Complex Table Question Answering with Multiple Cells Recall Based on Extended Cell Semantic Matching
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
- (1)
- Table question answering
- (2)
- Text classification
3. CBCM Table QA Method
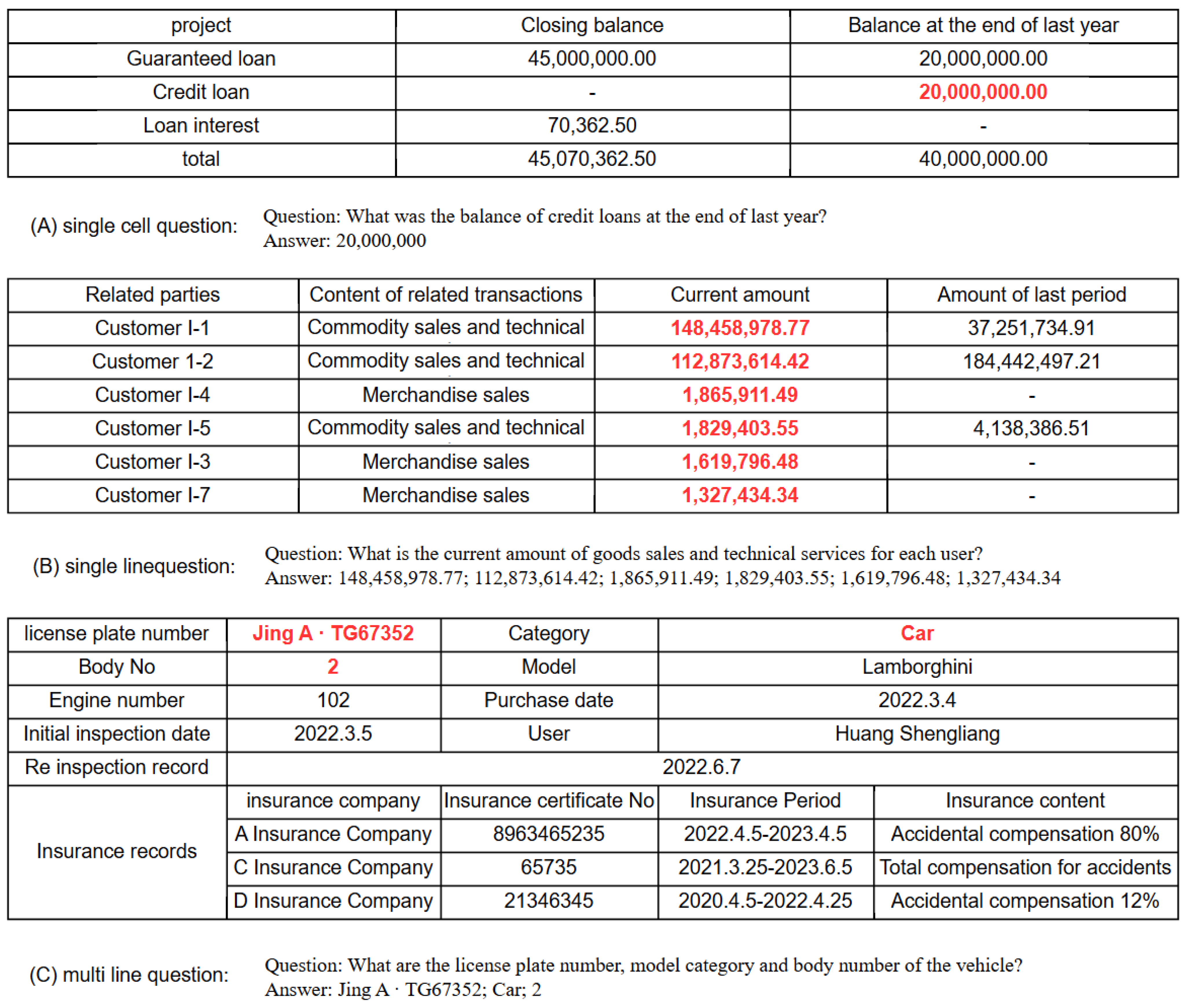
3.1. Cell Type Classification in Table Question Answering
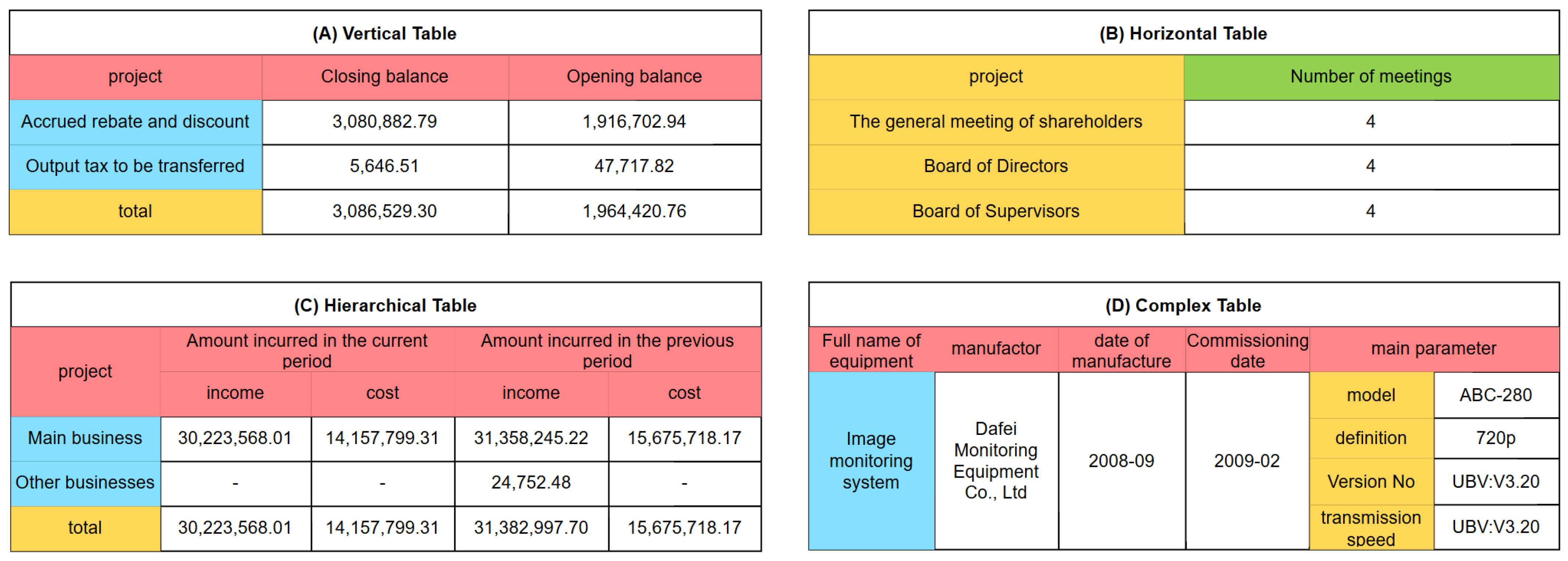
3.2. Definition of Table Types in Table Question Answering
3.3. Question Classification in Table Question Answering
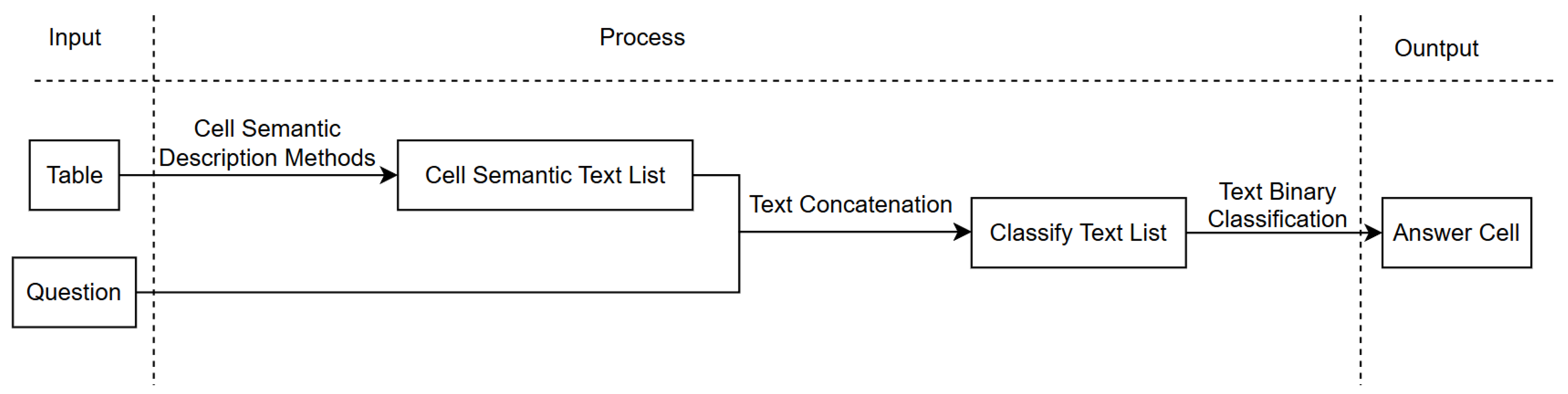
3.4. Extended Cell-Bycell Semantic Matching
| Algorithm 1 CBCM Algorithm |
| Require: Table T, Question Q Ensure: Answer Cells A |
|
4. Experiment
4.1. IM-TQA-X Benchmark Dataset
| Algorithm 2 IM-TQA-X Benchmark Construction |
| Require: IM-TQA dataset D Ensure: New Benchmark |
|
4.2. Table Question Answering Performance Validation
5. Discussion
5.1. Ablation Analysis
5.2. Complexity Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Implementation Details for TQA Experiments
- model_type: bert-base-chinese.
- num_train_epochs: 3
- learning_rate:
- train_instances: 28,438/19,827
References
- Rahul, K.; Banyal, R.K.; Arora, N. A systematic review on big data applications and scope for industrial processing and healthcare sectors. J. Big Data 2023, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Dong, B.; Wang, X.; Li, C. HIE-SQL: History Information Enhanced Network for Context-Dependent Text-to-SQL Semantic Parsing. In Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, B.; Geng, R.; Wang, L.; Qin, B.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Sun, J.; Li, Y. S2SQL: Injecting Syntax to Question-Schema Interaction Graph Encoder for Text-to-SQL Parsers. In Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Dubin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Xu, Y.; Karlsson, B.F.; Okumura, M. A Table Question Alignment based Cell-Selection Method for Table-Text QA. J. Nat. Lang. Process. 2024, 31, 189–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, U.; Suneja, S.; Samulowitz, H. Table Retrieval using LLMs and Semantic Table Similarity. In Proceedings of the Companion Proceedings of the ACM on Web Conference 2025, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 28 April 2025; pp. 1072–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Xu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Lou, J.G.; Karlsson, B.; Okumura, M. TACR: A Table Alignment-based Cell Selection Method for HybridQA. In Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Toronto, ON, Canada, 9–14 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hou, F.; Yuan, J.; Tian, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Fan, J.; He, Z. A survey of visual transformers. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 35, 7478–7498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, A.; Wu, K.; Sun, K.; Li, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H. DuSQL: A Large-Scale and Pragmatic Chinese Text-to-SQL Dataset. In Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.; Zhang, R.; Yang, K.; Yasunaga, M.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Li, I.; Yao, Q.; Roman, S.; et al. Spider: A Large-Scale Human-Labeled Dataset for Complex and Cross-Domain Semantic Parsing and Text-to-SQL Task. In Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Melbourne, Australia, 15–20 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M.; Hao, Y.; Jiang, W.; Lin, Z.; Lyu, Y.; She, Q.; Wang, W. IM-TQA: A Chinese Table Question Answering Dataset with Implicit and Multi-type Table Structures. In Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Toronto, ON, Canada, 9–14 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Katsis, Y.; Chemmengath, S.; Kumar, V.; Bharadwaj, S.; Canim, M.; Glass, M.; Gliozzo, A.; Pan, F.; Sen, J.; Sankaranarayanan, K.; et al. AIT-QA: Question Answering Dataset over Complex Tables in the Airline Industry. In Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Dong, H.; Wang, Z.; Jia, R.; Guo, J.; Gao, Y.; Han, S.; Lou, J.G.; Zhang, D. HiTab: A Hierarchical Table Dataset for Question Answering and Natural Language Generation. In Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Xie, Y.; Goncalves, L.; Gao, S.; Zhao, J. WikiDT: Visual-Based Table Recognition and Question Answering Dataset. In International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 406–437. [Google Scholar]
- Szałata, A.; Hrovatin, K.; Becker, S.; Tejada-Lapuerta, A.; Cui, H.; Wang, B.; Theis, F.J. Transformers in single-cell omics: A review and new perspectives. Nat. Methods 2024, 21, 1430–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dargahi Nobari, A.; Rafiei, D. Dtt: An example-driven tabular transformer for joinability by leveraging large language models. Proc. ACM Manag. Data 2024, 2, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Cao, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z. Table Fact Verification with Structure-Aware Transformer. In Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, P.; Neubig, G.; Yih, W.T.; Riedel, S. TaBERT: Pretraining for Joint Understanding of Textual and Tabular Data. In Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Gupta, A.; Upadhyay, S.; He, L.; Goel, R.; Paul, S. TableFormer: Robust Transformer Modeling for Table-Text Encoding. In Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenschlos, J.; Gor, M.; Müller, T.; Cohen, W. MATE: Multi-view Attention for Table Transformer Efficiency. In Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 1–6 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, M.; Canim, M.; Gliozzo, A.; Chemmengath, S.; Kumar, V.; Chakravarti, R.; Sil, A.; Pan, F.; Bharadwaj, S.; Fauceglia, N.R. Capturing Row and Column Semantics in Transformer Based Question Answering over Tables. In Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 1–6 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F.; Lei, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Lv, J.; Feng, F.; Chua, T.S. TAT-QA: A Question Answering Benchmark on a Hybrid of Tabular and Textual Content in Finance. In Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 1–6 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Nan, L.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, R.; Radev, D. ReasTAP: Injecting Table Reasoning Skills During Pre-training via Synthetic Reasoning Examples. In Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.B.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, L.; Hsieh, C.; Mao, Z.; Lin, X.V.; Verma, N.; Zhang, R.; Kryściński, W.; Schoelkopf, H.; Kong, R.; Tang, X.; et al. FeTaQA: Free-form Table Question Answering. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2022, 10, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Huang, M.; Zhang, P. MFORT-QA: Multi-hop Few-shot Open Rich Table Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 2024 10th International Conference on Computing and Artificial Intelligence, Bali, Indonesia, 26–29 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, K.; Sun, H.; Zhang, C. Toolqa: A dataset for LLM question answering with external tools. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 50117–50143. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Gupta, Y.; Chemmengath, S.; Sen, J.; Chakrabarti, S.; Bharadwaj, S.; Pan, F. Multi-Row, Multi-Span Distant Supervision For Table+Text Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Toronto, ON, Canada, 9–14 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Salton, G.; Buckley, C. Term-weighting approaches in automatic text retrieval. Inf. Process. Manag. 