Spark Configurations to Optimize Decision Tree Classification on UNSW-NB15
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
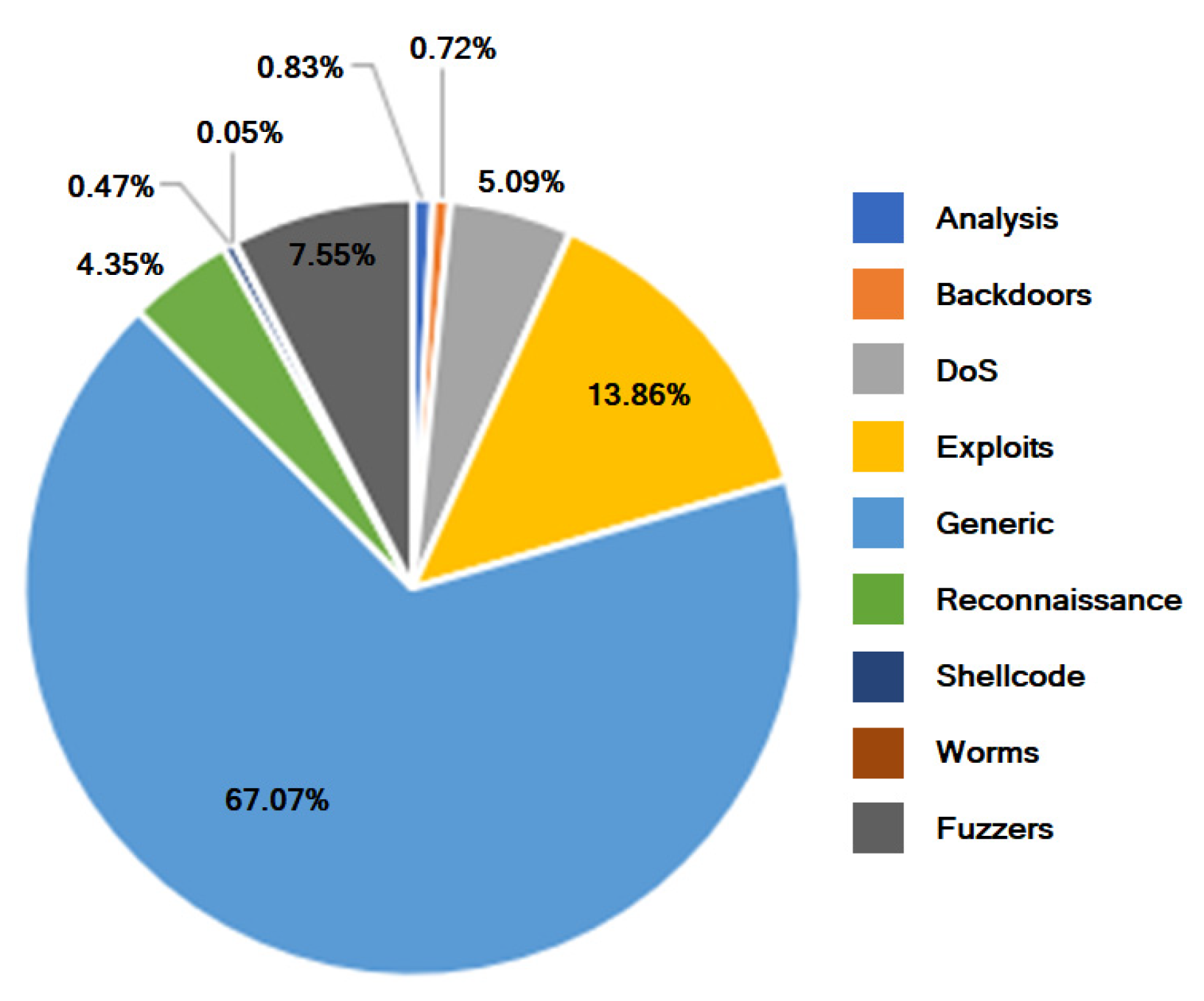
3. The UNSW-NB15 Dataset
4. Analysis Environment
4.1. Spark
4.2. Principle Component Analysis
4.3. Decision Tree
5. Methodology
Environmental Variables Used in Spark
- spark-shell—num-executors X—executor-cores X—executor-memory X
- Where X is a numeric value entered.
- org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession
- org.apache.spark.ml.linalg.Vectors
- org.apache.spark.ml.feature.{VectorAssembler, VectorIndexer, StringIndexer, OneHotEncoder}
- org.apache.spark.ml.feature.{IndexToString, StringIndexer, VectorIndexer}
- org.apache.spark.ml.feature.PCA
- org.apache.spark.ml.Pipeline
- org.apache.spark.ml.classification.LogisticRegression
- org.apache.spark.ml.classification.DecisionTreeClassificationModel
- org.apache.spark.ml.classification.DecisionTreeClassifier
- org.apache.spark.ml.evaluation.MulticlassClassificationEvaluator
- org.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.BinaryClassificationMetrics
- org.apache.spark.mllib.evaluation.MulticlassMetrics
6. Results and Discussion
6.1. Performance Based on Cores and Memory versus Execution Time
6.2. Performance Based on Statistical Metrics
7. Conclusions
8. Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bagui, S.; Simonds, J.; Plenkers, R.; Bennett, T.; Bagui, S. Classifying UNSW-NB15 Network Traffic in the Big Data Framework using Random Forest in Spark. Int. J. Big Data Intell. Appl. 2021, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UNSW-NB15 Dataset Description. Cyber Range Lab of the Australian Centre for Cyber Security (ACCS). Available online: https://www.unsw.adfa.edu.au/unsw-canberra-cyber/cybersecurity/ADFA-NB15-Datasets/. (accessed on 19 September 2019).
