Staged Parameter Identification Method for Non-Homogeneous Fractional-Order Hammerstein MISO Systems Using Multi-Innovation LM: Application to Heat Flow Density Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
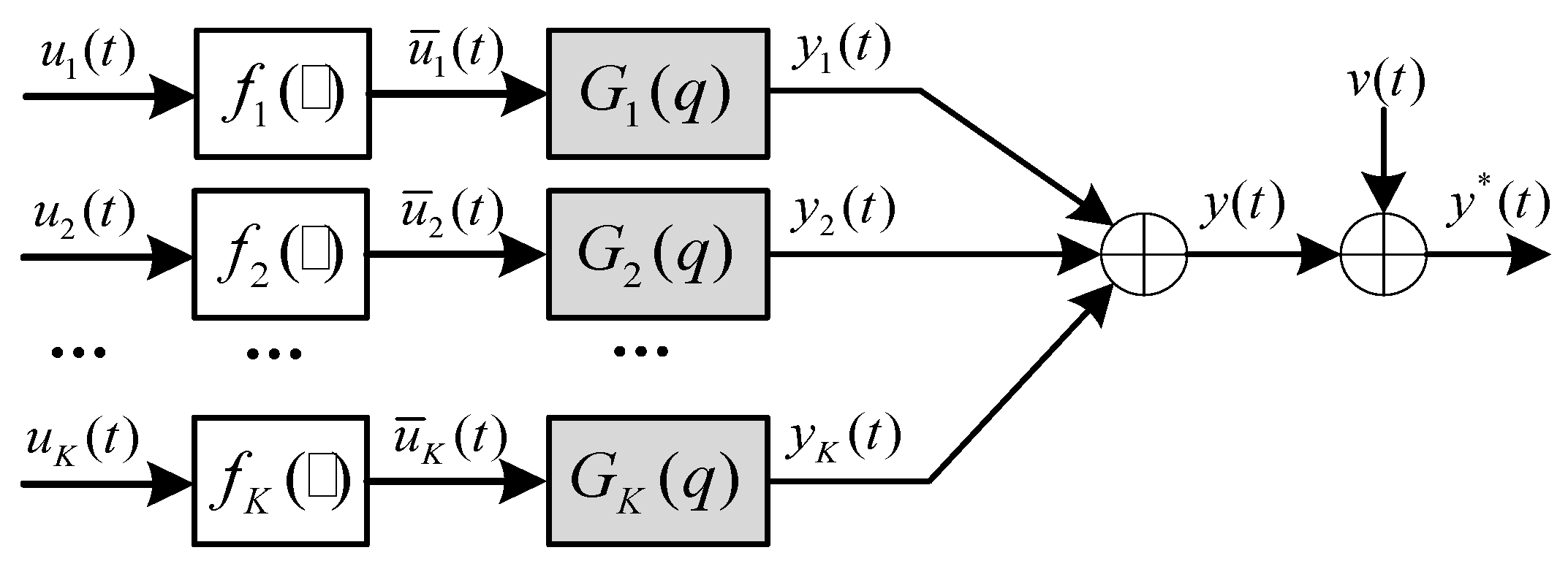
2. Non-Homogeneous Fractional-Order Hammerstein MISO Systems
2.1. System Representation
2.2. Fractional Calculation
2.3. Problem Description
3. Multi-Innovation LM Algorithm for NonlinearFractional-Order Models
3.1. Use MILM to Estimate the Coefficients of the Nonlinear Part and the Transfer Function
3.2. Estimating Fractional Orders of a Transfer Function Using MILM
- ◆
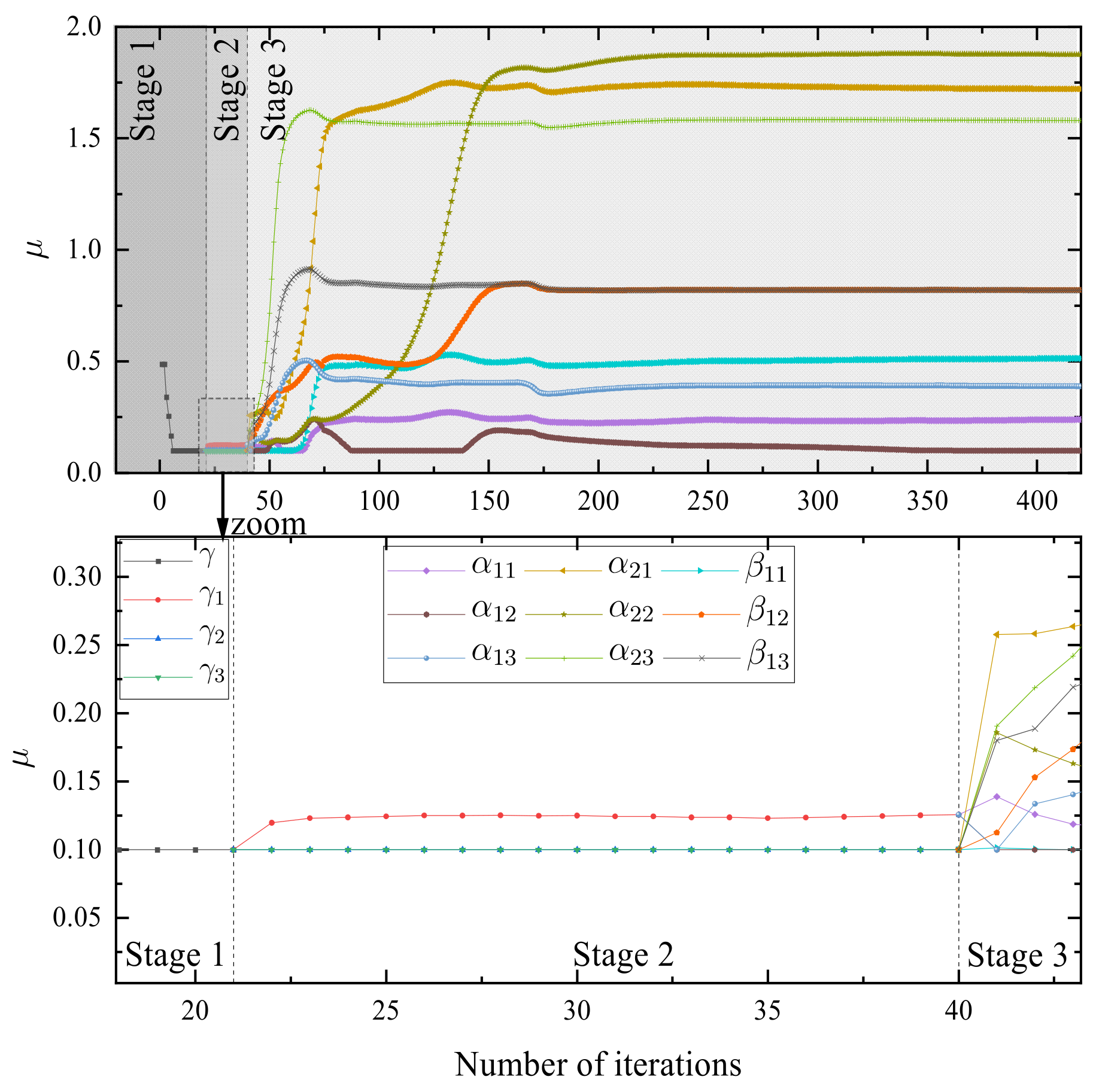
- First, in Stage 1, is defined by Equation (15), its initial value is a one-dimensional random number. In each estimation subsystem , the estimated fractional-order vectors and are solved as follows:where represents the estimated value of . Based on the MILM algorithm, its iteration method is as follows:where and are the gradient vector and Hessian matrix of the objective function versus , respectively, and their calculation method is as follows:wherewhere represents the sensitivity function, which is calculated as follows:
- ◆
- Secondly, in Stage 2, is defined by Equation (17). Its initial value of is calculated as follows:where represents the convergence value of in Stage 1, and represents a vector with all elements equal to 1. In each estimation subsystem , the estimation fractional-order vectors and are solved as follows:
- ◆
- Finally, in Stage 3, is defined by Equation (19). According to Equation (48), the initial value of calculation method iswhere represents the convergence value of the k-th element of the vector in Stage 2. In each estimation subsystem , the estimation fractional order vectors and are solved as follows:
