A Discrete Grey Seasonal Model with Fractional Order Accumulation and Its Application in Forecasting the Groundwater Depth
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Seasonal attributes of the grey prediction model are improved. Traditional grey forecasting models are weak in handling seasonal fluctuation data due to sample size limitations. To ameliorate this problem, seasonal variables are introduced into the proposed model. A fractional order accumulation operator is used to reduce the effect of seasonal data fluctuations.
- (2)
- Properties of the proposed model are proved. The proposed model is shown to be a derivative of the traditional grey prediction model, indicating that the new model has the fundamental properties and advantages of the grey prediction model. In addition, the seasonality and stability of the proposed model are demonstrated.
- (3)
- The performance of the proposed model is validated in a real case of Handan groundwater. The prediction performance of the proposed model is verified by the actual groundwater scenario in Handan. The introduction of real groundwater scenarios tests the practical application value of the proposed model.
2. Study Area and Data Description
2.1. Study Area
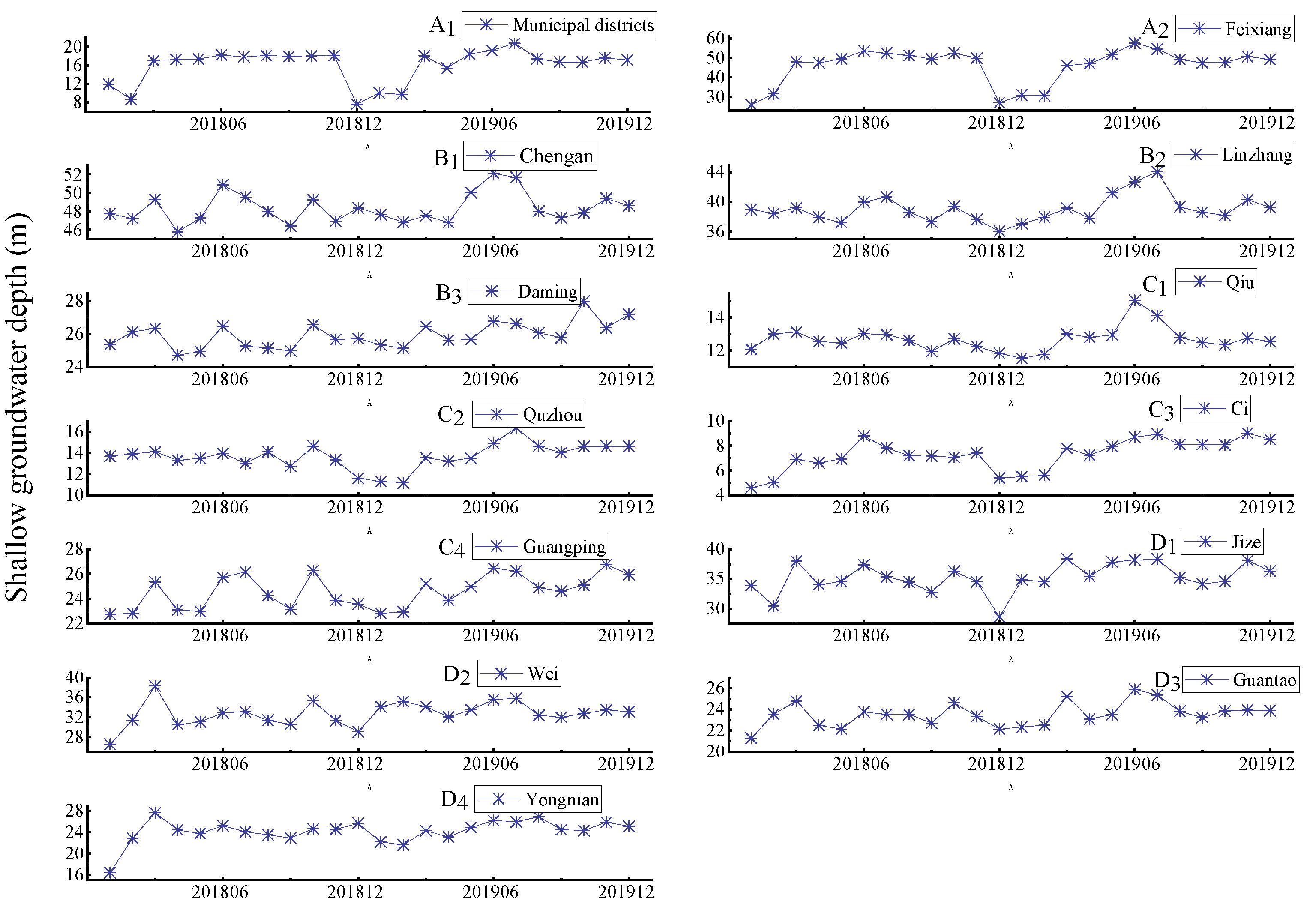
2.2. Data Description
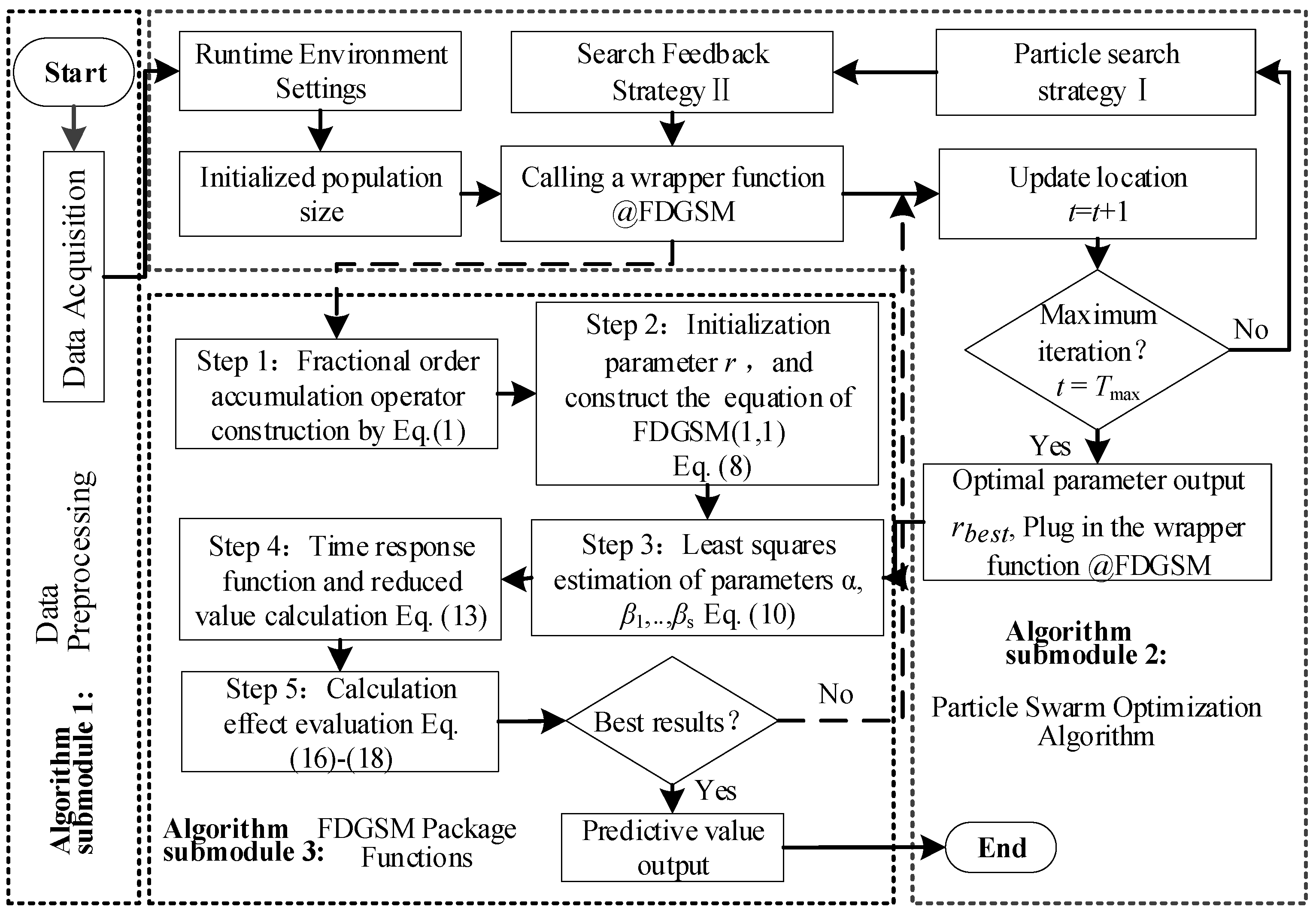
3. Method
3.1. Discrete Grey Model with Fractional Order Accumulation
3.2. The Establishment Process of the FDGSM(1,1) Model
3.3. The Properties of the FDGSM(1,1) Model
3.4. Stability Analysis of the Proposed Model
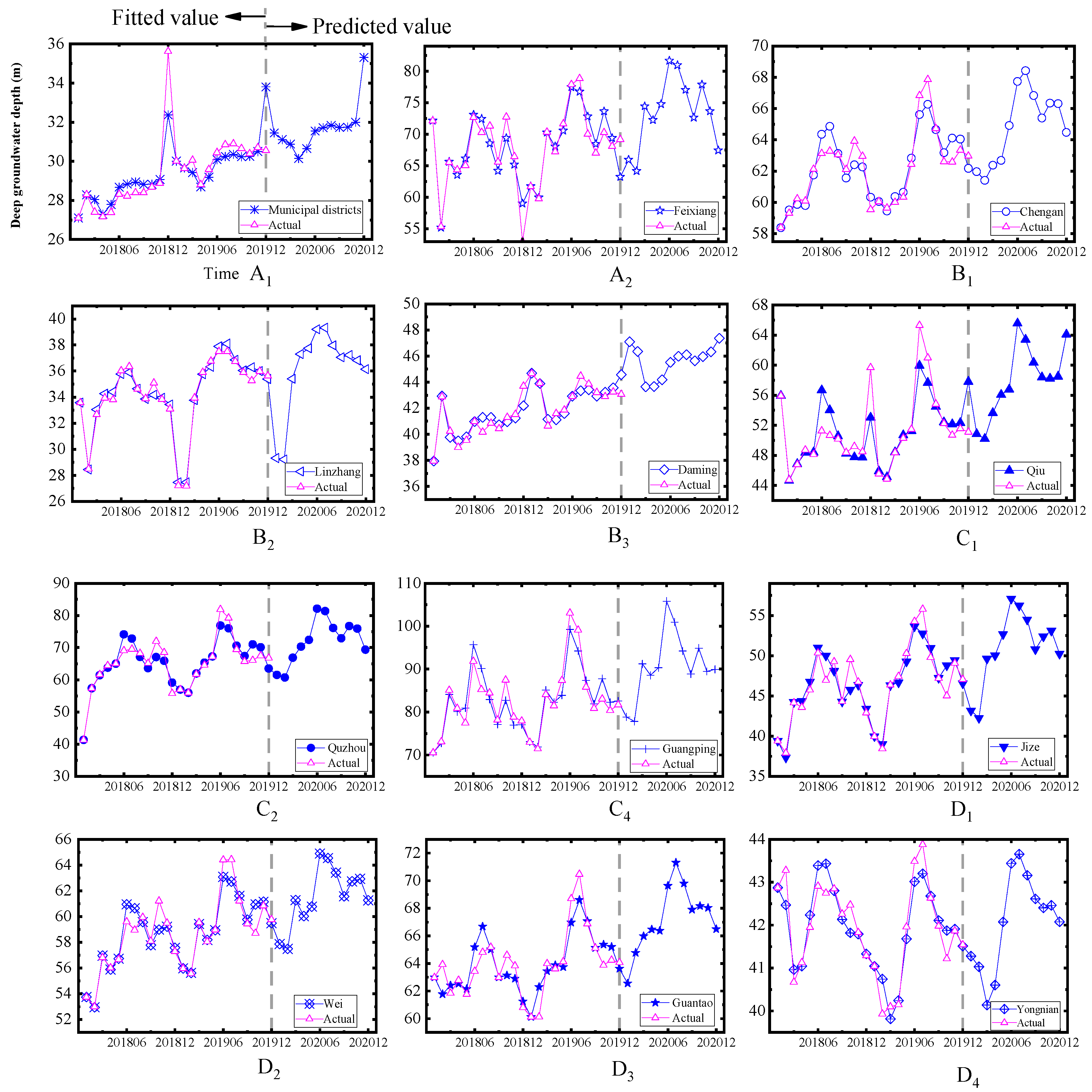
4. Prediction of Handan Groundwater Depth
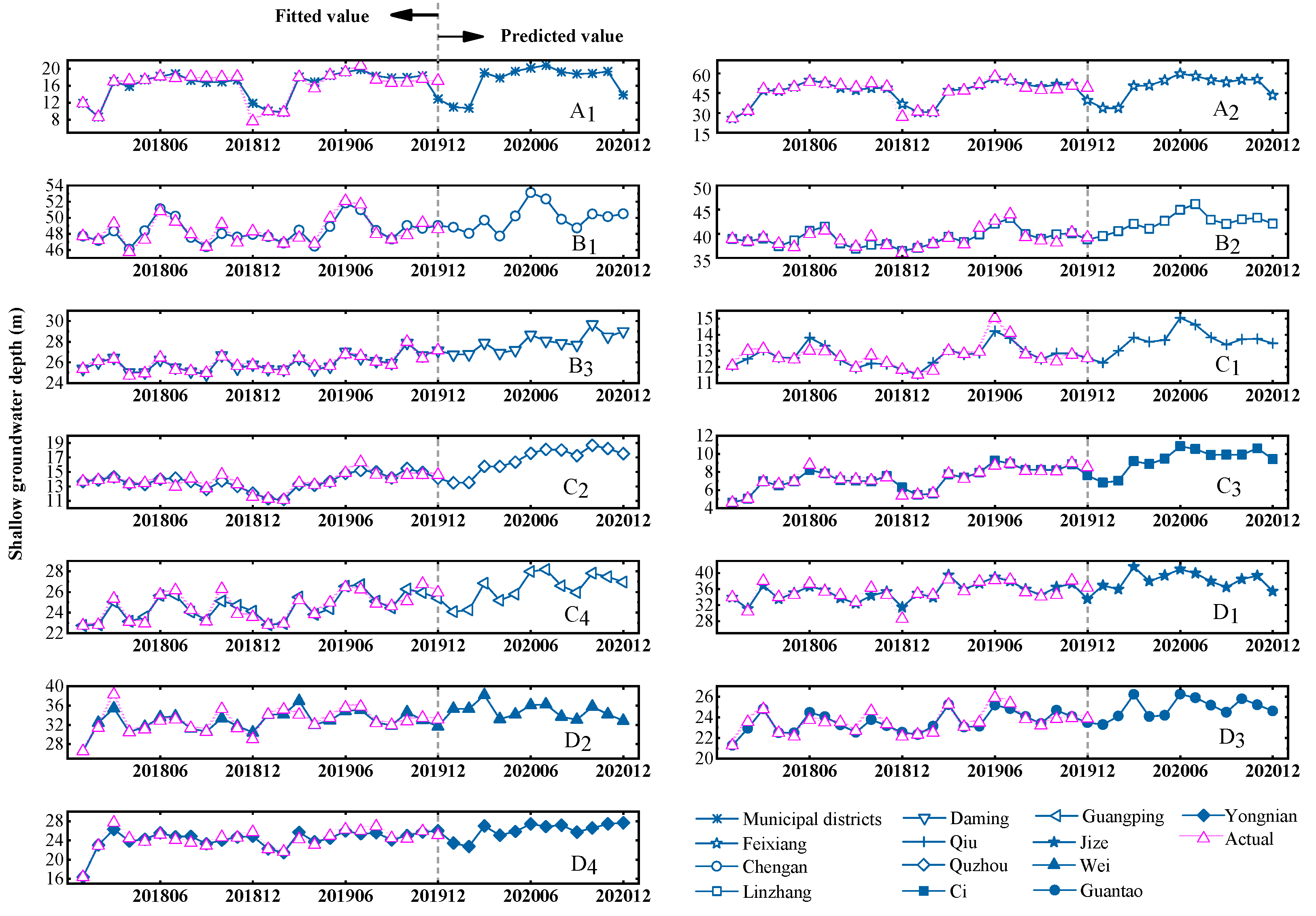
4.1. Prediction of Shallow Groundwater Depth in Handan
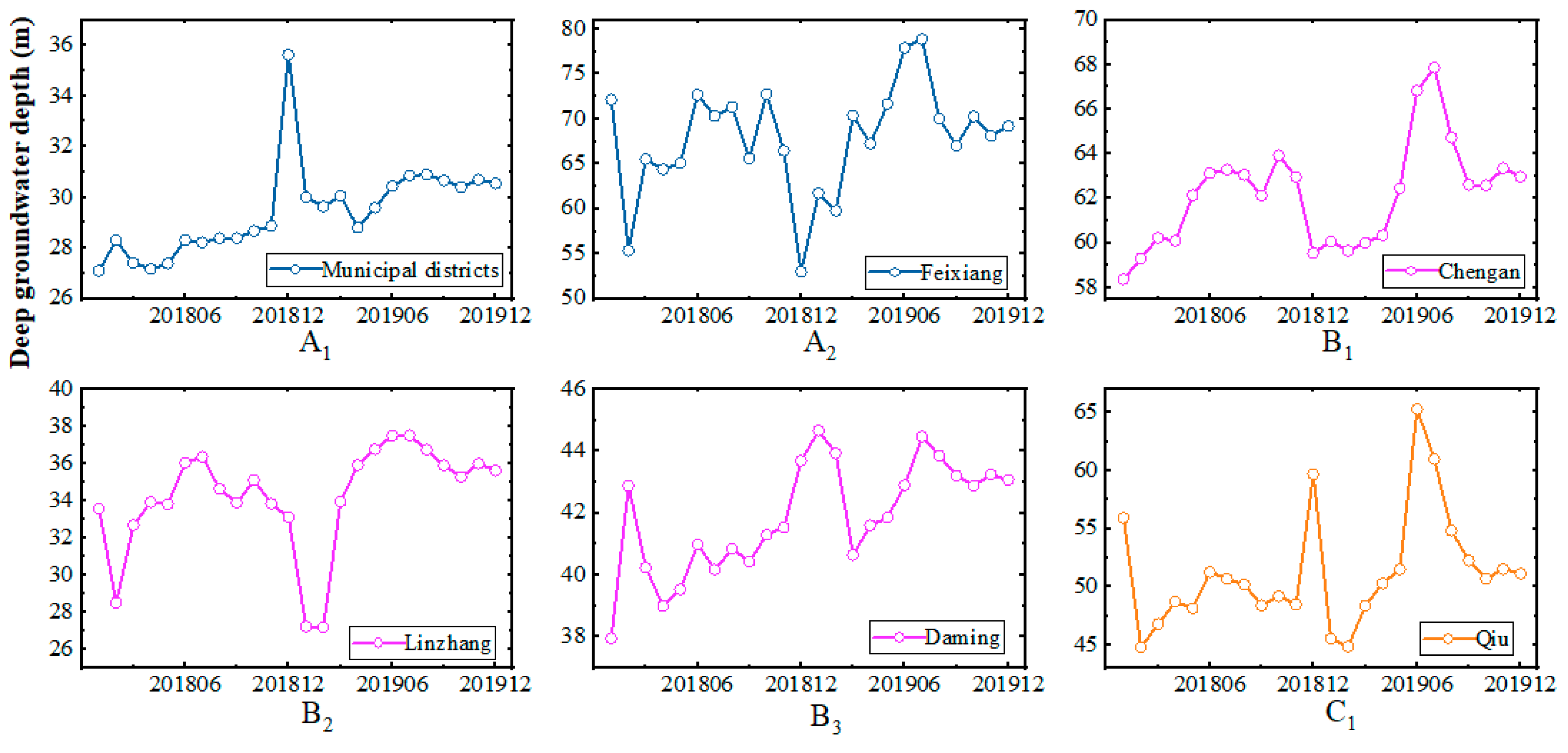
4.2. Prediction of Deep Groundwater in Handan
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The fractional-order accumulation operator is effective in reducing seasonal fluctuations in groundwater data. Data fluctuations are a major source of error in seasonal forecasting. The fractional-order accumulation operator gives relief from data series fluctuations. And the heuristic algorithm searches for the optimal parameters, which improves the data processing capability of the fractional order accumulation operator.
- (2)
- The introduction of seasonal parameters gives seasonality to the grey prediction model. Seasonal variables are derived from the training set and can reflect the cyclical characteristics of the study population. It is found through the proof of the nature of the FDGSM(1,1) model that the proposed model maintains the basic advantages of the traditional grey forecasting model and the new model is stable and seasonal.
