Improvement in Infection Prevention and Control Performance Following Operational Research in Sierra Leone: A Before (2021) and After (2023) Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Setting
2.2.1. General Setting
2.2.2. The IPC Program in Sierra Leone
2.2.3. The IPC Performance Assessments
2.2.4. Dissemination of Findings of the Operational Research Study
2.2.5. Recommendations Made and Actions Taken
2.3. Study Inclusion and Period
2.4. Data Variables and Sources
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of IPC Performance at the National IPC Unit
3.1.1. Change in IPC Performance Score between 2021 and 2023
3.1.2. Gaps in IPCAT Sub-Components in 2021 and 2023
3.2. Assessment of IPC Performance at District-Level Secondary Public Hospitals
3.2.1. Change in IPC Performance Score between 2021 and 2023
3.2.2. Gaps in IPCAF Sub-Components in 2021 and 2023
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Minimum Requirements for Infection Prevention and Control Programmes; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Report on Infection Prevention and Control: Executive Summary; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pittet, D.; Donaldson, L. Clean Care Is Safer Care: The First Global Challenge of the WHO World Alliance for Patient Safety. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2005, 26, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allegranzi, B.; Donaldson, L.J.; Kilpatrick, C.; Syed, S.; Twyman, A.; Kelley, E.; Pittet, D. Infection Prevention: Laying an Essential Foundation for Quality Universal Health Coverage. Lancet Glob. Health 2019, 7, e698–e700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Patient Safety: Health Care-Associated Infections. Available online: https://www.who.int/gpsc/country_work/gpsc_ccisc_fact_sheet_en.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- Allegranzi, B.; Nejad, S.B.; Combescure, C.; Graafmans, W.; Attar, H.; Donaldson, L.; Pittet, D. Burden of Endemic Health-Care-Associated Infection in Developing Countries: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet 2011, 377, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; OIE; World Health Organization. Global Database for the Tripartite Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Country Self-Assessment Survey (TrACSS). Available online: https://amrcountryprogress.org/#/map-view (accessed on 21 May 2022).
- World Health Assembly. Global Strategy on Infection Prevention and Control; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines on Core Components of Infection Prevention and Control Programmes at the National and Acute Health Care Facility Level; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Instructions for the National Infection Prevention and Control Assessment Tool 2 (IPCAT2); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Infection Prevention and Control Assessment Framework at the Facility Level; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tomczyk, S.; Twyman, A.; de Kraker, M.E.A.; Coutinho Rehse, A.P.; Tartari, E.; Toledo, J.P.; Cassini, A.; Pittet, D.; Allegranzi, B. The First WHO Global Survey on Infection Prevention and Control in Health-Care Facilities. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell-Jackson, T.; King, J.J.C.; Makungu, C.; Spieker, N.; Woodd, S.; Risha, P.; Goodman, C. Infection Prevention and Control Compliance in Tanzanian Outpatient Facilities: A Cross-Sectional Study with Implications for the Control of COVID-19. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e780–e789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, N.; Musa, E.; Cooper, C.; Van den Bergh, R.; Owiti, P.; Baller, A.; Siafa, T.; Woldeyohannes, D.; Shringarpure, K.; Gasasira, A. Infection Prevention and Control in Health Facilities in Post-Ebola Liberia: Don’t Forget the Private Sector! Public Health Action 2017, 7, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opollo, M.S.; Otim, T.C.; Kizito, W.; Thekkur, P.; Kumar, A.M.V.; Kitutu, F.E.; Kisame, R.; Zolfo, M. Infection Prevention and Control at Lira University Hospital, Uganda: More Needs to Be Done. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.A.; Khan, M.A.; Ikram, A.; Chaudhry, T.H.; Jabeen, A.; Quddous, A.; Haq, I.U. Assessment of Infection Prevention and Control (IPC) Implementation and Strategies Used for IPC Preparedness at Facility Level in Underdeveloped Areas of Pakistan. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 1997–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, M.G.D.; Anwar, M.M.U.; Sumon, S.A.; Hassan, M.Z.; Haque, T.; Mah-E-Muneer, S.; Rahman, A.; Abdullah, S.A.H.M.; Islam, M.S.; Styczynski, A.R.; et al. Infection Prevention and Control in Tertiary Care Hospitals of Bangladesh: Results from WHO Infection Prevention and Control Assessment Framework (IPCAF). Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2022, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health and Sanitation; Government of Sierra Leone Ebola Viral Disease Situation Report. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/sites/reliefweb.int/files/resources/Ebola-Situation-Report_Vol-260.pdf (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- Ministry of Health and Sanitation. National Infection Prevention and Control Guidelines; Ministry of Health and Sanitation: Freetown, Sierra Leone, 2015.
