Loss Characterization of a Conventional Variable Inlet Guide Vane †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
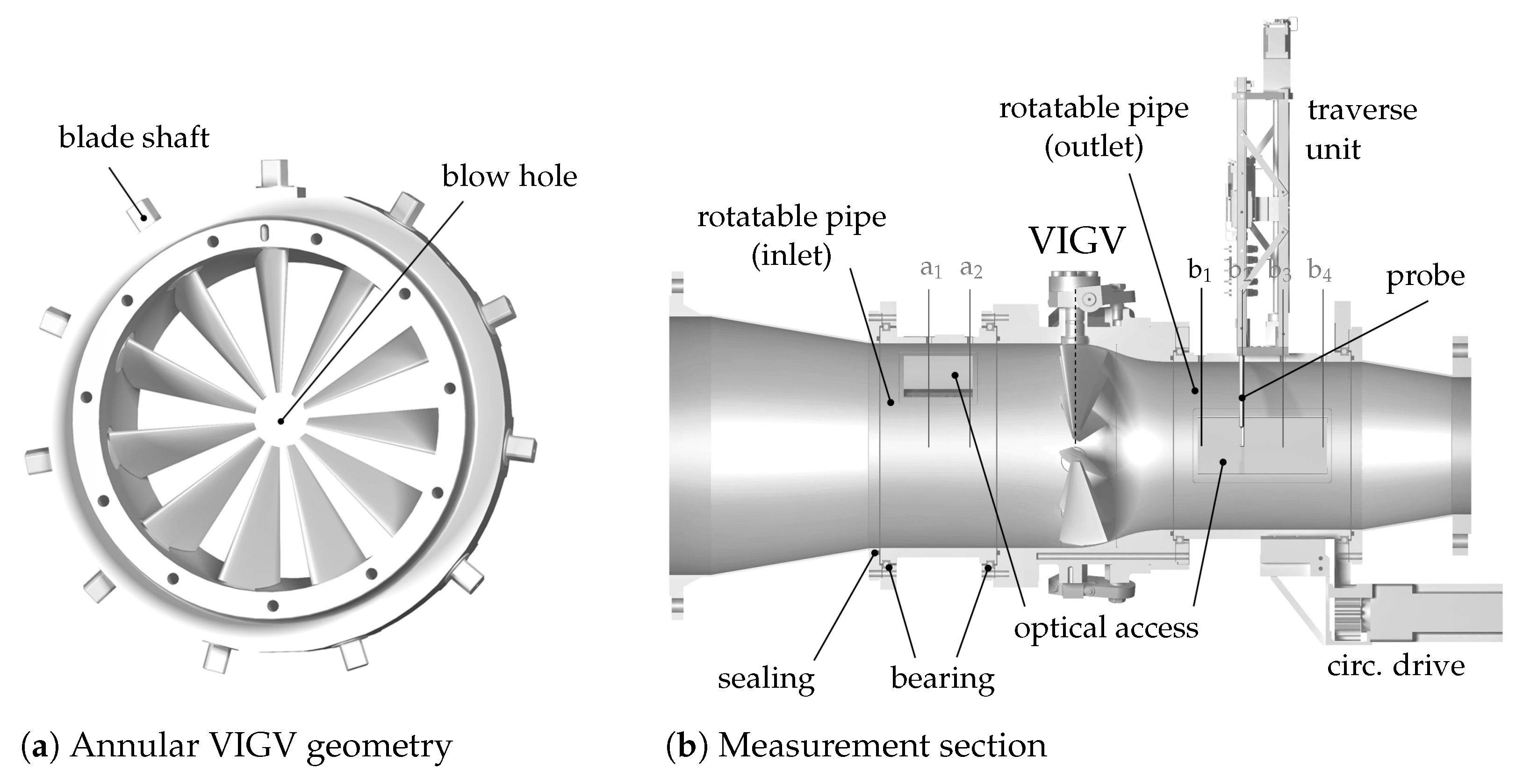
2. Experimental Setup
2.1. VIGV Test Facility
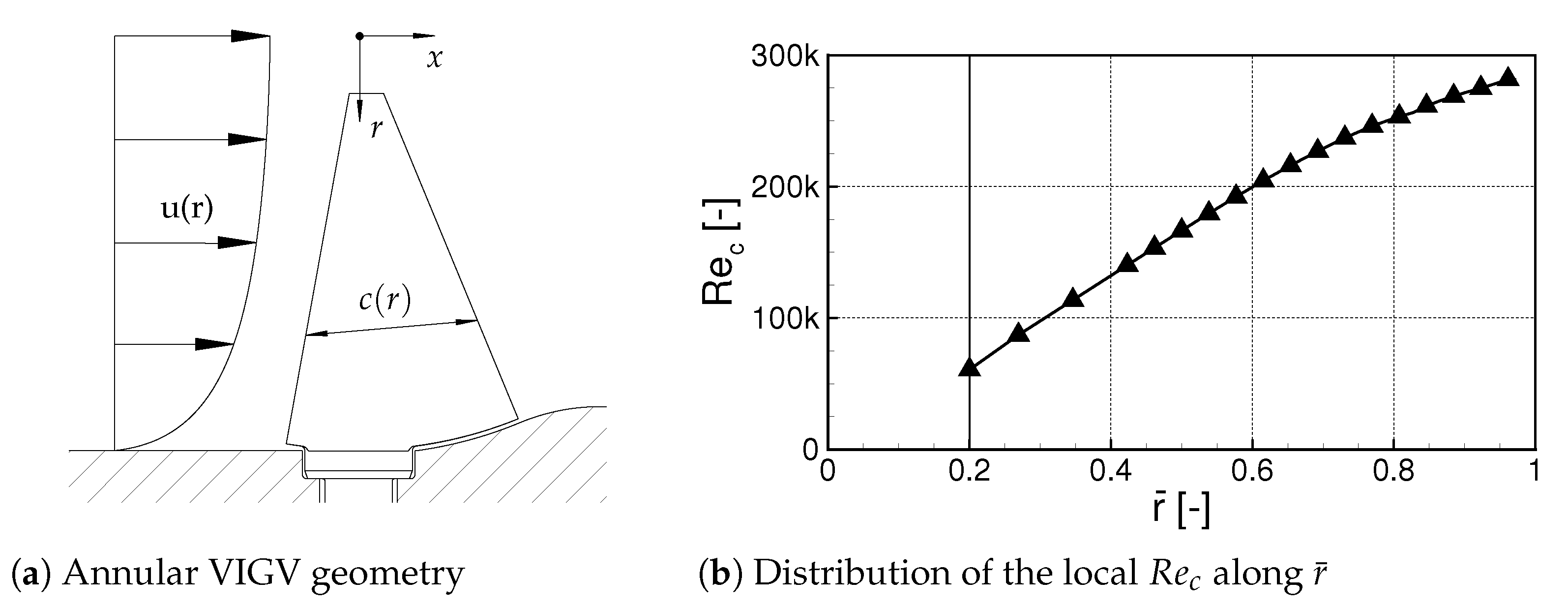
2.2. VIGV Cascade
2.3. Measurement Techniques and Operation
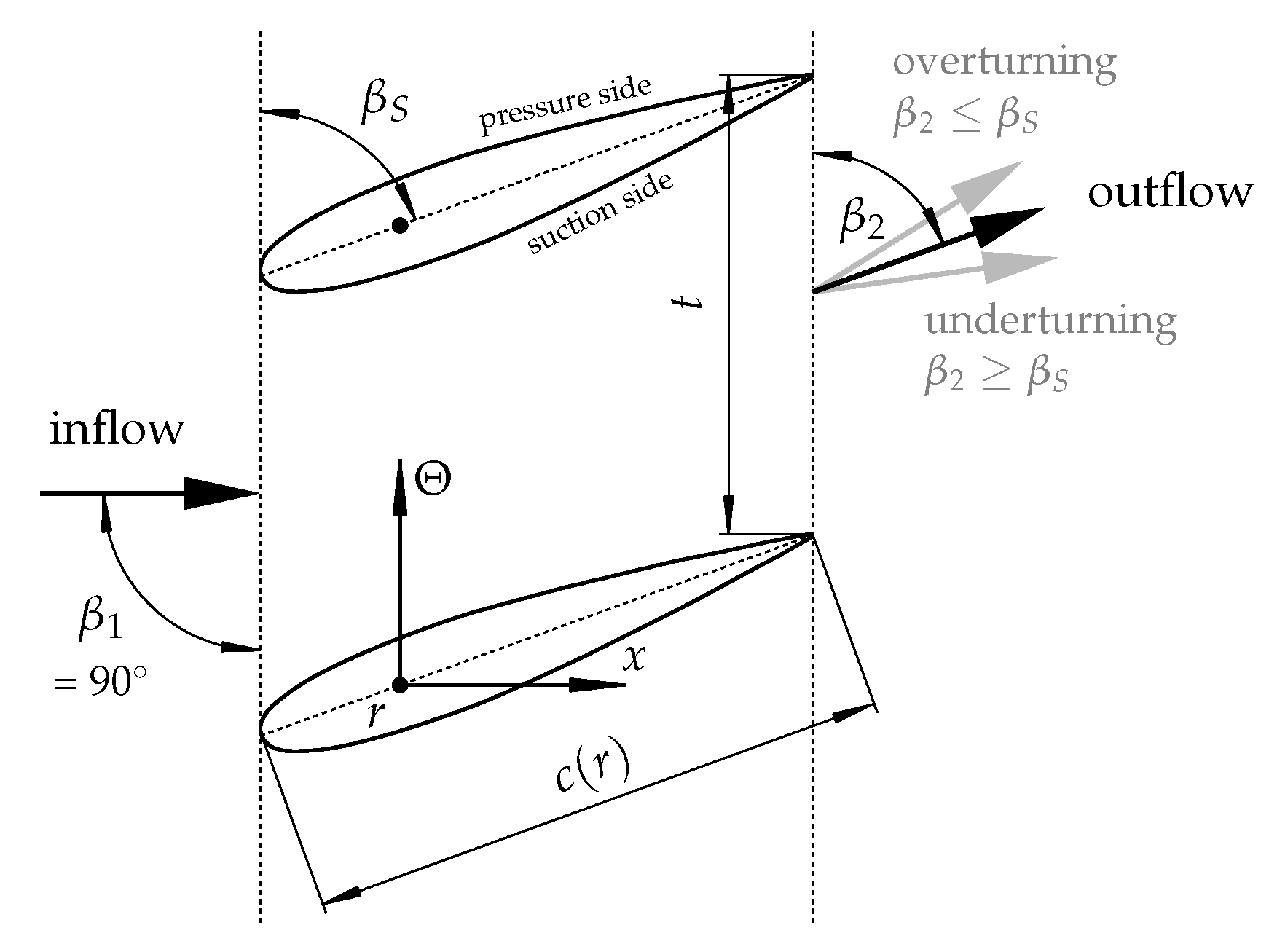
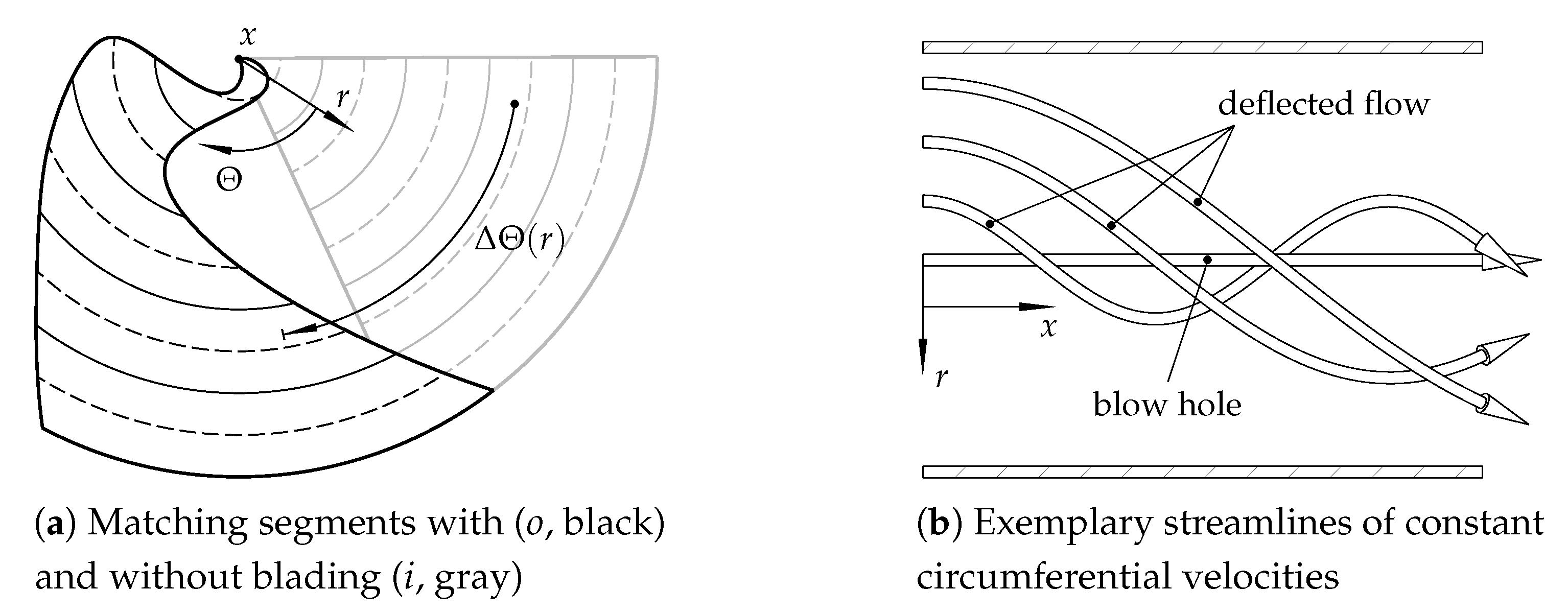
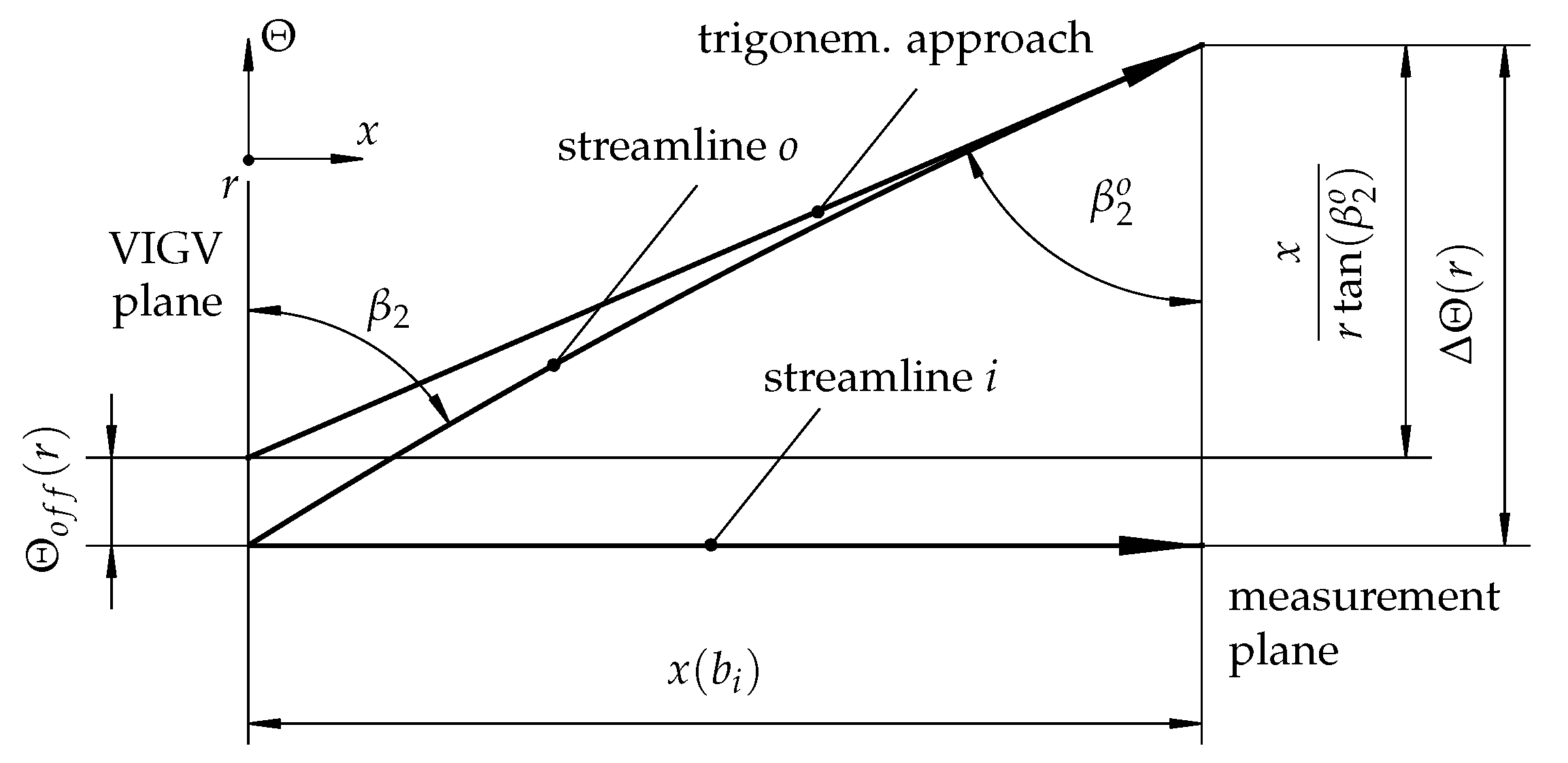
2.4. Loss Characterization and Flow Deflection
2.5. Inflow Correlation of the Total Pressure Loss
3. Results and Discussion
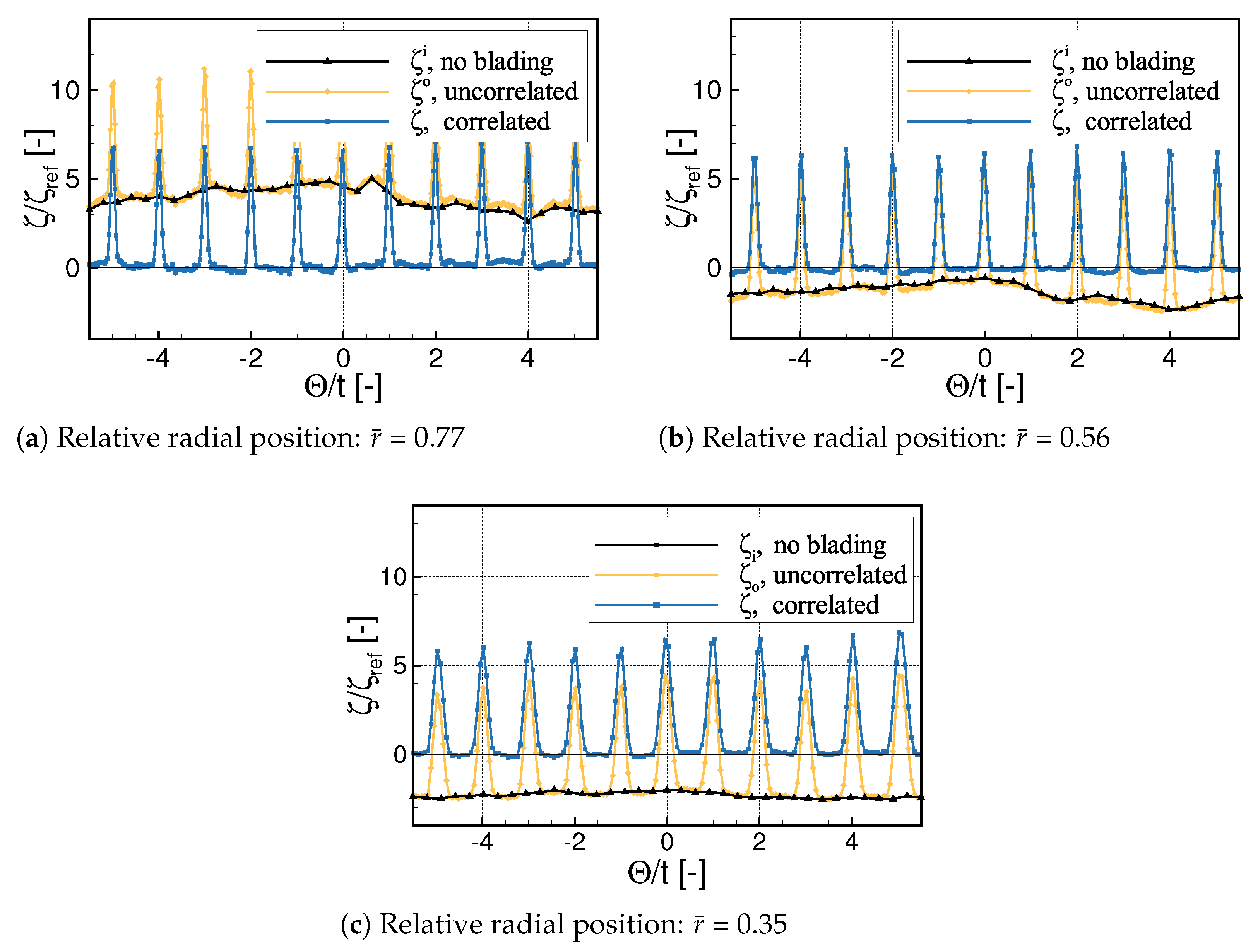
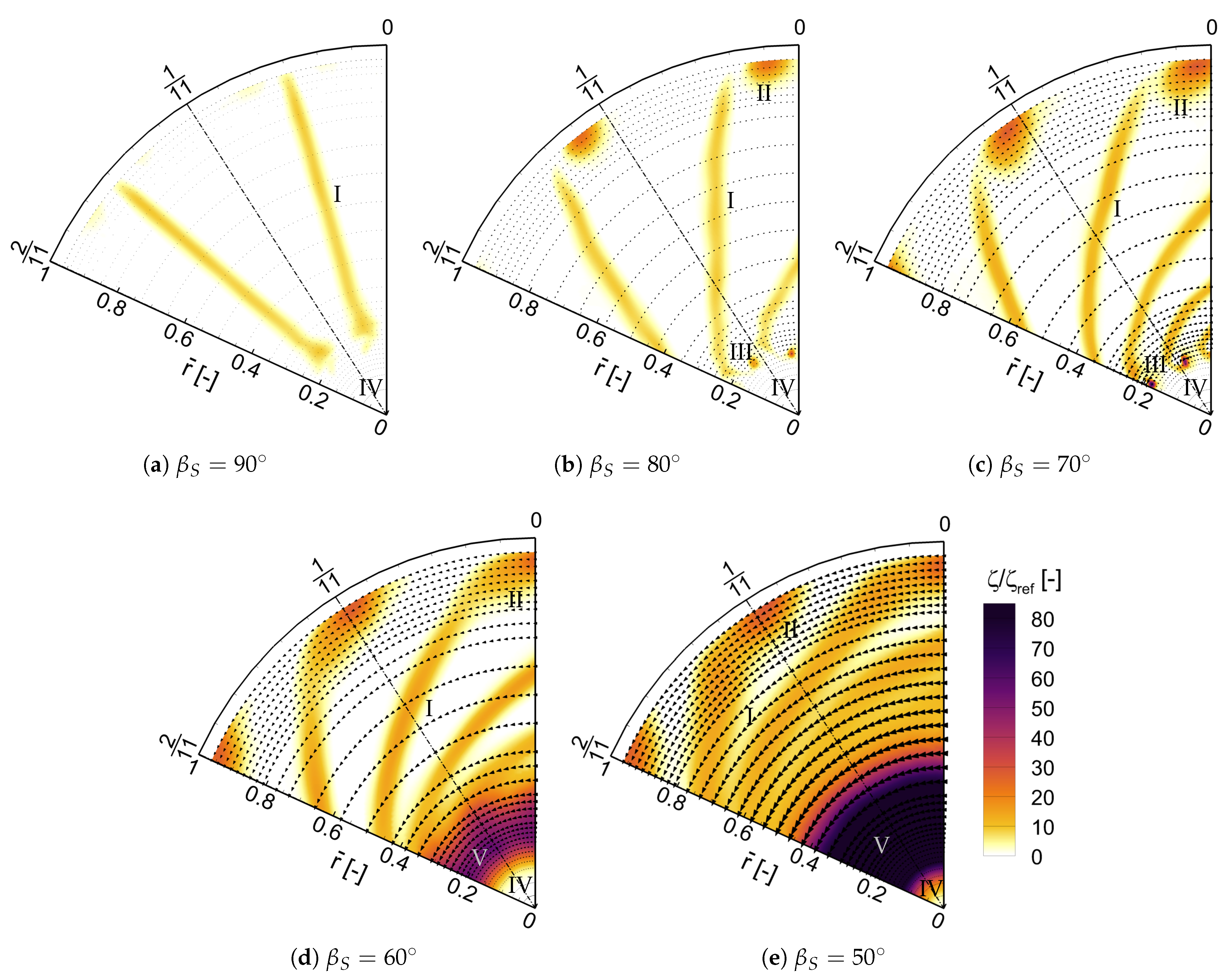
3.1. Performance along the Radius
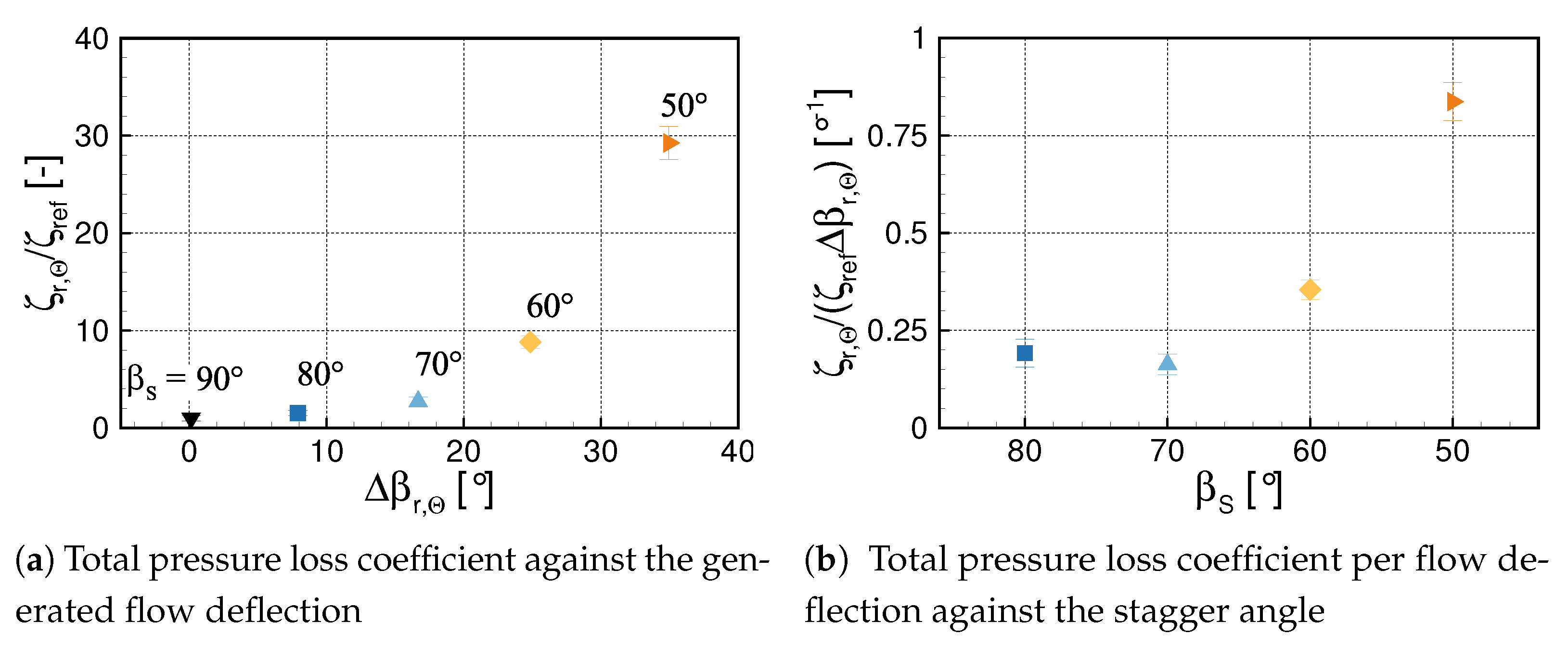
3.2. Overall Losses
4. Conclusions and Outlook
- From = 60 on, an increasing region of notable losses was observed downstream the region of the blade tips. Previous linear cascade measurements at an identical profile geometry by Händel et al. [10] already proved the tendency of the profile towards an open flow separation at the