Determination of a Numerical Surge Limit by Means of an Enhanced Greitzer Compressor Model †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Surge Limit as a Function of the System
1.2. Numerical Modeling and the Challenge with the Surge Limit
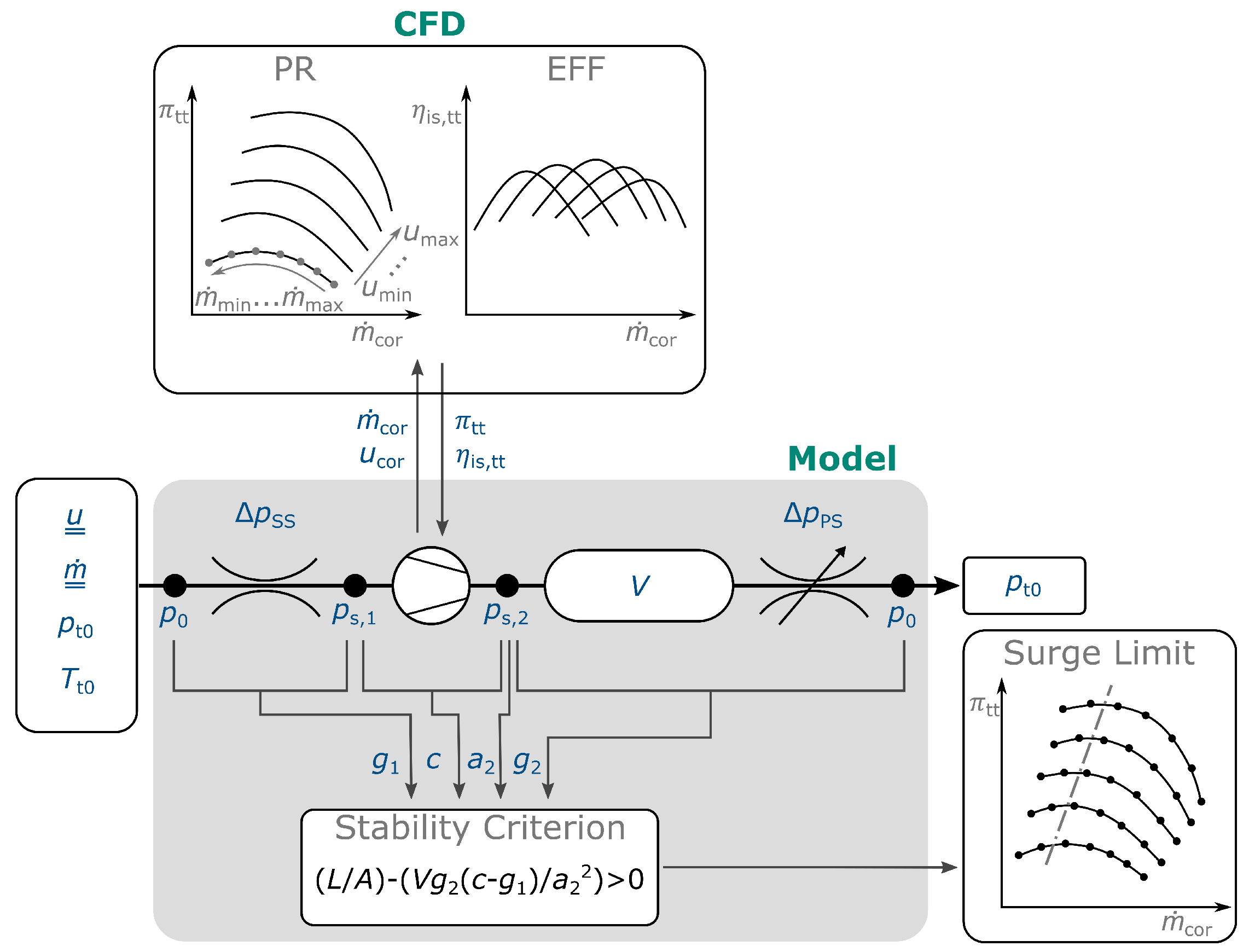
2. Determination of the Surge Limit
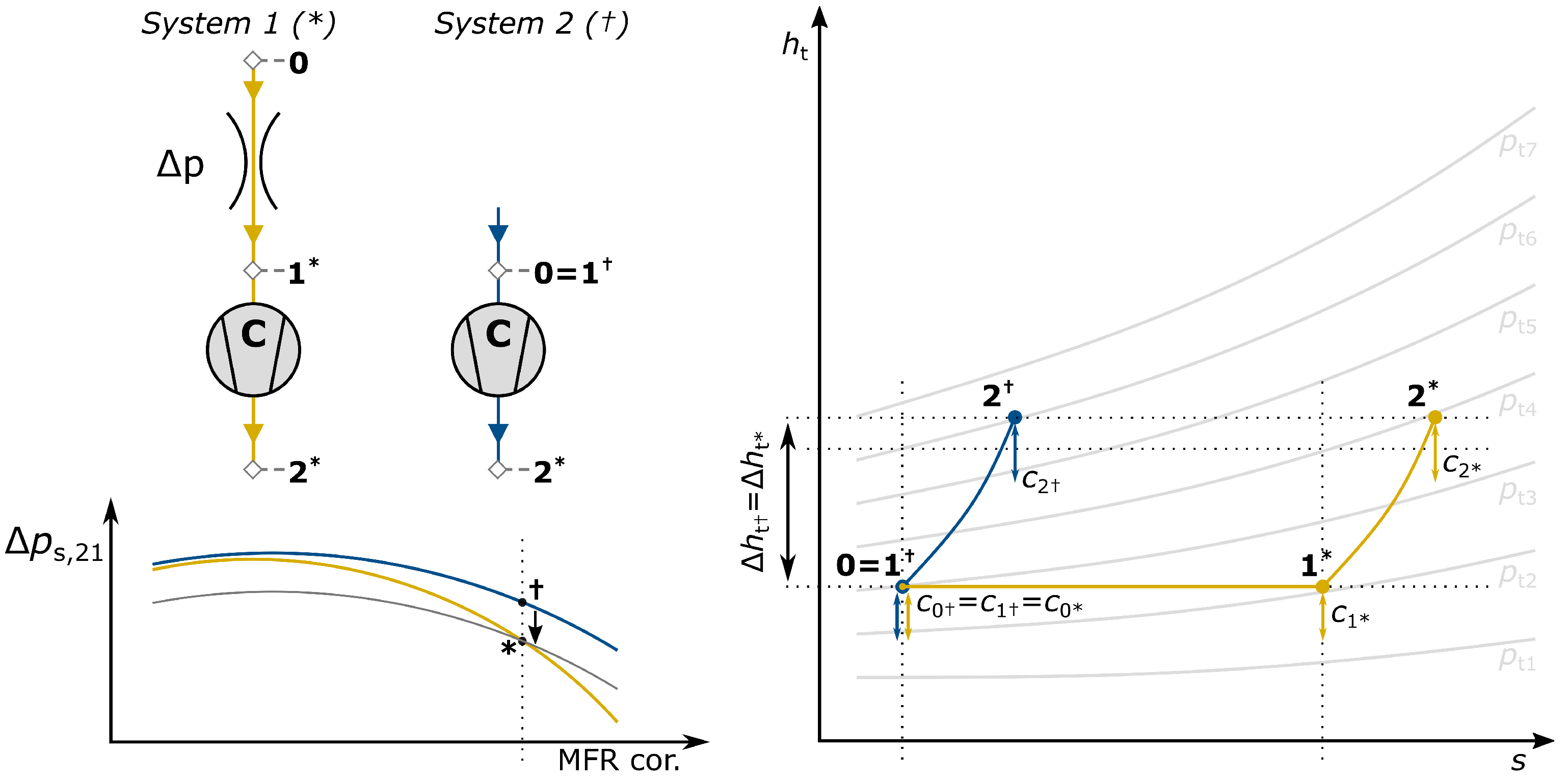
2.1. Methodology—Analytical Modeling of the Compression System
2.2. The Resulting Surge Limit for a System with Inlet Pressure Losses
2.3. Variation of the Inlet Pressure Loss and Its Influence on the Surge Limit
2.3.1. The Compressor Enthalpy Rise
- Air as ideal gas;
- The change in kinetic energy across a throttle is negligible;
- The compressor wheel (and no diffuser) is considered only;
- Reynolds number effects are neglected.