- (3)
- The predictive performance of the proposed model is validated in the Handan groundwater scenario. In this paper, a fully realistic short-term prediction scenario of groundwater depth is provided, and seasonal prediction of groundwater at different depths is accomplished based on the proposed model. The validation results show that the prediction error of the proposed model is within a reasonable interval and exhibits excellent prediction performance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Famiglietti, J.S. The global groundwater crisis. Nat. Clim. Change 2014, 4, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Wiese, D.N.; Reager, J.T.; Beaudoing, H.K.; Landerer, F.W.; Lo, M.H. Emerging trends in global freshwater availability. Nature 2018, 557, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, Y. Modeling groundwater depletion at regional and global scales: Present state and future prospects. Surv. Geophys. 2016, 37, 419–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasechko, S.; Perrone, D.; Befus, K.M.; Cardenas, M.B.; Ferguson, G.; Gleeson, T.; Luijendijk, E.; McDonnell, J.J.; Taylor, R.G.; Wada, Y.; et al. Global aquifers dominated by fossil groundwaters but wells vulnerable to modern contamination. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, S.M.; Zheng, C. Global change and the groundwater management challenge. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 3031–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellazzi, P.; Martel, R.; Rivera, A.; Huang, J.; Pavlic, G.; Calderhead, A.I.; Chaussard, E.; Garfias, J.; Salas, J. Groundwater depletion in Central Mexico: Use of GRACE and InSAR to support water resources management. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 5985–6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Qian, H.; Li, X. Challenges and prospects of sustainable groundwater management in an agricultural plain along the Silk Road Economic Belt, north-west China. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2018, 34, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.F.; Famiglietti, J.S. Sustainable groundwater management in the arid Southwestern US: Coachella Valley, California. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 4411–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.F.; Rulli, M.C.; Seveso, A.; D’Odorico, P. Increased food production and reduced water use through optimized crop distribution. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, R.; Devineni, N.; Raman, S. Can improved agricultural water use efficiency save India’s groundwater? Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 084022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.G.; Lo, M.; Swenson, S.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Tang, Q.; Skaggs, T.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Wu, R.J. Using satellite-based estimates of evapotranspiration and groundwater changes to determine anthropogenic water fluxes in land surface models. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 3021–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machiwal, D.; Jha, M.K.; Singh, V.P.; Mohan, C. Assessment and mapping of groundwater vulnerability to pollution: Current status and challenges. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 185, 901–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; O’Connor, D.; Hou, D.; Jin, Y.; Li, G.; Zheng, C.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.C.; Luo, J. Groundwater depletion and contamination: Spatial distribution of groundwater resources sustainability in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunink, J.E.; Contreras, S.; Soto-García, M.; Martin-Gorriz, B.; Martinez-Álvarez, V.; Baille, A. Estimating groundwater use patterns of perennial and seasonal crops in a Mediterranean irrigation scheme, using remote sensing. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 162, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Lall, U. Depletion and response of deep groundwater to climate-induced pumping variability. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Krause, P.; Panda, S.N.; Flugel, W. Rising water table: A threat to sustainable agriculture in an irrigated semi-arid region of Haryana, India. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béjar-Pizarro, M.; Guardiola-Albert, C.; García-Cárdenas, R.P.; Herrera, G.; Barra, A.; López Molina, A.; Tessitore, S.; Staller, A.; Ortega-Becerril, J.A.; García-García, R.P. Interpolation of GPS and geological data using InSAR deformation maps: Method and application to land subsidence in the alto guadalentín aquifer (SE Spain). Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, V.; Vafakhah, M.; Shirmohammadi, B.; Behnia, N. A wavelet-ANFIS hybrid model for groundwater level forecasting for different prediction periods. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 1301–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Panahi, M.; Khosravi, K.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Rezaie, F.; Parvinnezhad, D. Spatial prediction of groundwater potentiality using ANFIS ensembled with teaching-learning-based and biogeography-based optimization. J. Hydrol. 2019, 572, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.; Chang, L.; Huang, C.; Kao, I. Prediction of monthly regional groundwater levels through hybrid soft-computing techniques. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C.; Sudheer, C.; Mahammood, V.; Panigrahi, B.K. An integrated wavelet-support vector machine for groundwater level prediction in Visakhapatnam, India. Neurocomputing 2014, 145, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitsazan, N.; Tsai, F.T.C. A hierarchical Bayesian model averaging framework for groundwater prediction under uncertainty. Groundwater 2015, 53, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J. Introduction to grey system theory. J. Grey Syst. 1989, 1, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Liu, S.; Yao, L.; Yan, S.; Liu, D. Grey system model with the fractional order accumulation. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2013, 18, 1775–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Fang, Z.; Jiang, A.; Shang, G. The recursive grey model and its application. Appl. Math. Model. 2023, 119, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, S.; Hooshmand, R.; Parastegari, M. Short term electric load forecasting by wavelet transform and grey model improved by PSO (particle swarm optimization) algorithm. Energy 2014, 72, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, D.; Fang, Z.; Xu, H. Modelling and forecasting CO2 emissions in the BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) countries using a novel multi-variable grey model. Energy 2015, 79, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Deng, Y.; Ma, M. A novel kernel ridge grey system model with generalized Morlet wavelet and its application in forecasting natural gas production and consumption. Energy 2024, 287, 129630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Hao, M.; Hao, Y. Innovative ensemble system based on mixed frequency modeling for wind speed point and interval forecasting. Inf. Sci. 2023, 622, 560–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, W. A new perspective of wind speed forecasting: Multi-objective and model selection-based ensemble interval-valued wind speed forecasting system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 299, 117868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.; An, W. Probability density prediction for carbon allowance prices based on TS2Vec and distribution Transformer. Energy Econ. 2024, 140, 107986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.M.; Liu, S.F. Discrete GM (1, 1) and mechanism of grey forecasting model. Syst. Eng.-Theory Pract. 2005, 1, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Liu, S.; Yao, L.; Yan, S. The effect of sample size on the grey system model. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 37, 6577–6583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, F.Y.H.; Tzeng, G. Applied hybrid grey model to forecast seasonal time series. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2001, 67, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Wong, W.K. A seasonal discrete grey forecasting model for fashion retailing. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2014, 57, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Pei, L. A seasonal GM (1, 1) model for forecasting the electricity consumption of the primary economic sectors. Energy 2018, 154, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.F.; Li, N.; Zhao, T. Using the seasonal FGM (1, 1) model to predict the air quality indicators in Xingtai and Handan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 14683–14688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Ding, S. A novel discrete grey seasonal model and its applications. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2021, 93, 105493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebei Provincial Department of Water Resources. Report on Monitoring of Groundwater Level in Groundwater Overexploitation Area of Hebei Province. 2024. Available online: http://slt.hebei.gov.cn/dynamic/search.jsp (accessed on 7 December 2024).
