Partially Penetrated Well Solution of Fractal Single-Porosity Naturally Fractured Reservoirs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
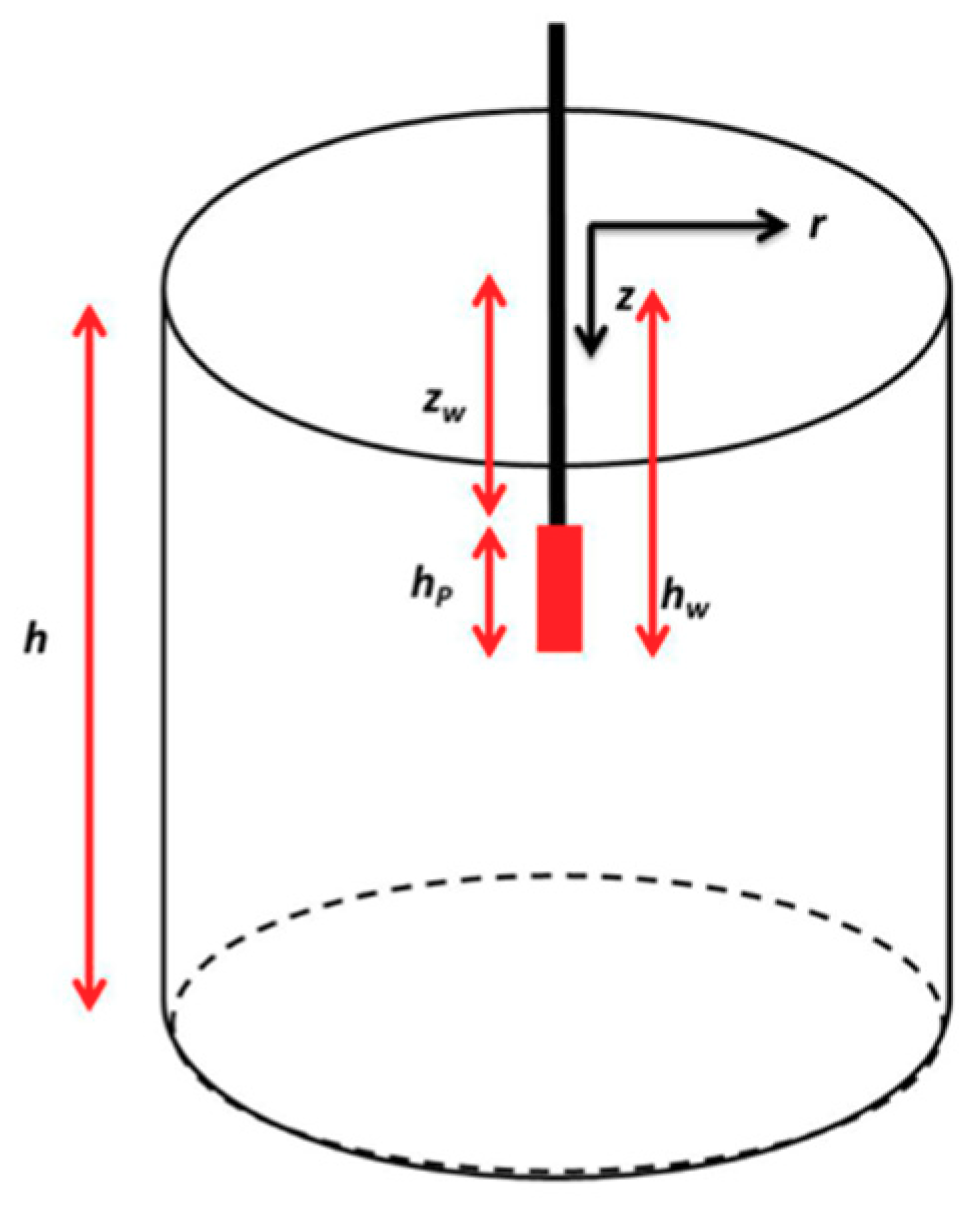
2. Problem Statement
3. Analytical Solution of the Problem
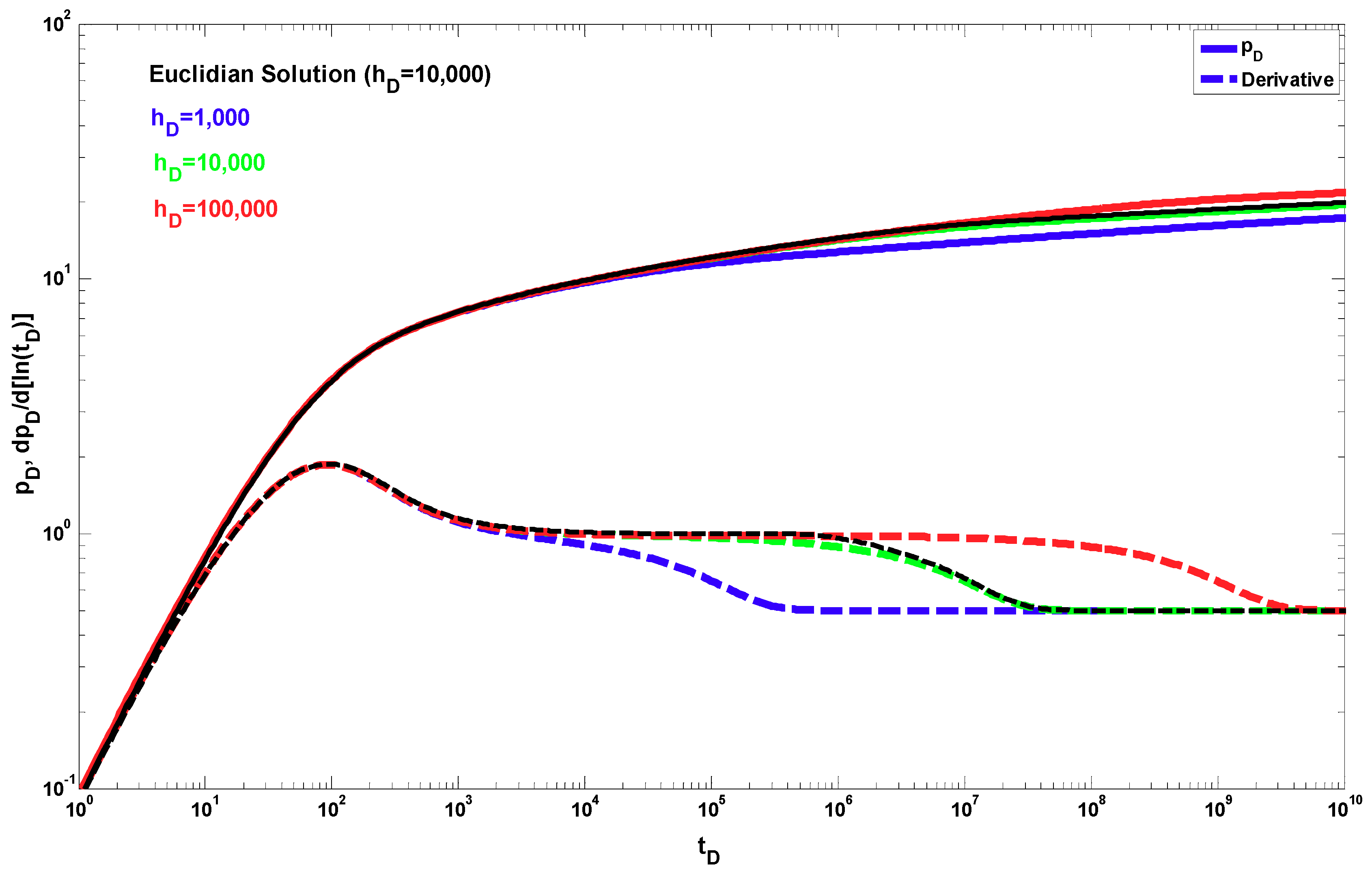
