Comparative Genomics Revealing the Genomic Characteristics of Klebsiella variicola Clinical Isolates in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sources of Bacterial Genomic Data
2.2. Genomic Characterization Analysis
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
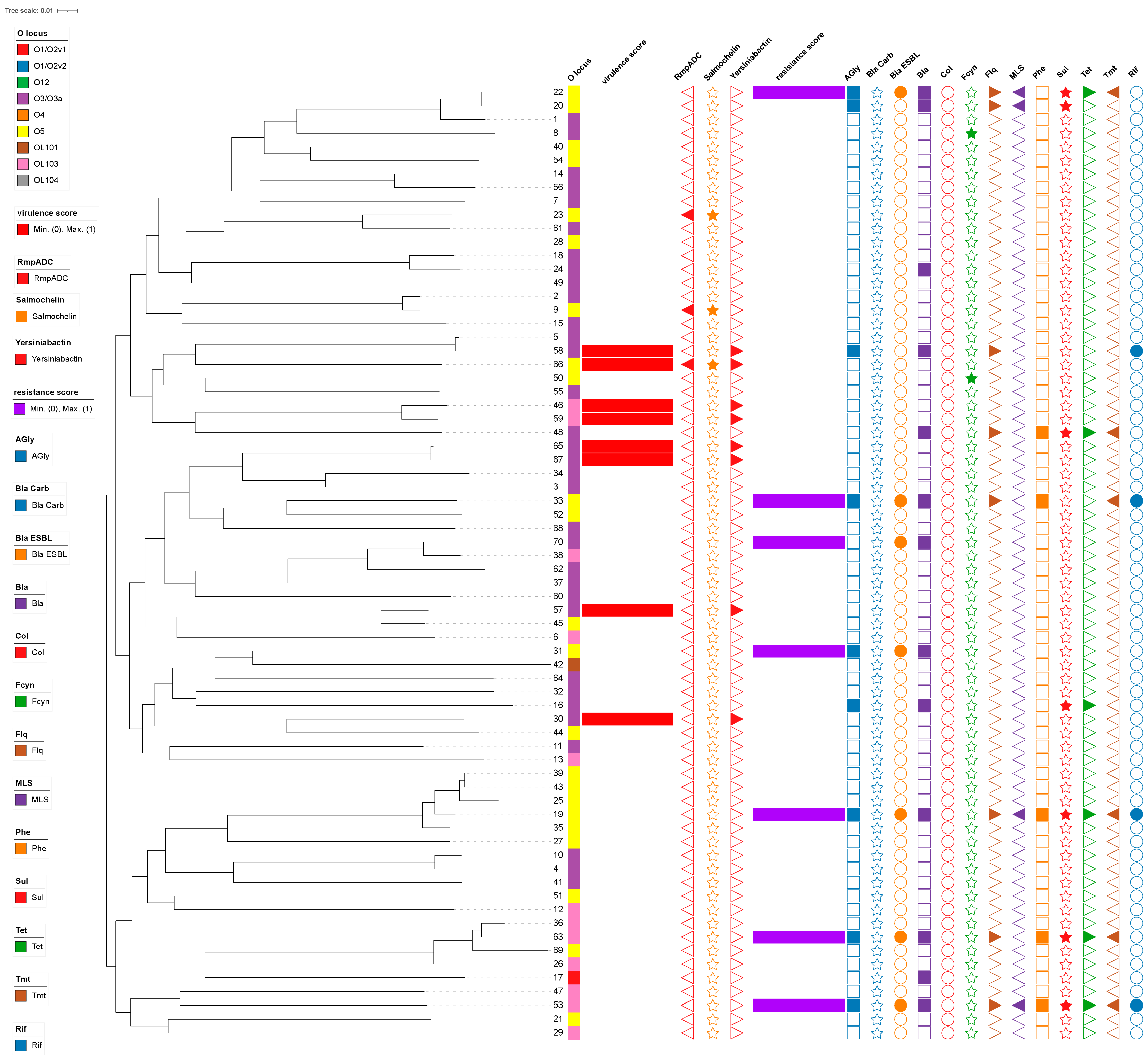
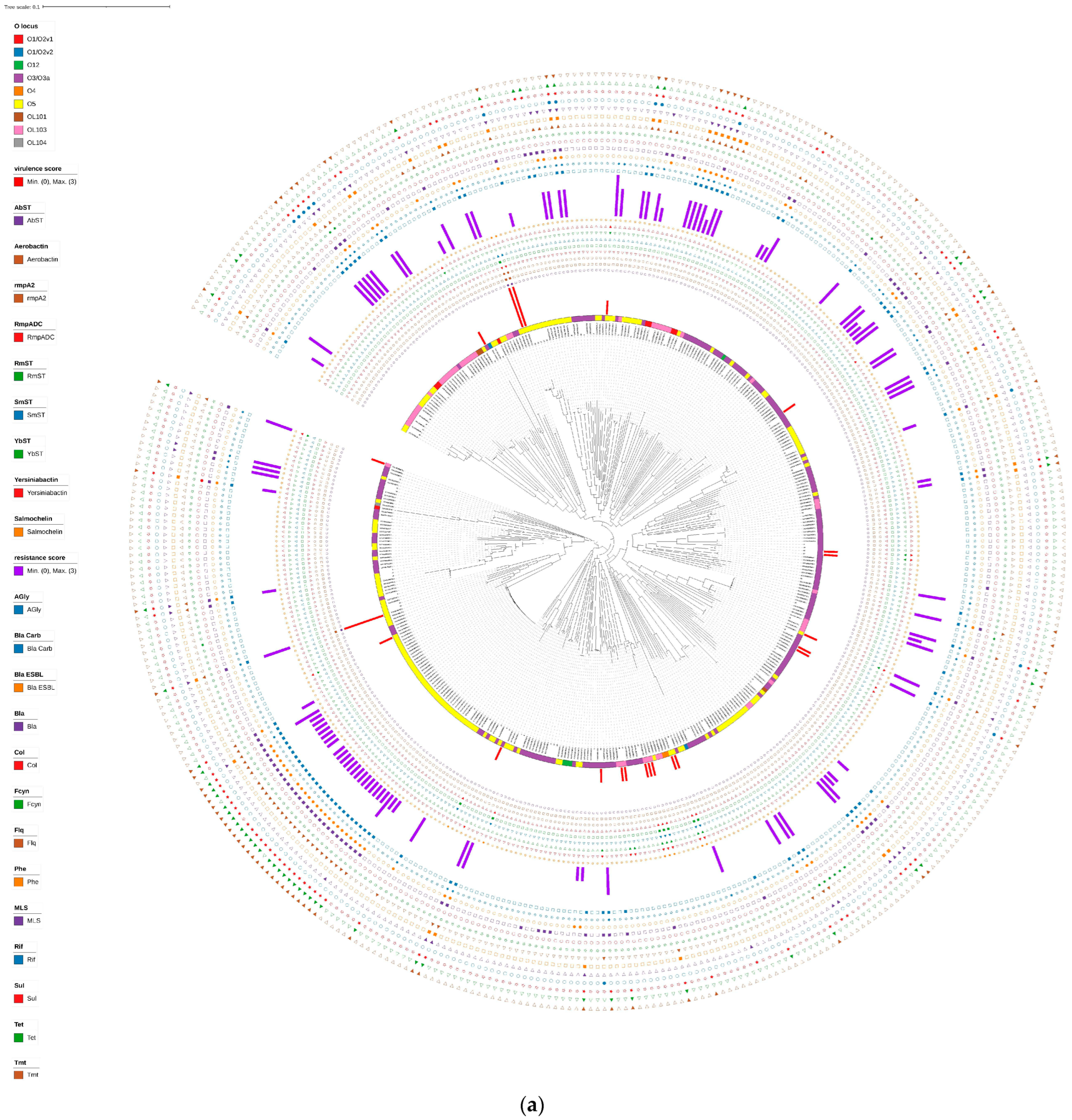
3.1. Drug Resistance and Virulence Gene Profiles of Klebsiella variicola Isolates from China
3.2. Serotyping and MLST of Klebsiella variicola
3.3. Plasmid Replicon Typing
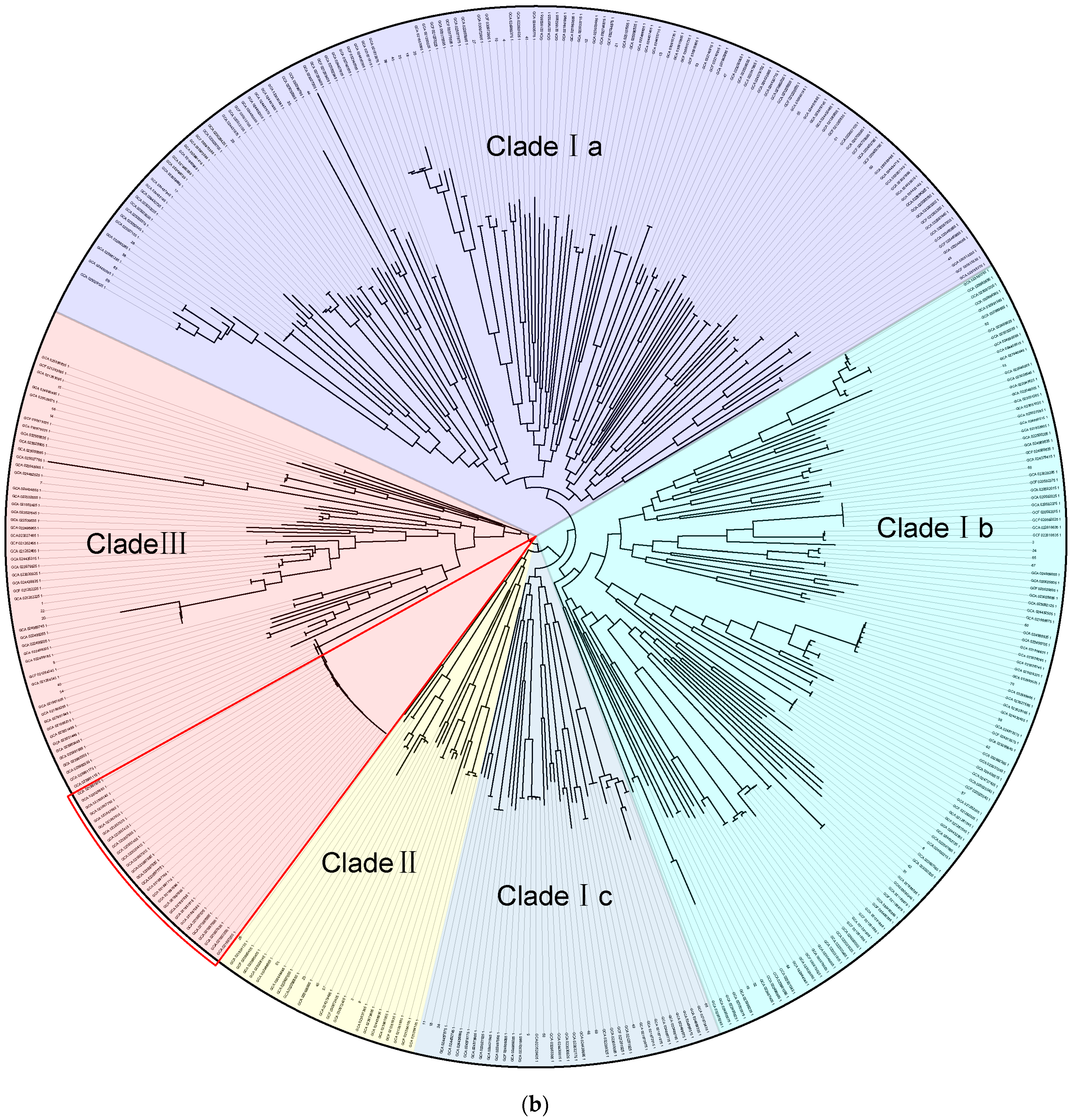
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of Klebsiella variicola
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodríguez-Medina, N.; Barrios-Camacho, H.; Duran-Bedolla, J.; Garza-Ramos, U. Klebsiella variicola: An emerging pathogen in humans. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 973–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadar, A.; Perdigão, J.; Campino, S.; Clark, T.G. Large-scale genomic analysis of global Klebsiella pneumoniae plasmids reveals multiple simultaneous clusters of carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent strains. Genome Med. 2023, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maatallah, M.; Vading, M.; Kabir, M.H.; Bakhrouf, A.; Kalin, M.; Nauclér, P.; Brisse, S.; Giske, C.G. Klebsiella variicola is a frequent cause of bloodstream infection in the Stockholm area, and associated with higher mortality compared to K. pneumoniae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.W.; Linson, S.E.; Saavedra, M.O.; Cantu, C.; Davis, J.J.; Brettin, T.; Olsen, R.J. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Human Clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Reveals Misidentification and Misunderstandings of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella variicola, and Klebsiella quasipneumoniae. mSphere 2017, 2, e00290-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, R.F.; Lainhart, W.; Twentyman, J.; Wallace, M.A.; Wang, B.; Burnham, C.A.; Rosen, D.A.; Dantas, G. Population structure, antibiotic resistance, and uropathogenicity of Klebsiella variicola. MBio 2018, 9, e02481-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrios-Camacho, H.; Aguilar-Vera, A.; Beltran-Rojel, M.; Aguilar-Vera, E.; Duran-Bedolla, J.; Rodriguez-Medina, N.; Lozano-Aguirre, L.; Perez-Carrascal, O.M.; Rojas, J.; Garza-Ramos, U. Molecular epidemiology of Klebsiella variicola obtained from different sources. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzana, R.; Jones, L.S.; Rahman, M.A.; Andrey, D.O.; Sands, K.; Portal, E.; Watkins, W.J.; Pervin, M.; Banerjee, M.; Walsh, T.R. Outbreak of hypervirulent Multi-Drug resistant Klebsiella variicola causing high mortality in neonates in Bangladesh. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 1225–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, N.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Jian, Z.; Liang, T.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, W.; He, J.; Cheng, X.; Li, H.; et al. Large-scale genomic epidemiology of Klebsiella pneumoniae identified clone divergence with hypervirulent plus antimicrobial-resistant characteristics causing within-ward strain transmissions. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0269821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, M.M.C.; Wick, R.R.; Watts, S.C.; Cerdeira, L.T.; Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. A genomic surveillance framework and genotyping tool for Klebsiella pneumoniae and its related species complex. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diancourt, L.; Passet, V.; Verhoef, J.; Grimont, P.A.D.; Brisse, S. Multilocus sequence typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae nosocomial isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4178–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.M.C.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Holt, K.E.; Wyres, K.L. Kaptive 2.0: Updated capsule and lipopolysaccharide locus typing for the Klebsiella pneumoniae species complex. Microb. Genom. 2022, 8, 000800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, S.N.; Slezak, T.; Hall, B.G. kSNP3.0: SNP detection and phylogenetic analysis of genomes without genome alignment or reference genome. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2877–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garza-Ramos, U.; Silva-Sanchez, J.; Barrios, H.; Rodriguez-Medina, N.; Martínez-Barnetche, J.; Andrade, V. Draft Genome Sequence of the First Hypermucoviscous Klebsiella variicola Clinical Isolate. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e01352-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Feng, Y.; McNally, A.; Zong, Z. Occurrence of colistin-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella variicola. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 3001–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Eisen, J.A. A simple, fast, and accurate method of phylogenomic inference. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; He, Z.; Hu, S.; Kang, Y.; Gao, Z. Complete Genomic Analysis of a Kingdom-Crossing Klebsiella variicola Isolate. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiley, J.L.; Mende, K.; Beckius, M.L.; Kaiser, S.J.; Carson, M.L.; Lu, D.; Whitman, T.J.; Petfield, J.L.; Tribble, D.R.; Blyth, D.M. Resistance patterns and clinical outcomes of Klebsiella pneumoniae and invasive Klebsiella variicola in trauma patients. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Liu, M.; Dong, X.