- Wu, L.; Liu, S.; Fang, Z.; Xu, H. Properties of the GM (1, 1) with fractional order accumulation. Appl. Math. Comput. 2015, 252, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, S.; Cui, W.; Liu, D.; Yao, T. Non-homogenous discrete grey model with fractional-order accumulation. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 25, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, S.; Yao, L. Discrete grey model based on fractional order accumulate. Syst. Eng.-Theory Pract. 2014, 34, 1822–1827. [Google Scholar]
- Salhein, K.; Kobus, C.J.; Zohdy, M. Forecasting Installation Capacity for the Top 10 Countries Utilizing Geothermal Energy by 2030. Thermo 2022, 2, 334–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

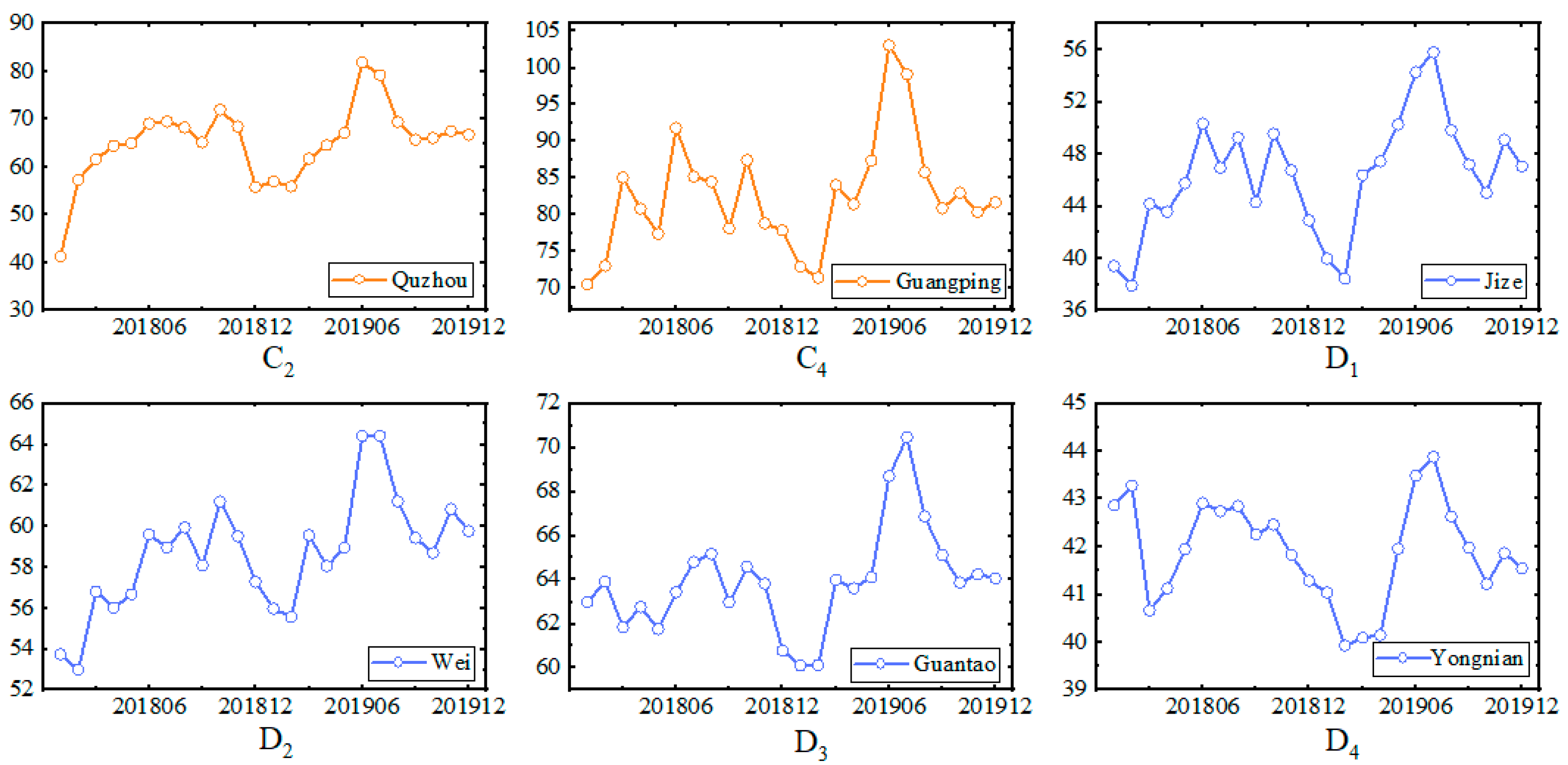
| Statistical Indicators | Shallow Groundwater | Deep Groundwater |
|---|---|---|
| Average value | 26.86 | 53.77 |
| Standard error | 0.38 | 0.65 |
| Median value | 27.17 | 53.82 |
| Standard deviation | 1.87 | 3.17 |
| Variance | 3.51 | 10.02 |
| Kurtosis | −0.26 | 1.14 |
| Skewness | −0.54 | 0.74 |
| Minimum value | 23.16 | 48.88 |
| Maximum values | 29.95 | 61.40 |
| Sum | 644.72 | 1290.36 |
| Number of observations | 24 | 24 |
| Number | County and District | The Optimal Order Number | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | Municipal districts | 0.99 | = 1.00, = [8.78, 8.49, 16.77, 15.39, 16.89, 17.55, 18.03, 16.39, 15.84, 15.82, 16.23, 10.65]. |
| A2 | Feixiang | 1.05 | = 1.01, = [33.36, 32.58, 48.77, 49.57, 53.24, 58.35, 56.54, 53.15, 51.19, 52.6, 52.5, 40.11]. |
| B1 | Chengan | 1.02 | = 1.00, = [48.85, 47.98, 49.49, 47.42, 49.76, 52.58, 51.73, 49.07, 47.84, 49.4, 48.96, 49.18]. |
| B2 | Linzhang | 1.05 | = 1.01, = [39.35, 40.08, 41.35, 40.16, 41.49, 43.59, 44.61, 41.18, 39.92, 40.51, 40.51, 38.97]. |
| B3 | Daming | 1.05 | = 1.01, = [27.23, 27.08, 28.02, 26.92, 27.03, 28.33, 27.66, 27.25, 26.93, 28.72, 27.44, 27.74]. |
| C1 | Qiu | 1.05 | = 1.01, = [12.39, 13.03, 13.82, 13.51, 13.54, 14.85, 14.4, 13.54, 12.98, 13.21, 13.13, 12.76]. |
| C2 | Quzhou | 1.2 | = 1.02, = [16.85, 16.35, 18.12, 18.08, 18.47, 19.51, 19.98, 19.78, 18.73, 19.7, 19.03, 17.93]. |
| C3 | Ci | 1.06 | = 1.02, = [5.24, 5.24, 7.24, 6.87, 7.33, 8.59, 8.2, 7.4, 7.24, 7.06, 7.57, 6.23]. |
| C4 | Guangping | 1.03 | = 1.01, = [23.36, 23.36, 25.81, 24.07, 24.51, 26.59, 26.69, 25, 24.21, 25.89, 25.46, 24.79]. |
| D1 | Jize | 0.98 | = 1.00, = [31.46, 30.28, 35.71, 31.88, 33.16, 34.5, 33.32, 31.12, 29.59, 31.45, 32.16, 28.11]. |
| D2 | Wei | 0.99 | = 1.00, = [32.24, 32.12, 34.82, 29.71, 30.61, 32.44, 32.54, 29.84, 29.13, 31.8, 30.08, 28.66]. |
| D3 | Guantao | 1.02 | = 1.00, = [22.52, 23.26, 25.27, 23.07, 23.05, 25.01, 24.6, 23.78, 22.99, 24.17, 23.52, 22.82. |
| D4 | Yongnian | 1.06 | = 1.01, = [24.83, 23.87, 27.89, 26.02, 26.6, 28.04, 27.42, 27.56, 26.02, 26.68, 27.37, 27.48]. |
| Number | County and District | MAPE | MAE | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | Municipal districts | 6.73% | 0.94 | 1.48 |
| A2 | Feixiang | 4.63% | 1.94 | 3.24 |
| B1 | Chengan | 1.10% | 0.53 | 0.66 |
| B2 | Linzhang | 1.50% | 0.59 | 0.78 |
| B3 | Daming | 0.58% | 0.15 | 0.18 |
| C1 | Qiu | 1.74% | 0.23 | 0.34 |
| C2 | Quzhou | 2.40% | 0.34 | 0.48 |
| C3 | Ci | 2.70% | 0.20 | 0.33 |
| C4 | Guangping | 1.55% | 0.39 | 0.52 |
| D1 | Jize | 2.62% | 0.91 | 1.17 |
| D2 | Wei | 2.51% | 0.85 | 1.19 |
| D3 | Guantao | 1.48% | 0.35 | 0.44 |
| D4 | Yongnian | 2.41% | 0.60 | 0.73 |
| Date | A | B | C | D | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Municipal Districts | Feixiang | Chengan | Linzhang | Daming | Qiu | Quzhou | Ci | Guangping | Jize | Wei | Guantao | Yongnian | |
| Fitted value | |||||||||||||
| Jan-2018 | 11.91 | 25.88 | 47.71 | 38.95 | 25.36 | 12.08 | 13.70 | 4.61 | 33.92 | 21.27 | 25.88 | 16.37 | 26.53 |