2.3.2. The Stability Map
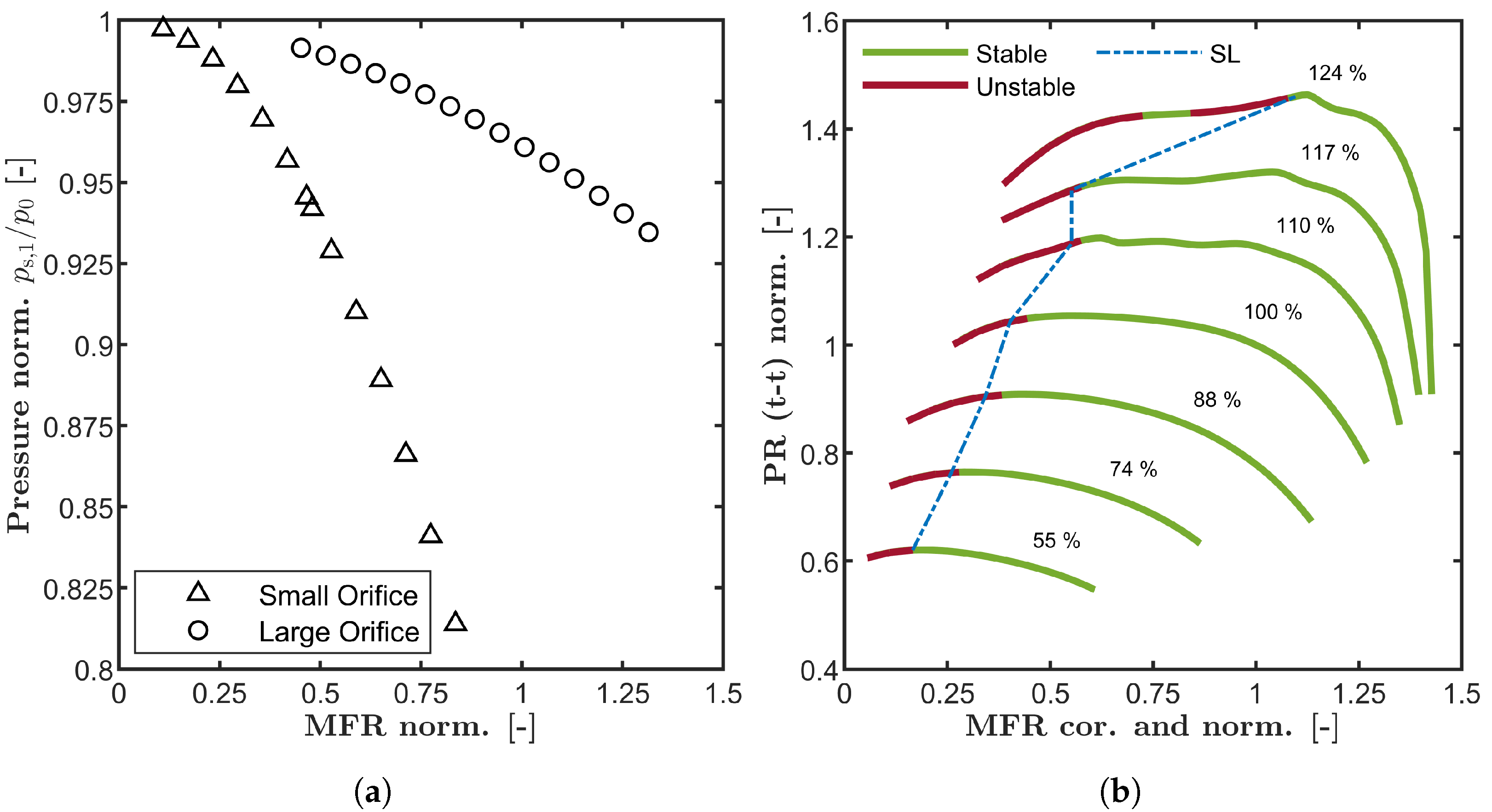
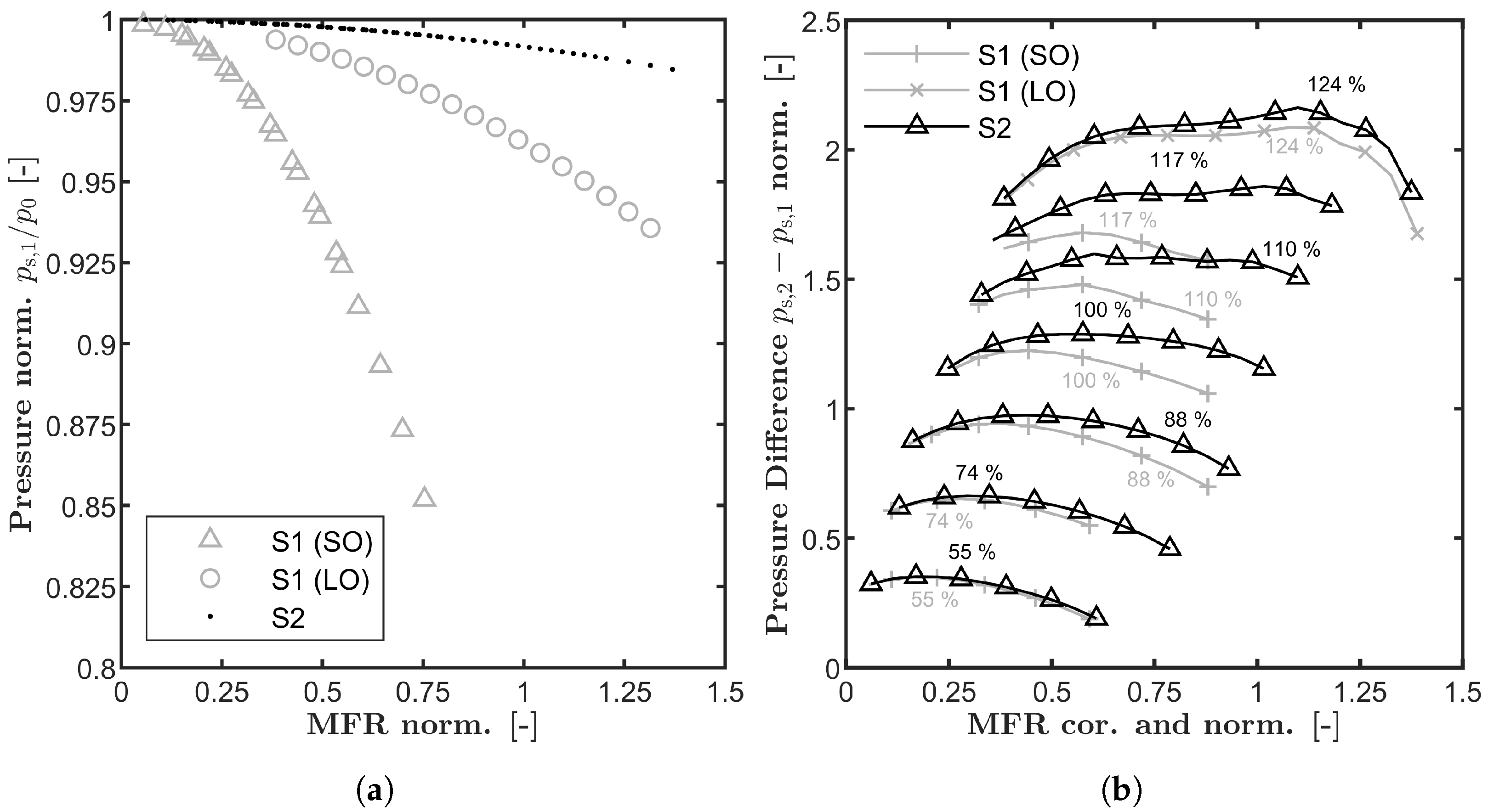
