Plasma Circulating Cell-Free DNA Facilitated the Detection of an Alveolar Echinococcosis Patient Initially Misdiagnosed as Cystic Echinococcosis: A Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
2.1. History
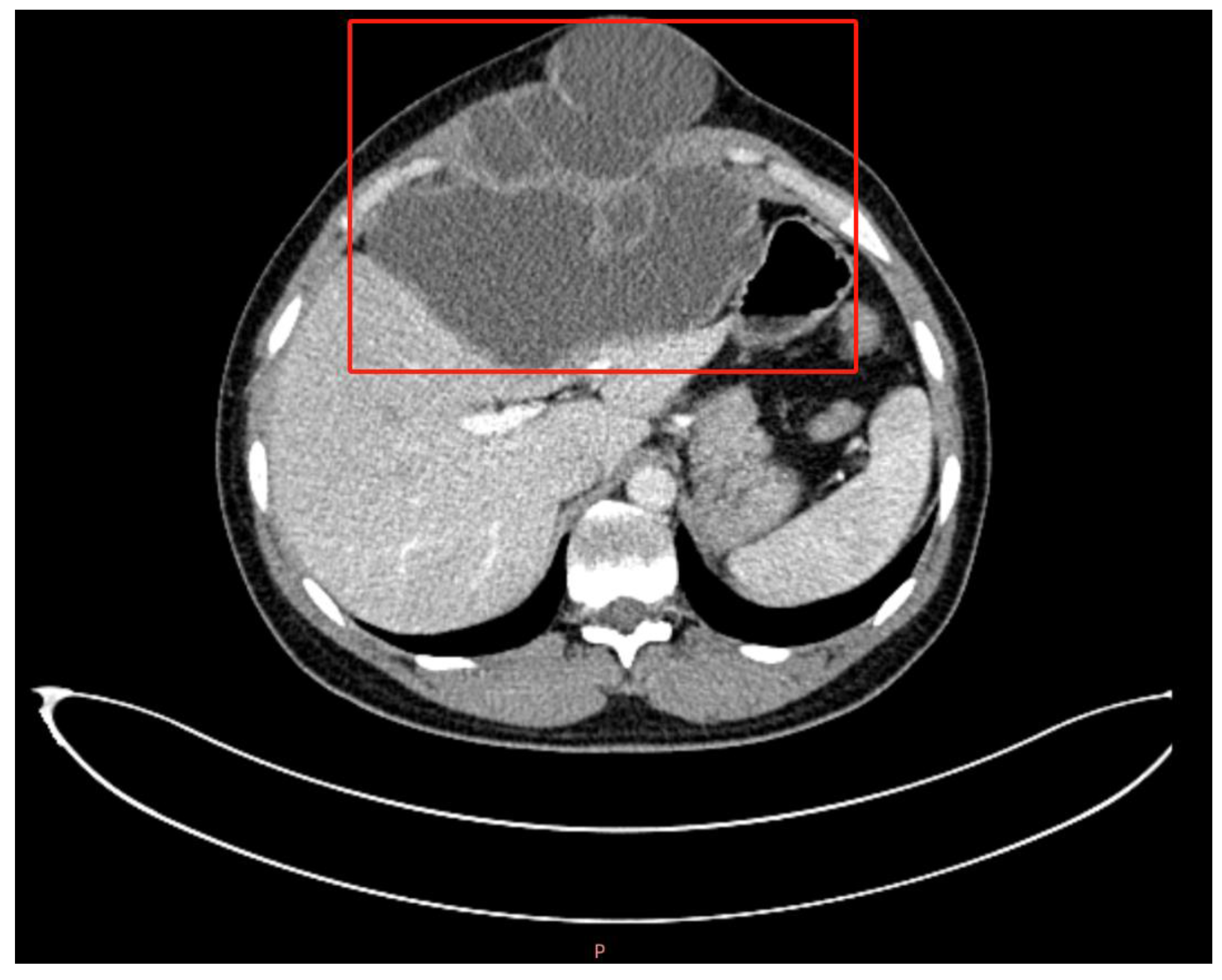
2.2. Investigations and Differential Diagnosis
2.3. The Plasma Cell-Free Echinococcus spp. DNA Analysis and ELISA Test
2.4. The Treatment
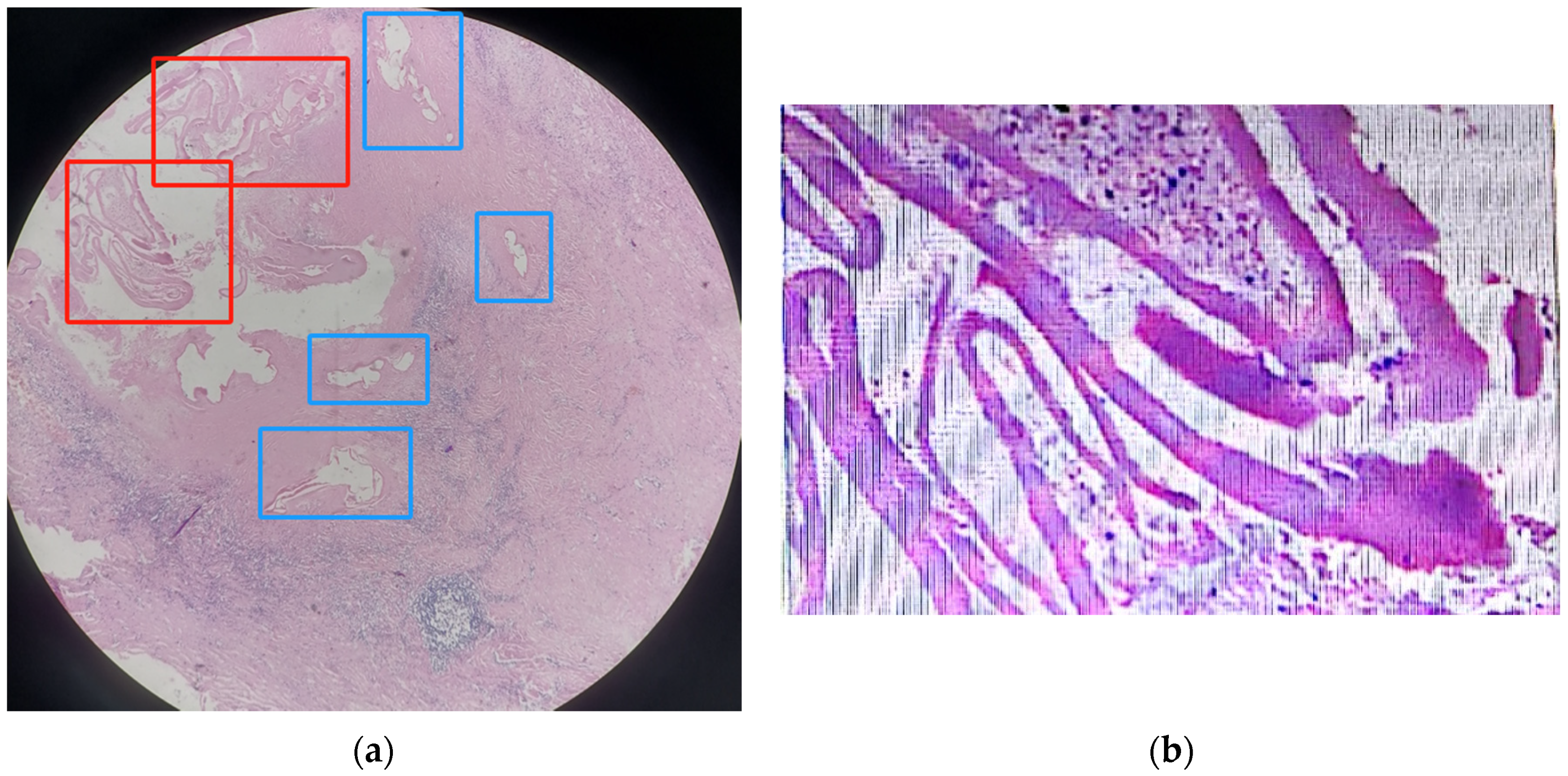
2.5. The Pathological Result
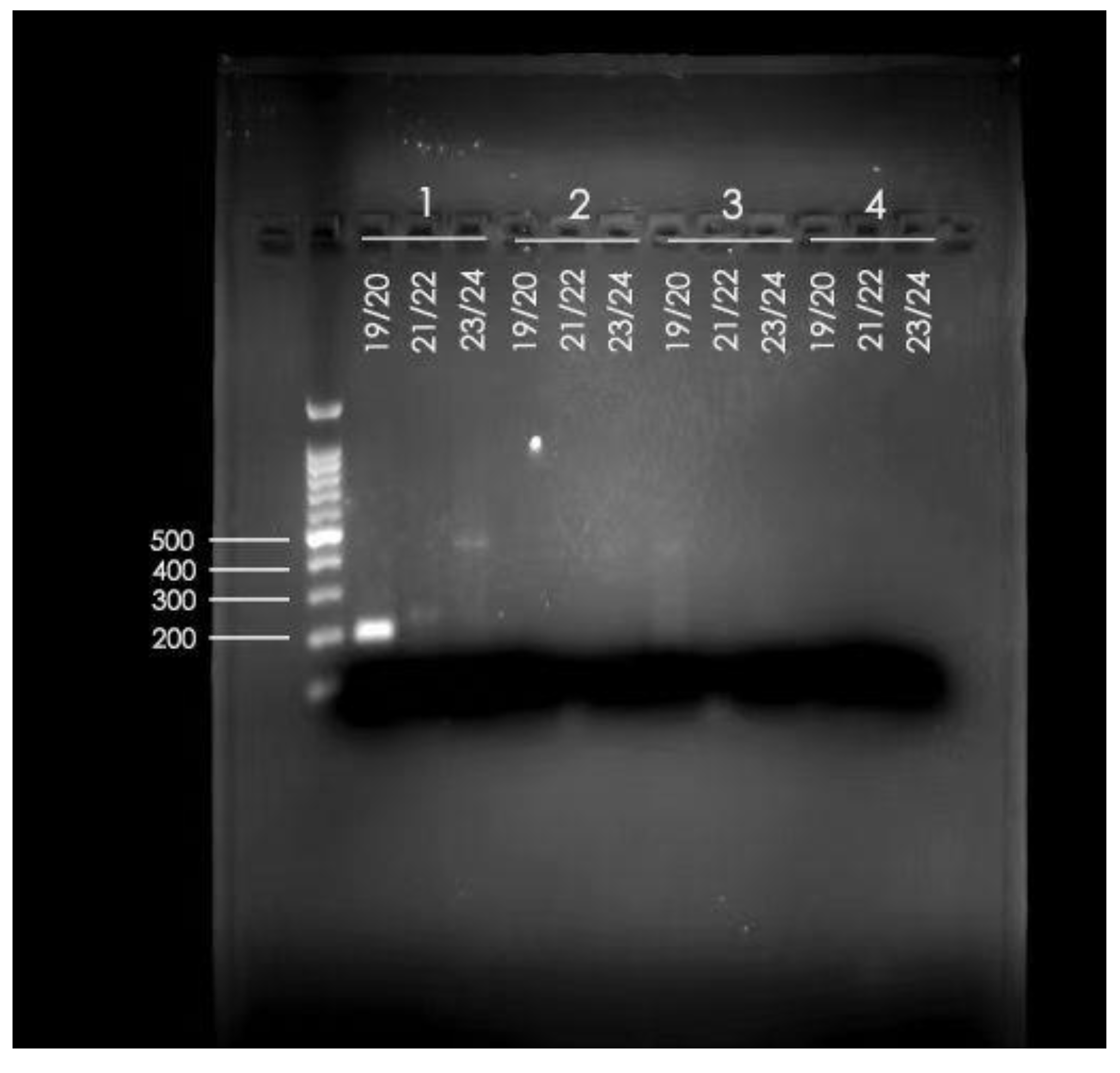
2.6. The PCR Results
3. Discussion
3.1. The Difference between CE and AE
3.1.1. The Difference between CE and AE in Aetiology and Staging Systems
3.1.2. The Difference between CE and AE in Geographical Distribution
3.1.3. The Difference between CE and AE in Imaging and Pathology
- “Juxtaposition of hyper and hypoechogenic areas in a pseudo-tumour with irregular limits and scattered calcification”;
- “Pseudo-cystic appearances due to a large area of central necrosis surrounded by an irregular hyperechogenic ring”;
- Size of the smallest cyst (CE/AE: >2/≤2 mm)
- Size of the largest cyst (CE/AE: >25/≤25 mm)
- Thickness of the laminated layer (CE/AE: >0.15/≤0.15 mm)
- Peri-cystic fibrosis (CE/AE: >0.6/≤0.6 mm)
- Striation of laminated layer (CE/AE: moderate-strong/weak)
- Number of cysts (CE/AE: ≤9/>9) [12]
- The size of the individual pseudocysts was smaller, usually between 1 mm and 2 cm in diameter.
- The striation of the AE laminated layer was not very obvious.