- Ministry of Health and Sanitation, Government of Sierra Leone. National Strategic Plan for Combating Antimicrobial Resistance; Ministry of Health and Sanitation, Government of Sierra Leone: Freetown, Sierra Leone, 2018.
- Derrick Fofanah, B.; Abrahamyan, A.; Maruta, A.; Kallon, C.; Thekkur, P.; Franklyn Kamara, I.; Kuria Njuguna, C.; Sylvester Squire, J.; Sam Kanu, J.; Jawo Bah, A.; et al. Achieving Minimum Standards for Infection Prevention and Control in Sierra Leone: Urgent Need for a Quantum Leap in Progress in the COVID-19 Era! Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TDR. SORT IT Operational Research and Training. Available online: https://tdr.who.int/activities/sort-it-operational-research-and-training (accessed on 27 January 2023).
- Zachariah, R.; Stewart, A.G.; Chakaya, J.M.; Teck, R.; Khogali, M.A.; Harries, A.D.; Seeley-Musgrave, C.; Samba, T.; Reeder, J.C. The Structured Operational Research and Training Initiative for Strengthening Health Systems to Tackle Antimicrobial Resistance and Improve Public Health in Low-and-Middle Income Countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariah, R.; Harries, A.D.; Ishikawa, N.; Rieder, H.L.; Bissell, K.; Laserson, K.; Massaquoi, M.; Van Herp, M.; Reid, T. Operational Research in Low-Income Countries: What, Why, and How? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harries, A.D.; Kumar, A.M.V.; Satyanarayana, S.; Thekkur, P.; Lin, Y.; Dlodlo, R.A.; Zachariah, R. How Can Operational Research Help to Eliminate Tuberculosis in the Asia Pacific Region? Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thekkur, P.; Takarinda, K.C.; Timire, C.; Sandy, C.; Apollo, T.; Kumar, A.M.; Satyanarayana, S.; Shewade, H.D.; Khogali, M.; Zachariah, R.; et al. Operational Research to Assess the Real-Time Impact of COVID-19 on TB and HIV Services: The Experience and Response from Health Facilities in Harare, Zimbabwe. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.M.; Harries, A.D.; Satyanarayana, S.; Thekkur, P.; Shewade, H.D.; Zachariah, R. What Is Operational Research and How Can National Tuberculosis Programmes in Low- and Middle-Income Countries Use It to End TB? Indian J. Tuberc. 2020, 67, S23–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.C.A.; Moreira, M.Â.L.; Costa, I.P.d.A.; Tenório, F.M.; Barud, N.A.; Fávero, L.P.; Al-Qudah, A.A.; Gomes, C.F.S.; dos Santos, M. Feasibility of a Hospital Information System for a Military Public Organization in the Light of the Multi-Criteria Analysis. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TDR. Communicating Research Findings with a KISS. Available online: https://tdr.who.int/newsroom/news/item/21-06-2021-communicating-research-findings-with-a-kiss (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Structured Operational Research Training IniTiative Summary Brief: Infection Prevention and Control in Sierra Leone: Need for a Quantum Leap Forwards. Available online: https://tdr.who.int/docs/librariesprovider10/sort-it/2.-bobson_fofanah_ipc.pdf?sfvrsn=e9dadab4_5 (accessed on 27 January 2023).
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation Sierra Leone Population and Housing Census 2015 | GHDx. Available online: http://ghdx.healthdata.org/record/sierra-leone-population-and-housing-census-2015 (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- Ministry of Health and Sanitation. Sierra Leone Basic Package of Essential Health Services; Ministry of Health and Sanitation: Freetown, Sierra Leone, 2015.