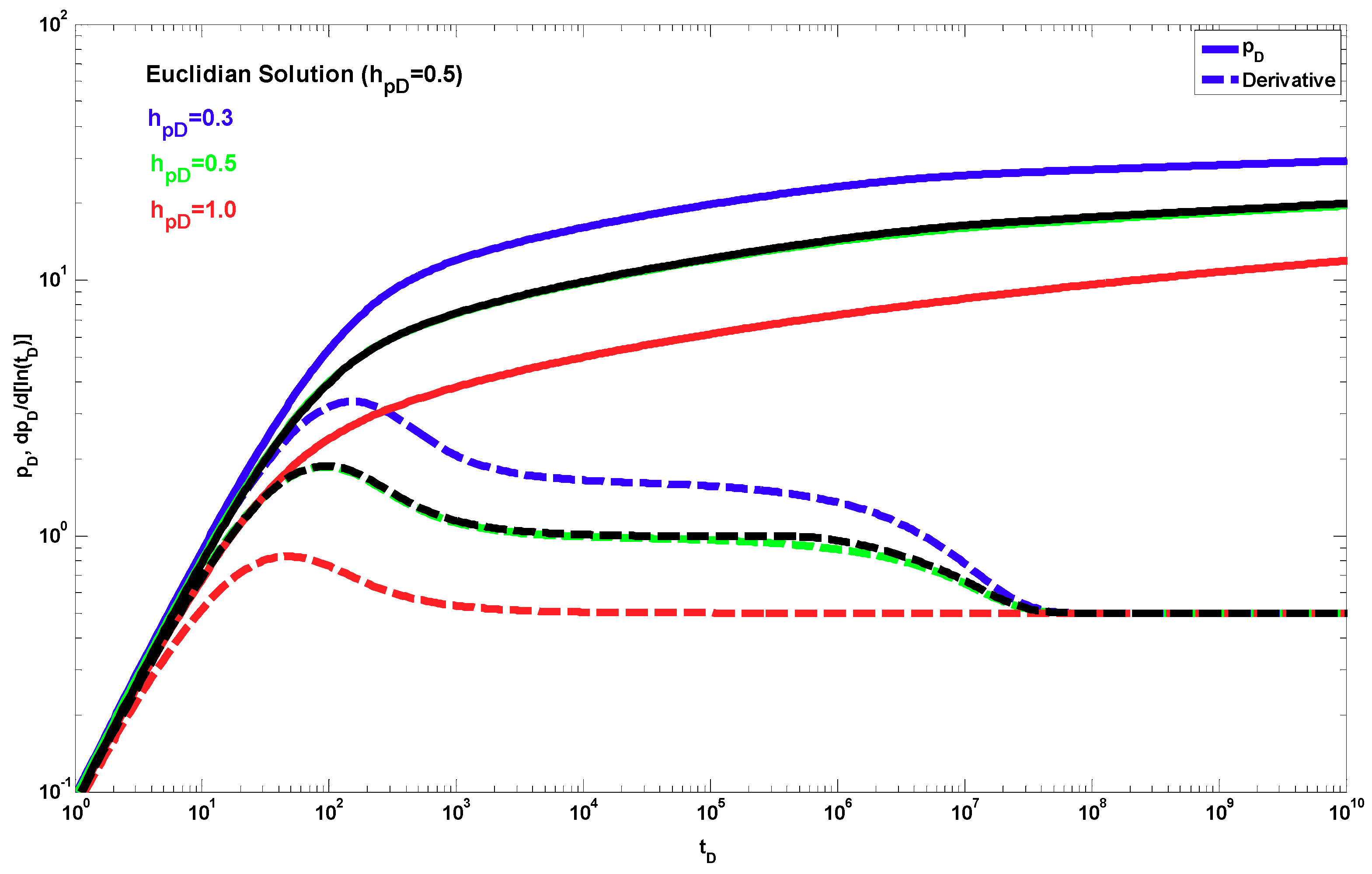
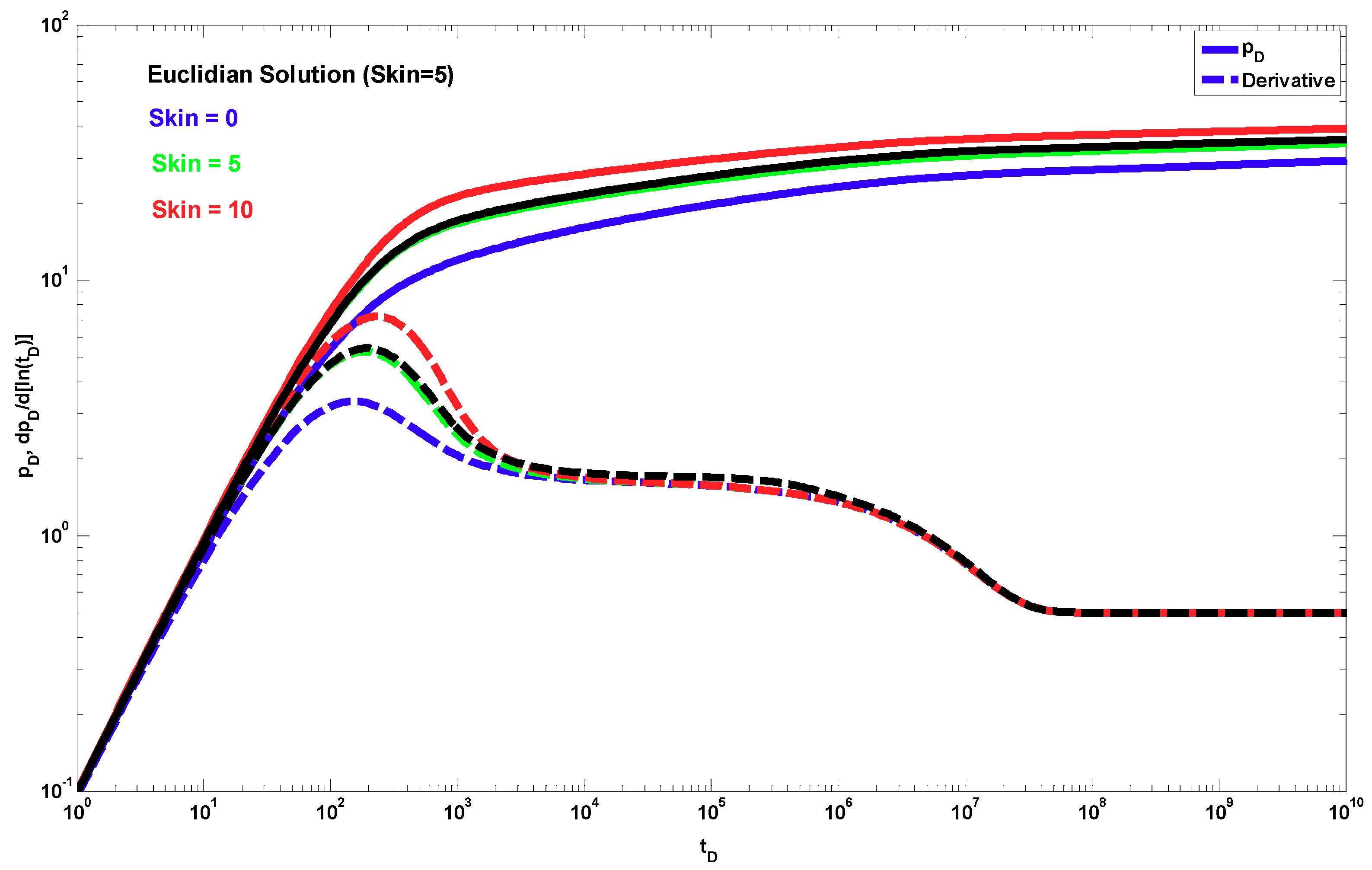
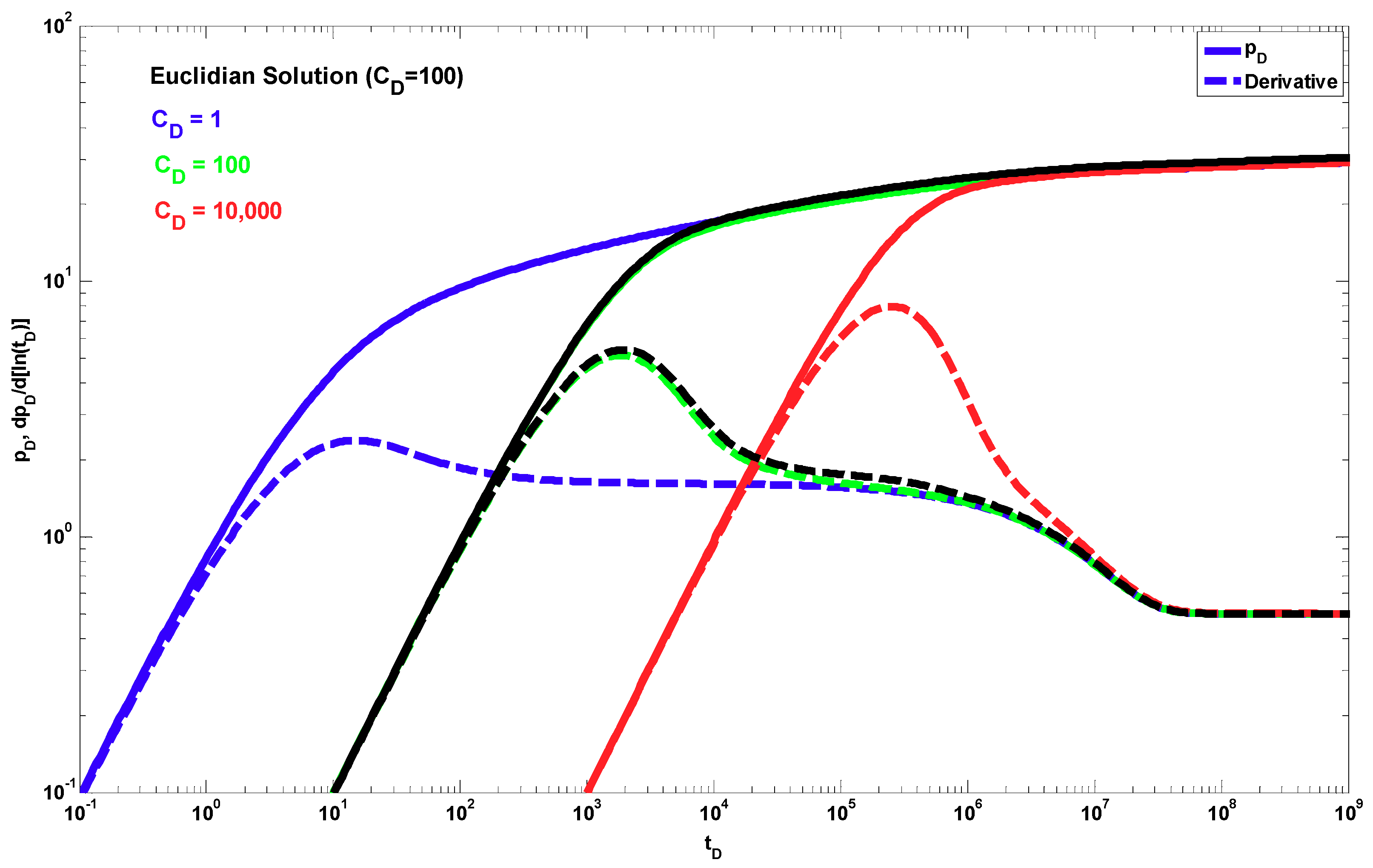
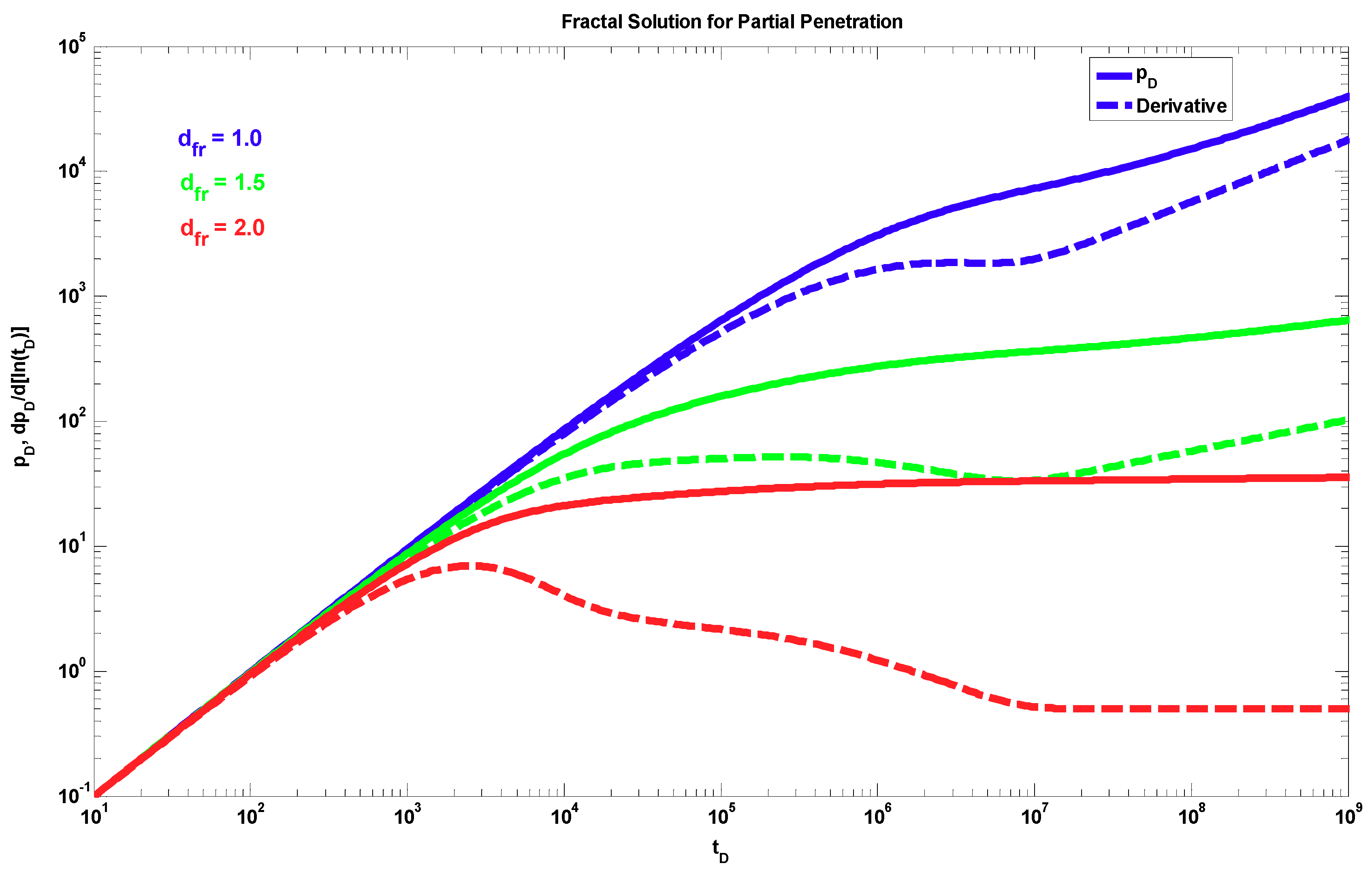
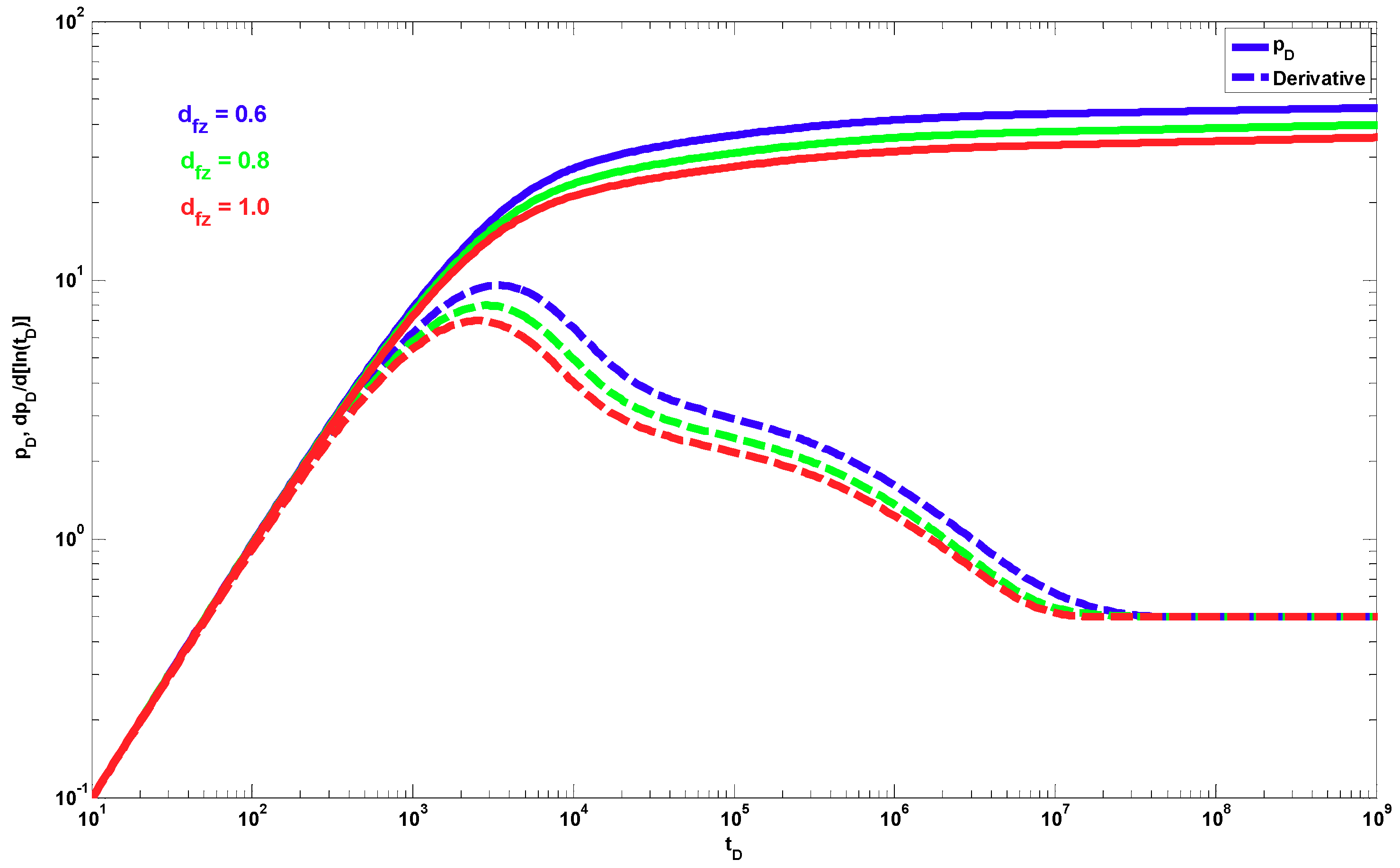
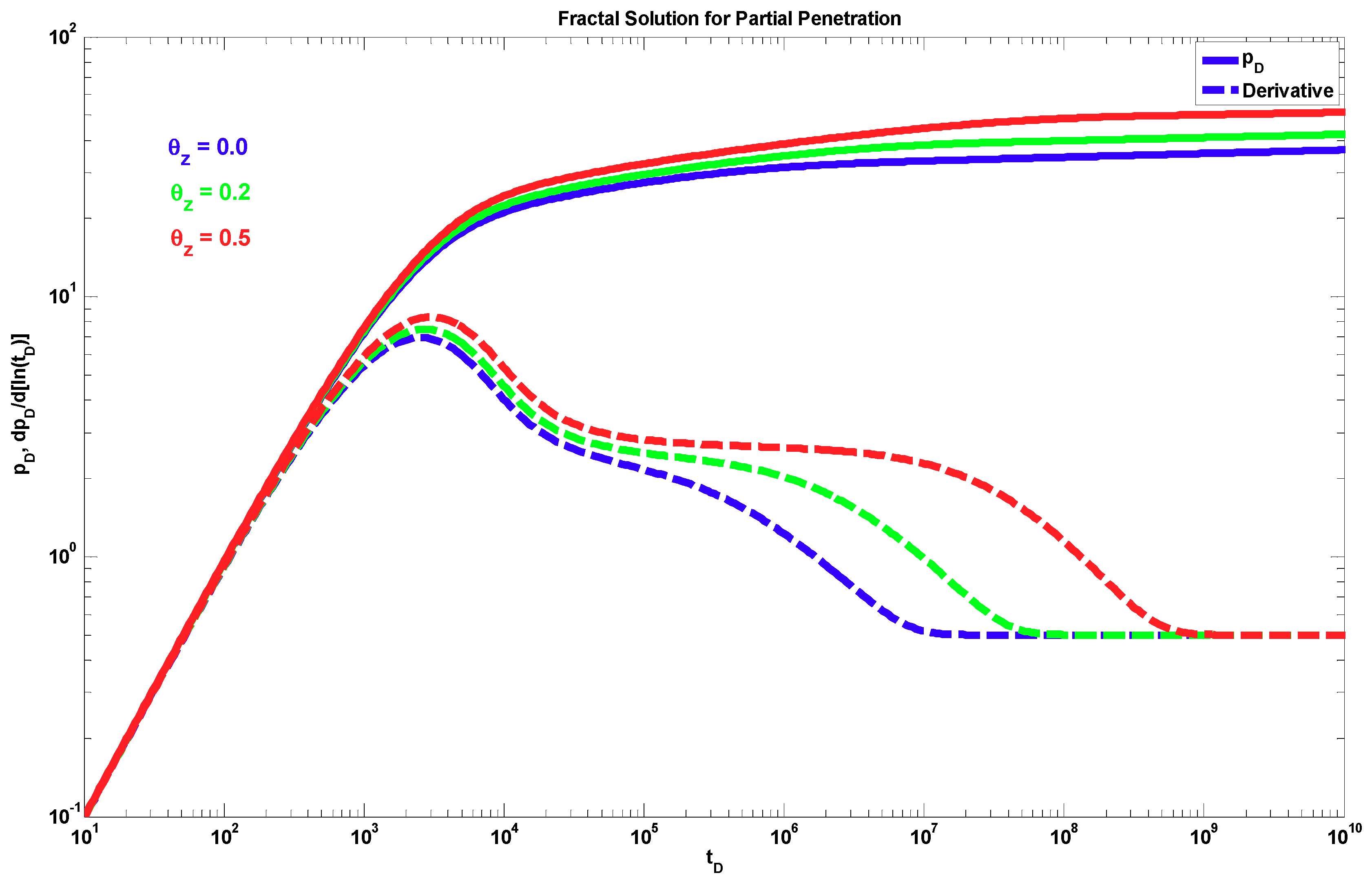
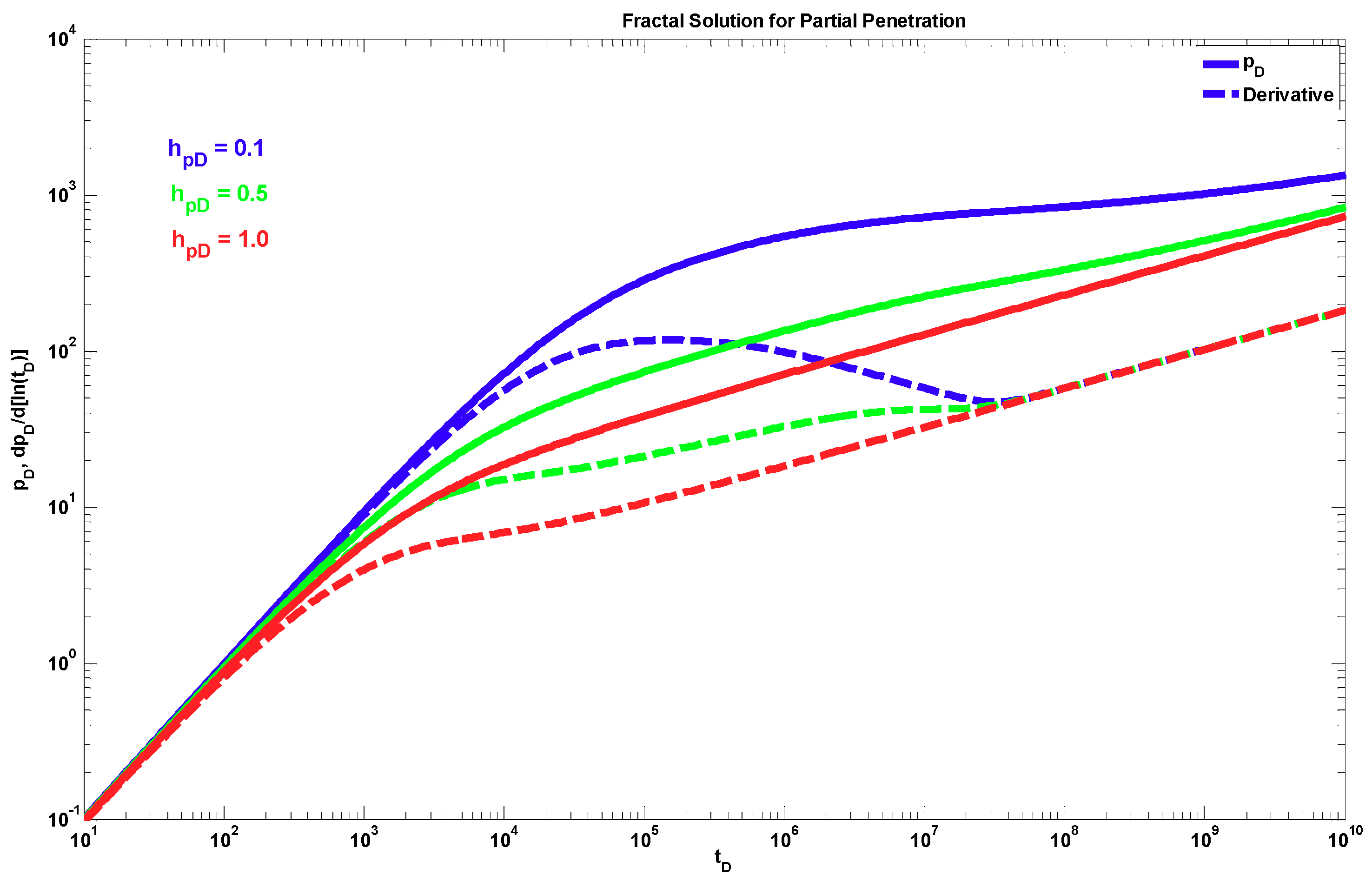
