The Impact of Sentinel-1-Corrected Fractal Roughness on Soil Moisture Retrievals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
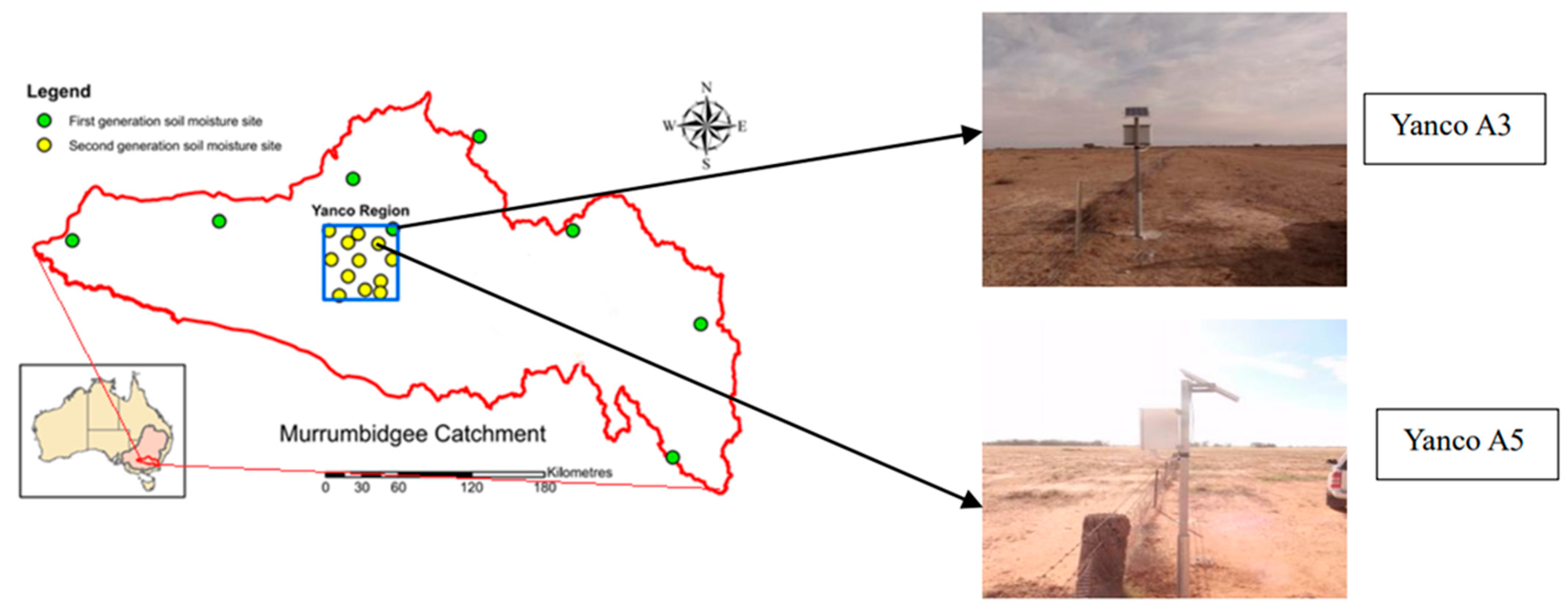
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Inversion of Soil Moisture from Sentinel-1 Backscattering
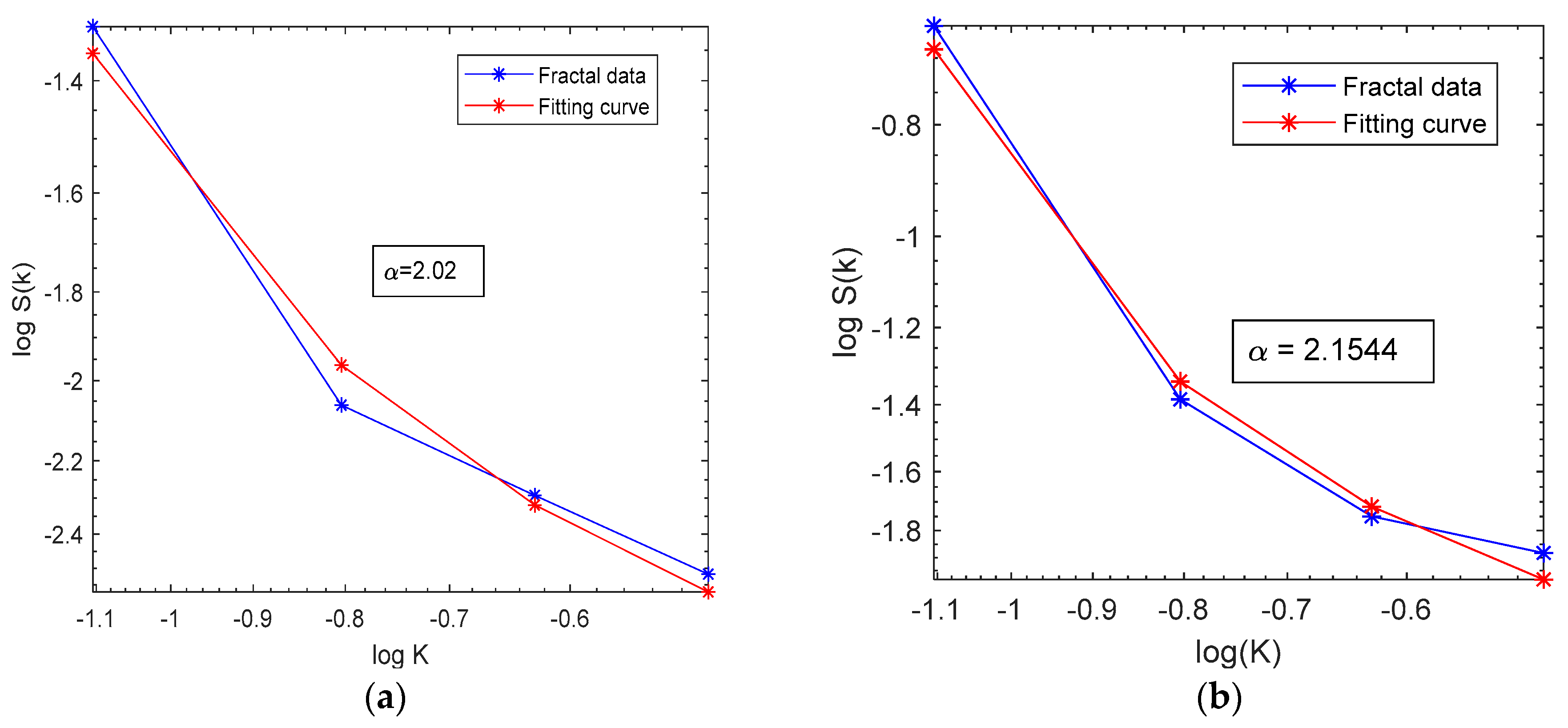
2.3. Fractal Roughness
3. Results and Discussion
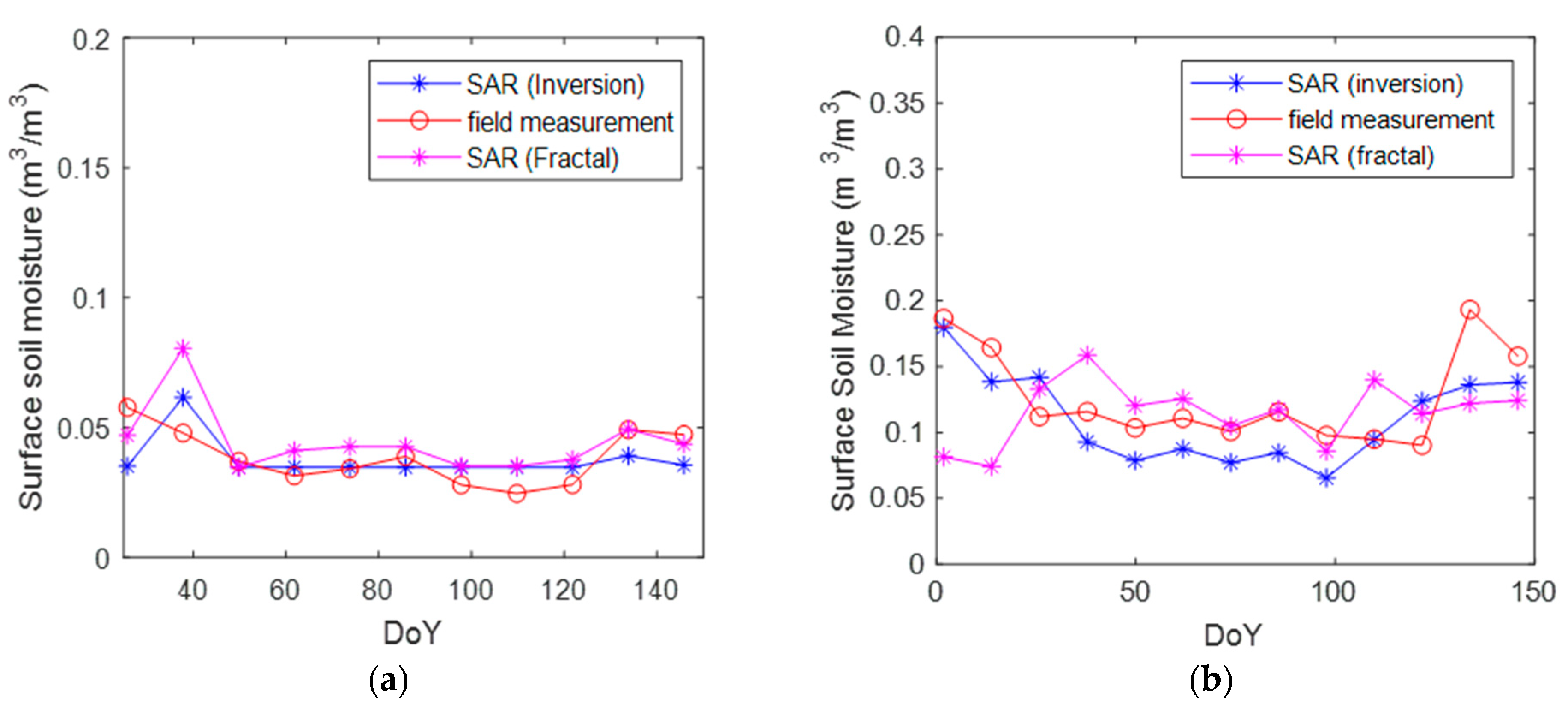
3.1. Validation of Soil Moisture Retrievals at Local Point Scales
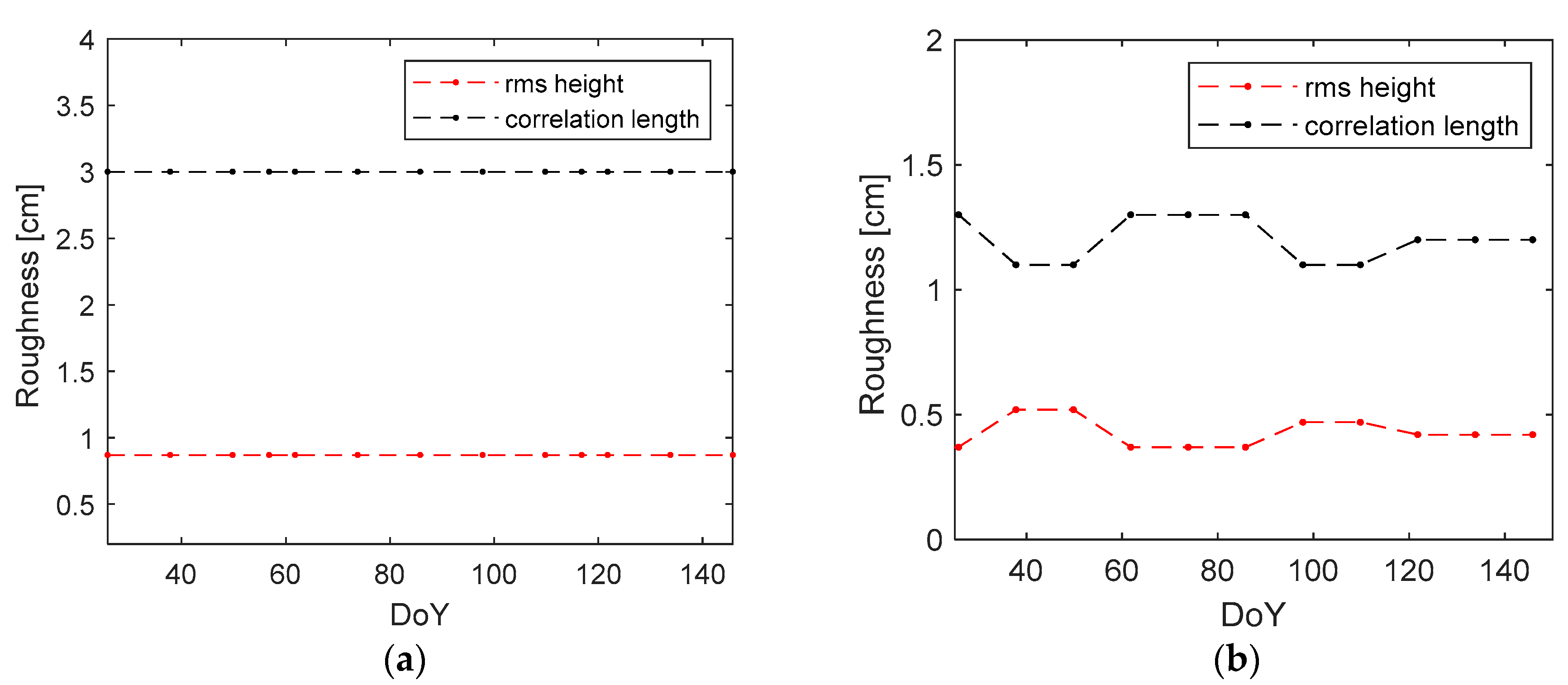
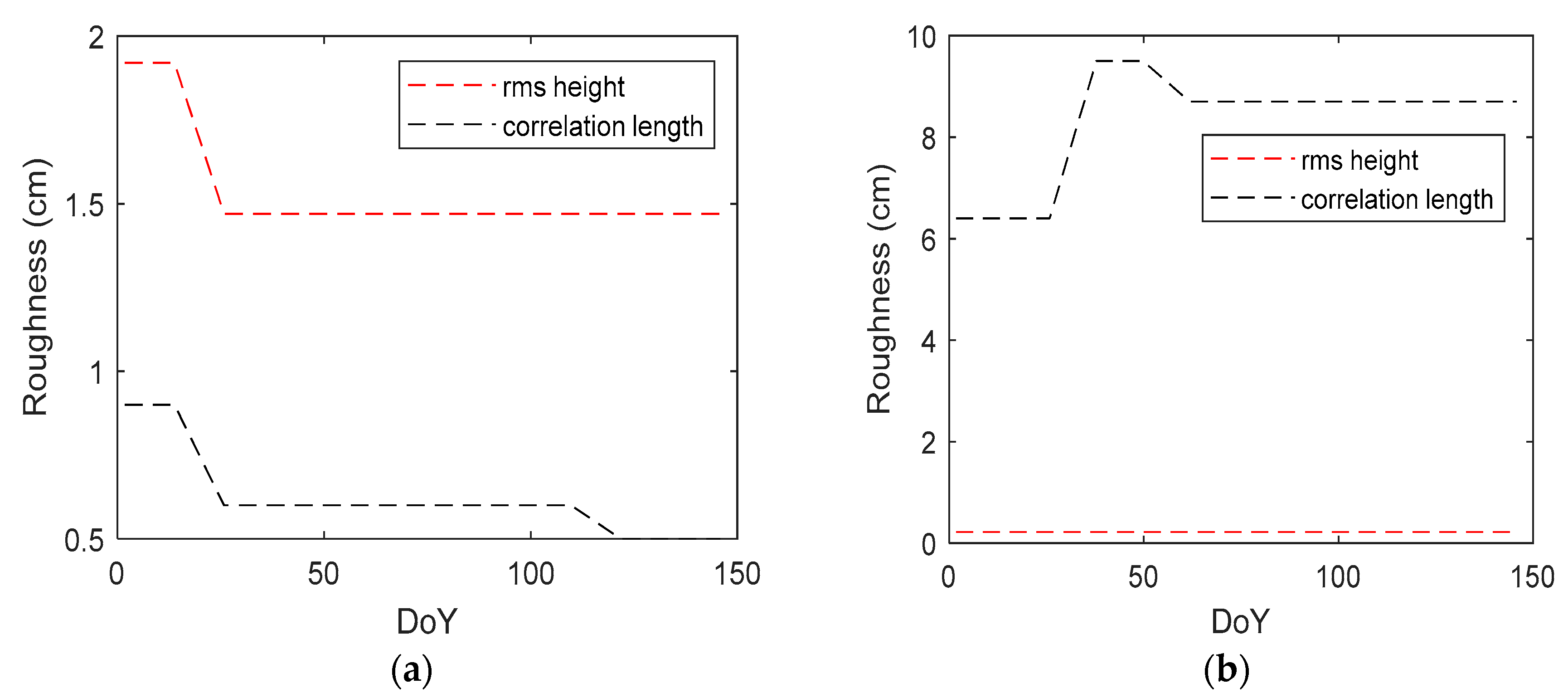
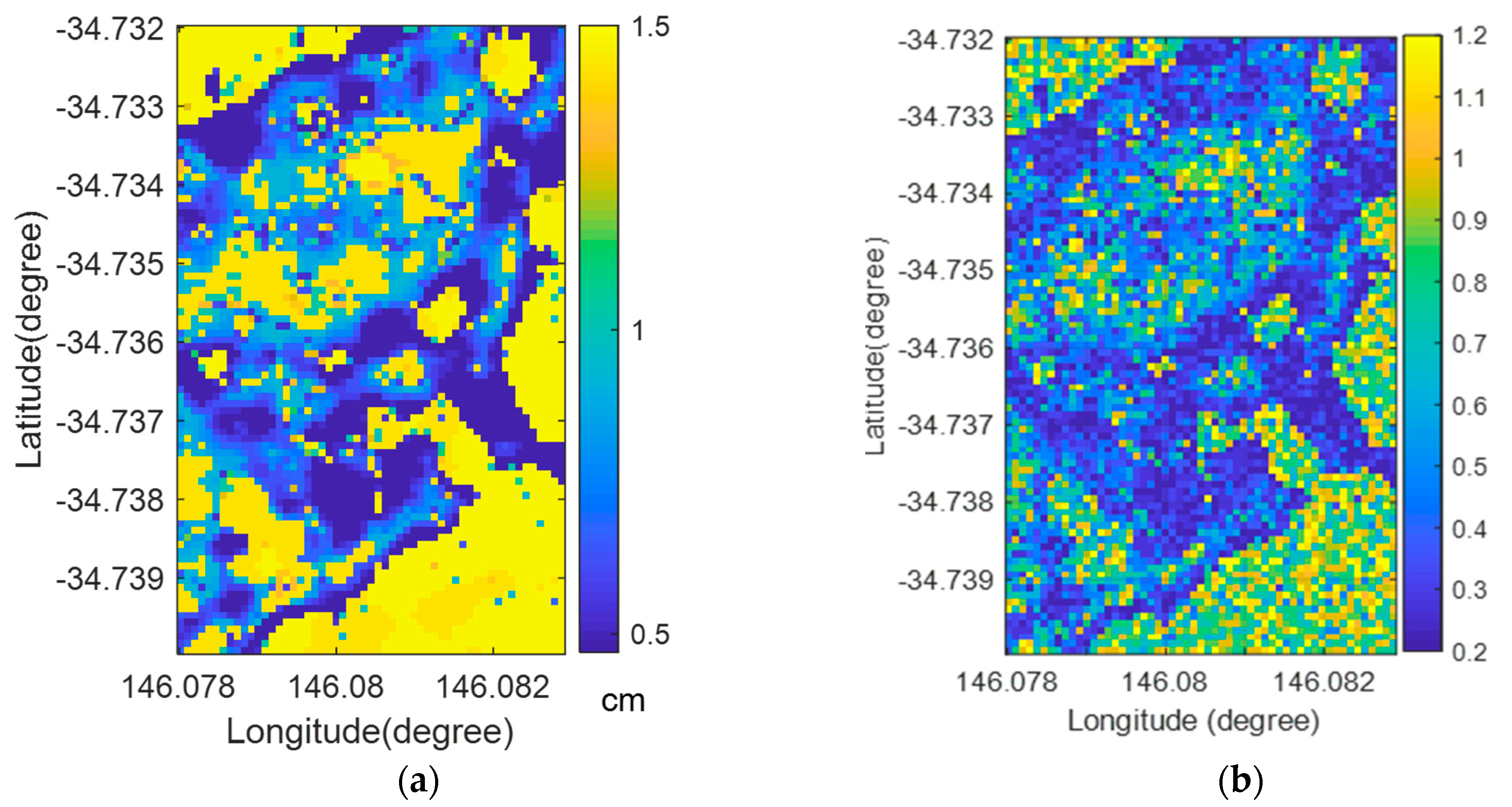
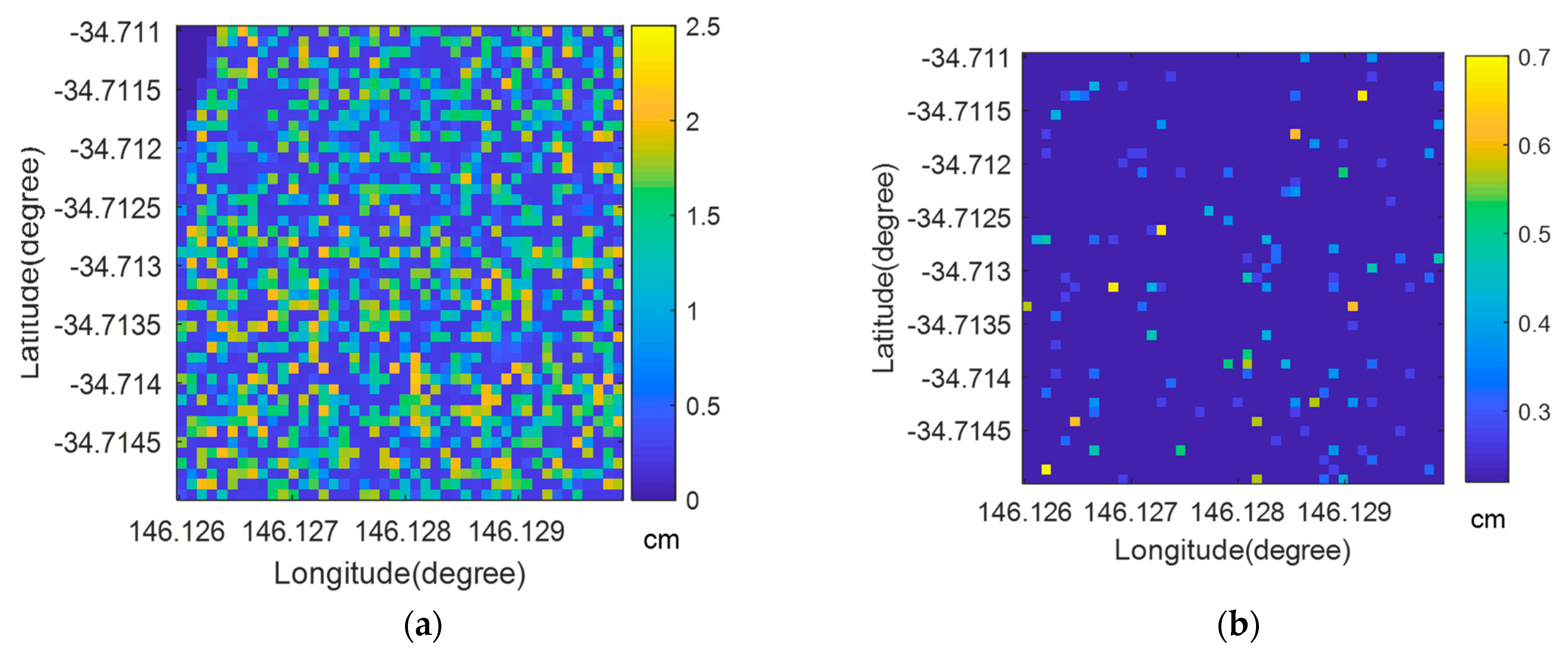
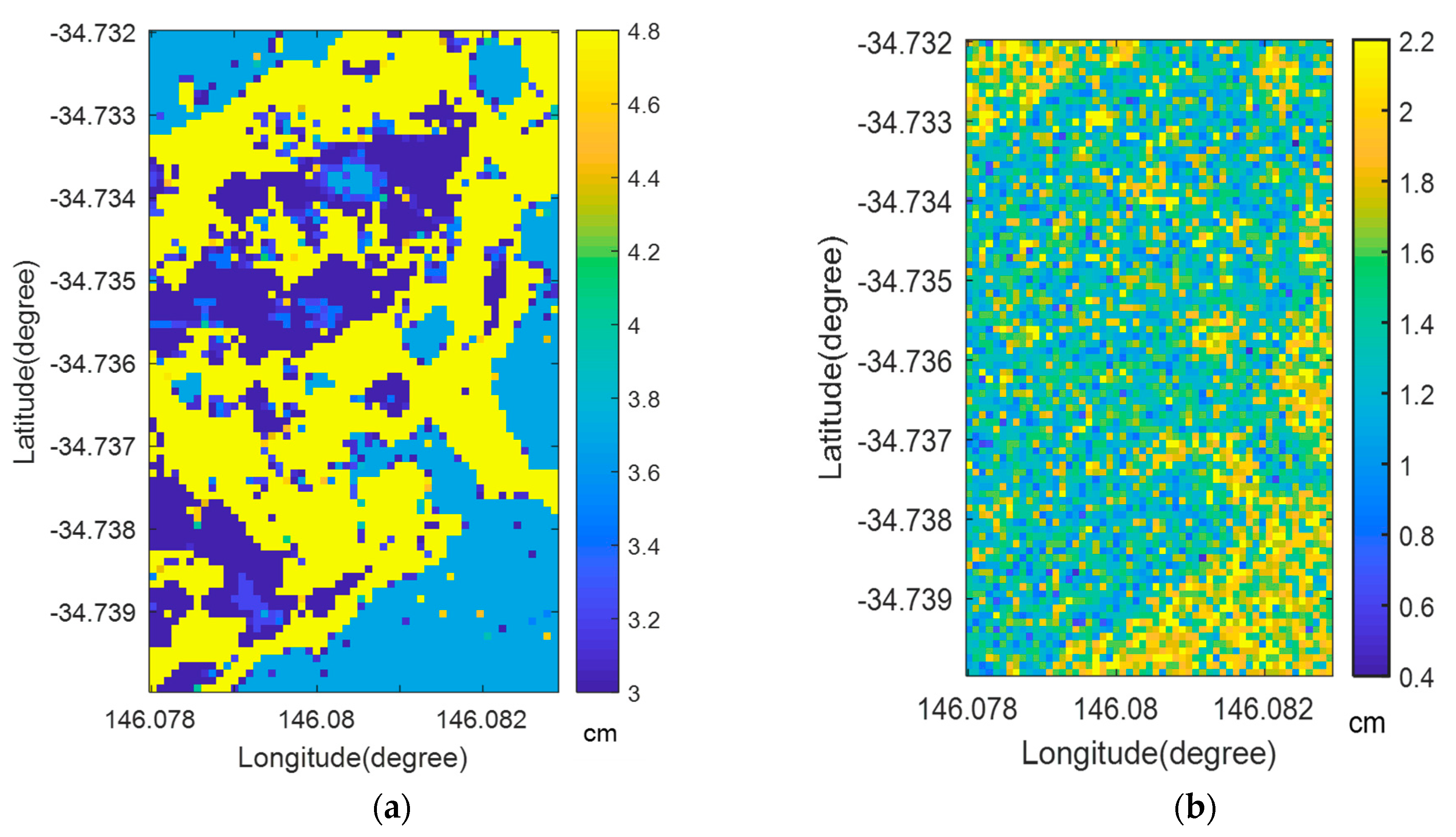
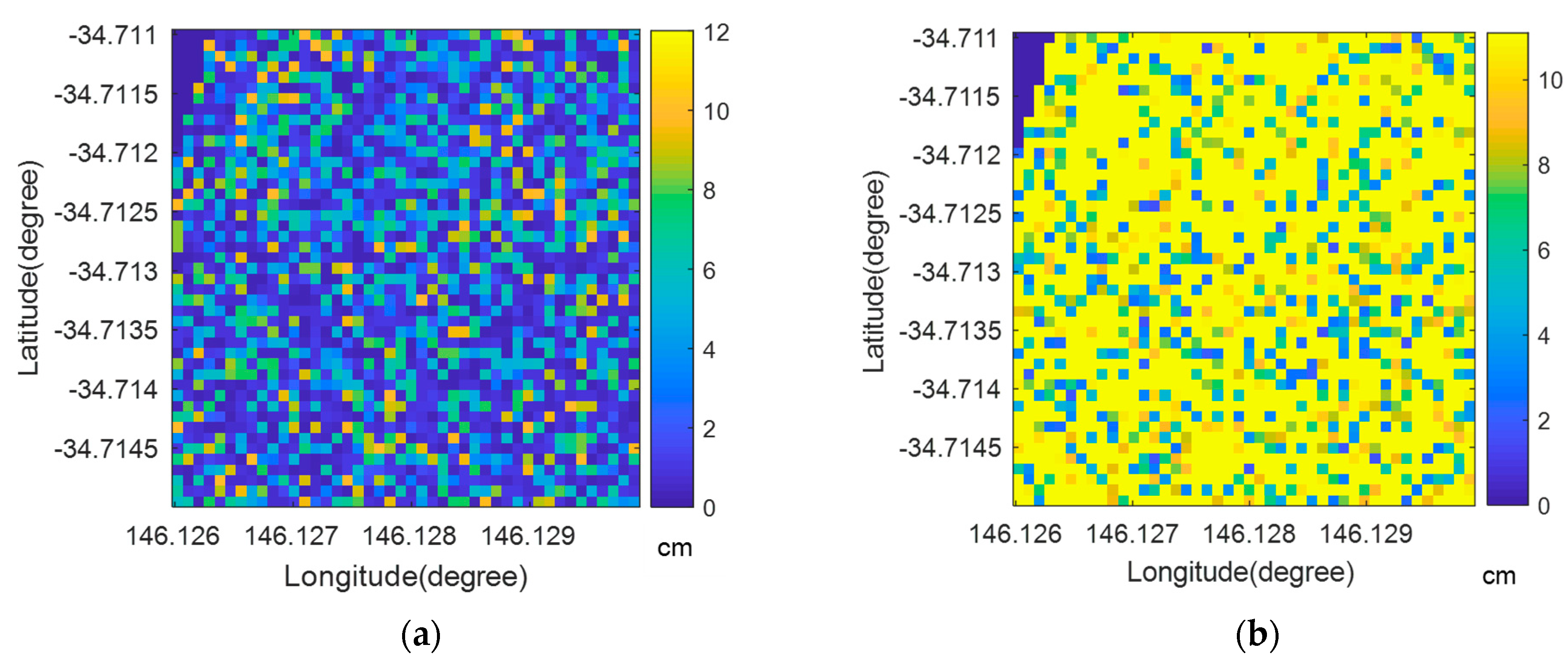
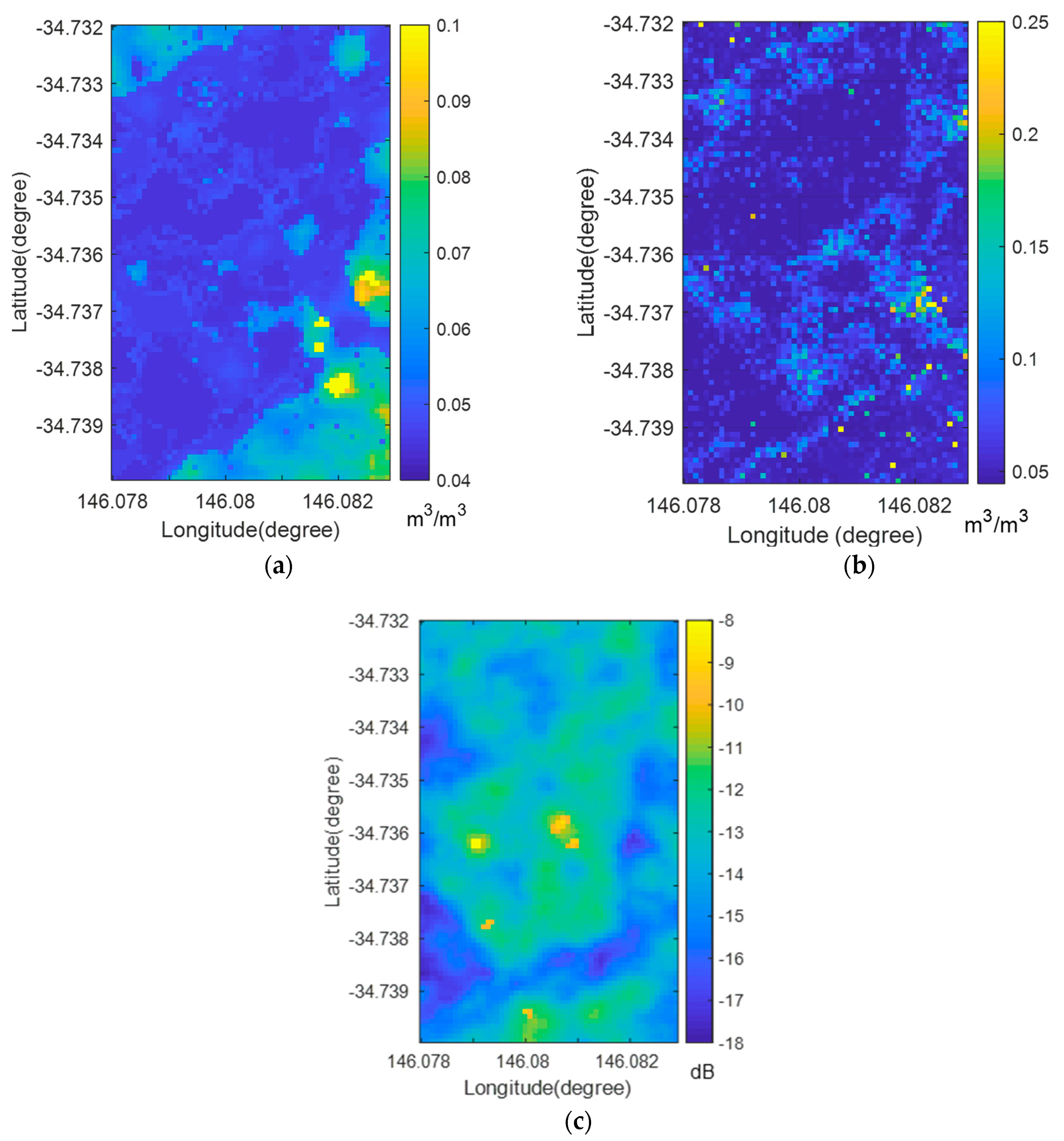
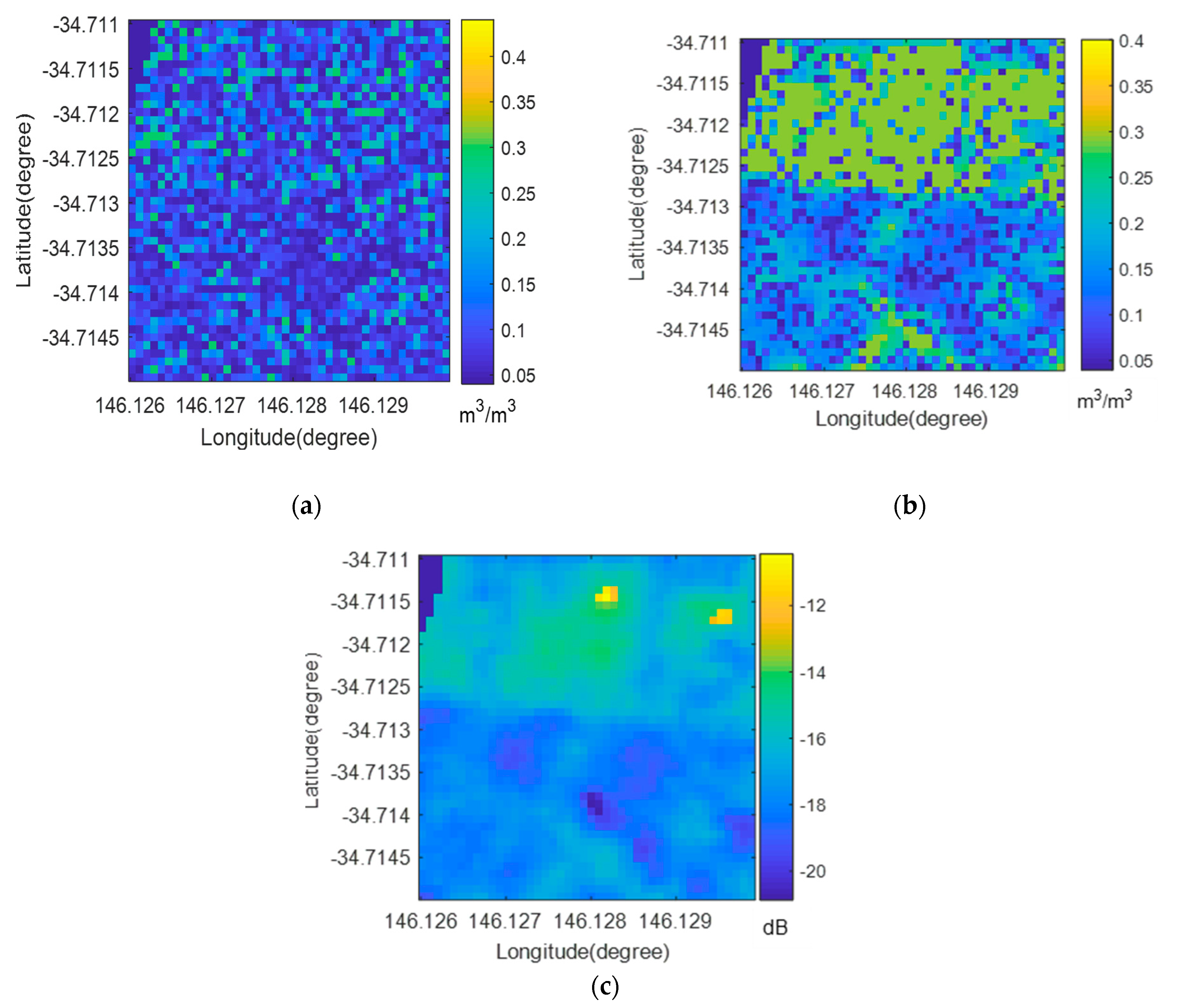
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Surface Roughness: Single-Scale vs. Multi-Scale
3.3. Impact of Roughness on Surface Soil Moisture Retrievals
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdelsalam, M.G.; Stern, R.J. Mapping Precambrian structures in the Sahara Desert with SIR-C/X-SAR radar: The Neoproterozoic Keraf Suture, NE Sudan. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 1996, 101, 23063–23076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, G.; Riccio, D.; Zinno, I. SAR Imaging of Fractal Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, S.; Kemper, T.; Riedlinger, T.; Kiefl, R.; Scholte, K.; Mehl, H. Satellite Image Analysis for Disaster and Crisis-Management Support. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.L.; Farr, T.G.; Zyl, J.J.v. Estimates of surface roughness derived from synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, W. Quantitative roughness characterization of geological surfaces and implications for radar signature analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 2397–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeks, R.; Smith, M.; Pak, K.; Gillespie, A. Inversions of SIR-C and AIRSAR data for the roughness of geological surfaces. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 59, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrab, A.; Zribi, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Mougenot, B.; Fanise, P.; Chabaane, Z.L. Retrieval of Both Soil Moisture and Texture Using TerraSAR-X Images. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10098–10116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattia, F.; Le Toan, T. Backscattering Properties of Multi-Scale Rough Surfaces. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 1999, 13, 493–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zribi, M.; Ciarletti, V.; Taconet, O. Validation of a Rough Surface Model Based on Fractional Brownian Geometry with SIRC and ERASME Radar Data over Orgeval. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 73, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, M.; Amini, J.; Notarnicola, C. Soil roughness retrieval from TerraSar-X data using neural network and fractal method. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 64, 1117–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornelsen, K.; Coulibaly, P. Advances in soil moisture retrieval from synthetic aperture radar and hydrological applications. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 460–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievens, H.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; De Keyser, E.; Vernieuwe, H.; Matgen, P.; Álvarez-Mozos, J.; De Baets, B. Effective roughness modelling as a tool for soil moisture retrieval from C- and L-band SAR. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzouki, A.; McNairn, H.; Pacheco, A. Mapping Soil Moisture Using RADARSAT-2 Data and Local Autocorrelation Statistics. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2011, 4, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabus, B.; Wehn, H.; Nolan, M. The Importance of Soil Moisture and Soil Structure for InSAR Phase and Backscatter, as Determined by FDTD Modeling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 2421–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Moran, M.S.; Thoma, D.P.; Bryant, R.; Holifield Collins, C.D.; Jackson, T.; Orr, B.J.; Tischler, M. Mapping surface roughness and soil moisture using multi-angle radar imagery without ancillary data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Moran, M.S.; Thoma, D.P.; Bryant, R.; Sano, E.E.; Holifield Collins, C.D.; Skirvin, S.; Kershner, C.; Orr, B.J. A derivation of roughness correlation length for parameterizing radar backscatter models. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 3995–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M.W.J.; Thuy Le, T.; Mattia, F.; Satalino, G.; Manninen, T.; Borgeaud, M. On the characterization of agricultural soil roughness for radar remote sensing studies. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattia, F.; Davidson, M.W.J.; Toan, T.L.; Haese, C.M.F.D.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; Gatti, A.M.; Borgeaud, M. A comparison between soil roughness statistics used in surface scattering models derived from mechanical and laser profilers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1659–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature, Revised and Enlarged ed.; WH Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschetti, G.; Iodice, A.; Migliaccio, M.; Riccio, D. Scattering from natural rough surfaces modeled by fractional Brownian motion two-dimensional processes. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1999, 47, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, G.D.; Iodice, A.; Riccio, D.; Ruello, G. A Novel Approach for Disaster Monitoring: Fractal Models and Tools. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri, A.; Amini, J.; Dehmollaian, M.; Kavoosi, M.A. Better Estimated IEM Input Parameters Using Random Fractal Geometry Applied on Multi-Frequency SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.R.; Mishra, J.; Palai, G. Analysing roughness of surface through fractal dimension: A review. Image Vis. Comput. 2019, 89, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, G.; Iodice, A.; Riccio, D.; Ruello, G. Imaging of Fractal Profiles. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3280–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.B.; Walker, J.P.; Western, A.W.; Young, R.I.; Ellett, K.M.; Pipunic, R.C.; Grayson, R.B.; Siriwardena, L.; Chiew, F.H.S.; Richter, H. The Murrumbidgee soil moisture monitoring network data set. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W07701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laur, H.; Bally, P.; Meadows, P.; Sanchez, J.; Schaettler, B.; Lopinto, E.; Esteban, D. ERS SAR calibration. Derivation of the backscattering coefficient in ESA ERS SAR PRI products. ESA/ESRIN ES-TN-RS-PM-HL09 2004, 2. Available online: https://earth.esa.int/eogateway/documents/20142/37627/ERS-SAR-Calibration-Issue2.f_05_DLFE-643.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- van der Velde, R.; Su, Z.; van Oevelen, P.; Wen, J.; Ma, Y.; Salama, M.S. Soil moisture mapping over the central part of the Tibetan Plateau using a series of ASAR WS images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Walker, J. Inversion of soil roughness for estimating soil moisture from time-series Sentinel-1 backscatter observations over Yanco sites. Geocarto Int. 2020, 37, 1850–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lindenschmidt, K.-E. Bias-Corrected RADARSAT-2 Soil Moisture Dynamics Reveal Discharge Hysteresis at An Agricultural Watershed. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, A.K. Microwave Scattering and Emission Models and Their Applications; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, C.A.; Jackson, T.J.; Rawls, W.J. Estimating soil water-holding capacities by linking the Food and Agriculture Organization Soil map of the world with global pedon databases and continuous pedotransfer functions. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 3653–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboob Kanafi, M.; Tuononen, A.J. Top topography surface roughness power spectrum for pavement friction evaluation. Tribol. Int. 2017, 107, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.N.J.; Albohr, O.; Tartaglino, U.; Volokitin, A.I.; Tosatti, E. On the nature of surface roughness with application to contact mechanics, sealing, rubber friction and adhesion. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2005, 17, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| YA3 | YA5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fractal | Inversion | Fractal | Inversion | ||