3.3. Computational Complexity Analysis
4. Simulation Examples
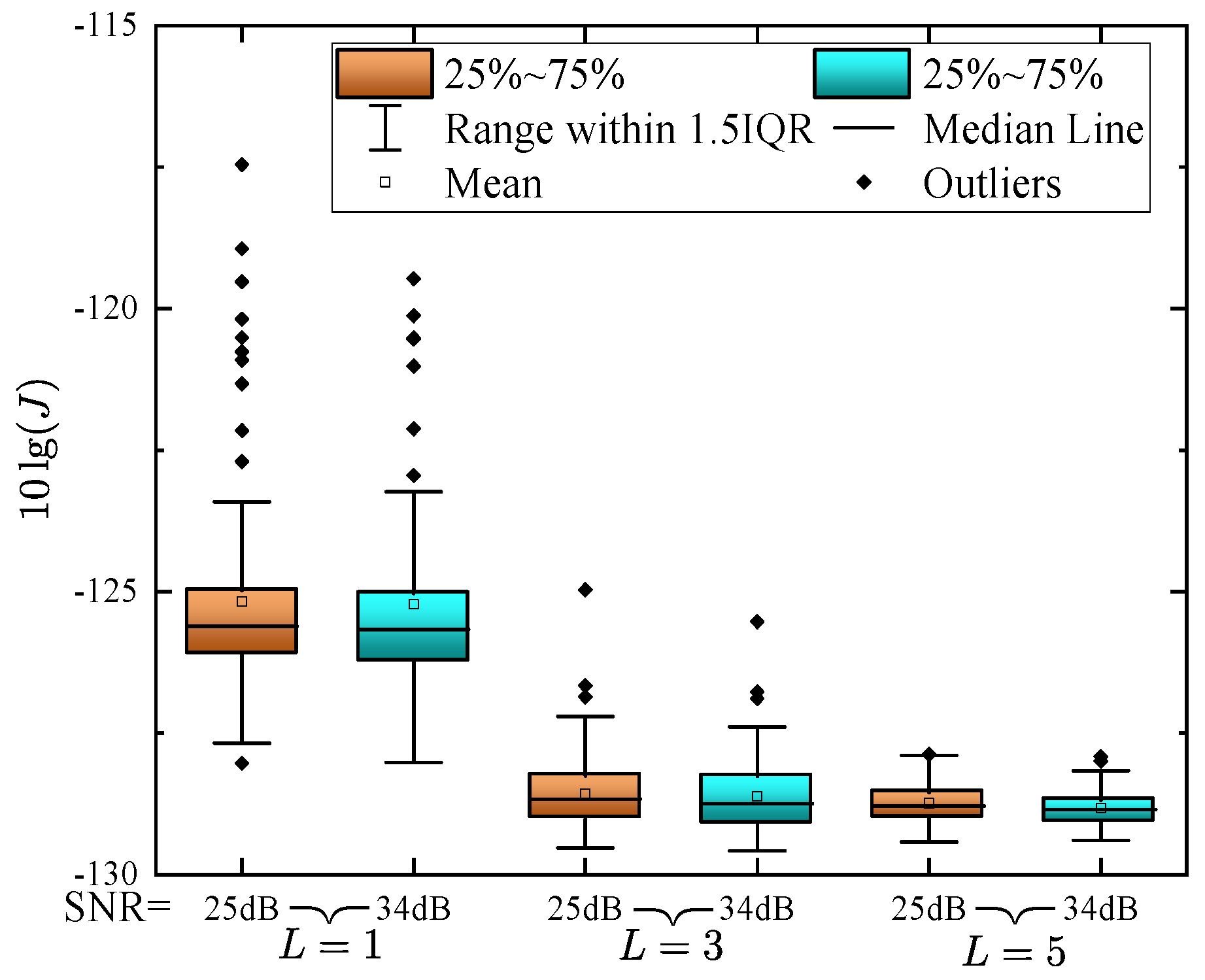
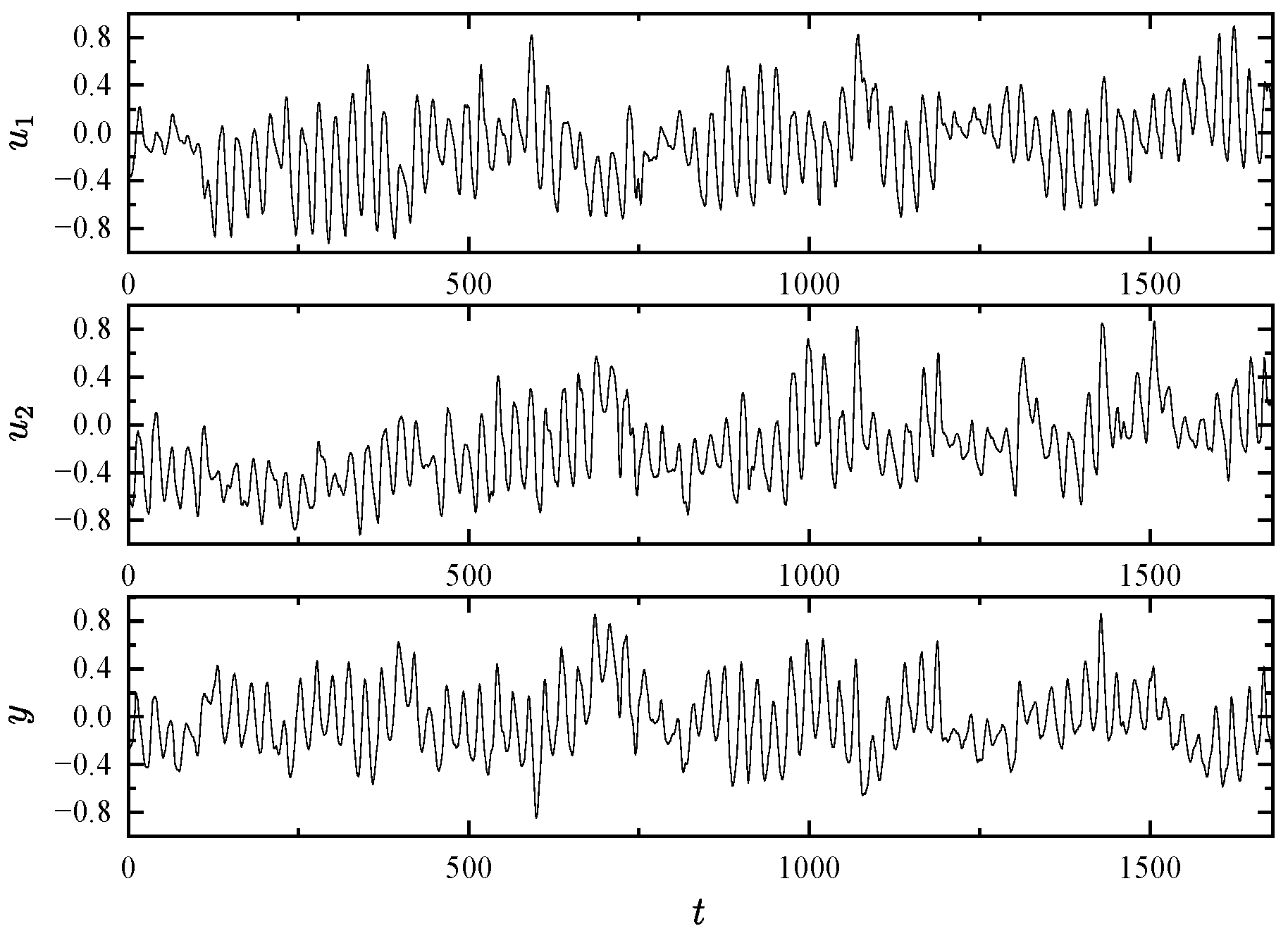
4.1. An Academic Example
4.2. Heat Flow Density Through a Two Layers Wall System Modeling
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salman, I.; Lin, Y.A.N.; Hamayun, M.T. Fractional order modeling and control of dissimilar redundant actuating system used in large passenger aircraft. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2018, 31, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Yu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zang, B.; Jiang, L. Synchrosqueezing transform meets α-stable distribution: An adaptive fractional lower-order SST for instantaneous frequency estimation and non-stationary signal recovery. Signal Process. 2022, 201, 108683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, S. An efficient computational method for local fractional transport equation occurring in fractal porous media. Comput. Appl. Math. 2020, 39, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirlik, T.; Benasciutti, D. Dirlik and tovo-benasciutti spectral methods in vibration fatigue: A review with a historical perspective. Metals 2021, 11, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingi, K.; Prusty, B.R. Forecasting models for chaotic fractional-order oscillators using neural networks. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 2021, 31, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.D.; Vadirajacharya, K.; Khubalkar, S.W. Design and tuning of digital fractional-order PID controller for permanent magnet DC motor. IETE J. Res. 2023, 69, 4349–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Elhattab, A.; Shu, X.; He, C. A second-order stochastic resonance method enhanced by fractional-order derivative for mechanical fault detection. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 106, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Lan, W.; Han, Q.L. Robust adaptive fault-tolerant consensus control for uncertain nonlinear fractional-order multi-agent systems with directed topologies. Automatica 2020, 117, 109011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.X.; Chen, P.Y.; Li, C.M.; Kuo, Y.C.; Pai, N.S.; Lin, C.H. Multilayer fractional-order machine vision classifier for rapid typical lung diseases screening on digital chest X-ray images. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 105886–105902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xiong, L.; Wang, Z.; Ma, M.; Wang, J. Fractional-order sliding mode control for damping of subsynchronous control interaction in DFIG-based wind farms. Wind Energy 2020, 23, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, J.; Liao, Y. Exponentially stable periodic oscillation and Mittag–Leffler stabilization for fractional-order impulsive control neural networks with piecewise Caputo derivatives. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 52, 9670–9683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elwy, O.; Said, L.A.; Madian, A.H.; Radwan, A.G. All possible topologies of the fractional-order Wien oscillator family using different approximation techniques. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 38, 3931–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, C. Identification of fractional-order Hammerstein nonlinear ARMAX system with colored noise. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 106, 3215–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q. Identification of fractional order Hammerstein models based on mixed signals. J. Control. Decis. 2022, 11, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laribi, S.; Mammar, K.; Sahli, Y.; Necaibia, A.; Arama, F.Z.; Ghaitaoui, T. PEMFC water diagnosis using PWM functionality signal and fractional order model. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 4214–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouOmar, M.S.; Zhang, H.J.; Su, Y.X. Fractional order fuzzy PID control of automotive PEM fuel cell air feed system using neural network optimization algorithm. Energies 2019, 12, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yin, H.; Huang, T.; Yuan, L.; Zheng, S.; Yin, L. Chaos in fractional-order discrete neural networks with application to image encryption. Neural Netw. 2020, 125, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, M.; Li, B. Besicovitch almost periodic solutions for fractional-order quaternion-valued neural networks with discrete and distributed delays. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2022, 45, 4791–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscarino, A.; Caponetto, R.; Graziani, S.; Murgano, E. Realization of fractional order circuits by a Constant Phase Element. Eur. J. Control 2020, 54, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Jin, M.; Ye, X.; Gao, H.; Chu, W.; Mao, J.; Thompson, M.L. Soil labile organic carbon fractions and soil enzyme activities after 10 years of continuous fertilization and wheat residue incorporation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamni, M.; Karmouni, H.; Sayyouri, M.; Qjidaa, H. Robust audio watermarking scheme based on fractional Charlier moment transform and dual tree complex wavelet transform. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 203, 117325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, N.R.; Kalpana, M.; Balasubramaniam, P. A novel audio encryption approach via finite-time synchronization of fractional order hyperchaotic system. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 18043–18067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Hongwei, W.; Chunlei, L. Hybrid identification method for fractional-order nonlinear systems based on the multi-innovation principle. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 15711–15726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, C. MILM hybrid identification method of fractional order neural-fuzzy Hammerstein model. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 108, 2337–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Hongwei, W.; Chunlei, L.; Xiaojing, M. Multi-innovation identification method for fractional Hammerstein state space model with colored noise. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 173, 113631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, S.; Malti, R.; Garnier, H.; Oustaloup, A. Parameter and differentiation order estimation in fractional models. Automatica 2013, 49, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayoufi, A.; Victor, S.; Chetoui, M.; Malti, R.; Aoun, M. Output Error MISO System Identification Using Fractional Models. Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal. 2021, 24, 1601–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, S.; Mayoufi, A.; Malti, R.; Chetoui, M.; Aoun, M. System identification of MISO fractional systems: Parameter and differentiation order estimation. Automatica 2022, 141, 110268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, X. Online identification of non-homogeneous fractional order Hammerstein continuous systems based on the principle of multi-innovation. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 20111–20125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, N.H.; Nikan, O.; Rasoulizadeh, M.N.; Jafari, H.; Gasimov, Y.S. Numerical computation of the time non-linear fractional generalized equal width model arising in shallow water channel. Therm. Sci. 2020, 24, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H.; Ganji, R.M.; Ganji, D.D.; Hammouch, Z.; Gasimov, Y.S. A novel numerical method for solving fuzzy variable-order differential equations with Mittag-Leffler kernels. Fractals 2023, 31, 2340063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutiba, M.; Baghli-Bendimerad, S.; El Houda Bouzara-Sahraoui, N. Numerical solution by finite element method for time Caputo-Fabrizio fractional partial diffusion equation. Adv. Math. Models Appl. 2024, 9, 316–328. [Google Scholar]
- Narsale, S.M.; Lodhi, R.K.; Jafari, H. A numerical study for non-linear multi-term fractional order differential equations. Adv. Math. Models Appl. 2024, 9, 193–204. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Ahemaide, M. Identification of fractional order non– homogeneous Hammerstein-Wiener MISO continuous systems. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 197, 110400. [Google Scholar]