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; Cheng, F.; Guo, J.; Lu, S.; Wan, F.; et al. Characterization of IncHI1B Plasmids Encoding Efflux Pump TmexCD2-ToprJ2 in Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella variicola, Klebsiella quasipneumoniae, and Klebsiella michiganensis Strains. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 759208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, K.L.; Findlay, J.; Doumith, M.; Mather, B.; Meunier, D.; D’Arcy, S.; Pike, R.; Mustafa, N.; Howe, R.; Wootton, M.; et al. IMI-2 carbapenemase in a clinical Klebsiella variicola isolated in the UK. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2129–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, N.; Aung, M.S.; Urushibara, N.; Kawaguchiya, M.; Ohashi, N.; Taniguchi, K.; Kudo, K.; Ito, M.; Kobayashi, N. Prevalence, clonal diversity, and antimicrobial resistance of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae and Klebsiella variicola clinical isolates in northern Japan. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2023, 35, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif, Y.; Monk, J.M.; Machado, H.; Kavvas, E.; Palsson, B.O. Systems Biology and Pangenome of Salmonella O-Antigens. MBio 2019, 10, e01247-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Score | Genes | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| resistance score | blaESBL | blaCARB | Col |
| 0 | − | − | / |
| 1 | + | − | +/− |
| 2 | +/− | + | - |
| 3 | +/− | + | + |
| virulence score | ybt | clb | iuc |
| 0 | − | − | − |
| 1 | + | − | − |
| 2 | +/− | + | − |
| 3 | − | − | + |
| 4 | + | − | + |
| 5 | + | + | + |
| Plasmid Replicons | No. of Strains (n = 70) | Carriage Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Col(Ye4449) | 1 | 1.43% |
| ColpVC | 2 | 2.86% |
| ColRNAI | 19 | 27.14% |
