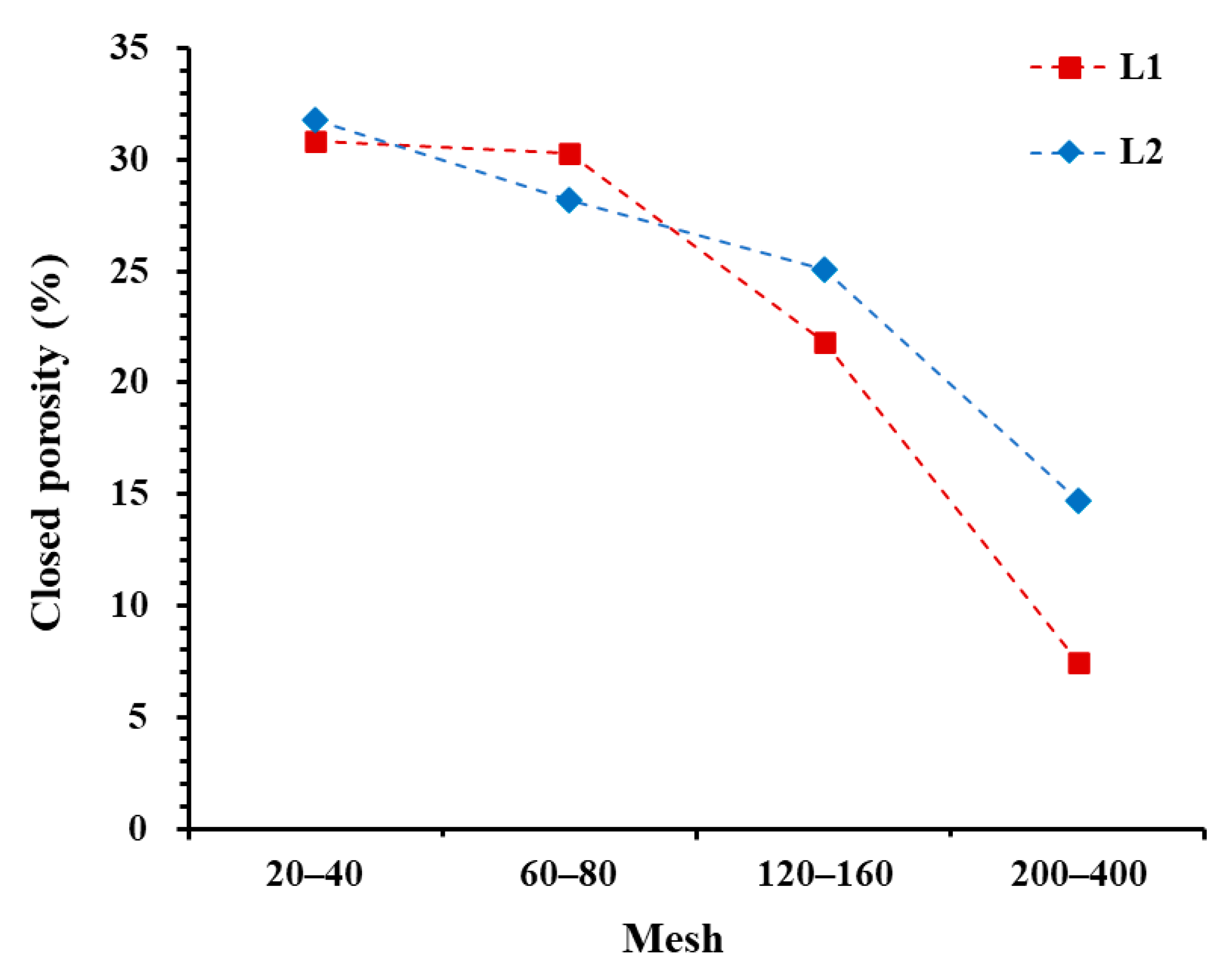
- Increased crushing leads to the continuous generation of new artificial pores. Compared to the 20–40-mesh samples, the 200–400-mesh shale samples with high brittle mineral content generate 58% more artificial pores. However, connectivity does not improve in the early stages of crushing. The closed porosity of the 120–160-mesh samples is only reduced by an average of 7.86% compared to the 20–40-mesh samples. When the particle size reaches 200–400 mesh, the closed porosity decreases significantly, leading to an effective improvement in connectivity. Therefore, to ensure the accuracy of shale pore structure, it is recommended to use 60–80-mesh samples for experiments using powder samples.
