Rebalancing in Supervised Contrastive Learning for Long-Tailed Visual Recognition
Abstract
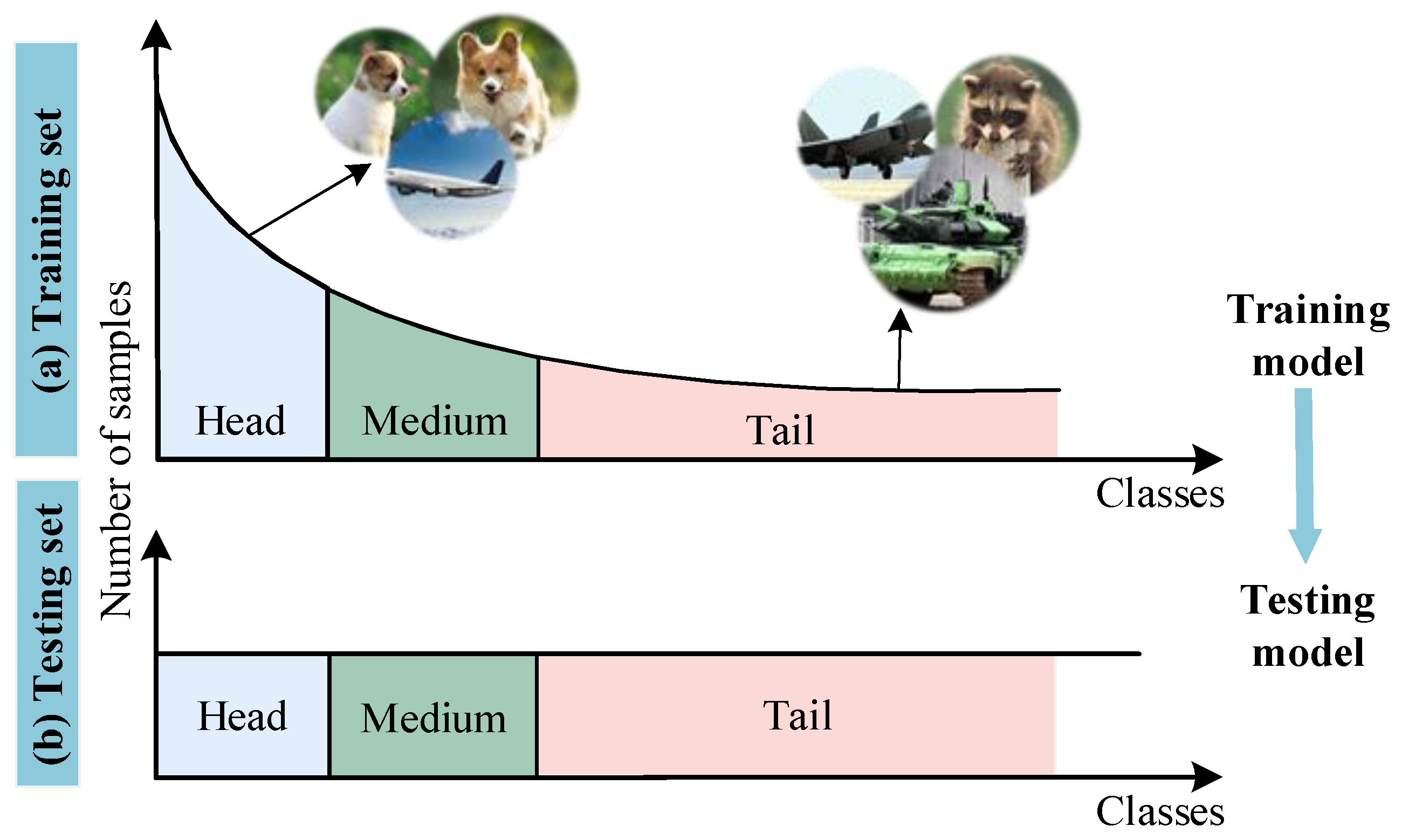
1. Introduction
- We propose an adaptive focal gradient-weighted rebalancing factor that dynamically integrates class frequency statistics and gradient magnitude information. It automatically adjusts the importance weight of each sample during training, simultaneously enhancing gradient focus on tail classes while preventing representation degradation of head classes, thereby constructing a balanced feature space.