| Feb-2018 | 8.66 | 31.48 | 47.17 | 38.43 | 25.98 | 12.52 | 13.89 | 5.05 | 31.08 | 22.93 | 31.48 | 23.01 | 32.45 |
| Mar-2018 | 17.00 | 46.97 | 48.35 | 39.02 | 26.43 | 13.05 | 14.33 | 6.97 | 36.90 | 24.79 | 46.97 | 26.28 | 35.42 |
| Apr-2018 | 15.81 | 46.76 | 46.09 | 37.44 | 25.03 | 12.59 | 13.36 | 6.49 | 33.50 | 22.50 | 46.76 | 23.84 | 30.54 |
| May-2018 | 17.43 | 49.97 | 48.36 | 38.63 | 25.03 | 12.56 | 13.30 | 6.95 | 35.03 | 22.49 | 49.97 | 24.23 | 31.57 |
| Jun-2018 | 18.21 | 54.71 | 51.11 | 40.60 | 26.26 | 13.83 | 14.02 | 8.23 | 36.65 | 24.46 | 54.71 | 25.51 | 33.54 |
| Jul-2018 | 18.81 | 52.53 | 50.19 | 41.50 | 25.50 | 13.31 | 14.14 | 7.82 | 35.74 | 24.06 | 52.53 | 24.73 | 33.78 |
| Aug-2018 | 17.30 | 49.09 | 47.54 | 38.02 | 25.10 | 12.44 | 13.70 | 7.08 | 33.76 | 23.27 | 49.09 | 24.83 | 31.22 |
| Sep-2018 | 16.84 | 47.30 | 46.37 | 36.93 | 24.83 | 11.93 | 12.60 | 7.02 | 32.40 | 22.53 | 47.30 | 23.26 | 30.61 |
| Oct-2018 | 16.90 | 48.92 | 48.01 | 37.71 | 26.68 | 12.22 | 13.75 | 6.94 | 34.39 | 23.79 | 48.92 | 24.01 | 33.38 |
| Nov-2018 | 17.40 | 48.93 | 47.61 | 37.83 | 25.39 | 12.18 | 13.01 | 7.56 | 35.30 | 23.17 | 48.93 | 24.72 | 31.79 |
| Dec-2018 | 11.92 | 36.71 | 47.90 | 36.44 | 25.79 | 11.85 | 12.07 | 6.29 | 31.46 | 22.55 | 36.71 | 24.84 | 30.46 |
| Jan-2019 | 10.06 | 30.66 | 47.64 | 37.04 | 25.35 | 11.54 | 11.31 | 5.45 | 34.90 | 22.33 | 30.66 | 22.23 | 34.12 |
| Feb-2019 | 9.78 | 30.56 | 46.85 | 37.95 | 25.31 | 12.26 | 11.19 | 5.61 | 33.92 | 23.14 | 30.56 | 21.46 | 34.14 |
| Mar-2019 | 18.08 | 47.22 | 48.45 | 39.37 | 26.37 | 13.07 | 13.30 | 7.73 | 39.51 | 25.22 | 47.22 | 25.66 | 36.95 |
| Apr-2019 | 16.86 | 47.67 | 46.45 | 38.31 | 25.33 | 12.77 | 13.18 | 7.38 | 35.97 | 23.06 | 47.67 | 23.70 | 31.99 |
| May-2019 | 18.46 | 51.35 | 48.91 | 39.86 | 25.58 | 12.86 | 13.68 | 7.93 | 37.39 | 23.14 | 51.35 | 24.42 | 32.96 |
| Jun-2019 | 19.23 | 56.43 | 51.80 | 42.10 | 27.00 | 14.23 | 14.80 | 9.28 | 38.93 | 25.18 | 56.43 | 25.93 | 34.88 |
| Jul-2019 | 19.82 | 54.52 | 50.99 | 43.22 | 26.40 | 13.78 | 15.23 | 8.93 | 37.96 | 24.82 | 54.52 | 25.33 | 35.10 |
| Aug-2019 | 18.29 | 51.30 | 48.42 | 39.93 | 26.12 | 12.97 | 15.04 | 8.25 | 35.93 | 24.08 | 51.30 | 25.56 | 32.51 |
| Sep-2019 | 17.83 | 49.70 | 47.33 | 38.99 | 25.94 | 12.50 | 14.16 | 8.24 | 34.53 | 23.39 | 49.70 | 24.12 | 31.88 |
| Oct-2019 | 17.89 | 51.48 | 49.03 | 39.90 | 27.88 | 12.83 | 15.50 | 8.20 | 36.49 | 24.67 | 51.48 | 24.97 | 34.63 |
| Nov-2019 | 18.39 | 51.63 | 48.68 | 40.14 | 26.67 | 12.83 | 14.92 | 8.87 | 37.37 | 24.09 | 51.63 | 25.76 | 33.02 |
| Dec-2019 | 12.90 | 39.54 | 49.02 | 38.85 | 27.13 | 12.54 | 14.13 | 7.64 | 33.50 | 23.48 | 39.54 | 25.96 | 31.68 |
| Predicted value | |||||||||||||
| Jan-2020 | 11.04 | 33.61 | 48.80 | 39.55 | 26.76 | 12.26 | 13.51 | 6.84 | 24.09 | 36.92 | 35.33 | 23.29 | 23.42 |
| Feb-2020 | 10.76 | 33.61 | 48.05 | 40.54 | 26.77 | 13.00 | 13.52 | 7.03 | 24.25 | 35.93 | 35.35 | 24.13 | 22.72 |
| Mar-2020 | 19.06 | 50.37 | 49.69 | 42.05 | 27.88 | 13.84 | 15.76 | 9.19 | 26.85 | 41.51 | 38.15 | 26.22 | 26.97 |
| Apr-2020 | 17.83 | 50.91 | 47.72 | 41.05 | 26.89 | 13.57 | 15.75 | 8.88 | 25.18 | 37.95 | 33.18 | 24.08 | 25.07 |
| May-2020 | 19.43 | 54.67 | 50.21 | 42.67 | 27.19 | 13.68 | 16.36 | 9.46 | 25.77 | 39.36 | 34.14 | 24.17 | 25.83 |
| Jun-2020 | 20.20 | 59.83 | 53.12 | 44.99 | 28.65 | 15.06 | 17.59 | 10.85 | 27.98 | 40.89 | 36.06 | 26.23 | 27.38 |
| Jul-2020 | 20.79 | 58.00 | 52.34 | 46.17 | 28.08 | 14.63 | 18.12 | 10.54 | 28.16 | 39.91 | 36.27 | 25.89 | 26.82 |
| Aug-2020 | 19.27 | 54.85 | 49.80 | 42.93 | 27.84 | 13.84 | 18.04 | 9.88 | 26.58 | 37.87 | 33.68 | 25.16 | 27.10 |
| Sep-2020 | 18.81 | 53.32 | 48.73 | 42.04 | 27.70 | 13.39 | 17.26 | 9.91 | 25.95 | 36.47 | 33.05 | 24.48 | 25.69 |
| Oct-2020 | 18.87 | 55.17 | 50.45 | 43.01 | 29.67 | 13.74 | 18.69 | 9.91 | 27.80 | 38.43 | 35.79 | 25.78 | 26.58 |