- Under microscopy, necrotic degeneration was often around the parasitic lesion, which is generally poorly demarcated from the surrounding tissue. CE, on the other hand, is generally a single cyst, larger in diameter, with an inner wall that is often smooth and demarcated from the surrounding area.
3.2. Misdiagnosis of Echinococcosis
3.3. Using cfDNA NGS to Facilitate the Diagnosis of Echinococcosis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casulli, A.; Siles-Lucas, M.; Tamarozzi, F. Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 663–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casulli, A.; Barth, T.F.E.; Tamarozzi, F. Echinococcus multilocularis. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 738–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houston, S.; Belga, S.; Buttenschoen, K.; Cooper, R.; Girgis, S.; Gottstein, B.; Low, G.; Massolo, A.; MacDonald, C.; Müller, N.; et al. Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of Alveolar Echinococcosis: An Emerging Infectious Disease in Alberta, Canada. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 104, 1863–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massolo, A.; Klein, C.; Kowalewska-Grochowska, K.; Belga, S.; MacDonald, C.; Vaughan, S.; Girgis, S.; Giunchi, D.; Bramer, S.A.; Santa, M.A.; et al. European Echinococcus multilocularis Identified in Patients in Canada. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 384–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotwa, J.D.; Isaksson, M.; Jardine, C.M.; Campbell, G.D.; Berke, O.; Pearl, D.L.; Mercer, N.J.; Osterman-Lind, E.; Peregrine, A.S. Echinococcus multilocularis Infection, Southern Ontario, Canada. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polish, L.B.; Pritt, B.; Barth, T.F.E.; Gottstein, B.; O’Connell, E.M.; Gibson, P.C. First European Haplotype of Echinococcus multilocularis Identified in the United States: An Emerging Disease? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezsényi, B.; Dubóczki, Z.; Strausz, T.; Csulak, E.; Czoma, V.; Káposztás, Z.; Fehérvári, M.; Somorácz, Á.; Csilek, A.; Oláh, A.; et al. Emerging human alveolar echinococcosis in Hungary (2003–2018): A retrospective case series analysis from a multi-centre study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Accelerating Work to Overcome the Global Impact of Neglected Tropical Diseases: A Roadmap for Implementation: Executive Summary; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Echinococcosis. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/echinococcosis (accessed on 24 October 2023).
- McManus, D.P.; Gray, D.J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y. Diagnosis, treatment, and management of echinococcosis. BMJ 2012, 344, e3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Vuitton, L.; Tuxun, T.; Li, J.; Vuitton, D.A.; Zhang, W.; McManus, D.P. Echinococcosis: Advances in the 21st Century. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00075-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinehr, M.; Micheloud, C.; Grimm, F.; Kronenberg, P.A.; Grimm, J.; Beck, A.; Nell, J.; Meyer Zu Schwabedissen, C.; Furrer, E.; Müllhaupt, B.; et al. Pathology of Echinococcosis: A Morphologic and Immunohistochemical Study on 138 Specimens With Focus on the Differential Diagnosis Between Cystic and Alveolar Echinococcosis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2020, 44, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, E.; Kern, P.; Vuitton, D.A. Expert consensus for the diagnosis and treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcosis in humans. Acta Trop. 2010, 114, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; McManus, D.P. Recent advances in the immunology and diagnosis of echinococcosis. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 47, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberli, A.; Furrer, L.; Skoko, L.; Müller, N.; Gottstein, B.; Bittel, P. A novel multiplex real-time polymerase chain reaction for the molecular diagnosis of metacestode infections in human patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2023, 29, 1451.e1–1451.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, J.; Zhang, G.; Yu, W.; He, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhong, B.; Wang, Q.; Liao, S.; Li, R.; Chen, F.; et al. Molecular characterization of human echinococcosis in Sichuan, Western China. Acta Trop. 2019, 190, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerda, J.R.; Buttke, D.E.; Ballweber, L.R. Echinococcus spp. Tapeworms in North America. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Wang, Q.; Liao, S.; Zhong, B.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.; He, W.; Xie, F.; Zou, B.; Xu, K. Echinococcosis prevalence in humans in Shiqu County of Sichuan in 2017. J. Prev. Med. Inf. 2018, 34, 545–549. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, J.Y.; Zhang, G.J.; Liao, S.; Huang, Y.; Yu, W.J.; He, W.; Yang, G.Y.; Li, T.Y.; Chen, X.W.; Zhong, B.; et al. A multiplex PCR for differential detection of Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto, Echinococcus multilocularis and Echinococcus canadensis in China. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2019, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Liu, L.; He, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, G.; Yu, W.; He, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; et al. A multiplex PCR for the identification of Echinococcus multilocularis, E. granulosus sensu stricto and E. canadensis that infect human. Parasitology 2019, 146, 1595–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Danzeng, W.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Qiangba, G.; Zhang, Q.; Renzhen, N.; Basang, Z.; et al. Comprehensive characterization of plasma cell-free Echinococcus spp. DNA in echinococcosis patients using ultra-high-throughput sequencing. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Shen, S.; Jin, X.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Chen, W. Cell-free DNA as a diagnostic tool for human echinococcosis. Trends Parasitol. 2021, 37, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Gongsang, Q.; Ji, J.; Li, J.; Qi, F.; Li, J.; Qiangba, G.; Danzeng, W.; Chen, F.; Zhou, H.; et al. Characterizing dynamic changes of plasma cell-free Echinococcus granulosus DNA before and after cystic echinococcosis treatment initiation. Genomics 2021, 113, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyachenko, V.; Beck, E.; Pantchev, N.; Bauer, C. Cost-effective method of DNA extraction from taeniid eggs. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 102, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkel, A.; Njoroge, E.M.; Zimmermann, A.; Wälz, M.; Zeyhle, E.; Elmahdi, I.E.; Mackenstedt, U.; Romig, T. A PCR system for detection of species and genotypes of the Echinococcus granulosus-complex, with reference to the epidemiological situation in eastern Africa. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowles, J.; Blair, D.; McManus, D.P. Genetic variants within the genus Echinococcus identified by mitochondrial DNA sequencing. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1992, 54, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurt, A.; Avcioglu, H.; Guven, E.; Balkaya, I.; Oral, A.; Kirman, R.; Bia, M.M.; Akyuz, M. Molecular Characterization of Echinococcus multilocularis and Echinococcus granulosus from Cysts and Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Samples of Human Isolates in Northeastern Turkey. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2020, 20, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, P.S.; Larrieu, E. Control of cystic echinococcosis/hydatidosis: 1863–2002. Adv. Parasitol. 2006, 61, 443–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, P.S.; McManus, D.P.; Lightowlers, M.W.; Chabalgoity, J.A.; Garcia, H.H.; Gavidia, C.M.; Gilman, R.H.; Gonzalez, A.E.; Lorca, M.; Naquira, C.; et al. Prevention and control of cystic echinococcosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Gesang, D.; Wan, L.; Li, J.; Qiangba, G.; Danzeng, W.; Basang, Z.; Renzhen, N.; Yin, J.; Gongsang, Q.; et al. Echinococcus spp. and genotypes infecting humans in Tibet Autonomous Region of China: A molecular investigation with near-complete/complete mitochondrial sequences. Parasites Vectors 2022, 15, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Han, X.; Tian, Q.; Zhao, S.; A, J. Hepatic cystic and alveolar echinococcosis co-infections: A report of 3 cases. Chin. J. Schistosomiasis Control. 2019, 32, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Ma, Y.; Ban, R.; Shi, Q. Case Report: Diagnosis of Human Alveolar Echinococcosis via Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 666225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerakoon, K.G.; McManus, D.P. Cell-free DNA as a diagnostic tool for human parasitic infections. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Shen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, G.; Jin, X. Plasma Circulating Cell-Free DNA Facilitated the Detection of an Alveolar Echinococcosis Patient Initially Misdiagnosed as Cystic Echinococcosis: A Case Report. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9040088
Zhao Y, Shi Y, Shen S, Zhang Y, Wei G, Jin X. Plasma Circulating Cell-Free DNA Facilitated the Detection of an Alveolar Echinococcosis Patient Initially Misdiagnosed as Cystic Echinococcosis: A Case Report. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2024; 9(4):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9040088
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yanping, Yiyang Shi, Shu Shen, Yan Zhang, Gengfu Wei, and Xin Jin. 2024. "Plasma Circulating Cell-Free DNA Facilitated the Detection of an Alveolar Echinococcosis Patient Initially Misdiagnosed as Cystic Echinococcosis: A Case Report" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 9, no. 4: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9040088
APA StyleZhao, Y., Shi, Y., Shen, S., Zhang, Y., Wei, G., & Jin, X. (2024). Plasma Circulating Cell-Free DNA Facilitated the Detection of an Alveolar Echinococcosis Patient Initially Misdiagnosed as Cystic Echinococcosis: A Case Report. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 9(4), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9040088





