Characteristics of Pathogenic Escherichia coli Associated with Diarrhea in Children under Five Years in Northwestern Ethiopia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
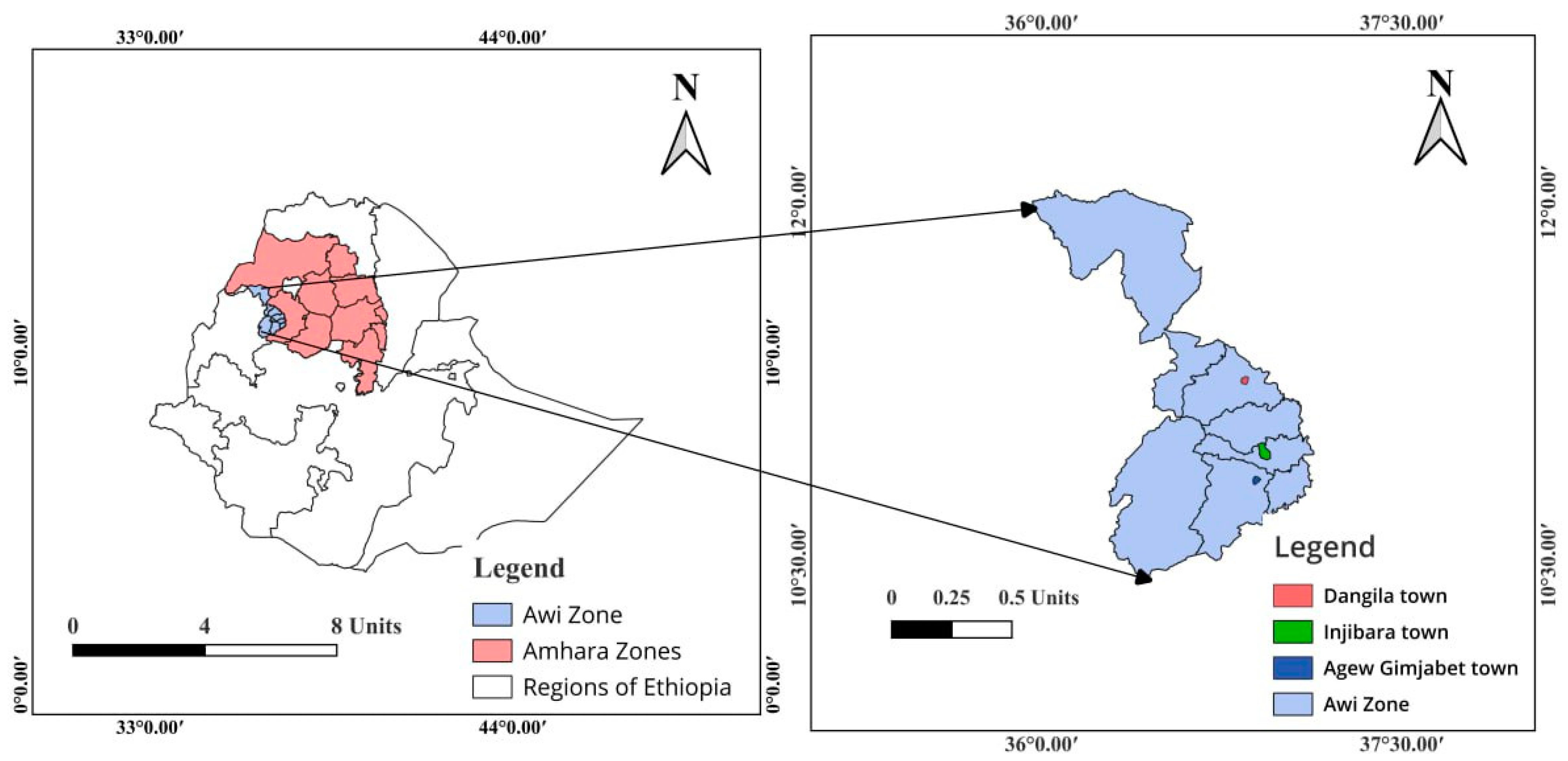
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. Study Design and Subjects, and Sampling
2.3. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
2.4. DNA Extraction and Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.5. Susceptibility Testing
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Escherichia coli Isolation
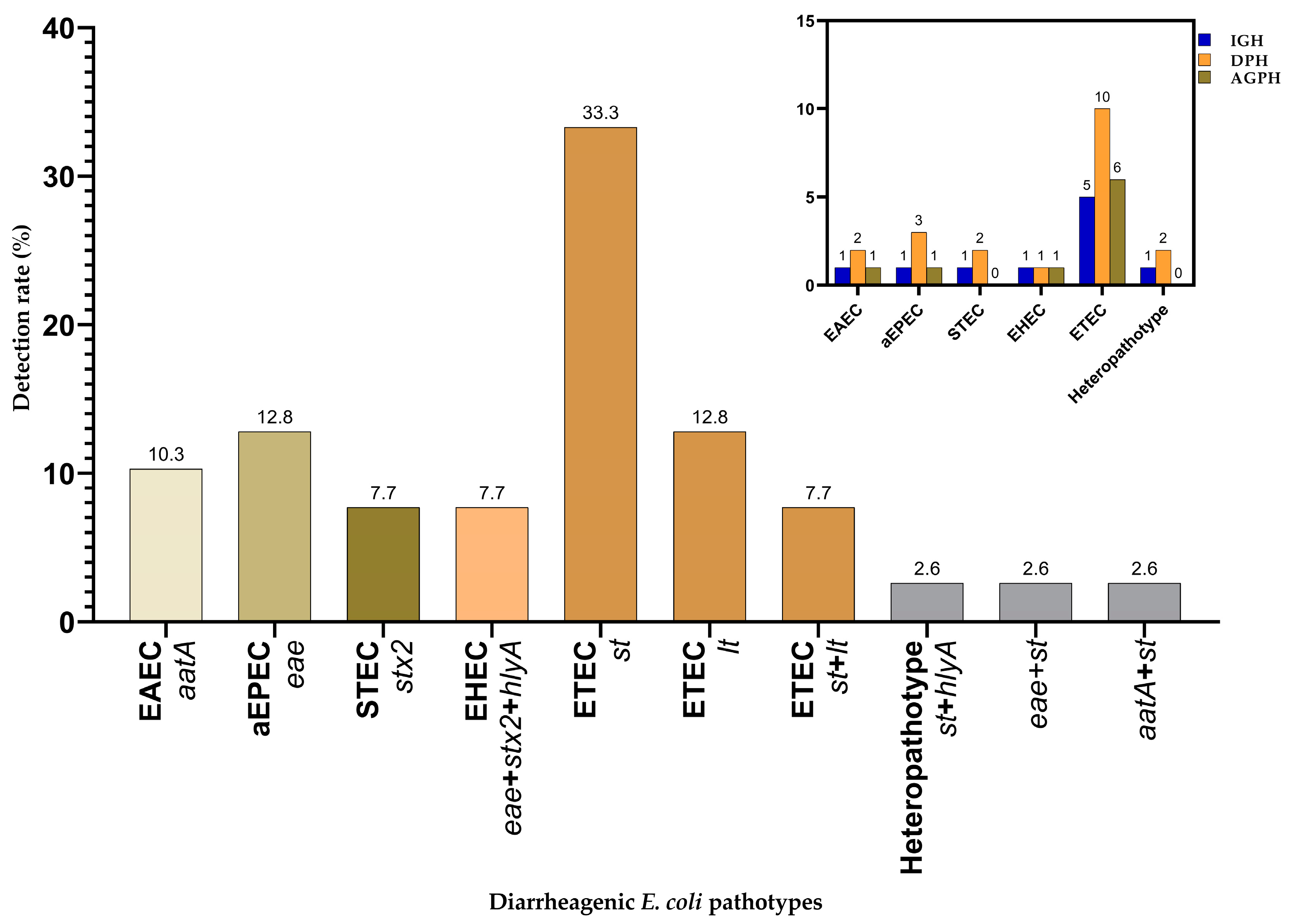
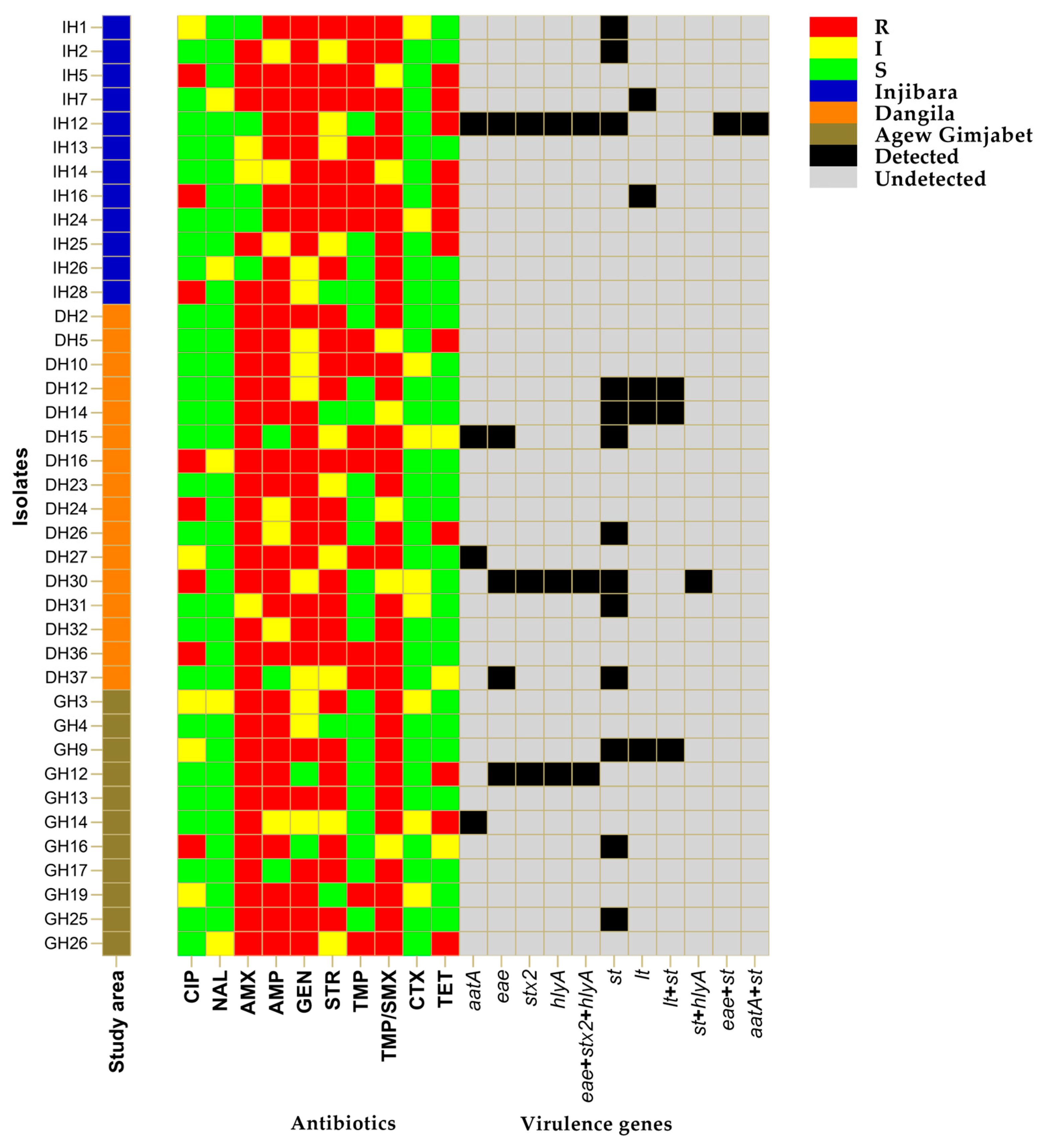
3.2. Occurrence of Virulence Genes and DEC Pathotypes
3.3. Antimicrobial Resistance in DEC Isolates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Croxen, M.A.; Finlay, B.B. Molecular mechanisms of Escherichia coli pathogenicity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambertini, E.; Karns, J.S.; Van Kessel, J.A.S.; Cao, H.; Schukken, Y.H.; Wolfgang, D.R.; Smith, J.M.; Pradhan, A.K. Dynamics of Escherichia coli virulence factors in dairy herds and farm environments in a longitudi-nal study in the United States. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 4477–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L.T. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shen, M.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Luo, X.; Jia, X.; Ma, Y. Virulence gene profiles and molecular genetic characteristics of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli from a hospital in western China. Gut Pathog. 2018, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesser, K.J.; Levy, K. Updates on defining and detecting diarrheagenic Escherichia coli pathotypes. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 33, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendary, M.M.; El-Hamid, M.I.A.; Alhomrani, M.; Alamri, A.S.; Elshimy, R.; Mosbah, R.A.; Bahnass, M.M.; Omar, N.N.; Al-Sanea, M.M.; Elmanakhly, A.R.; et al. What Is behind the Correlation Analysis of Diarrheagenic E. coli Pathotypes? Biology 2022, 11, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqua, M.; Michelacci, V.; Di Martino, M.L.; Tozzoli, R.; Grossi, M.; Colonna, B.; Morabito, S.; Prosseda, G. The intriguing evolutionary journey of enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC) toward pathogenicity. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.F.; Lourenço, R.F.; Maeda, D.L.N.F.; Cintra, M.d.J.; Nakao, N.; Mathias-Santos, C.; Luiz, W.B.; Ferreira, L.C.d.S. Strain-specific transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of heat-labile toxin expression by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2020, 51, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhong, Z.; Luo, Y.; Cox, E.; Devriendt, B. Heat-stable enterotoxins of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and their impact on host immunity. Toxins 2019, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joffré, E.; Rojas, V.I. Molecular epidemiology of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli (Eaec) isolates of hospitalized children from bolivia reveal high heterogeneity and multidrug-resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, A.; Aslani, M.; Bouzari, S. Escherichia coli: A brief review of diarrheagenic pathotypes and their role in diarrheal diseases in Iran. Iran J. Microbiol. 2012, 4, 102–117. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhnert, P.; Boerlin, P.; Frey, J. Target genes for virulence assessment of Escherichia coli isolates from water, food and the environment. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 24, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, T.A.; Elias, W.P.; Scaletsky, I.C.; Guth, B.E.C.; Rodrigues, J.F.; Piazza, R.M.; Ferreira, L.; Martinez, M.B. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Diarrhoeal Disease. 