| Nov-2020 | 19.37 | 55.38 | 50.12 | 43.31 | 28.49 | 13.75 | 18.22 | 10.61 | 27.47 | 39.30 | 34.19 | 25.20 | 27.40 |
| Dec-2020 | 13.88 | 43.35 | 50.48 | 42.07 | 28.98 | 13.47 | 17.53 | 9.42 | 26.94 | 35.43 | 32.85 | 24.61 | 27.64 |
| Number | County and District | The Optimal Order Number | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | Municipal districts | 1 | = 1.00, = [28.64, 28.17, 27.82, 26.96, 27.35, 28.13, 28.18, 28.16, 27.93, 27.82, 27.95, 31.13]. |
| A2 | Feixiang | 0.99 | = 1.00, = [56.26, 54.15, 64.16, 61.52, 63.69, 70.2, 69.01, 64.67, 59.95, 64.86, 60.23, 53.74]. |
| B1 | Chengan | 1.02 | = 1.00, = [61.22, 60.47, 61.23, 61.36, 63.4, 66.06, 66.62, 64.86, 63.21, 63.94, 63.71, 61.66]. |
| B2 | Linzhang | 0.16 | = 0.96, = [−3.22, 1.57, 8.24, 5.33, 3.97, 4.87, 3.69, 2.13, 2.23, 3.17, 2.7, 2.35]. |
| B3 | Daming | 1.02 | = 1.01, = [44.41, 43.47, 40.54, 40.28, 40.55, 41.66, 41.9, 41.78, 41.08, 41.17, 41.28, 42.07]. |
| C1 | Qiu | 1.06 | = 1.01, = [48.83, 47.42, 50.2, 52.17, 52.47, 60.82, 58.57, 55.02, 52.39, 51.51, 51.11, 56.05]. |
| C2 | Quzhou | 1.05 | = 1.01, = [60.59, 59.07, 64.58, 67.72, 69.49, 78.88, 78.08, 72.48, 68.65, 71.73, 70.44, 63.33]. |
| C4 | Guangping | 1.05 | = 1.01, = [77.56, 75.71, 88.39, 85.56, 86.81, 101.78, 96.94, 89.66, 83.43, 88.44, 82.47, 81.99]. |
| D1 | Jize | 1.02 | = 1.01, = [39.13, 37.86, 44.88, 45.09, 47.46, 51.62, 50.54, 48.49, 44.44, 45.66, 46.03, 42.84]. |
| D2 | Wei | 0.99 | = 1.00, = [52.77, 52.29, 55.95, 54.53, 55.12, 59.1, 58.55, 57.25, 55.26, 56.3, 56.34, 54.53]. |
| D3 | Guantao | 1.02 | = 1.00, = [60.8, 62.77, 63.76, 64.04, 63.71, 66.74, 68.23, 66.51, 64.37, 64.34, 63.95, 62.14]. |
| D4 | Yongnian | 1.03 | = 1.00, = [43.97, 43.66, 42.71, 43.1, 44.52, 45.87, 46.09, 45.57, 44.98, 44.7, 44.7, 44.25]. |
| Date | A | B | C | D | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Municipal Districts | Feixiang | Chengan | Linzhang | Daming | Qiu | Quzhou | Guangping | Jize | Wei | Guantao | Yongnian | |
| Fitted value | ||||||||||||
| Jan-2018 | 27.10 | 72.15 | 58.38 | 33.58 | 37.95 | 55.93 | 41.36 | 70.52 | 39.42 | 53.74 | 62.99 | 42.87 |
| Feb-2018 | 28.28 | 55.20 | 59.51 | 28.45 | 42.93 | 44.65 | 57.34 | 72.76 | 37.33 | 52.94 | 61.77 | 42.47 |
| Mar-2018 | 28.04 | 65.64 | 59.87 | 33.05 | 39.76 | 46.84 | 61.45 | 84.10 | 44.25 | 56.96 | 62.41 | 40.96 |
| Apr-2018 | 27.30 | 63.56 | 59.80 | 34.26 | 39.49 | 48.37 | 63.76 | 80.10 | 44.36 | 55.88 | 62.52 | 41.04 |
| May-2018 | 27.79 | 66.16 | 61.75 | 34.41 | 39.80 | 48.39 | 65.02 | 80.96 | 46.77 | 56.72 | 62.14 | 42.23 |
| Jun-2018 | 28.68 | 73.11 | 64.35 | 35.78 | 40.98 | 56.65 | 74.12 | 95.70 | 51.01 | 60.94 | 65.19 | 43.39 |
| Jul-2018 | 28.84 | 72.44 | 64.87 | 35.90 | 41.30 | 54.02 | 72.83 | 90.19 | 50.00 | 60.65 | 66.68 | 43.43 |
| Aug-2018 | 28.94 | 68.54 | 63.12 | 34.64 | 41.29 | 50.55 | 67.14 | 82.94 | 48.11 | 59.57 | 65.01 | 42.80 |
| Sep-2018 | 28.82 | 64.19 | 61.55 | 33.86 | 40.72 | 48.23 | 63.59 | 77.14 | 44.29 | 57.78 | 62.98 | 42.13 |
| Oct-2018 | 28.83 | 69.41 | 62.40 | 34.17 | 40.96 | 47.75 | 67.05 | 82.72 | 45.78 | 58.98 | 63.13 | 41.82 |
| Nov-2018 | 29.07 | 65.18 | 62.27 | 33.94 | 41.24 | 47.72 | 65.92 | 76.96 | 46.38 | 59.21 | 62.89 | 41.79 |
| Dec-2018 | 32.37 | 59.00 | 60.33 | 33.44 | 42.19 | 53.02 | 59.11 | 77.05 | 43.41 | 57.58 | 61.25 | 41.33 |
| Jan-2019 | 30.01 | 61.76 | 60.06 | 27.47 | 44.69 | 45.90 | 56.97 | 73.09 | 39.98 | 55.97 | 60.11 | 41.04 |
| Feb-2019 | 29.66 | 59.96 | 59.45 | 27.46 | 43.89 | 45.11 | 55.99 | 71.86 | 39.02 | 55.62 | 62.28 | 40.74 |
| Mar-2019 | 29.43 | 70.25 | 60.37 | 33.77 | 41.14 | 48.41 | 61.99 | 85.13 | 46.32 | 59.41 | 63.44 | 39.81 |
| Apr-2019 | 28.69 | 68.05 | 60.64 | 35.77 | 41.12 | 50.69 | 65.33 | 82.27 | 46.68 | 58.19 | 63.88 | 40.24 |