| IncFIA(HI1)_HI1 | 7 | 10.00% |
| IncFIB(K)_Kpn3 | 40 | 57.14% |
| IncFIB(Mar)_pNDM-Mar | 2 | 2.86% |
| IncFIB(pENTAS01)_pENTAS01 | 4 | 5.71% |
| IncFIB(pKPHS1)_pKPHS1 | 3 | 4.29% |
| IncFII(K) | 1 | 1.43% |
| IncFII(pHN7A8)_pHN7A8 | 12 | 17.14% |
| IncFII(pKPX1) | 1 | 1.43% |
| IncFII(pRSB107)_pRSB107 | 2 | 2.86% |
| IncFII_pKP91 | 33 | 47.14% |
| IncHI1B_pNDM-MAR | 7 | 10.00% |
| IncHI2 | 1 | 1.43% |
| IncHI2A | 1 | 1.43% |
| IncL/M | 1 | 1.43% |
| IncN | 1 | 1.43% |
| IncQ1 | 1 | 1.43% |
| IncR | 8 | 11.43% |
| IncU | 1 | 1.43% |
| IncX2 | 2 | 2.86% |
| pSL483 | 1 | 1.43% |
| IncFIB(K)_Kpn3 + IncFII_pKP91 | 28 | 40.00% |
| IncFIB(K)_Kpn3 + ColRNAI | 13 | 18.57% |
| IncFII_pKP91 + ColRNAI | 11 | 15.71% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, F.; Liu, F.-Y.; Zhong, Y.-M. Comparative Genomics Revealing the Genomic Characteristics of Klebsiella variicola Clinical Isolates in China. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9080180
Yang F, Liu F-Y, Zhong Y-M. Comparative Genomics Revealing the Genomic Characteristics of Klebsiella variicola Clinical Isolates in China. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2024; 9(8):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9080180
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Fang, Fei-Yi Liu, and Yi-Ming Zhong. 2024. "Comparative Genomics Revealing the Genomic Characteristics of Klebsiella variicola Clinical Isolates in China" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 9, no. 8: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9080180
APA StyleYang, F., Liu, F.-Y., & Zhong, Y.-M. (2024). Comparative Genomics Revealing the Genomic Characteristics of Klebsiella variicola Clinical Isolates in China. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 9(8), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9080180