| Roughness | rms height (cm) | 0.42 | 0.87 | 0.22 | 1.47 |
| Correlation length (cm) | 1.22 | 3.00 | 8.63 | 0.57 | |
| Soil moisture | Mean (m3/m3) | 0.04 | 0.037 | 0.12 | 0.10 |
| RMSE (m3/m3) | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.033 | 0.03 | |
| Bias (m3/m3) | 0.01 | −0.001 | 0.005 | −0.02 | |
| Cost in backscattering (dB) * | 0.03 | 0.78 | 0.013 | 0.01 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.-C. The Impact of Sentinel-1-Corrected Fractal Roughness on Soil Moisture Retrievals. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8030137
Lee JH, Kim H-C. The Impact of Sentinel-1-Corrected Fractal Roughness on Soil Moisture Retrievals. Fractal and Fractional. 2024; 8(3):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8030137
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ju Hyoung, and Hyun-Cheol Kim. 2024. "The Impact of Sentinel-1-Corrected Fractal Roughness on Soil Moisture Retrievals" Fractal and Fractional 8, no. 3: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8030137
APA StyleLee, J. H., & Kim, H.-C. (2024). The Impact of Sentinel-1-Corrected Fractal Roughness on Soil Moisture Retrievals. Fractal and Fractional, 8(3), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8030137