- Matignon, D. Stability properties for generalized fractional differential systems. EDP Sci. 1998, 5, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammar, K.; Djamah, T.; Bettayeb, M. Nonlinear system identification using fractional Hammerstein–Wiener models. Nonlinear Dyn. 2019, 98, 2327–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Ding, L.; Wang, Z.; Liang, S. Parameter identification of fractional-order time delay system based on Legendre wavelet. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 163, 108141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moor, B.; De Gersem, P.; De Schutter, B.; Favoreel, W. DAISY: A database for identification of systems. J. A 1997, 38, 5. [Google Scholar]
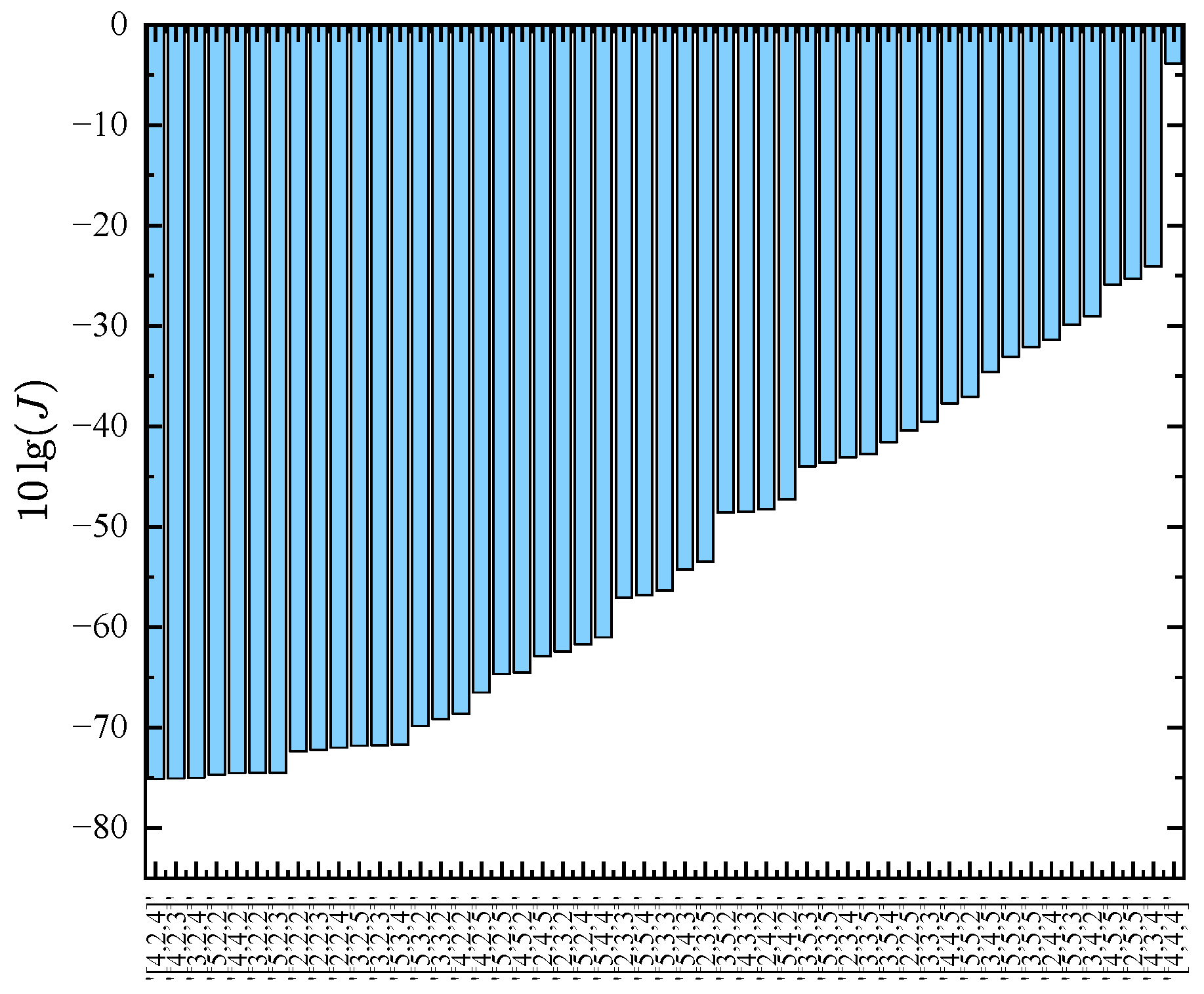
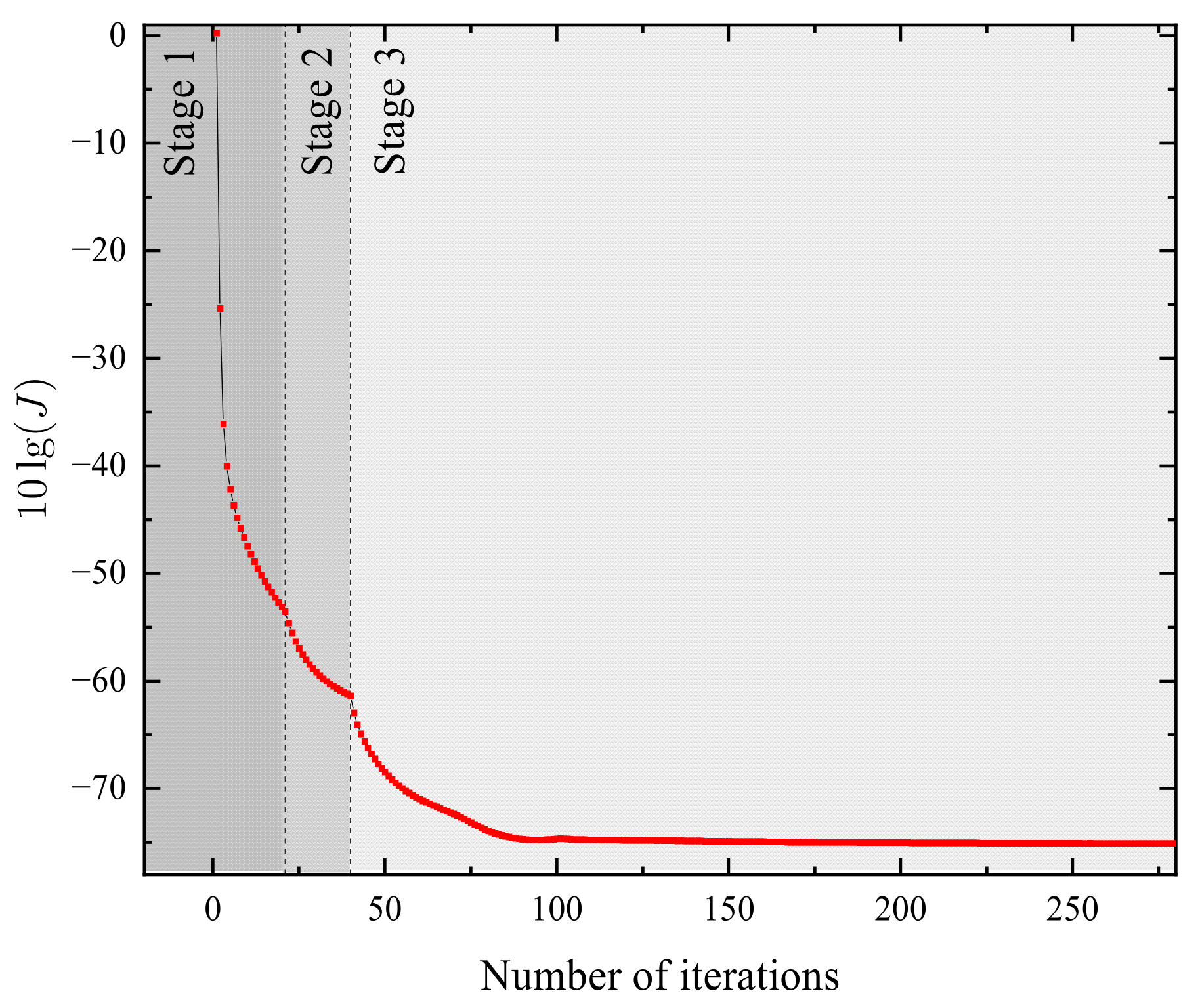
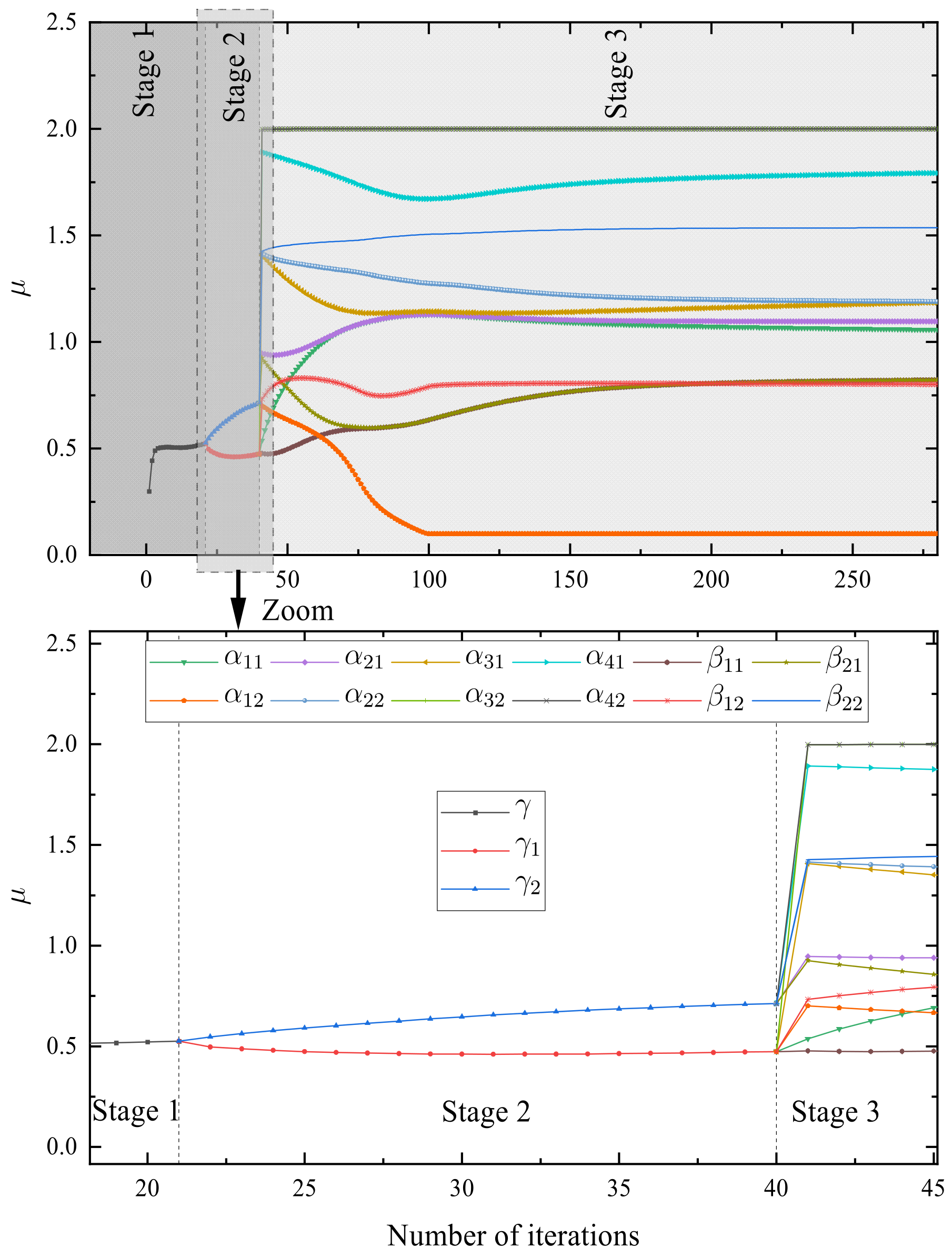
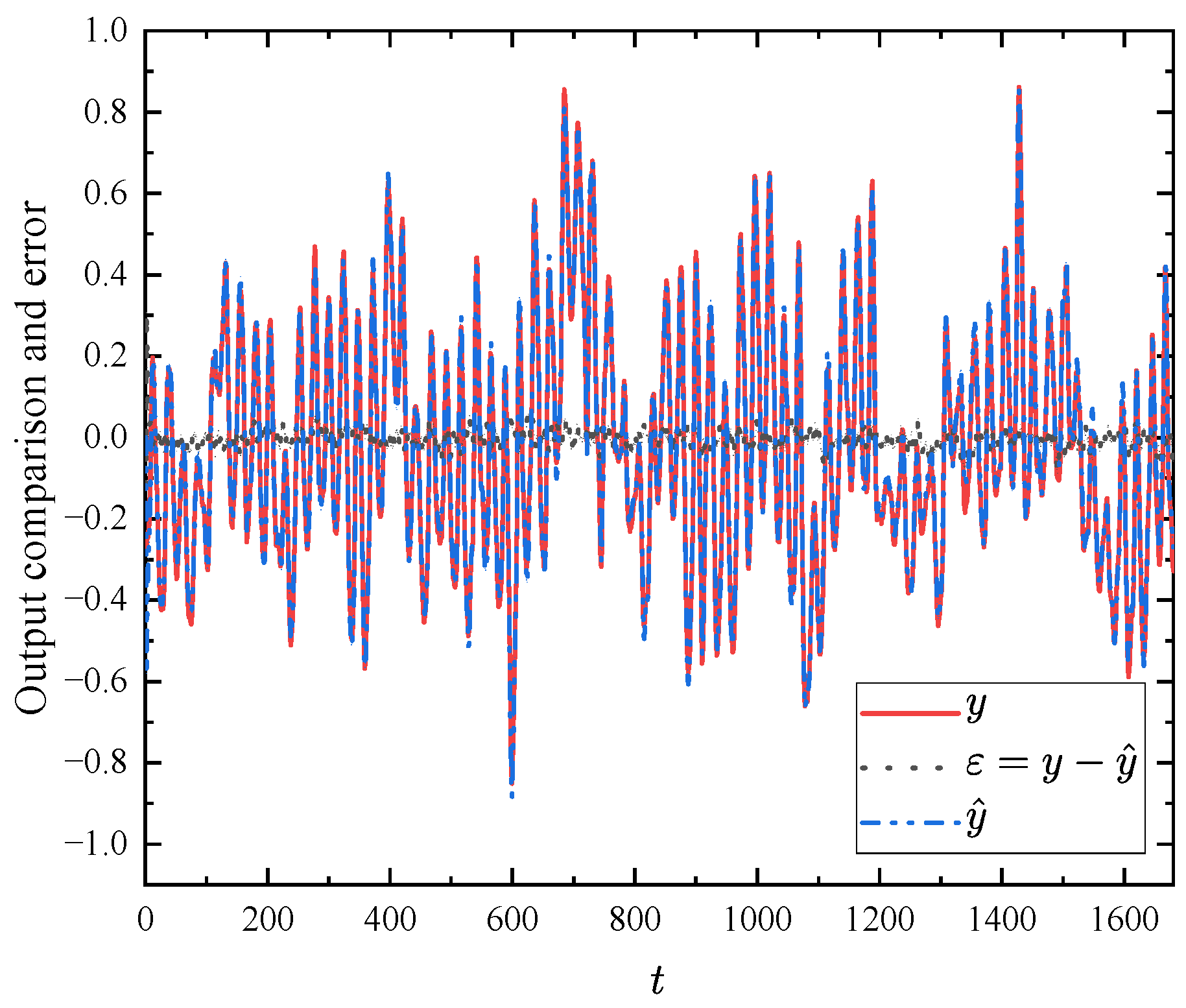
| Stage | Equation | Calculation Amount | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Equation (44) Equation (47) | 4 | 1 |
| 2 | Equation (44) Equation (50) | ||
| 3 | Equation (44) Equation (53) |
| Ture | Estimates (SNR = 25 dB) | Estimates (SNR = 34 dB) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.954041 ± 0.04224 | 0.963504 ± 0.00318 | |
| 1.1 ± 0.00001 | 1.1 ± 0.00001 | |
| 2 ± 0.00001 | 1.9985 ± 0.04019 | |
| 0.490984 ± 0.0276 | 0.504801 ± 0.00502 | |
| 0.500751 ± 0.000648 | 0.0500529 ± 0.00004 | |
| 1 | 1 | |
| 0.488174 ± 0.004843 | 0.495444 ± 0.00246 | |
| 0.1800045 ± 0.001908 | 0.223436 ± 0.000645 | |
| 1.735957 ± 0.029478 | 1.723453 ± 0.004743 | |
| 0.475162 ± 0.011939 | 0.477988 ± 0.00368 | |
| 0.594816 ± 0.01381 | 0.589707 ± 0.004302 | |
| 1.800045 ± 0.001908 | 1.800448 ± 0.001315 | |
| 0.40967 ± 0.013693 | 0.402033 ± 0.005661 | |
| 0.300015 ± 0.0002 | 0.299971 ± 0.00001 | |
| 1 | 1 | |
| 0.813024 ± 0.00671 | 0.809725 ± 0.003573 | |
| 0.114096 ± 0.01612 | 0.110667 ± 0.004548 | |