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diarrhoeal-disease (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Cohen, A.L.; Platts-Mills, J.A.; Nakamura, T.; Operario, D.J.; Antoni, S.; Mwenda, J.M.; Weldegebriel, G.; Rey-Benito, G.; de Oliveira, L.H.; Ortiz, C.; et al. Aetiology and incidence of diarrhoea requiring hospitalisation in children under 5 years of age in 28 low-income and middle-income countries: Findings from the Global Pediatric Diarrhea Surveillance network. BMJ Glob. Health 2022, 7, e009548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demissie, G.D.; Yeshaw, Y.; Aleminew, W.; Akalu, Y. Diarrhea and associated factors among under five children in sub-Saharan Africa: Evidence from demographic and health surveys of 34 sub-Saharan countries. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, E.; Mondanizadeh, M.; van Belkum, A.; Ghaznavi-Rad, E. Multi-drug-resistant diarrheagenic Escherichia coli pathotypes in pediatric patients with gastroen-teritis from central Iran. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mernie, G.; Kloos, H.; Adane, M. Prevalence of and factors associated with acute diarrhea among children under five in rural areas in Ethiopia with and without implementation of community-led total sanitation and hygiene. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesfin, Y.; Argaw, M. Burden of Diarrheal Disease among Under Five Children in Ethiopia, 2000–2016: Findings from the Global Health Estimates 2016. Health Sci. J. 2021, 15, 801. Available online: http://www.hsj.gr/ (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Alebel, A.; Tesema, C.; Temesgen, B.; Gebrie, A.; Petrucka, P.; Kibret, G.D. Prevalence and determinants of diarrhea among under-five children in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Burden of Disease Collaborative Network. Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 (GBD 2019) Results. Seattle, United States: Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME). 2021. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/causes-of-death-in-children-under-5?country=~ETH (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Breijyeh, Z.; Jubeh, B.; Karaman, R. Resistance of gram-negative bacteria to current antibacterial agents and approaches to resolve it. Molecules 2020, 25, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousham, E.K.; Unicomb, L.; Islam, M.A. Human, animal and environmental contributors to antibiotic resistance in low-resource settings: Integrating behavioural, epidemiological and One Health approaches. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20180332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemeda, B.A.; Assefa, A.; Jaleta, M.B.; Amenu, K.; Wieland, B. Antimicrobial resistance in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prevalence in foods, food handlers, animals, and the environment. One Health 2021, 13, 100286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolde, A.; Deneke, Y.; Sisay, T.; Mathewos, M.; Fesseha, H. Isolation of Escherichia coli and Its Associated Risk Factor from Diarrheic Children in Wolaita Sodo Town, Southern Ethiopia. Res. Rep. Trop. Med. 2021, 12, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adugna, A.; Kibret, M.; Abera, B.; Nibret, E.; Adal, M. Antibiogram of E. coli serotypes isolated from children aged under five with acute diarrhea in Bahir Dar town. Afr. Health Sci. 2015, 15, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenebe, T.; Mitiku, M.; Alem, Y. Prevalence of Escherichia coli in Under-Five Children with Diarrhea in Ethiopia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 8844294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getaneh, D.K.; Hordofa, L.O.; Ayana, D.A.; Tessema, T.S.; Regassa, L.D. Prevalence of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and associated factors in under-five children in Eastern Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelelie, T.Z.; Eguale, T.; Yitayew, B.; Abeje, D.; Alemu, A.; Seman, A.; Jass, J.; Mihret, A.; Abebe, T. Molecular epidemiology and antimicrobial susceptibility of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli isolated from children under age five with and without diarrhea in Central Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessesse, D.N.; Tarekegn, A.A. Prevalence and associated factors of diarrhea among under-five children in the Jawi district, Awi Zone Ethiopia, 2019. Community based comparative cross-sectional study. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 890304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azage, M.; Kumie, A.; Worku, A.; Bagtzoglou, A.C. Childhood diarrhea in high and low hotspot districts of Amhara Region, northwest Ethiopia: A multilevel modeling. J. Health. Popul. Nutr. 2016, 35, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hailu, B.; Ji-Guo, W.; Hailu, T. Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene Risk Factors on the Prevalence of Diarrhea among Under-Five Children in the Rural Community of Dangila District, Northwest Ethiopia. J. Trop. Med. 2021, 2021, 2688500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosek, M.; Bern, C.; Guerrant, R.L. The global burden of diarrhoeal disease, as estimated from studies published between 1992 and 2000. Bull. World Health Organ. 2003, 81, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, P.J.; Markey, B.K.; Leonard, F.C.; Hartigan, P.; Fanning, S.; Fitzpatrick, E.S. Veterinary Microbiology and Microbial Disease, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, A.; Ghosh, S.; Ramamurthy, T.; Yamasaki, S.; Tsukamoto, T.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Nair, G.B.; Takeda, Y. Shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli from healthy cattle in a semi-urban community in Calcutta, India. Indian J. Med. Res. 1999, 110, 83–85. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Yamasaki, S.; Sato, T.; Ramamurthy, T.; Pal, A.; Datta, S.; Chowdhury, N.R.; Das, S.C.; Sikdar, A.; Tsukamoto, T.; et al. Prevalence and Genetic Profiling of Virulence Determinants of Non-O157 Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Cattle, Beef, and Humans, Calcutta, India. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nada, R.A.; Shaheen, H.I.; Touni, I.; Fahmy, D.; Armstrong, A.W.; Weiner, M.; Klena, J.D. Design and validation of a multiplex polymerase chain reaction for the identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and associated colonization factor antigens. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 67, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cruz, C.B.N.; de Souza, M.C.S.; Serra, P.T.; Santos, I.; Balieiro, A.; Pieri, F.A.; Nogueira, P.A.; Orlandi, P.P. Virulence factors associated with pediatric shigellosis in Brazilian Amazon. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 539697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornieporth, N.G.; John, J.; Salgado, K.; de Jesus, P.; Latham, E.; Melo, M.C.; Gunzburg, S.T.; Riley, L.W. Differentiation of Pathogenic Escherichia coli Strains in Brazilian Children by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 1371–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havt, A.; Lima, I.F.; Medeiros, P.H.; Clementino, M.A.; Santos, A.K.; Amaral, M.S.; Veras, H.N.; Prata, M.M.; Lima, N.L.; Di Moura, A.; et al. Prevalence and virulence gene profiling of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli in malnourished and nourished Brazilian children. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 89, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, M.; Kruger, E.; Durán, C.; Lagos, R.; Levine, M.; Prado, V.; Toro, C.; Vidal, R. Single multiplex PCR assay to identify simultaneously the six categories of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli associated with enteric infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5362–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunzburg, S.T.; Tornieporth, N.G.; Riley, L.W. Riley, Identification of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli by PCR-Based Detection of the Bun-dle-Forming Pilus Gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 1375–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, S.A.; Ahmed, S.F.; Aziz, M.H.A.; Zakaria, A.M.; Klena, J.D.; Pangallo, D. Prevalence and characterization of shiga-toxin O157:H7 and non-O157:H7 enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli isolated from different sources. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2013, 27, 3834–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 30th ed.; Supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, H.K.; Dabo, N.T.; Muhammad, B.; García-Soto, S.; Ugarte-Ruiz, M.; Alvarez, J. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Pathotypes from Children Younger Than 5 Years in Kano State, Nigeria. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broujerdi, S.M.; Ardakani, M.R.; Rezatofighi, S.E. Characterization of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli strains associated with diarrhea in children, Khouzestan, Iran. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2018, 12, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webale, M.K.; Guyah, B.; Wanjala, C.; Nyanga, P.L.; Webale, S.K.; Abonyo, C.; Kitungulu, N.; Kiboi, N.; Bowen, N. Phenotypic and Genotypic Antibiotic Resistant diarrheagenic Escherichia coli pathotypes isolated from Children with Diarrhea in Nairobi City, Kenya. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2020, 30, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khairy, R.M.M.; Fathy, Z.A.; Mahrous, D.M.; Mohamed, E.S.; Abdelrahim, S.S. Prevalence, phylogeny, and antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli pathotypes isolated from children less than 5 years old with community acquired- diarrhea in Upper Egypt. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabika, R.M.; Liabagui, S.L.O.; Moundounga, H.K.; Mounioko, F.; Souza, A.; Yala, J.F. Molecular Prevalence and Epidemiological Characteristics of Diarrheagenic E. coli in Children under 5 Years Old in the City of Koula-Moutou, East-Central Gabon. Open J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatub, W.T.; Jafar, N.A.-H.; Melconian, A.K. Detection of diarrheagenic E. coli among children under 5 year’s age in Tikrit city of Iraq by using single multiplex PCR technique. Plant Arch. 2021, 21, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mero, S.; Timonen, S.; Lääveri, T.; Løfberg, S.; Kirveskari, J.; Ursing, J.; Rombo, L.; Kofoed, P.-E.; Kantele, A. Prevalence of diarrhoeal pathogens among children under five years of age with and without diarrhoea in guinea-bissau. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, A.; Abd, H.; Sandstrom, G. Microbial aetiology of acute diarrhoea in children under five years of age in Khartoum, Sudan. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sereme, Y.; Toumi, E.; Saifi, E.; Faury, H.; Skurnik, D. Maternal immune factors involved in the prevention or facilitation of neonatal bacterial infections. Cell. Immunol. 2024, 395–396, 104796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langel, S.N.; Blasi, M.; Permar, S.R. Maternal immune protection against infectious diseases. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 660–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.G. Maternal immunity, a way to confer protection against enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J. Pediatr. 2017, 93, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera-Insua, I.; Gomez, H.F.; Diaz-Gonzalez, V.A.; Chaturvedi, P.; Newburg, D.S.; Cleary, T.G. Human milk lipids bind Shiga toxin. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2001, 501, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turin, C.G.; Ochoa, T.J. The Role of Maternal Breast Milk in Preventing Infantile Diarrhea in the Developing World. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2014, 1, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, J.R.; Meacham, S.L.; Warehime, J.; Stokes, S.A.; Ogle, J.; Leto, D.; Bax, M.; Dauer, A.M.; Lozovski, J.M. Relationships between the weaning period and the introduction of complementary foods in the transmission of gastrointestinal parasitic infections in children in Honduras. Res. Rep. Trop. Med. 2018, 9, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogbo, F.A.; Nguyen, H.; Naz, S.; Agho, K.E.; Page, A. The association between infant and young child feeding practices and diarrhoea in Tanzanian children. Trop. Med. Health 2018, 46, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Hauser, A.A.; Sobhan, S.; Huda, T.M.N.; Waid, J.L.; Wendt, A.S.; Islam, M.A.; Rahman, M.; Gabrysch, S. Key Food Hygiene Behaviors to Reduce Microbial Contamination of Complementary Foods in Rural Bangladesh. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2022, 107, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, M.E.; Uwiera, R.R.E.; Inglis, G.D. Enteric Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Cattle, and the Use of Mice as a Model to Elucidate Key Aspects of the Host-Pathogen-Microbiota Interaction: A Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 937866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Graham, J.P.; Eisenberg, J.N.S. Eisenberg, Livestock ownership among rural households and child morbidity and mortality: An analysis of demographic health survey data from 30 Sub-Saharan African Countries (2005–2015). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budge, S.; Hutchings, P.; Parker, A.; Tyrrel, S.; Tulu, T.; Gizaw, M.; Garbutt, C. Do domestic animals contribute to bacterial contamination of infant transmission pathways? Formative evidence from Ethiopia. J. Water Health 2019, 17, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belete, M.A.; Demlie, T.B.; Chekole, W.S.; Tessema, T.S. Molecular identification of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli pathotypes and their antibiotic resistance patterns among diarrheic children and in contact calves in Bahir Dar city, Northwest Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilchez, S.; Reyes, D.; Paniagua, M.; Bucardo, F.; Möllby, R.; Weintraub, A. Prevalence of diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli in children from León, Nicaragua. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, E.E.; Yameen, M.A.; Igwenyi, I.O.; Okafor, A.C.; Obeten, U.N.; Obasi, D.O.; Ezeilo, U.R.; David, C.N. The frequency of virulent genes and antimicrobial resistance patterns of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli isolated from stools of children presenting with diarrhea in a tertiary hospital in Abakaliki, Nigeria. Int. J. One Health 2020, 6, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Jain, S.; Changotra, H.; Shrivastava, R.; Kumar, Y.; Grover, N.; Vashistt, J. Molecular characterization of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli pathotypes: Association of virulent genes, serogroups, and antibiotic resistance among moderate-to-severe diarrhea patients. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2018, 32, e22388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Venkatesh, V.; Kumar, R.; Kashyap, S.; Kumar, M.; Maurya, A.K.; Dhole, T.N.; Singh, M. Etiological agents of diarrhea in hospitalized pediatric patients with special emphasis on diarrheagenic Escherichia coli in North India. J. Lab. Physicians 2019, 11, 068–074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipkirui, E.; Koech, M.; Ombogo, A.; Kirera, R.; Ndonye, J.; Kipkemoi, N.; Kirui, M.; Philip, C.; Roth, A.; Flynn, A.; et al. Molecular characterization of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli toxins and colonization factors in children under five years with acute diarrhea attending Kisii Teaching and Referral Hospital, Kenya. Trop. Dis. Travel Med. Vaccines 2021, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subekti, D.; Lesmana, M.; Tjaniadi, P.; Machpud, N.; Sriwati; Sukarma; Daniel, J.; Alexander, W.; Campbell, J.; Corwin, A.; et al. Prevalence of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) in hospitalized acute diarrhea patients in Denpasar, Bali, Indonesia. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2003, 47, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghi, F.; Zeighami, H.; Hajiahmadi, F.; Khoshvaght, H.; Bayat, M. Frequency and antimicrobial resistance of diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli from young children in Iran. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodas, C.; Mamani, R.; Blanco, J.; Blanco, J.E.; Wiklund, G.; Svennerholm, A.-M.; Sjöling, Å.; Iniguez, V. Enterotoxins, colonization factors, serotypes and antimicrobial resistance of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) strains isolated from hospitalized children with diarrhea in Bolivia. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, T.J.; Contreras, C.A. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection in children. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 24, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Le Van, P.; Le Huy, C.; Gia, K.N.; Weintraub, A. Detection and characterization of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli from young children in Hanoi, Vi-etnam. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zil-E-Huma, Z.-E.; Tareen, A.M.; Ullah, K.; Asmat, T.M.; Samad, A.; Iqbal, A.; Mustafa, M.Z.; Ahmad, I.; Rahman, S.U. Incidence of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli pathotypes in children suffering from diarrhea in Ter-tiary Care Hospitals, Quetta, Pakistan. Pak. J. Zool. 2019, 51, 2015–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onanuga, A.; Igbeneghu, O.; Lamikanra, A. A study of the prevalence of diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli in children from Gwagwalada, Federal Capital Territory, Nigeria. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2014, 17, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhu, X.; Hou, H.; Lu, Y.; Yu, J.; Mao, L.; Mao, L.; Sun, Z. Characteristics of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli among children under 5 years of age with acute diarrhea: A hospital based study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltai, N.O.; Al Thani, A.A.; Al Hadidi, S.H.; Al Ansari, K.; Yassine, H.M. Antibiotic resistance and virulence patterns of pathogenic Escherichia coli strains associated with acute gastroenteritis among children in Qatar. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Deng, Y.; Qu, M.; Liu, G.R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Yan, H.Q.; Gao, Z.Y.; Liu, B.W.; et al. Etiological surveillance and analysis of infectious diarrhea in Beijing in year 2010. Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2011, 45, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonkoungou, I.J.O.; Somda, N.S.; Traoré, O.; Zoma, S.; Garba, Z.; Drabo, K.M.; Barro, N. Detection of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli in human diarrheic stool and drinking water samples in Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 15, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dulaimi, T.H.; Aziz, H.W.; Al-Marzoqi, A.H.; Al-Aziz, S.A.; Mohsin, S.A.A. Molecular Characterization and Antibiotic Susceptibility of Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli from Children. Med. J. Babylon 2015, 12, 541–550. [Google Scholar]
- Braz, V.S.; Melchior, K.; Moreira, C.G. Escherichia coli as a Multifaceted Pathogenic and Versatile Bacterium. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 548492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, P.; Ajjampur, S.S.R.; Chidambaram, D.; Chandrabose, G.; Thangaraj, B.; Sarkar, R.; Samuel, P.; Rajan, D.P.; Kang, G. Pathotypes of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli in children attending a tertiary care hospital in South India. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 68, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunbiyi, T.S.; Fayemi, O.E.; Akanni, G.B.; Ayolabi, C.I.; Hald, T. Molecular Characterization of Hetero-Pathogenic and Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli Pathotypes in Diarrheic Children under Five Years and Exposure Environment in Ogun State, South-West Nigeria. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiboonchutikula, C.; Bin Kim, H.; Honda, H.; Loo, A.Y.X.; Cheng, V.C.