1988, 24, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolov, T.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2013, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sowmya, B.; Srinivasa, K. Large scale multi-label text classification of a hierarchical dataset using rocchio algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computation System and Information Technology for Sustainable Solutions (CSITSS), Bengaluru, India, 6–8 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, Z.; Long, J.; Zhang, H. Turning from TF-IDF to TF-IGM for term weighting in text classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 66, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodhi, H.; Saunders, C.; Shawe-Taylor, J.; Cristianini, N.; Watkins, C. Text classification using string kernels. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 1 January 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Yan, S.; Wong, K.C. Verbal aggression detection on Twitter comments: Convolutional neural network for short-text sentiment analysis. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 10809–10818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowsari, K.; Heidarysafa, M.; Brown, D.E.; Meimandi, K.J.; Barnes, L.E. RMDL: Random Multimodel Deep Learning for Classification. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Information System and Data Mining, Lakeland, FL, USA, 9–11 April 2018; pp. 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Han, X.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Sun, M.; Liu, Q. ERNIE: Enhanced Language Representation with Informative Entities. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hearst, M.A.; Dumais, S.T.; Osuna, E.; Platt, J.; Scholkopf, B. Support vector machines. IEEE Intell. Syst. Their Appl. 1998, 13, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Train Set | Test Set | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table Number | Question Number | Table Number | Question Number | |
| Total | 907 | 3771 | 183 | 768 |
| Classification by table type (According to Section 3.2) | ||||
| Complex (TT1) | 223 | 1,014 | 66 | 306 |
| Vertical (TT2) | 224 | 849 | 45 | 174 |
| Horizontal (TT3) | 229 | 933 | 38 | 129 |
| Hierarchical (TT4) | 231 | 1075 | 34 | 159 |
| Classification by question type (According to Section 3.3) | ||||
| Single cell query (TQ1) | – | 2112 | – | 404 |
| Single line query (TQ2) | – | 1630 | – | 317 |
| Multi-cell query (TQ3) | – | 29 | – | 47 |