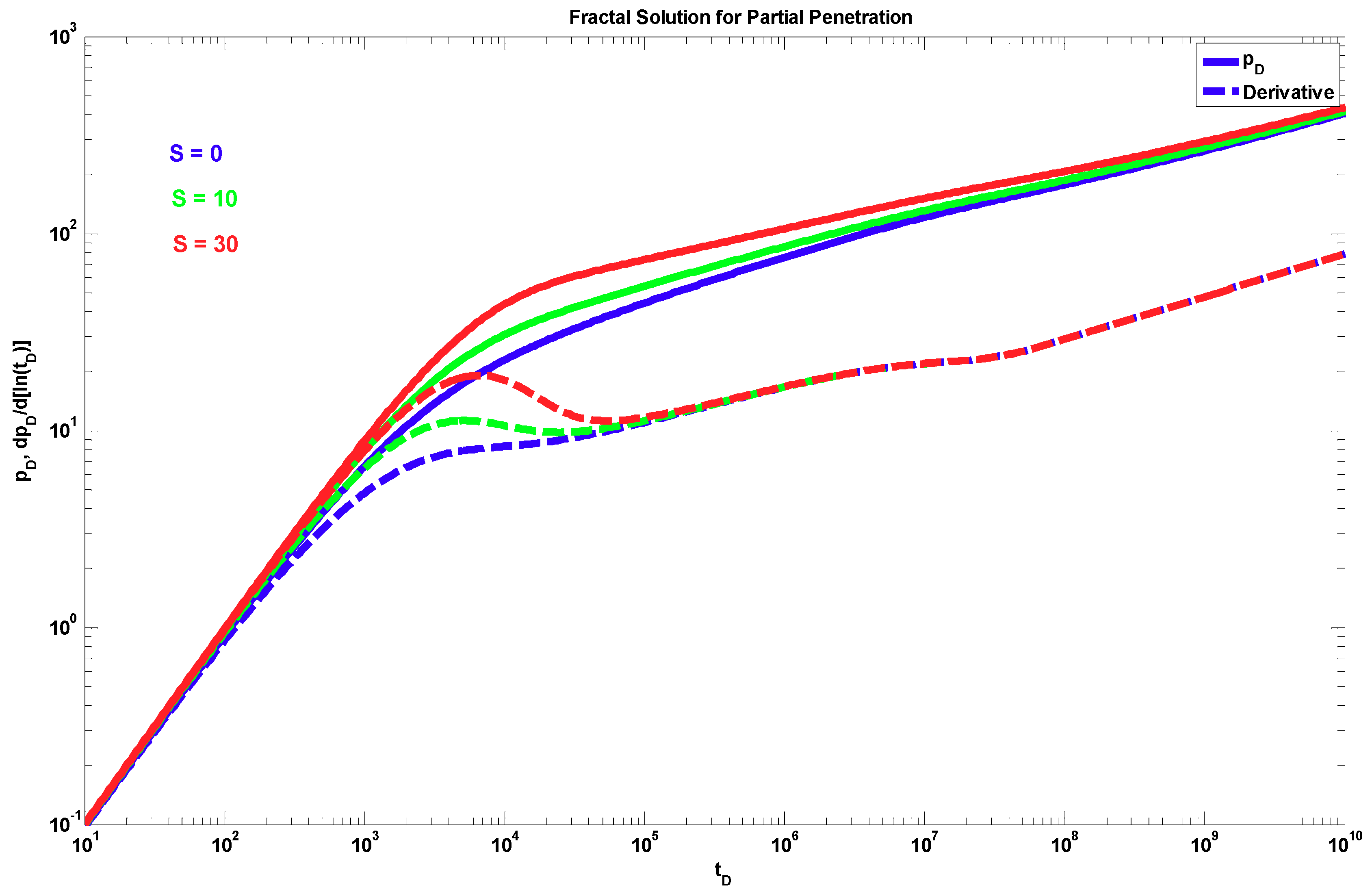
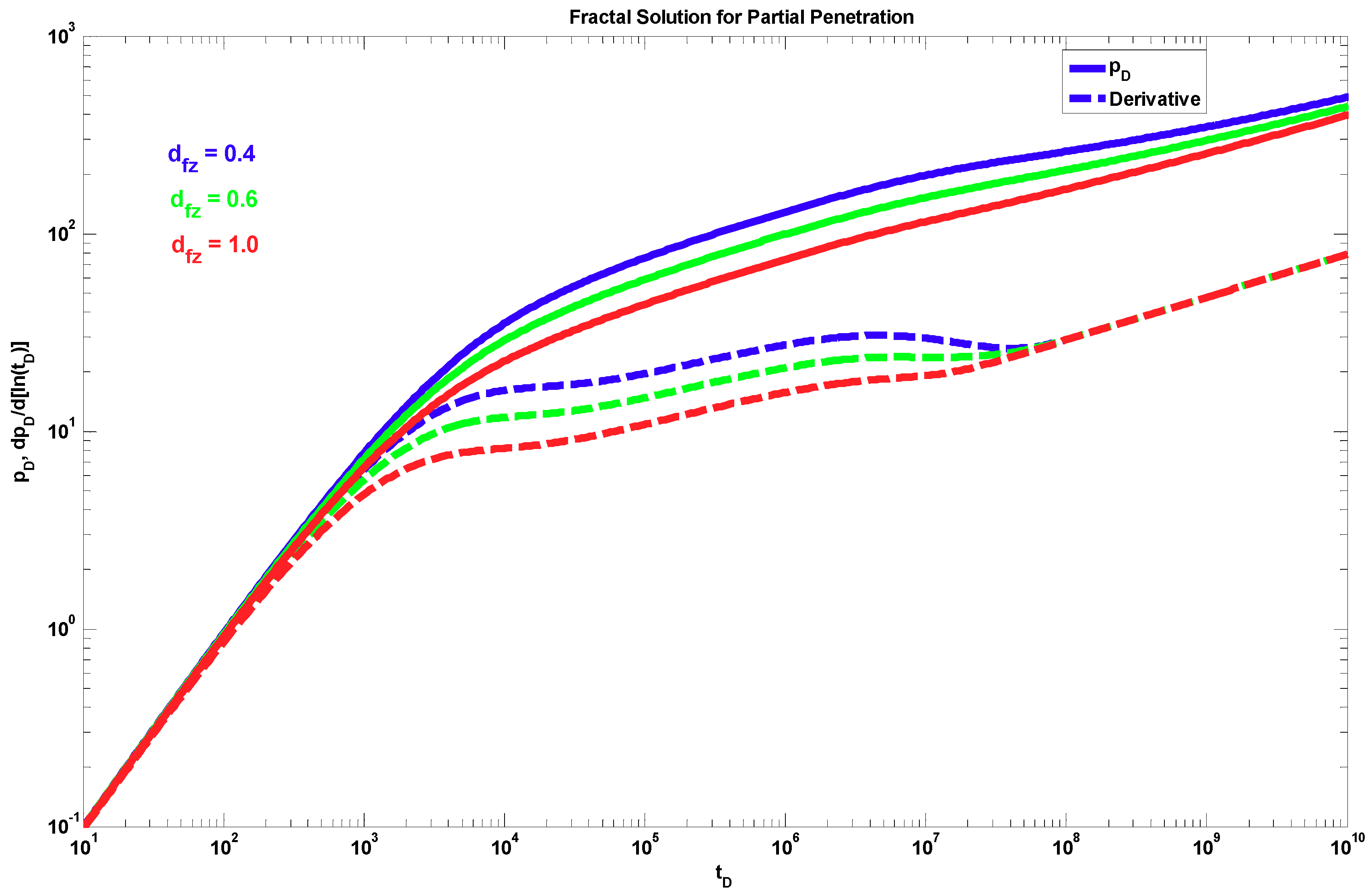
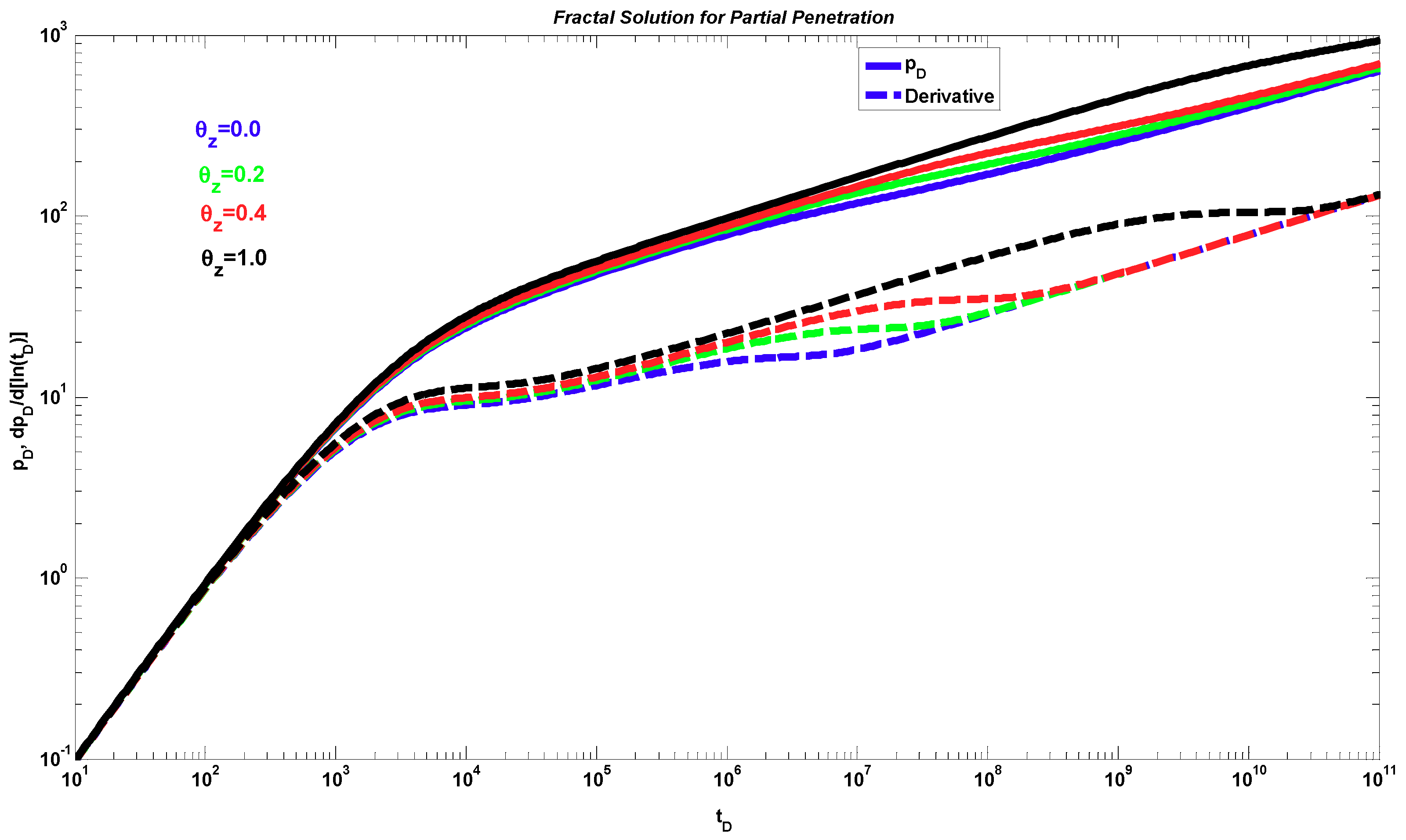
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- The new fractal analytical solution for a constant rate describes the pressure-transient behavior for partially penetrating wells in a single-porosity naturally fractured reservoir and includes the traditional Euclidean solution as a special case.
- The proposed fractal solution generates a power-law response at late times during the transient period after the wellbore storage, mechanical skin, and partial penetration effects have ended. This behavior occurs when the radial fractal parameters are different from the Euclidean values, i.e., dfr < 2 and θr > 0.
- A different behavior to the power-law response occurs when dfz < 1 and θz > 0. The effect of these parameters is shown only during the partial penetration period, and after this period, the traditional radial behavior (if dfr = 2 and θr = 0) or a power-law behavior (when dfr < 2 and/or θr > 0) can be present.
- The typical spherical flow regime due to partial penetration is only present when the fractal parameters in the radial direction have the Euclidean values, i.e., dfr = 2 and θr = 0.
- An expression is provided to evaluate the pseudo-skin due to the partial penetration effects that consider fractal behavior in both the radial and vertical directions.