referred stagger angle and comparable local Reynolds numbers. Therefore, the reconsideration of the current blade design is recommended to ensure attached flow at further decreased stagger angles. Especially split blade geometries as investigated in linear cascade measurements by Bross and Stark [7] and Händel et al. [8] show promise to extend the efficient operational range of the annular VIGV.
- Moreover, the blocking of the center by a hub is suggested. Low local Reynolds numbers are hence prevented by accelerated flow conditions and the elimination of short chord lengths in the core region. Thus, lower profile losses as they were observed along higher , a certain shift of the devastating open flow separation towards lower stagger angles , and the suppression of the blade-tip vortex are expected. Instead of the blade tip losses, blade-hub flow interactions and tip gap effects will induce new losses. It is to be investigated if the expected benefits prevail with the induced hub-blade and tip clearance losses.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Symbols | |
| Measurement plane i [-] | |
| c | Chord length [m] |
| Mach number [-] | |
| p | Pressure [Pa] |
| q | Dynamic pressure [Pa] |
| r | Radial axis [m] |
| r relative to local pipe radius [-] | |
| Integral Reynolds number [-] | |
| Local Reynolds number [-] | |
| t | Pitch [] |
| x | Pipe center line axis [m] |
| Stagger angle [] | |
| Circumferential flow deflection [] | |
| Pipe circumferential axis [] | |
| Angular flow deflection [] | |
| Total pressure loss coefficient [-] | |
| Sub-/Superscripts | |
| 1, 2 | Without or with effect of VIGV |
| D | Inlet diameter of VIGV |
| i | Measurement without blading |
| o | Wake measurement incl. blading |
| Offset | |
| Integral reference at | |
| t | Total value |
| Mass averaged over , r | |
| Acronyms | |
| DMS | Demand side management |
| VIGV | Variable inlet guide vane |
| IGCC | Integrally geared centrifugal compressor |
References