-C.; Camins, B.; Jantarathaneewat, K.; Apisarnthanarak, P.; Rutjanawech, S.; Apisarnthanarak, A. Antibiotic prescribing behavior among physicians in Asia: A multinational survey. Antimicrob. Steward. Health Epidemiol. 2023, 3, e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chem, E.D.; Anong, D.N.; Akoachere, J.-F.K.T. Prescribing patterns and associated factors of antibiotic prescription in primary health care facilities of Kumbo East and Kumbo West Health Districts, North West Cameroon. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Madec, J.-Y.; Lupo, A.; Schink, A.-K.; Kieffer, N.; Nordmann, P.; Schwarz, S. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Johansson, M.H.K.; Munk, P.; Malorny, B.; Skarżyńska, M.; Wadepohl, K.; Moyano, G.; Hesp, A.; Veldman, K.T.; Bossers, A.; et al. Genomic evolution of antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addis, G.T.; Dagnew, S.B.; Anagaw, A.; Ayele, T.M.; Tadesse, T.Y. Evaluation of antibiotic utilization pattern in the treatment of acute diarrheal diseases at Debre Tabor comprehensive specialized hospital, Debre Tabor, Ethiopia: A retrospective cross-sectional study. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekleab, A.M.; Asfaw, Y.M.; Weldetsadik, A.Y.; Amaru, G.M. Antibiotic prescribing practice in the management of cough or diarrhea among children attending hospitals in Addis Ababa: A cross-sectional study. Pediatr. Health Med. Ther. 2017, 8, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonko, M.D.A.; Tahita, M.C.; Kiemde, F.; Lompo, P.; Yougbaré, S.; Some, A.M.; Tinto, H.; Mens, P.F.; Menting, S.; Schallig, H.D.F.H. Antibiotic susceptibility profile of bacterial isolates from febrile children under 5 years of age in Nanoro, Burkina Faso. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2021, 26, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, W.K.; Kariuki, S.M.; Schnabel, D.; Boga, H.I.; Waiyaki, P.G.; Wamae, C.N. Antibiotic susceptibility of Enteric pathogens from the Maasai community, Narok and Kajiado Districts, Kenya. Afr. J. Health Sci. 2011, 19, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada-García, T.; Cerna, J.F.; Paheco-Gil, L.; Velázquez, R.F.; Ochoa, T.J.; Torres, J.; DuPont, H.L. Drug-resistant Diarrheogenic Escherichia coli, Mexico. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1306–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Shek, A.; Shrivastava, S.; Verma, A.K. Isolation, Identification, Molecular Characterization and Antibiogram of E. coli Isolates from Neonatal Calves. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2019, 8, 1996–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer | Nucleotide Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Target Gene | Pathotypes | Annealing Temperature | Amplicon Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVT1 EVT2 | F: CAACACTGGATGATCTCAGC R: CCCCCTCAACTGCTAATA | stx2 | STEC/EHEC | 55 °C | 350 | [35] |
| EAE-1 EAE-2 | F: AAACAGGTGAAACTGTTGCC R: CTCTGCAGATTAACCTCTGC | eae | EPEC/EHEC | 55 °C | 490 | [36] |
| ST1 ST2 | F: TTT ATT TCT GTA TTG TCT T R: GCAGGATTACAACACAATTC | st | ETEC | 55 °C | 294 | [37] |
| IAL F IAL R | F: CTGGATGGTATGGTGAGG R: GGAGGCCAACAACATTATTTCC | ial | EIEC | 55 °C | 320 | [38] |
| LT1 LT2 | F: GGCGACAGATTATACCGTGC R: CCGAATTCTGTTATATATGTC | lt | ETEC | 48 °C | 696 | [39] |
| EAEC F EAEC R | F: CTGGCGAAAGACTGTATCAT R: CAATGTATAGAAATCCGCTGTT | aatA | EAEC | 48 °C | 630 | [40] |
| daaE1 daaE2 | F: GAACGTTGGTTAATGTGGGGT R: TATTCACCGGTCGGTTATCAG | daaE | DAEC | 47 °C | 542 | [41] |
| BFPF BFPR | F: AATGGTGCTTGCGCTTGCTGC R: GCCGCTTTATCCAACCTGGTA | bfpA | EPEC | 57 °C | 324 | [42] |
| EHEC F EHEC R | F: ACGATGTGGTTTATTCTGGA R: CTTCACGTCACCATACATAT | hlyA | EHEC | 45 °C | 167 | [43] |
| Variables | No. of Tested (N = 107) | Culture-Positive (N = 79) | PCR-Positive (DEC) (N = 39) | Total | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGH n = 43 | DPH n = 38 | AGPH n = 26 | IGH n = 32 | DPH n = 29 | AGPH n = 18 | IGH n = 12 | DPH n = 16 | AGPH n = 11 | Totalt n = 107 | Totalc n = 79 | Totalp n = 39 | |
| Sex | ||||||||||||