- Leveraging the balanced feature representations enabled by the rebalancing factor, we introduce a prototype-aware discriminative enhancement module. This module constrains the geometric structure of prototypes through an aggregation–separation loss and incorporates swapped prediction to achieve dual-branch supervision alignment between features and prototypes. This approach reconstructs the feature space from global balance to local discriminability, alleviating the limitation of traditional contrastive learning that relies solely on inter-sample similarity.
- Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance.
2. Related Work
2.1. Long-Tailed Visual Recognition
2.2. Contrastive Learning
2.3. Prototype Learning for Long-Tailed Recognition
3. Method
3.1. Preliminaries
3.2. Analysis
- The negative sample exhibits a skewed class distribution. Let , , and denote the number of head, medium, and tail class samples in the dataset, respectively. The head class proportion in the dataset isWithin the of size Q, the empirical head class proportion is . When in the dataset, the queue proportion approaches 1, causing the negative sampling process to become heavily biased toward head classes while suppressing gradient contributions from tail classes. This imbalance ultimately degrades model performance.
- The class imbalance in negative sampling critically distorts gradient updates during long-tailed learning. Following BCL [25], we reformulate the supervised contrastive loss at the class level for theoretical analysis:where denotes anchor features from the same class as . During backpropagation, the gradient update for each sample i can be derived via the chain rule, with its mathematical formulation expressed asTo account for the long-tailed distribution, the impact on gradient updates can be approximated aswhere denotes the positive sample pair similarity, while represents the negative sample pair similarity. For analytical simplicity, the above formulation presents only the approximated gradient updates for head and tail classes. When , this bias causes gradient updates to concentrate predominantly on head class samples while suppressing updates from tail classes, consequently impairing the model’s ability to learn discriminative features for tail classes. Furthermore, the temperature parameter governs the concentration of similarity distributions. In long-tailed data scenarios, an excessively small value exacerbates class imbalance by further strengthening the dominance of head class samples.
3.3. Rebalancing Supervised Contrastive Learning
3.3.1. Rebalancing Factor
3.3.2. Prototype-Aware Discriminative Enhancement Module
3.4. Model Training
4. Experience
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
| Imbalance Factor | 100 | 50 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cross Entropy (CE) | 38.6 | 44.0 | 56.4 |
| CE-DRW | 41.1 | 45.6 | 57.9 |
| LDAM-DRW [9] | 41.7 | 47.9 | 57.3 |
| BBN [30] | 42.6 | 47.1 | 59.2 |
| CMO [27] | 43.9 | 48.3 | 59.5 |
| MoCo v2 [24] | 44.6 | 50.2 | 63.1 |
| SupCon [14] | 45.8 | 52.0 | 64.4 |
| Hybrid-SC [31] | 46.7 | 51.8 | 63.0 |
| ResLT [49] | 48.2 | 52.7 | 62.0 |
| BCL [25] | 51.9 | 56.4 | 64.6 |
| SBCL [50] | 44.9 | 48.7 | 57.9 |
| CC-SAM [51] | 49.2 | 51.9 | 62.0 |
| GLC-E [52] | 47.9 | 52.4 | 62.2 |
| GLC-E [52] | 47.9 | 52.4 | 62.2 |
| BS † [53] | 50.8 | 54.2 | 63.0 |
| ProCo † [26] | 52.6 | 57.0 | 65.0 |
| Reb-SupCon (Ours) † | 52.7 | 56.5 | 64.8 |
| Methods | All | Many | Medium | Few |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE | 41.6 | 64.0 | 33.8 | 5.8 |
| Focal Loss [54] | 43.7 | 64.3 | 37.1 | 8.2 |
| LWS [55] | 49.9 | 60.2 | 47.2 | 30.3 |
| LADE [56] | 51.9 | 62.3 | 49.3 | 31.2 |
| SBCL [50] | 52.5 | - | - | - |
| TSC [10] | 52.4 | 63.5 | 49.7 | 30.4 |
| CC-SAM [51] | 54.4 | - | - | - |
| GLC-E [52] | 53.6 | - | - | - |
| DSCL [36] | 57.5 | 68.3 | 54.9 | 35.2 |
| BS † [53] | 55.4 | 65.8 | 53.2 | 34.1 |
| ProCo † [26] | 57.5 | - | - | - |
| Reb-SupCon (Ours) † | 56.9 | 64.9 | 54.2 | 35.6 |
4.4. Ablation Study
4.5. Hyperparameter Sensitivity Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Xu, L.; Lu, X.; Yu, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhao, H. Fastersal: Robust and real-time single-stream architecture for rgb-d salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 27, 2477–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadraoui, A.; Zemmouri, E. Pyramid scene parsing network for driver distraction classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Smart Environment, Errachidia, Morocco, 23–25 November 2023; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Elsken, T.; Metzen, J.H.; Hutter, F. Neural architecture search: A survey. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2019, 20, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Liu, L.; Musial, K.; Gabrys, B. Nats-bench: Benchmarking nas algorithms for architecture topology and size. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 3634–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part v 13. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Miao, Z.; Zhan, X.; Wang, J.; Gong, B.; Yu, S.X. Large-scale long-tailed recognition in an open world. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 115–20 June 2019; pp. 2537–2546. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, K.; Wei, C.; Gaidon, A.; Arechiga, N.; Ma, T. Learning imbalanced datasets with label-distribution-aware margin loss. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Cao, P.; Yuan, Y.; Fan, L.; Yang, Y.; Feris, R.S.; Indyk, P.; Katabi, D. Targeted supervised contrastive learning for long-tailed recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 6918–6928. [Google Scholar]
- Mojahed, A.J.; Moattar, M.H.; Ghaffari, H. Supervised Density-Based Metric Learning Based on Bhattacharya Distance for Imbalanced Data Classification Problems. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2024, 8, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Li, Q.; Ouyang, W.; Yin, C.; Yan, J. Equalization loss for long-tailed object recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 11662–11671. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Zhong, Z.; Liu, S.; Yu, B.; Jia, J. Parametric contrastive learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 715–724. [Google Scholar]
- Khosla, P.; Teterwak, P.; Wang, C.; Sarna, A.; Tian, Y.; Isola, P.; Maschinot, A.; Liu, C.; Krishnan, D. Supervised contrastive learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 18661–18673. [Google Scholar]
- Rezvani, S.; Wang, X. A broad review on class imbalance learning techniques. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 143, 110415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; Pang, G.; Bai, X.; Li, T.; Zheng, J. Out-of-distribution detection in long-tailed recognition with calibrated outlier class learning. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2024, 38, 4216–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D. Probability guided loss for long-tailed multi-label image classification. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2023, 37, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Xie, S.; Rohrbach, M.; Yan, Z.; Gordo, A.; Feng, J.; Kalantidis, Y. Decoupling representation and classifier for long-tailed recognition. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.09217. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y. Divide and retain: A dual-phase modeling for long-tailed visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 35, 13538–13549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Tsuchida, R.; Petersson, L.; Barnes, N. Label shift estimation for class-imbalance problem: A bayesian approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 1073–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Rani, V.; Nabi, S.T.; Kumar, M.; Mittal, A.; Kumar, K. Self-supervised learning: A succinct review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 2761–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, J.; Chen, T.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Q.; Sun, Z.; Luo, H.; Tao, D. A survey on self-supervised learning: Algorithms, applications, and future trends. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 9052–9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Fan, H.; Wu, Y.; Xie, S.; Girshick, R. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 9729–9738. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Fan, H.; Girshick, R.; He, K. Improved baselines with momentum contrastive learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.04297. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.P.P.; Jiang, Y.G. Balanced contrastive learning for long-tailed visual recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 6908–6917. [Google Scholar]
- Du, C.; Wang, Y.; Song, S.; Huang, G. Probabilistic contrastive learning for long-tailed visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 5890–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Hong, Y.; Heo, B.; Yun, S.; Choi, J.Y. The majority can help the minority: Context-rich minority oversampling for long-tailed classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 6887–6896. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Hu, L.; Liu, J.; Tao, D. CRmix: A regularization by clip** images and replacing mixed samples for imbalanced classification. Digit. Signal Process. 2023, 135, 103951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hong, Z.; Yang, X. Cost-sensitive online adaptive kernel learning for large-scale imbalanced classification. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 35, 10554–10568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Cui, Q.; Wei, X.S.; Chen, Z.M. Bbn: Bilateral-branch network with cumulative learning for long-tailed visual recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 9719–9728. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Han, K.; Wei, X.S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L. Contrastive learning based hybrid networks for long-tailed image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 943–952. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, B.; Li, Y.; Xie, S.; Yuan, Z.; Feng, J. Exploring balanced feature spaces for representation learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 26–30 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Fu, S.; Ding, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, H. Uniformly distributed category prototype-guided vision-language framework for long-tail recognition. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October 2023; pp. 5027–5037. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Wang, S.; Cai, R.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Tang, W.; Kot, A. Suppress and rebalance: Towards generalized multi-modal face anti-spoofing. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Grill, J.B.; Strub, F.; Altché, F.; Tallec, C.; Richemond, P.; Buchatskaya, E.; Doersch, C.; Avila Pires, B.; Guo, Z.; Gheshlaghi Azar, M.; et al. Bootstrap your own latent-a new approach to self-supervised learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 21271–21284. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, S.; Zhang, S. Decoupled contrastive learning for long-tailed recognition. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2024, 38, 6396–6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, J.S.; Yoon, I.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Choi, J.W. Distribution-Aware Robust Learning from Long-Tailed Data with Noisy Labels. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 160–177. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Yang, Y. Inflated episodic memory with region self-attention for long-tailed visual recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 4344–4353. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.-S.; Xu, S.-L.; Chen, H.; Xiao, L.; Peng, Y. Prototype-based classifier learning for long-tailed visual recognition. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2022, 65, 160105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Chen, W.; Huang, A.; Zhao, T. Prototype Alignment with Dedicated Experts for Test-Agnostic Long-Tailed Recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 27, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Li, M.; Lu, Y.; Cheung, Y.M.; Wang, H. Long-tailed visual recognition via self-heterogeneous integration with knowledge excavation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 23695–23704. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X.; Bovik, A.C. Gradient magnitude similarity deviation: A highly efficient perceptual image quality index. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 23, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, M.; Misra, I.; Mairal, J.; Goyal, P.; Bojanowski, P.; Joulin, A. Unsupervised learning of visual features by contrasting cluster assignments. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 9912–9924. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Jia, M.; Lin, T.Y.; Song, Y.; Belongie, S. Class-balanced loss based on effective number of samples. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9268–9277. [Google Scholar]
- Van Horn, G.; Mac Aodha, O.; Song, Y.; Cui, Y.; Sun, C.; Shepard, A.; Adam, H.; Perona, P.; Belongie, S. The inaturalist species classification and detection dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8769–8778. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Girshick, R.; Dollár, P.; Tu, Z.; He, K. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1492–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Cubuk, E.D.; Zoph, B.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Randaugment: Practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 702–703. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Liu, S.; Tian, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Jia, J. Reslt: Residual learning for long-tailed recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 3695–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, T. Subclass-balancing contrastive learning for long-tailed recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 5395–5407. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, L.; Zhao, P.; Heng, P.A.; Gong, W. Class-conditional sharpness-aware minimization for deep long-tailed recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 3499–3509. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Cheung, Y.M.; Lu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Lan, W.; Huang, H. Adjusting logit in Gaussian form for long-tailed visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2024, 5, 5026–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.Q.; Thu, M.T.H. Smooth Balance Softmax for Long-Tailed Image Classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Information and Communication Technology, Thai Nguyen, Vietnam, 16–17 November 2024; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 323–331. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan, D.; Girshick, R.; Ramanathan, V.; He, K.; Paluri, M.; Li, Y.; Bharambe, A.; Van Der Maaten, L. Exploring the limits of weakly supervised pretraining. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 181–196. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Han, S.; Choi, K.; Seo, S.; Kim, B.; Chang, B. Disentangling label distribution for long-tailed visual recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 6626–6636. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, H.P.; Chang, S.C.; Pan, J.Y.; Wei, W.; Juan, D.C. Remix: Rebalanced mixup. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 95–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Lian, L.; Miao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yu, S.X. Long-tailed recognition by routing diverse distribution-aware experts. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.01809. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Xian, Y.; Yu, N.; Singh, A. Learning prototype classifiers for long-tailed recognition. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.00491. [Google Scholar]




| Datasets | Number of Classes | Training/Test Samples | IF |
|---|---|---|---|
| CIFAR-LT | 100 | 10.8 K/10 K | {100, 50, 10} |
| ImageNet-LT | 1000 | 115.8 K/50 K | 256 |
| iNaturalist 2018 | 8142 | 437.5 K/24.4 K | 500 |
| Datasets | CIFAR-100-LT | ImageNet-LT | iNaturalist 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Backbone | ResNet-32 | ResNet-50/ResNext-50 | ResNet-50 |
| Input resolution | 32 × 32 | 224 × 224 | 224 × 224 |
| Epochs | 400 | 400 | 400 |
| Batch size | 128 | 256 | 512 |
| Initial learning rate | 0.02 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Temperature | 0.05 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Methods | All | Many | Medium | Few |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE | 61.0 | 73.9 | 63.5 | 55.5 |
| LDAM-DRW [9] | 66.1 | - | - | - |
| BS [53] | 70.0 | 70.0 | 70.2 | 69.9 |
| Remix [57] | 70.5 | - | - | - |
| RIDE(3E) [58] | 72.2 | 70.2 | 72.2 | 72.7 |
| TSC [10] | 69.7 | 72.6 | 70.6 | 67.8 |
| PC [59] | 70.6 | 71.6 | 70.6 | 70.2 |
| SHIKE [41] | 74.5 | - | - | - |
| DSCL [36] | 72.0 | 74.2 | 72.9 | 70.3 |
| BS † [53] | 71.8 | - | - | - |
| Reb-SupCon (Ours) † | 73.0 | 71.9 | 73.2 | 72.5 |
| Imbalance Factor | 100 | 50 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SupCon | 45.8 | 52.0 | 64.4 |
| + Rebalancing factor | 50.2 | 55.1 | 64.5 |
| + Prototype module | 48.7 | 54.7 | 64.5 |
| Reb-SupCon | 52.7 | 56.5 | 64.8 |
| Top-1 Accuracy | Class-Avg Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 49.3 | 25.8 |
| 0.5 | 0.1 | 52.7 | 30.1 |
| 1.0 | 0.1 | 51.1 | 28.5 |
| 0.5 | 0.05 | 51.7 | 28.9 |
| 0.5 | 0.5 | 50.4 | 26.7 |
| K | All | Many | Medium | Few | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800 | (0.5, 0.3, 0.2) | 55.1 | 64.3 | 52.7 | 33.9 |
| 5000 | (0.5, 0.3, 0.2) | 56.5 | 64.7 | 53.9 | 35.1 |
| 3000 | (0.5, 0.3, 0.2) | 56.9 | 64.9 | 54.2 | 35.6 |
| 3000 | (0.6, 0.2, 0.2) | 56.2 | 65.1 | 53.6 | 34.8 |
| 3000 | (0.4, 0.4, 0.2) | 55.9 | 64.5 | 53.2 | 34.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, J.; Lei, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Li, S. Rebalancing in Supervised Contrastive Learning for Long-Tailed Visual Recognition. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9080204
Lv J, Lei J, Zhang J, Chen C, Li S. Rebalancing in Supervised Contrastive Learning for Long-Tailed Visual Recognition. Big Data and Cognitive Computing. 2025; 9(8):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9080204
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Jiahui, Jun Lei, Jun Zhang, Chao Chen, and Shuohao Li. 2025. "Rebalancing in Supervised Contrastive Learning for Long-Tailed Visual Recognition" Big Data and Cognitive Computing 9, no. 8: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9080204
APA StyleLv, J., Lei, J., Zhang, J., Chen, C., & Li, S. (2025). Rebalancing in Supervised Contrastive Learning for Long-Tailed Visual Recognition. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 9(8), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9080204