- (3)
- Crushing has a minor impact on the SSA of deep shale. The total SSA of the 200–400-mesh samples is only 16.5% higher on average than that of the 20–40-mesh samples. The SSA of deep shale is mainly contributed by micropores (pore diameter < 2 nm), which account for an average of 55.35% of the total SSA.
- (4)
- The mass fractal dimension of deep shale samples increases as particle size decreases. Compared to the 20–40-mesh samples, the mass fractal dimension of the 200–400-mesh samples increases by an average of 10.12%. Therefore, analyses based on small-particle shale samples may overestimate the mass fractal dimension of shale, thereby overestimating the heterogeneity of the shale PSD.
- (5)
- As particle size decreases, more macropores are generated, and the surface of macropores is smoother than that of micropores and mesopores. Consequently, the surface fractal dimension of deep shale samples decreases with decreasing particle size.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SANS | small-angle neutron scattering |
| LP-N2GA | low-pressure nitrogen gas adsorption |
| LP-CO2GA | low-pressure carbon dioxide gas adsorption |
| LPGA | low-pressure gas adsorption |
| CSNS | China Spallation Neutron Source |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller |
| DFT | density functional theory |
| SLD | scattering length density |
| TOC | total organic carbon |
| PSDM | polydisperse size distribution model |
| PSD | pore size distribution |
| SSA | specific surface area |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- Vidic, R.D.; Brantley, S.L.; Vandenbossche, J.M.; Yoxtheimer, D.; Abad, J.D. Impact of shale gas development on regional water quality. Science 2013, 340, 1235009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.H.; Zhang, X.W.; Xiong, W.; Liu, Y.Y.; Gao, J.L.; Yu, R.Z.; Sun, Y.P.; Wu, J.; Kang, L.X.; Zhao, S.P. Prospects and challenges of shale gas development in China. Pet. Sci. Bulletin 2023, 4, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Pan, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, F.; Han, L.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, H.; Li, W. Study on the effect of cemented natural fractures on hydraulic fracture propagation in volcanic reservoirs. Energy 2022, 241, 122845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Guo, M.; Zhao, P. Characteristics of pore structure and gas content of the lower Paleozoic shale from the Upper Yangtze plate, south China. Energies 2021, 14, 7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, T.; Wiggins-Camacho, J.D.; Ellis, G.S.; Lewan, M.D.; Zhang, X. Experimental investigation of changes in methane adsorption of bitumen-free Woodford Shale with thermal maturation induced by hydrous pyrolysis. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 59, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Xiong, J.; Liu, X. An investigation of the fractal characteristics of the Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation shale using nitrogen adsorption analysis. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 27, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Dong, X.; Wang, J.; Schmitt, D.R.; Xu, C.; Mohammed, T.; Chen, D. Measurement of total porosity for gas shales by gas injection porosimetry (GIP) method. Fuel 2016, 186, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Tang, D.; Zhao, J.; Li, S. A precise measurement method for shale porosity with low-field nuclear magnetic resonance: A case study of the Carboniferous–Permian strata in the Linxing area, eastern Ordos Basin, China. Fuel 2015, 143, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ning, Z.; Kong, D.; Liu, H. Pore structure of shales from high pressure mercury injection and nitrogen adsorption method. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2013, 24, 450–455. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Tian, H.; Xiao, X.; Cheng, P.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Z. The effect of particle size on low-pressure gas adsorption experiments for high-maturity shale. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2020, 31, 1271–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Mastalerz, M.; Hampton, L.; Drobniak, A.; Loope, H. Significance of analytical particle size in low-pressure N2 and CO2 adsorption of coal and shale. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2017, 178, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Peng, P.A. The effect of sample particle size on the determination of pore structure parameters in shales. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2016, 163, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, S.; Fu, D.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, C. Changes in the pore characteristics of shale during comminution. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2016, 34, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Cao, Y.; Chen, S.J.; Lu, J.G.; Huang, C.X.; Zhu, H.H.; Zhan, P.; Gao, Y. Influence of particle size on gas-adsorption experiments of shales: An example from a Longmaxi shale sample from the Sichuan Basin, China. Fuel 2016, 186, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, B.; Wood, D.A.; Vishal, V.; Singh, A.K. Pore characteristics of distinct thermally mature shales: Influence of particle size on low-pressure CO2 and N2 adsorption. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 8175–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Jia, A.; He, S.; Hu, Q.; Dong, T.; Hou, Y.; Yan, J. Water adsorption characteristics of organic-rich Wufeng and Longmaxi shales, Sichuan Basin (China). J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 193, 107387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; He, S.; Hu, Q.; Sun, M.; Hu, D.; Yi, J. Applying SANS technique to characterize nano-scale pore structure of Longmaxi shale, Sichuan Basin (China). Fuel 2017, 197, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cheng, G. Technical aspects of the pore structure in shale measured by small-angle and ultrasmall-angle neutron scattering: A mini review. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radliński, A.P.; Boreham, C.J.; Lindner, P.; Randl, O.; Wignall, G.D.; Hinde, A.; Hope, J.M. Small angle neutron scattering signature of oil generation in artificially and naturally matured hydrocarbon source rocks. Org. Geochem. 2000, 31, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, D.; Cai, Y.; Yao, Y.; Pan, Z.; Zhou, Y. Application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) in coalbed methane and shale reservoirs: A review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2020, 218, 103261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, B.; Vishal, V.; Singh, D.P. Applicability of low-pressure CO2 and N2 adsorption in determining pore attributes of organic-rich shales and coals. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, M.; Jiang, W.; Lei, R.; Wu, Z. DFT modeling of CO2 and Ar low-pressure adsorption for accurate nanopore structure characterization in organic-rich shales. Fuel 2017, 204, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, L.F.; Sakurovs, R.; Blach, T.P.; He, L.; Melnichenko, Y.B.; Mildner, D.F.R.; Alcantar-Lopez, L. A USANS/SANS Study of the Accessibility of Pores in the Barnett Shale to Methane and Water. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, C.R.; Freeman, M.; He, L.; Agamalian, M.; Melnichenko, Y.B.; Mastalerz, M.; Bustin, R.M.; Radliński, A.P.; Blach, T.P. Characterization of tight gas reservoir pore structure using USANS/SANS and gas adsorption analysis. Fuel 2012, 95, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, J.; Melnichenko, Y.B.; Mastalerz, M.; Furmann, A.; Clarkson, C.R. Hierarchical pore morphology of Cretaceous shale: A small-angle neutron scattering and ultrasmall-angle neutron scattering study. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 6336–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Yu, B.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, R.; Melnichenko, Y.B.; Cheng, G. Pore characteristics of Longmaxi shale gas reservoir in the northwest of Guizhou, China: Investigations using small-angle neutron scattering (SANS), helium pycnometry, and gas sorption isotherm. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2017, 171, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.a.W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ostadhassan, M.; Jang, H.W.; Zakharova, N.V.; Shokouhimehr, M. Comparison of fractal dimensions from nitrogen adsorption data in shale via different models. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 2298–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, P.; Avnir, D. Chemistry in non-integer dimensions between two and three. I. Fractal theory of heterogeneous surfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 3558–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, L.; Mastalerz, M.; Schimmelmann, A. The effect of analytical particle size on gas adsorption porosimetry of shale. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2015, 138, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zheng, F.; Hu, C.; Wang, B.; Peng, K.; Liu, H. Characterization of microscopic pore structures in shale reservoirs. Acta Petrolei Sinica 2013, 34, 301–311. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Li, X.; Guo, W.; Ju, W.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Z.; Qian, C.; Shen, W. Characteristics and dominant factors for natural fractures in deep shale gas reservoirs: A case study of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in Luzhou block, southern China. Lithosphere 2022, 2022, 9662175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample No. | TOC | Quartz | Calcite | Dolomite | Plagioclase | Pyrite | Illite | Montmorillonite | Chlorite | Density (g/cm3) | SLD (1010·cm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 3.81 | 61.34 | 2.52 | 3.69 | 6.34 | 4.11 | 16.04 | 2.82 | 3.14 | 2.45 | 4.08 |
| L2 | 4.37 | 56.98 | 7.57 | 12.1 | 2.52 | 3.02 | 14.72 | 2.5 | 0.59 | 2.53 | 4.22 |
| Sample No. | Mesh | Mass Fractal Dimension | Fractal Fitting Equation | R2 | Qmin | Qmax | Porod Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 20–40 | 2.706 | 0.998 | 0.00515 | 0.28702 | 5.94 | |
| 60–80 | 2.720 | 0.998 | 0.00515 | 0.362356 | 6.09 | ||
| 120–160 | 2.810 | 0.998 | 0.00515 | 0.304241 | 6.71 | ||
| 200–400 | 2.945 | 0.999 | 0.00515 | 0.255447 | 9.03 | ||
| L2 | 20–40 | 2.658 | 0.996 | 0.00515 | 0.190885 | 4.75 | |
| 60–80 | 2.680 | 0.996 | 0.00515 | 0.270773 | 4.85 | ||
| 120–160 | 2.791 | 0.994 | 0.00515 | 0.270773 | 5.43 | ||
| 200–400 | 2.961 | 0.997 | 0.00515 | 0.270773 | 7.15 |
| Sample No. | Mesh | Surface Fractal Dimension | Fractal Fitting Equation | R2 | Nitrogen Porosity (%) | Carbon Dioxide Porosity (%) | Closed Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 20–40 | 2.828 | 0.931 | 4.12 | 0.67 | 30.67 | |
| 60–80 | 2.818 | 0.935 | 4.24 | 0.62 | 30.37 | ||
| 120–160 | 2.806 | 0.959 | 5.25 | 0.58 | 21.82 | ||
| 200–400 | 2.777 | 0.993 | 8.36 | 0.59 | 7.43 | ||
| L2 | 20–40 | 2.834 | 0.939 | 3.30 | 0.53 | 31.81 | |
| 60–80 | 2.821 | 0.942 | 3.53 | 0.53 | 28.16 | ||
| 120–160 | 2.810 | 0.965 | 4.12 | 0.59 | 25.10 | ||
| 200–400 | 2.780 | 0.992 | 6.18 | 0.52 | 14.68 |
| Sample No. | Mesh | SANS SSA (m2/g) | LP-N2GA SAS (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 20–40 | 41.50 | 12.19 |
| 60–80 | 44.12 | 12.15 | |
| 120–160 | 45.81 | 13.01 | |
| 200–400 | 47.91 | 16.36 | |
| L2 | 20–40 | 28.47 | 9.13 |
| 60–80 | 30.36 | 9.33 | |
| 120–160 | 31.29 | 9.63 | |
| 200–400 | 33.48 | 11.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, H.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Chen, L.; Shen, W.; Guo, W.; He, W.; Zhou, Y. Effect of Particle Size on Pore Structure and Fractal Characteristics of Deep Siliceous Shales in Southern Sichuan, China, Measured Using Small-Angle Neutron Scattering and Low-Pressure Nitrogen Adsorption. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9030165
Zhan H, Li X, Hu Z, Chen L, Shen W, Guo W, He W, Zhou Y. Effect of Particle Size on Pore Structure and Fractal Characteristics of Deep Siliceous Shales in Southern Sichuan, China, Measured Using Small-Angle Neutron Scattering and Low-Pressure Nitrogen Adsorption. Fractal and Fractional. 2025; 9(3):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9030165
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Hongming, Xizhe Li, Zhiming Hu, Liqing Chen, Weijun Shen, Wei Guo, Weikang He, and Yuhang Zhou. 2025. "Effect of Particle Size on Pore Structure and Fractal Characteristics of Deep Siliceous Shales in Southern Sichuan, China, Measured Using Small-Angle Neutron Scattering and Low-Pressure Nitrogen Adsorption" Fractal and Fractional 9, no. 3: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9030165
APA StyleZhan, H., Li, X., Hu, Z., Chen, L., Shen, W., Guo, W., He, W., & Zhou, Y. (2025). Effect of Particle Size on Pore Structure and Fractal Characteristics of Deep Siliceous Shales in Southern Sichuan, China, Measured Using Small-Angle Neutron Scattering and Low-Pressure Nitrogen Adsorption. Fractal and Fractional, 9(3), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9030165