- Moustafa, N.; Slay, J. UNSW-NB15: A comprehensive data set for network intrusion detection systems (UNSW-NB15 network data set). In Proceedings of the Military Communications and Information Systems Conference (MilCIS), Canberra, Australia, 10–12 November 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guller, M. Big Data Analytics with Spark: A Practitioner’s Guide to Using Spark for Large Scale Data Analysis, 1st ed.; Apress: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kasongo, M.S.; Sun, Y. Performance Analysis of Intrusion Detection Systems Using a Feature Selection Method on the UNSW-NB15 Dataset. J. Big Data 2020, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sinha, D.; Das, A.K.; Pandey, S.C.; Goswami, R.T. An integrated rule based intrusion detection system: Analysis on UNSW-NB15 data set and the real time online dataset. Clust. Comput. 2019, 23, 1397–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafaeipour, A.; Jahangard Rafsanjani, A.; Ahmadi, M.; Arockia Dhanraj, J. Investigating the performance of Hadoop and Spark platforms on machine learning algorithms. J. Supercomput. 2020, 77, 1273–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Qiao, Z.; Li, L.; Zheng, Q. Parameter Optimization of Spark in Heterogeneous Environment Based on Hyperband. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Big Data Economy and Information Management (BDEIM), Sanya, China, 3–5 December 2021; pp. 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Chai, S.; Zhang, B.; Xia, Y. Research on Network Intrusion Detection Based on Incremental Extreme Learning Machine and Adaptive Principal Component Analysis. Energies 2019, 12, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, H.; Blech, J.; Chen, H. A Machine learning based intrusion detection approach for industrial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Buenos Aires, Argentina, 26–28 February 2020; pp. 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, N.; Adi, E.; Turnbull, B.; Hu, J. A New Threat Intelligence Scheme for Safeguarding Industry 4.0 Systems. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 32910–32924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheshasaayee, A.; Lakshmi, J.V.N. An insight into tree-based machine learning techniques for big data analytics using Apache Spark. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Instrumentation and Control Technologies (ICICICT), Kerala, India, 6–7 July 2017; pp. 1740–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belouch, M.; El Hadaj, S.; Idhammad, M. Performance evaluation of intrusion detection based on machine learning using Apache Spark. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 127, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroniotis, N.; Moustafa, N.; Sitnikova, E.; Slay, J. Towards Developing Network Forensic Mechanism for Botnet Activities in the IoT Based on Machine Learning Techniques. In International Conference on Mobile Networks and Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moustafa, N.; Slay, J. The evaluation of Network Anomaly Detection Systems: Statistical analysis of the UNSW-NB15 data set and the comparison with the KDD99 data set. Inf. Secur. J. 2016, 25, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagui, S.; Benson, D. Android Adware Detection Using Machine Learning. Int. J. Cyber Res. Educ. 2021, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, C.; Shiva, S.; Bedi, H.; Dasgupta, D. AVOIDIT: A cyber attack taxonomy. In Proceedings of the 9th Annual Symposium on Information Assurance (ASIA’14), Albany, NY, USA, 3–4 June 2014; pp. 2–12. [Google Scholar]
- Alibaba Cloud. Configure Spark-Submit Parameters—EMR Development Guide | Alibaba Cloud Documentation Center. Available online: https://www.alibabacloud.com/help/en/doc-detail/28124.html (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Spark.apache.org. Overview—Spark 2.4.0 Documentation. 2022. Available online: https://spark.apache.org/docs/2.4.0/ (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Spark.apache.org. Spark Release 3.0.0 | Apache Spark. 2022. Available online: https://spark.apache.org/releases/spark-release-3-0-0.html (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- NVIDIA. NVIDIA Apache Spark 3.0 For Analytics & ML Data Pipelines. 2022. Available online: https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/deep-learning-ai/solutions/data-science/apache-spark-3/ (accessed on 15 March 2022).