| 1.874833 ± 0.01404 | 1.883352 ± 0.00602 | |
| 1.499388 ± 0.11051 | 1.497258 ± 0.002258 | |
| 1.906755 ± 0.00676 | 1.906323 ± 0.00207 | |
| 1.2068 ± 0.006935 | 1.206316 ± 0.001229 | |
| 0.615202 ± 0.006313 | 0.613663 ± 0.000871 | |
| 0.799962 ± 0.00676 | 0.799991 ± 0.00001 | |
| 1 | 1 | |
| 0.817697 ± 0.00432 | 0.817434 ± 0.000618 | |
| 0.388925 ± 0.00782 | 0.390009 ± 0.00177 | |
| 1.580773 ± 0.00448 | 1.581597 ± 0.00122 |
| [34] | This Paper | |
| MSE | 2.55 × 10−2 | 5.47 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Wang, H.; An, Y. Staged Parameter Identification Method for Non-Homogeneous Fractional-Order Hammerstein MISO Systems Using Multi-Innovation LM: Application to Heat Flow Density Modeling. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9030150
Liu C, Wang H, An Y. Staged Parameter Identification Method for Non-Homogeneous Fractional-Order Hammerstein MISO Systems Using Multi-Innovation LM: Application to Heat Flow Density Modeling. Fractal and Fractional. 2025; 9(3):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9030150
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chunlei, Hongwei Wang, and Yi An. 2025. "Staged Parameter Identification Method for Non-Homogeneous Fractional-Order Hammerstein MISO Systems Using Multi-Innovation LM: Application to Heat Flow Density Modeling" Fractal and Fractional 9, no. 3: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9030150
APA StyleLiu, C., Wang, H., & An, Y. (2025). Staged Parameter Identification Method for Non-Homogeneous Fractional-Order Hammerstein MISO Systems Using Multi-Innovation LM: Application to Heat Flow Density Modeling. Fractal and Fractional, 9(3), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9030150