- Gellings, C.W. The Concept of Demand-Side Management for Electric Utilities. Proc. IEEE 1985, 73, 1468–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häfner, L. Demand Side Management: Entscheidungsunterstützungssysteme für die flexible Beschaffung von Energie unter integrierten Chancen- und Risikoaspekten. HMD. Theor. Und Prax. Der Wirtsch. 2018, 55, 627–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, A.; Abele, E.; Buhl, H.U. Energieflexibilität in der Deutschen Industrie; Frauenhofer Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 2019; ISBN 978-3-8396-1479-2. [Google Scholar]
- Beaty, P.J.; Eisele, K.; Maceyka, T.D.; Schwarz, C. Integrally Geared API 617 Process Gas Compressors; Texas A&M University, Turbomachinery Laboratories: College Station, TX, USA, 2000; pp. 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, U.; Böhle, M. Theoretische und experimentelle Untersuchungen an ungestaffelten Gittern aus Profilen mit mechanischen Klappen. Forsch. Im Ingenieurwesen 1990, 56, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, A.; Goldhahn, E.; Van den Braembussche, R.A.; Seume, J.R. Novel IGV Designs for Centrifugal Compressors and Their Interaction with the Impeller. ASME J. Turbomach. 2012, 134, 021006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bross, S.; Stark, U. Entwicklung neuer Schaufelgitter aus Profilen variabler Geometrie zum Einsatz in Leiträdern drallgerelgeter Turbomaschinen-Teil I. Forsch. Im Ingenieurwesen 1994, 60, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Händel, D.; Niehuis, R.; Klausmann, J. Aerodynamic Investigation of an Advanced VIGV Design of Adjustable Geometry for Very High Flow Turning; ASME Turbo Expo: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassens, I.; Rautenberg, M. Flow Measurements Behind the Inlet Guide Vane of a Centrifugal Compressor; ASME Turbo Expo: Stockholm, Sweden, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Händel, D.; Niehuis, R.; Rockstroh, U. Aerodynamic Investigation of a Variable Inlet Guide Vane with Symmetric Profile; ASME Turbo Expo: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Händel, D.; Rockstroh, U.; Niehuis, R. Experimental Investigation of Transition and Seperation Phenomena on an Inlet Guide Vane with Symmetric Profile at Different Stagger Angles and Reynolds Numbers. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Transport Phenomena and Dynamics of Rotating Machinery, Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–28 February 2014. FR305. [Google Scholar]
- Coppinger, M.; Swain, E. Performance Prediction of an Industrial Centrifugal Compressor Inlet Guide Vane System. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2000, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, R.; Wacker, C.; Niehuis, R. A New Test Facility for Advanced Testing of Variable Inlet Guide Vanes; MTT Measuring Techniques in Turbomachinery; 2020, MTT2520A18. Available online: https://www.meastechturbo.com/paper-archives/mtt2520-santorini-2020 (accessed on 16 July 2021).
- Amecke, J. Auswertung von Nachlaufmessungen an Ebenen Schaufelgittern; Messbericht 67 A 49; AVA Göttingen: Gottingen, Germany, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Sieverding, C.H. Recent Progress in Understanding of Basic Aspects of Secondary Flows in Turbine Blade Passages. ASME J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 1985, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, J.D. Loss Mechanisms in Turbomachinery. ASME J. Turbomach. 1993, 115, 621–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.I. Wing Tip Vortices. In Fluid Mechanics and Its Applications; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.N.; Hagelstein, D.; Kassens, I.; Hasermann, H.; Haupt, U.; Rautenberg, M. Overshoot of the Rankine Vortex Formed in the Flow Field Behind the Inlet Guide Vane of Centrifugal Compressors; ASME Turbo Expo: Indianapolis, IN, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Händel, D. Experimentelle Untersuchung und Weiterentwicklung eines Variablen Eintrittsleitapparates für die Vordrallregelung in Turbomaschinen; Verlag Dr. Hut: Munich, Germany, 2018; ISBN 978-38439-3874-7. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY-NC-ND) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frank, R.G.; Wacker, C.; Niehuis, R. Loss Characterization of a Conventional Variable Inlet Guide Vane. Int. J. Turbomach. Propuls. Power 2021, 6, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp6030030
Frank RG, Wacker C, Niehuis R. Loss Characterization of a Conventional Variable Inlet Guide Vane. International Journal of Turbomachinery, Propulsion and Power. 2021; 6(3):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp6030030
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrank, Roman G., Christian Wacker, and Reinhard Niehuis. 2021. "Loss Characterization of a Conventional Variable Inlet Guide Vane" International Journal of Turbomachinery, Propulsion and Power 6, no. 3: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp6030030
APA StyleFrank, R. G., Wacker, C., & Niehuis, R. (2021). Loss Characterization of a Conventional Variable Inlet Guide Vane. International Journal of Turbomachinery, Propulsion and Power, 6(3), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijtpp6030030