| May-2019 | 29.19 | 70.57 | 62.83 | 36.32 | 41.60 | 51.26 | 67.28 | 83.93 | 49.27 | 58.93 | 63.74 | 41.68 |
| Jun-2019 | 30.08 | 77.46 | 65.62 | 37.89 | 42.91 | 59.95 | 76.88 | 99.27 | 53.65 | 63.07 | 66.96 | 43.01 |
| Jul-2019 | 30.25 | 76.74 | 66.27 | 38.10 | 43.34 | 57.65 | 76.00 | 94.23 | 52.76 | 62.73 | 68.60 | 43.20 |
| Aug-2019 | 30.36 | 72.82 | 64.65 | 36.86 | 43.42 | 54.47 | 70.64 | 87.38 | 50.97 | 61.60 | 67.05 | 42.68 |
| Sep-2019 | 30.24 | 68.44 | 63.18 | 36.04 | 42.92 | 52.40 | 67.36 | 81.91 | 47.23 | 59.76 | 65.13 | 42.11 |
| Oct-2019 | 30.25 | 73.64 | 64.11 | 36.30 | 43.23 | 52.14 | 71.06 | 87.78 | 48.80 | 60.94 | 65.35 | 41.87 |
| Nov-2019 | 30.50 | 69.40 | 64.04 | 35.99 | 43.56 | 52.31 | 70.14 | 82.28 | 49.46 | 61.14 | 65.19 | 41.91 |
| Dec-2019 | 33.81 | 63.21 | 62.17 | 35.39 | 44.57 | 57.79 | 63.52 | 82.59 | 46.56 | 59.48 | 63.62 | 41.51 |
| Predicted value | ||||||||||||
| Jan-2020 | 31.45 | 65.96 | 61.96 | 29.32 | 47.11 | 50.84 | 61.54 | 78.84 | 43.18 | 57.85 | 62.55 | 41.28 |
| Feb-2020 | 31.11 | 64.16 | 61.40 | 29.21 | 46.36 | 50.19 | 60.72 | 77.80 | 42.27 | 57.49 | 64.77 | 41.03 |
| Mar-2020 | 30.88 | 74.45 | 62.37 | 35.40 | 43.65 | 53.64 | 66.87 | 91.25 | 49.62 | 61.27 | 65.98 | 40.14 |
| Apr-2020 | 30.14 | 72.25 | 62.68 | 37.30 | 43.66 | 56.05 | 70.34 | 88.56 | 50.03 | 60.03 | 66.47 | 40.60 |
| May-2020 | 30.65 | 74.77 | 64.91 | 37.75 | 44.18 | 56.75 | 72.41 | 90.36 | 52.67 | 60.76 | 66.37 | 42.07 |
| Jun-2020 | 31.55 | 81.67 | 67.74 | 39.21 | 45.53 | 65.56 | 82.13 | 105.85 | 57.09 | 64.89 | 69.63 | 43.44 |
| Jul-2020 | 31.72 | 80.95 | 68.43 | 39.32 | 45.99 | 63.39 | 81.36 | 100.95 | 56.24 | 64.54 | 71.31 | 43.65 |
| Aug-2020 | 31.84 | 77.03 | 66.83 | 37.97 | 46.09 | 60.32 | 76.10 | 94.23 | 54.49 | 63.40 | 69.79 | 43.16 |
| Sep-2020 | 31.73 | 72.66 | 65.39 | 37.06 | 45.63 | 58.37 | 72.93 | 88.89 | 50.79 | 61.56 | 67.90 | 42.61 |
| Oct-2020 | 31.75 | 77.87 | 66.35 | 37.23 | 45.96 | 58.22 | 76.73 | 94.88 | 52.40 | 62.73 | 68.16 | 42.40 |
| Nov-2020 | 32.00 | 73.64 | 66.31 | 36.82 | 46.32 | 58.49 | 75.91 | 89.50 | 53.09 | 62.92 | 68.03 | 42.46 |
| Dec-2020 | 35.31 | 67.46 | 64.47 | 36.14 | 47.36 | 64.08 | 69.38 | 89.92 | 50.23 | 61.26 | 66.49 | 42.08 |
| Date | A | B | C | D | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Municipal Districts | Feixiang | Chengan | Linzhang | Daming | Qiu | Quzhou | Guangping | Jize | Wei | Guantao | Yongnian | |
| MAPE | 1.90% | 2.56% | 1.06% | 0.92% | 1.10% | 3.05% | 2.90% | 2.48% | 2.17% | 1.00% | 1.35% | 0.73% |
| MAE | 0.59 | 1.72 | 0.73 | 0.41 | 0.47 | 1.74 | 2.22 | 2.17 | 1.06 | 0.65 | 0.9 | 0.39 |
| RMSE | 1.03 | 2.38 | 0.87 | 0.56 | 0.62 | 2.67 | 2.74 | 2.7 | 1.54 | 0.97 | 1.23 | 0.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Wu, L.; Yin, K.; Yang, W.; Huang, C. A Discrete Grey Seasonal Model with Fractional Order Accumulation and Its Application in Forecasting the Groundwater Depth. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9020117
Zhang K, Wu L, Yin K, Yang W, Huang C. A Discrete Grey Seasonal Model with Fractional Order Accumulation and Its Application in Forecasting the Groundwater Depth. Fractal and Fractional. 2025; 9(2):117. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9020117
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Kai, Lifeng Wu, Kedong Yin, Wendong Yang, and Chong Huang. 2025. "A Discrete Grey Seasonal Model with Fractional Order Accumulation and Its Application in Forecasting the Groundwater Depth" Fractal and Fractional 9, no. 2: 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9020117
APA StyleZhang, K., Wu, L., Yin, K., Yang, W., & Huang, C. (2025). A Discrete Grey Seasonal Model with Fractional Order Accumulation and Its Application in Forecasting the Groundwater Depth. Fractal and Fractional, 9(2), 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9020117