| Female | 20 (38.5) | 18 (34.6) | 14 (26.9) | 15 (39.5) | 17 (44.7) | 6 (15.8) | 5 (31.3) | 8 (50) | 3 (18.8) | 52 (48.6) | 38 (48.1) | 16 (41) |
| Male | 23 (41.8) | 20 (36.4) | 12 (21.8) | 17 (41.5) | 12 (29.3) | 12 (29.3) | 7 (30.4) | 8 (34.8) | 8 (34.8) | 55 (51.4) | 41 (51.9) | 23 (58.9) |
| Age class | ||||||||||||
| 0–6 months | 6 (37.5) | 4 (25) | 6 (37.5) | 3 (42.8) | 2 (28.6) | 2 (28.6) | 2 (66.6) | 0 | 1 (33.3) | 16 (14.9) | 7 (8.9) | 3 (7.7) |
| 7–24 months | 20 (58.8) | 12 (72.8) | 2 (5.8) | 15 (68.2) | 7 (31.8) | 0 | 3 (33.3) | 6 (66.6) | 0 | 34 (31.8) | 22 (27.8) | 9 (23.1) |
| 25–60 months | 17 (29.8) | 22 (38.6) | 18 (31.6) | 14 (28) | 20 (40) | 16 (32) | 7 (25.9) | 10 (37) | 10 (37) | 57 (53.3) | 50 (63.3) | 27 (69.2) |
| Feeding | ||||||||||||
| Mother’s milk | 4 (36.4) | 4 (36.4) | 3 (27.3) | 2 (33.3) | 3 (50) | 1 (16.6) | 2 (66.6) | 1 (33.3) | 0 | 11 (10.3) | 6 (7.6) | 3 (7.7) |
| Breast + complementary | 23 (63.8) | 8 (22.2) | 5 (13.8) | 18 (64.3) | 6 (21.4) | 4 (14.3) | 7 (43.8) | 4 (25) | 3 (18.8) | 36 (33.6) | 28 (35.4) | 16 (41) |
| Solid food | 16 (26.6) | 26 (43.3) | 18 (30) | 12 (44.4) | 20 (74.1) | 13 (48.1) | 3 (13.6) | 11 (50) | 8 (36.4) | 60 (56.1) | 27 (34.2) | 22 (56.4) |
| Source of water | ||||||||||||
| Tap water | 31 (42.5) | 22 (30.1) | 20 (27.4) | 22 (42.3) | 16 (30.8) | 14 (26.9) | 8 (33.3) | 7 (29.2) | 9 (37.5) | 73 (68.2) | 52 (65.8) | 24 (61.5) |
| Well | 10 (34.5) | 14 (48.3) | 5 (17.2) | 9 (37.5) | 11 (45.8) | 4 (16.6) | 2 (16.6) | 8 (66.6) | 2 (16.6) | 29 (27.1) | 24 (30.4) | 12 (30.8) |
| Boiled | 2 (40) | 2 (40) | 1 (20) | 1 (33.3) | 2 (66.6) | 0 | 2 (66.6) | 1 (33.3) | 0 | 5 (4.7) | 3 (3.8) | 3 (7.7) |
| Contact with animals | ||||||||||||
| Yes | 26 (45.6) | 16 (28.1) | 15 (26.3) | 19 (46.3) | 12 (29.3) | 10 (21.4) | 8 (36.4) | 8 (36.4) | 6 (27.3) | 57 (53.3) | 41 (51.9) | 22 (56.4) |
| No | 17 (34) | 22 (44) | 11 (22) | 13 (34.2) | 17 (44.7) | 8 (21.1) | 4 (23.5) | 8 (47) | 5 (29.4) | 50 (46.8) | 38 (48.1) | 17 (43.6) |
| Pattern No. | Antibiotic-Resistant Patterns | No. of Antibiotics (Classes) | MDR Isolates |
|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | |||
| 1 * | GEN, AMX | 2 (2) | 4 * |
| 2 * | AMX, TMP/SMX | 2 (2) | 2 * |
| 3 | AMP, TMP/SMX, STR | 3 (3) | 4 (12.1) |
| 4 | TET, AMX, TMP/SMX | 3 (3) | 3 (9.1) |
| 5 | TMP, TET, GEN, TMP/SMX | 4 (3) | 6 (18.2) |
| 6 | GEN, AMX, TMP/SMX, STR | 4 (3) | 3 (9.1) |
| 7 | AMP, AMX, TMP/SMX, STR | 4 (3) | 4 (12.1) |
| 8 | TET, AMP, GEN, AMX, STR | 5 (3) | 3 (9.1) |
| 9 | TMP, AMP, AMX, GEN, STR | 5 (3) | 2 (6.1) |
| 10 | TMP, TET, AMP, GEN, AMX, STR | 6 (4) | 4 (12.1) |
| 11 | TMP, AMP, GEN, AMX, TMP/SMX, STR | 6 (3) | 3 (9.1) |
| 12 | TMP, TET, AMP, GEN, AMX, TMP/SMX, STR | 7 (4) | 1 (3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mulu, B.M.; Belete, M.A.; Demlie, T.B.; Tassew, H.; Sisay Tessema, T. Characteristics of Pathogenic Escherichia coli Associated with Diarrhea in Children under Five Years in Northwestern Ethiopia. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9030065
Mulu BM, Belete MA, Demlie TB, Tassew H, Sisay Tessema T. Characteristics of Pathogenic Escherichia coli Associated with Diarrhea in Children under Five Years in Northwestern Ethiopia. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2024; 9(3):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9030065
Chicago/Turabian StyleMulu, Berihun Mossie, Mequanint Addisu Belete, Tiliksew Bialfew Demlie, Habtamu Tassew, and Tesfaye Sisay Tessema. 2024. "Characteristics of Pathogenic Escherichia coli Associated with Diarrhea in Children under Five Years in Northwestern Ethiopia" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 9, no. 3: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9030065
APA StyleMulu, B. M., Belete, M. A., Demlie, T. B., Tassew, H., & Sisay Tessema, T. (2024). Characteristics of Pathogenic Escherichia coli Associated with Diarrhea in Children under Five Years in Northwestern Ethiopia. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 9(3), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed9030065