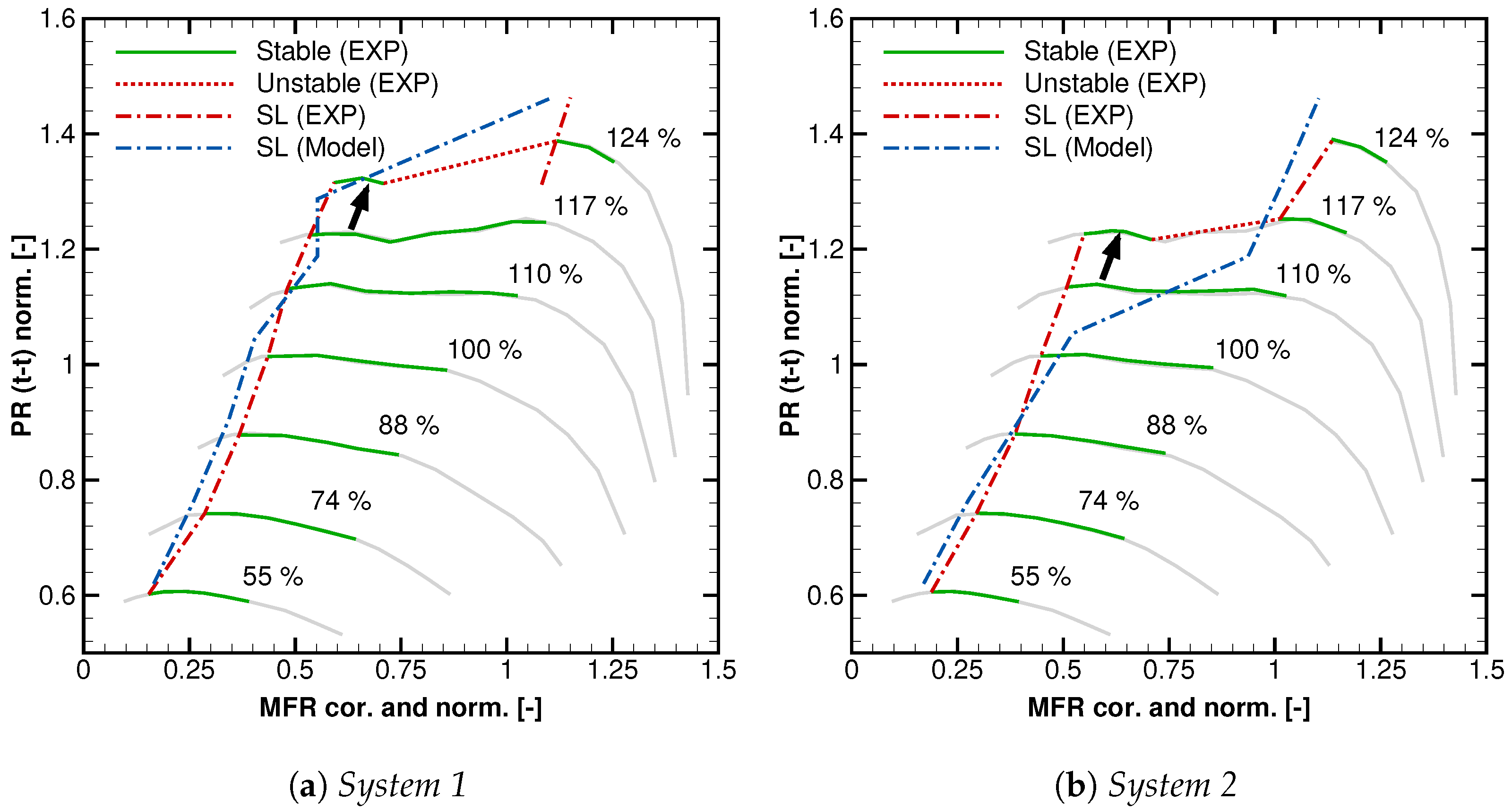
3. Experimental Validation
- There can be multiple surge limits for one speedline;
- The experimental and numerical surge limits match very well;
- The alternating stable and unstable regions can be predicted very well.