| Environment Variables | Function |
|---|---|
| --num-executors | The number of executors to be created |
| --executor-cores | The number of threads used by each executor, which equals the maximum number of tasks that can be executed concurrently by each executor |
| --executor-memory | The maximum amount of memory to be allocated to each executor. The allocated memory cannot be greater than the maximum available memory per node |
| Run | # of Executors # of Executor Cores | Executor Memory | Cores Used | Dead Cores | Execution Time (min) | Memory Used (GB) | Spark Jobs Run | # of Executors | Completed Tasks | Dead Tasks | Read/Write (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Executors: 4 Cores: 4 | 19 GB | 8 | 16 | 6.9 | 64.6 | 37 | 6 | 1151 | 17.5 | |
| 2 | Executors: 5 Cores: 2 | 19 GB | 12 | 0 | 3.5 | 64.5 | 37 | 6 | 621 | 13.5 | |
| 3 | Executors: 10 Cores: 2 | 19 GB | 24 | 0 | 3.0 | 128.7 | 37 | 12 | 1183 | 17.4 | |
| 4 | Executors: 10 Cores: 6 | 19 GB | 60 | 0 | 2.0 | 107.3 | 37 | 10 | 3017 | 27.5 | |
| 5 | Executors: 12 Cores: 5 | Default—1 GB | 80 | 45 | 2.5 | 6.8 | 37 | 16 | 3012 | 2188 | 28.2 |
| 6 | Executors: 8 Cores: 5 | Default—1 GB | 65 | 40 | 2.7 | 5.4 | 37 | 12 | 1996 | 1964 | 22.7 |
| 7 | Executors: 10 Cores: 2 | Default—1 GB | 30 | 10 | 3.1 | 6.3 | 37 | 15 | 1205 | 518 | 17.9 |
| 8 | Executors: 10 Cores: 6 | Default—1 GB | 108 | 54 | 2.8 | 7.7 | 37 | 18 | 3017 | 2405 | 27 |
| 9 | Executors: 10 Cores: 6 | 10 GB | 60 | 0 | 2.5 | 55.8 | 37 | 10 | 3017 | 28.4 | |
| 10 | Executors: 10 Cores: 6 | 11 GB | 60 | 0 | 2.2 | 61.5 | 37 | 10 | 3017 | 27 | |
| 11 | Executors: 10 Cores: 6 | 5 GB | 60 | 0 | 2.0 | 27.2 | 37 | 10 | 3017 | 27.4 |
| Run # | # of Executors # of Executor Cores | Executor Memory | Precision | Recall | F Measure | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run 1 | Executors: 4 Cores: 4 | 19 GB | 0.9453 | 0.9635 | 0.9543 | 0.9777 |
| Run 2 | Executors: 5 Cores: 2 | 19 GB | 0.9304 | 0.9745 | 0.9947 | 0.9607 |
| Run 3 | Executors: 10 Cores: 2 | 19 GB | 0.9543 | 0.9519 | 0.9549 | 0.9548 |
| Run 4 | Executors: 10 Cores: 6 | 19 GB | 0.9777 | 0.982 | 0.9909 | 0.9766 |
| Run 5 | Executors: 12 Cores: 5 | Default—1 GB | 0.938 | 0.9699 | 0.9537 | 0.9803 |
| Run 6 | Executors: 8 Cores: 5 | Default—1 GB | 0.9561 | 0.9571 | 0.9855 | 0.9753 |
| Run 7 | Executors: 10 Cores: 2 | Default—1 GB | 0.9573 | 0.9425 | 0.9498 | 0.9682 |
| Run 8 | Executors: 10 Cores: 6 | Default—1 GB | 0.9605 | 0.9502 | 0.9556 | 0.9723 |
| Run 9 | Executors: 10 Cores: 6 | 10 GB | 0.953 | 0.9509 | 0.9519 | 0.9761 |
| Run 10 | Executors: 10 Cores: 6 | 11 GB | 0.9493 | 0.9628 | 0.956 | 0.9777 |
| Run 11 | Executors: 10 Cores: 6 | 5 GB | 0.9502 | 0.9594 | 0.9549 | 0.9761 |
| Author and Year | Precision | F Measure | AUC | Accuracy | FAR | Recall | Specificity | Total Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belouch et al., 2018 | NA | NA | NA | 95.82% | 92.52% | 97.1% | 4.93 | |
| Koroniotis et al., 2018 | NA | NA | NA | 92.30% | 11.71% | NA | NA | NA |
| Moustafa and Slay, 2016 | NA | NA | NA | 85.56% | 15.78% | NA | NA | NA |
| This paper (Bagui, et al.)—Parallel Spark implementation | 96.58% | 97.34% | 98.30% | 98.89% | 0.79% | 97.10% | 99.20% | 2.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bagui, S.; Walauskis, M.; DeRush, R.; Praviset, H.; Boucugnani, S. Spark Configurations to Optimize Decision Tree Classification on UNSW-NB15. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2022, 6, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc6020038
Bagui S, Walauskis M, DeRush R, Praviset H, Boucugnani S. Spark Configurations to Optimize Decision Tree Classification on UNSW-NB15. Big Data and Cognitive Computing. 2022; 6(2):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc6020038
Chicago/Turabian StyleBagui, Sikha, Mary Walauskis, Robert DeRush, Huyen Praviset, and Shaunda Boucugnani. 2022. "Spark Configurations to Optimize Decision Tree Classification on UNSW-NB15" Big Data and Cognitive Computing 6, no. 2: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc6020038
APA StyleBagui, S., Walauskis, M., DeRush, R., Praviset, H., & Boucugnani, S. (2022). Spark Configurations to Optimize Decision Tree Classification on UNSW-NB15. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 6(2), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc6020038