- To determine the pseudo-damage due to restricted penetration, horizontal permeability, vertical to horizontal permeability ratio, mechanical skin, and the four fractal parameters, it is necessary to resort to a type–curve matching process of the pressure data and its semi-logarithmic derivative using a robust optimizer that minimizes the difference between the real data and the analytical solution.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| ct | Compressibility [psi−1] |
| C | Wellbore storage constant [bbl/psi] |
| CD | Dimensionless wellbore storage constant |
| dfr | Fractal dimension in the radial direction (1 ≤ dfr ≤ 2) |
| dfz | Fractal dimension in the vertical direction (0 ≤ dfz ≤ 1) |
| h | Formation thickness [ft] |
| hp | Producing interval [ft] |
| hpD | Dimensionless producing interval |
| hwD | Dimensionless depth at bottom of producing interval |
| kr | Permeability in the radial direction, [mD] |
| kz | Permeability in the vertical direction, [mD] |
| krw | Reference radial permeability at the wellbore, [mD] |
| kzw | Reference vertical permeability at the top of the anticline, [mD] |
| Kν | Modified Bessel function of order ν |
| Jν | Bessel function of order ν |
| p | Pressure, [psi] |
| pi | Initial pressure, [psi] |
| pwD | Dimensionless wellbore pressure |
| q | Production rate, [bpd] |
| rw | Wellbore radius, [ft] |
| rD | Dimensionless radius |
| s | Laplace domain parameter |
| S | Mechanical skin factor |
| t | Time, [hours] |
| tD | Dimensionless time |
| z | Vertical depth from the top of the dome, [ft] |
| zD | Dimensionless vertical depth |
| zw | Top position of open interval, [ft] |
| zwD | Dimensionless depth at top of open interval |
| zwmD | Dimensionless depth at medium of open interval |
| μ | Fluid viscosity, [cp] |
| ø | Porosity |
| θr | Connectivity index in the radial direction (0 ≤ θr ≤ 1) |
| θz | Connectivity index in the vertical direction (0 ≤ θz ≤ 1) |
| ξ(s) | Pseudo-skin due to partial penetration considering fractal behavior |
Appendix A. Solution in the Radial Direction
Appendix B. Solution in the Vertical Direction
References
- Brons, F.; Martin, V.E. The Effect of Restricted Fluid Entry on Well Productivity. In Proceedings of the 34th SPE Annual Meeting, Dallas, TX, USA, 4–7 October 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Gringarten, A.C.; Ramey, H.J., Jr. An Approximate Infinite Conductivity Partially Penetrating Line-Source Solution Well. SPE J. 1975, 15, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilhartz, H.L., Jr.; Ramey, H., Jr. The Combined Effect of Storage, Skin, and Partial Penetration on Well Test Analysis. In Proceedings of the SPE 52nd Annual Fall Technical Conference and Exhibition, Denver, CO, USA, 19–21 October 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Yildiz, T.; Bassiouni, Z. Transient Pressure Analysis in Partially-Penetrating Wells. In Proceedings of the SPE International Technical Meeting, Calgary, AB, Canada, 10–13 June 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Ozkan, E.; Raghavan, R. New Solutions for Well-Test-Analysis Problems: Part 1—Analytical Considerations. SPE Form. Eval. 1991, 6, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, E.; Raghavan, R. New Solutions for Well-Test-Analysis Problems: Part 2—Computational Considerations and Applications. SPE Form. Eval. 1991, 6, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.D.; Mamora, D.D.; Lee, W.J. Transient Pressure Analysis for Partially Penetrating Wells in Naturally Fractured Reservoirs. In Proceedings of the SPE Rocky Mountain Regional/Low Permeability Reservoirs Symposium and Exhibition, Denver, CO, USA, 12–15 March 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes, G.; Camacho, R.; Vasquez, M. Pressure Transient and Decline Curve Behaviors for Partially Penetrating Wells Completed in Naturally Fractured-Vuggy Reservoirs. In Proceedings of the 2004 SPE International Petroleum Conference in Mexico, Puebla Pue, 7–9 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, F.; Barreto, A.; Peres, A. A Novel Uniform-Flux Solution based on Green’s Functions for Modeling the Pressure Transient Behavior of a Restricted-Entry Well in Anisotropic Gas Reservoirs. SPE J. 2016, 21, 1–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razminia, K.; Razminia, A.; Dastikhan, Z. A comprehensive Solution for Partially Penetrating Wells with Various Reservoir Structures. J. Oil Gas Petrochem. Tech. 2016, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; Yortsos, Y.C. Pressure Transient Analysis of Fractal Reservoirs. SPE Form. Eval. 1990, 289, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña, J.A.; Ershaghi, I.; Yortsos, Y.C. Practical Application of Fractal Pressure-Transient Analysis in Naturally Fractured Reservoirs. SPE Form. Eval. 1995, 10, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamenco, L.F.; Camacho, R.G. Determination of Fractal Parameters of Fractured Networks Using Pressure-Transient Data. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2003, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Posadas, R.; Camacho, R.G. Influence and determination of Mechanical Skin in a Reservoir with a Fractal Behavior. In Proceedings of the SPE Heavy and Extra Heavy Oil Conference, Lima, Peru, 19–20 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cossio, M.; Moridis, G.J.; Blasingame, T.A. A Semianalytic Solution for Flow in Finite-Conductivity Vertical Fractures by Use of Fractal Theory. SPE J. 2013, 18, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shahvali, M.; Su, Y. A semi-analytical fractal model for production from tight oil reservoirs with hydraulically fractured horizontal wells. Fuel 2015, 158, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; He, D.; Wang, J.; Qi, Y. A Coupled Model for Fractured Shale Reservoirs with Characteristics of Continuum Media and Fractal Geometry. In Proceedings of the SPE Asia Pacific Unconventional Resources Conference and Exhibition, Brisbane, Australia, 9–11 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Raghavan, R.; Chen, C. Rate decline, power laws, and subdiffusion in fractured rocks. In Proceedings of the SPE Low Perm Symposium, Denver, CO, USA, 5–6 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.; Jiang, X.; Chen, S. Parameter estimation for the fractional fractal diffusion model based on its numerical solution. Comput. Math. Appl. 2016, 71, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; He, Z.; Agrawal, O.P. Numerical and analytical solutions of new generalized fractional diffusion equation. Comput. Math. Appl. 2013, 66, 2019–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, R.; Chen, C. Fractional diffusion in rocks produced by horizontal wells with multiple, transverse hydraulic fractures of finite conductivity. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2013, 109, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Everdingen, A.F.; Hurst, W. The Application of Laplace Transformation to Flow Problems in Reservoirs. Trans. AIME 1949, 180, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehfest, H. Numerical Inversion of Laplace Transforms. Commun. ACM 1970, 13, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, N.N. Special Functions and Their Applications; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Bramowitz, M.; Stegun, I. Handbook of Mathematical Functions; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Gradshteyn, I.S.; Ryzhik, I.M. Table of Integrals, Series, and Products; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Posadas-Mondragón, R.; Camacho-Velázquez, R.G. Partially Penetrated Well Solution of Fractal Single-Porosity Naturally Fractured Reservoirs. Fractal Fract. 2019, 3, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract3020023
Posadas-Mondragón R, Camacho-Velázquez RG. Partially Penetrated Well Solution of Fractal Single-Porosity Naturally Fractured Reservoirs. Fractal and Fractional. 2019; 3(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract3020023
Chicago/Turabian StylePosadas-Mondragón, Ricardo, and Rodolfo G. Camacho-Velázquez. 2019. "Partially Penetrated Well Solution of Fractal Single-Porosity Naturally Fractured Reservoirs" Fractal and Fractional 3, no. 2: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract3020023
APA StylePosadas-Mondragón, R., & Camacho-Velázquez, R. G. (2019). Partially Penetrated Well Solution of Fractal Single-Porosity Naturally Fractured Reservoirs. Fractal and Fractional, 3(2), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract3020023