| Test Number | Cell Semantics | Text Concatenation Order | Text Classification Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CT1 | Question Text + Cell Semantic Text | Fully connected classification |
| 2 | CT2 | ||
| 3 | CT3 | ||
| 4 | CT4 | ||
| 5 | CT1 | Cell Semantic Text + Question Text | |
| 6 | CT2 | ||
| 7 | CT3 | ||
| 8 | CT4 |
| Model | Experiments | Overall Accuracy | Classification by Table Type | Classification by Question Type | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complex | Vertical | Horizontal | Hierarchical | Single Cell | Single Line | Multi Line | |||
| CBCM | 1 | 40.4% | 19.9% | 62.6% | 46.5% | 50.3% | 46.3% | 37.5% | 8.5% |
| 2 | 38.3% | 18.6% | 56.3% | 50.4% | 46.5% | 43.1% | 36.3% | 10.6% | |
| 3 | 50.5% | 45.4% | 59.8% | 58.2% | 44.0% | 55.9% | 46.1% | 34.0% | |
| 4 | 48.3% | 44.1% | 58.0% | 54.3% | 40.9% | 54.5% | 43.2% | 29.8% | |
| 5 | 38.9% | 16.3% | 62.1% | 49.6% | 48.4% | 45.8% | 35.6% | 2.1% | |
| 6 | 41.7% | 24.2% | 56.9% | 51.2% | 50.9% | 49.0% | 37.5% | 6.4% | |
| 7 | 49.3% | 41.2% | 60.9% | 59.8% | 44.7% | 55.7% | 44.8% | 25.5% | |
| 8 | 49.1% | 41.5% | 57.5% | 55.8% | 49.1% | 55.4% | 44.5% | 25.5% | |
| RGCNRCI | – | 48.0% | 27.8% | 70.1% | 48.1% | 62.9% | 52.7% | 48.6% | 4.3% |
| Text Binary Classification Method | Text Classification Accuracy | Table Question Answering Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| SVM | 71.72% | 1.69% |
| Random Forest | 78.80% | 2.21% |
| k-Nearest Neighbor | 81.64% | 3.25% |
| Linear Classifier | 97.00% | 49.00% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Shen, D. Complex Table Question Answering with Multiple Cells Recall Based on Extended Cell Semantic Matching. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9, 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9100265
Chen H, Shen D. Complex Table Question Answering with Multiple Cells Recall Based on Extended Cell Semantic Matching. Big Data and Cognitive Computing. 2025; 9(10):265. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9100265
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hainan, and Dongqi Shen. 2025. "Complex Table Question Answering with Multiple Cells Recall Based on Extended Cell Semantic Matching" Big Data and Cognitive Computing 9, no. 10: 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9100265
APA StyleChen, H., & Shen, D. (2025). Complex Table Question Answering with Multiple Cells Recall Based on Extended Cell Semantic Matching. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 9(10), 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9100265