4. Conclusions
4.1. The System Influence on Stability Limiting Parameters
4.2. The Numerical Convergence Is No Good Indicator for Surge
4.3. There Is Not a Single Surge Limit
4.4. Modeling the System Dynamic Behavior Is Necessary to Determine a Surge Limit
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Abbreviations | |
| C | Compressor |
| EFF | Efficiency |
| EGT | Exhaust gas treatment |
| EXP | Experiment |
| ICE | Internal combustion engine |
| LO | Large orifice |
| MFR | Mass flow rate |
| MS | Measurement section |
| PR | Pressure ratio |
| S1 | System 1 |
| S2 | System 2 |
| SO | Small orifice |
| SL | Surge limit |
| T | Turbine |
| TC | Turbocharger |
| t-t | Total-total |
| Latin Symbols | |
| A | Cross section area |
| a | Speed of sound |
| B | Greitzer B-parameter |
| c | Compressor characteristic |
| Stability criterion | |
| Efficiency | |
| g | Throttle characteristic |
| h | Specific Enthalpy |
| L | Length |
| Mass flow rate | |
| Pressure ratio | |
| p | Pressure |
| s | Specific Entropy |
| T | Temperature |
| u | Circumferential Velocity |
| V | Volume |
| v | Abolute velocity |
| w | Relative velocity |
| Subscripts/Superscripts | |
| 0 | Ambient |
| 1 | Compressor Inlet |
| 2 | Compressor Outlet |
| C | Compressor |
| cor | Corrected |
| is | Isentropic |
| P | Plenum |
| ps | Pressure Side |
| ref | Reference |
| s | Static |
| ss | Suction Side |
| t | Total |
| tt | Total-total |
References
- Greitzer, E.M. Surge and Rotating Stall in Axial Flow Compressors—Part I: Theoretical Compression System Model. J. Eng. Power 1976, 98, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greitzer, E.M. Surge and Rotating Stall in Axial Flow Compressors—Part II: Experimental Results and Comparison with Theory. J. Eng. Power 1976, 98, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, D.A.; Cumpsty, N.A.; Greitzer, E.M. Surge Dynamics in a Free-Spool Centrifugal Compressor System. J. Turbomach. 1992, 114, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grapow, F.; Liśkiewicz, G. Study of the Greitzer Model for Centrifugal Compressors: Variable Lc Parameter and Two Types of Surge. Energies 2020, 13, 6072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, K.H.; Brace, C.J.; Budd, C.J.; Copeland, C.D.; Milewski, P.A. Modeling Axisymmetric Centrifugal Compressor Characteristics From First Principles. J. Turbomach. 2020, 142, 091010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, K.H.; Kennedy, I.J.; Brace, C.J.; Milewski, P.A.; Copeland, C.D. Development and Validation of a Model for Centrifugal Compressors in Reversed Flow Regimes. In Volume 8: Industrial and Cogeneration, Manufacturing Materials and Metallurgy, Marine, Microturbines, Turbochargers, and Small Turbomachines; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, K. Development and Validation of a Mathematical Model for Surge in Radial Compressors. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bath, Bath, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, K.H.; Kennedy, I.J.; Brace, C.J.; Milewski, P.A.; Copeland, C.D. Development and Validation of a Model for Centrifugal Compressors in Reversed Flow Regimes. J. Turbomach. 2021, 143, 101001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, K.; Kennedy, I.; Archer, J.; Eynon, P.; Horsley, J.; Brace, C.; Copeland, C.; Milewski, P. A New First-Principles Model to Predict Mild and Deep Surge for a Centrifugal Compressor. Energy 2022, 244, 123050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.Y.; Lin, Z.; Goyne, C.; Allaire, P.E. An Enhanced Greitzer Compressor Model Including Pipeline Dynamics and Surge. J. Vib. Acoust. 2011, 133, 051005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dielenschneider, T.; Ratz, J.; Leichtfuß, S.; Schiffer, H.P.; Eißler, W. On the Challenge of Determining the Surge Limit of Turbocharger Compressors: Part 1 - Experimental and Numerical Analysis of the Operating Limits. In Volume 6: Ceramics and Ceramic Composites, Coal, Biomass, Hydrogen, and Alternative Fuels, Microturbines, Turbochargers, and Small Turbomachines; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semlitsch, B.; Jyothishkumar, V.; Mihaescu, M.; Fuchs, L.; Gutmark, E.J. Investigation of the Surge Phenomena in a Centrifugal Compressor Using Large Eddy Simulation. In Volume 7A: Fluids Engineering Systems and Technologies; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semlitsch, B.; Mihăescu, M. Flow Phenomena Leading to Surge in a Centrifugal Compressor. Energy 2016, 103, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundström, E.; Semlitsch, B.; Mihăescu, M. Generation Mechanisms of Rotating Stall and Surge in Centrifugal Compressors. Flow Turbul. Combust. 2017, 100, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margot, X.; Gil, A.; Tiseira, A.; Lang, R. Combination of CFD and Experimental Techniques to Investigate the Flow in Centrifugal Compressors Near the Surge Line. In SAE Technical Paper Series; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.; Wade, R.; Morelli, A.; Miazgowicz, K.; Lizotte, B. Surge Prediction in a Single Sequential Turbocharger (SST) Compressor Using Computational Fluid Dynamics. In SAE Technical Paper Series; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehner, R.; Selamet, A.; Keller, P.; Becker, M. Simulation of Deep Surge in a Turbocharger Compression System. J. Turbomach. 2016, 138, 111002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeckel, T.; Paul, D.; Leichtfuß, S.; Schiffer, H.P.; Eißler, W. Determination of a Numerical Surge Limit by Means of an Enhanced Greitzer Compressor Model. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Turbomachinery Fluid Dynamics and Thermodynamics, Paper n. ETC2023-225, Budapest, Hungary, 24–28 April 2023; European Turbomachinery Society: Florence, Italy, 2023. Available online: https://www.euroturbo.eu/publications/conference-proceedings-repository/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Bühler, J.; Leichtfuß, S.; Schiffer, H.P.; Lischer, T.; Raabe, S. Surge Limit Prediction for Automotive Air-Charged Systems. Int. J. Turbomach. Propuls. Power 2019, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bühler, J. Über den Einfluss Aerodynamischer Effekte und Systemischer Größen auf das Kennfeld von Radialverdichtern. Ph.D. Thesis, Shaker Verlag, Düren, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dielenschneider, T.; Bühler, J.; Leichtfuß, S.; Schiffer, H.P. Some Guidelines for the Experimental Characterization of Turbocharger Compressors. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Turbomachinery Fluid Dynamics and Thermodynamics, Lausanne, Switzerland, 8–12 April 2019; European Turbomachinery Society: Florence, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baehr, H.D.; Kabelac, S. Thermodynamik; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
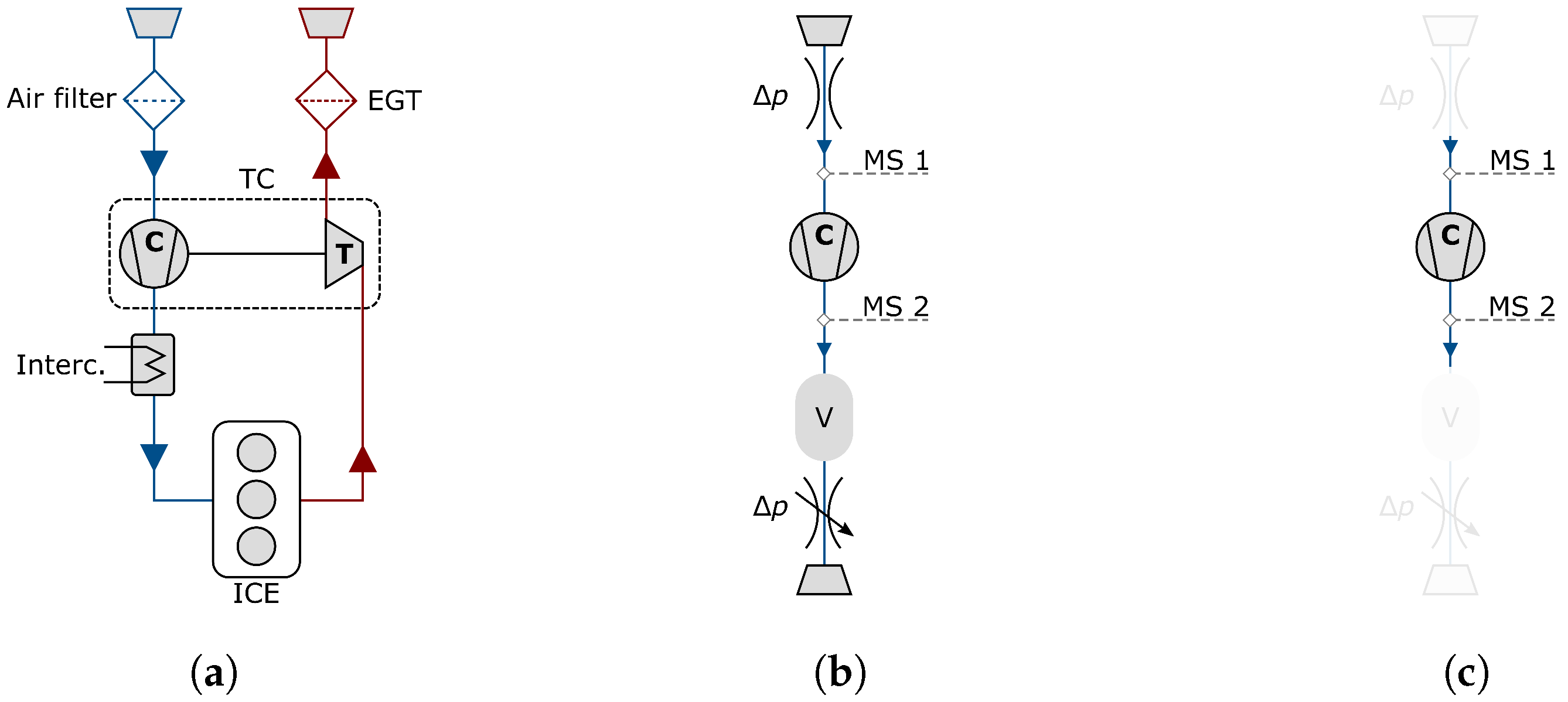

| Parameter | Calculation | System 1 | System 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| L | Environment to compressor inlet | 7.5 m | 0.25 m |
| A | Impeller intake cross section | 6.21 × 10 −4 m2 | 6.21 × 10 −4 m2 |
| V | Outlet plenum | 1.29 × 10 −3 m3 | 1.29 × 10 −3 m3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY-NC-ND) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haeckel, T.; Paul, D.; Leichtfuß, S.; Schiffer, H.-P.; Eißler, W. Determination of a Numerical Surge Limit by Means of an Enhanced Greitzer Compressor Model. Int. J. Turbomach. Propuls. Power 2023, 8, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp8040048
Haeckel T, Paul D, Leichtfuß S, Schiffer H-P, Eißler W. Determination of a Numerical Surge Limit by Means of an Enhanced Greitzer Compressor Model. International Journal of Turbomachinery, Propulsion and Power. 2023; 8(4):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp8040048
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaeckel, Tobias, Dominik Paul, Sebastian Leichtfuß, Heinz-Peter Schiffer, and Werner Eißler. 2023. "Determination of a Numerical Surge Limit by Means of an Enhanced Greitzer Compressor Model" International Journal of Turbomachinery, Propulsion and Power 8, no. 4: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp8040048
APA StyleHaeckel, T., Paul, D., Leichtfuß, S., Schiffer, H.-P., & Eißler, W. (2023). Determination of a Numerical Surge Limit by Means of an Enhanced Greitzer Compressor Model. International Journal of Turbomachinery, Propulsion and Power, 8(4), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp8040048