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariah, R.; Reid, T.; Ford, N.; Van den Bergh, R.; Dahmane, A.; Khogali, M.; Delaunois, P.; Harries, A.D. The 2012 World Health Report “No Health without Research”: The Endpoint Needs to Go beyond Publication Outputs. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2012, 17, 1409–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariah, R.; Reid, T.; Van den Bergh, R.; Dahmane, A.; Kosgei, R.J.; Hinderaker, S.G.; Tayler-Smith, K.; Manzi, M.; Kizito, W.; Khogali, M.; et al. Applying the ICMJE Authorship Criteria to Operational Research in Low-Income Countries: The Need to Engage Programme Managers and Policy Makers. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2013, 18, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartari, E.; Tomczyk, S.; Pires, D.; Zayed, B.; Coutinho Rehse, A.P.; Kariyo, P.; Stempliuk, V.; Zingg, W.; Pittet, D.; Allegranzi, B. Implementation of the Infection Prevention and Control Core Components at the National Level: A Global Situational Analysis. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 108, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, G.B.; Miller, V.; Nicholas, C.; Hess, S.; Cordes, M.K.; Fortune, J.B.; Blondin, J.; Ashikaga, T.; Ricci, M. A Multitiered Strategy of Simulation Training, Kit Consolidation, and Electronic Documentation Is Associated with a Reduction in Central Line-Associated Bloodstream Infections. Am. J. Infect. Control 2014, 42, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peredo, R.; Sabatier, C.; Villagrá, A.; González, J.; Hernández, C.; Pérez, F.; Suárez, D.; Vallés, J. Reduction in Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infections in Critically Ill Patients through a Multiple System Intervention. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, A.R.; Guastelli, L.R.; de Araújo, C.M.P.; dos Santos, J.L.S.; Lamblet, L.C.R.; Silva, M.; de Lima, G.; Cal, R.G.R.; Paes, Â.T.; Neto, M.C.; et al. Positive Deviance: A New Strategy for Improving Hand Hygiene Compliance. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2010, 31, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Fleming Fund Sierra Leone | AMR Action Plan. Available online: https://www.flemingfund.org/countries/sierra-leone/ (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- Hirai, M.; Nyamandi, V.; Siachema, C.; Shirihuru, N.; Dhoba, L.; Baggen, A.; Kanyowa, T.; Mwenda, J.; Dodzo, L.; Manangazira, P.; et al. Using the Water and Sanitation for Health Facility Improvement Tool (WASH FIT) in Zimbabwe: A Cross-Sectional Study of Water, Sanitation and Hygiene Services in 50 COVID-19 Isolation Facilities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, N.; Martinsen, A.L.; Sani, A.; Assigbley, E.K.E.; Azzouz, C.; Hayter, A.; Ayite, K.; Baba, A.A.B.; Davi, K.M.; Gelting, R. Strengthening Healthcare Facilities Through Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH) Improvements: A Pilot Evaluation of “WASH FIT” in Togo. Health Secur. 2018, 16, S24–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mode of Delivery * | To Whom (Numbers $) | Where | When |
|---|---|---|---|
| Three-min Lightning PowerPoint presentation | National IPC program (7) | National IPC unit | March 2022 |
| MoHS stakeholders (32) | National SORT IT module 4 | April 2022 | |
| MoHS stakeholders (16) | MoHS stakeholders meeting | July 2022 | |
| Published article [22] | Global and national IPC professional groups | Social media platforms—Whatsapp, Facebook, and LinkedIn | May 2022 |
| Hospital IPC focal points (16) and WHO AFRO IPC Team (2) | WhatsApp, email exchange, and during a consultative meeting to develop the national IPC action plan | February 2023 | |
| Ten-min technical PowerPoint presentation | Hospital IPC focal point (12) | IPC training | June 2022 |
| Hospital managers and IPC focal points (24) | National SORT IT dissemination meeting | November 2022 | |
| Plain language handouts [31] | Global and national IPC professional groups | Social media platforms—Whatsapp, Facebook, and LinkedIn | April 2022 |
| Researchers, AMR advocates, and community | WHO Sierra Leone website | March 2023 |
| Recommendation | Action Status * | Details of Action (When) |
|---|---|---|
| Advocate for dedicated budget for IPC activities | Fully implemented | Activation of national IPC advisory committee headed by the deputy chief medical officer (public health), which advocated for a dedicated budget for an IPC program in October 2022.Funding secured for the national IPC unit to develop the national IPC action plan in March 2023. |
| Distribution of national IPC guidelines to health facilities | Fully implemented | The WHO printed 1200 copies of the updated national IPC guidelines, which were shared with all the health facilities in September 2022. |
| Dedicated time allocated to IPC staff at health facilities to adapt and implement IPC guidelines | Fully implemented | The WHO and National IPC unit shared ‘terms of reference’ for full-time IPC focal points in August 2022. |
| Clear goals, targets, and activities introduced in the monitoring framework for health facilities | Fully implemented | National IPC unit and WHO disseminated the updated monitoring frameworks in July 2022.IPC focal points of hospitals were trained on the monitoring frameworks in August 2022. |
| Increase the healthcare workforce | Not implemented | |
| Safe and sufficient water supplies | Not implemented | This recommendation was not directly implemented. However, in December 2022, the WASH manager (co-investigator in the previous study), with support from the WHO and national WASH and IPC unit, implemented the WASH-FIT in-depth assessment to investigate and quantify the needs for effective WASH implementation in hospitals. Based on WASH-FIT assessment, the specific actions at facility level were recommended. |
| Adequate numbers of functional toilet facilities | ||
| Facilities for sterilization and disinfection | ||
| Waste disposal | ||
| Supply of consumables such as soap, alcohol-based hand rub, and personal protective equipment | Partially implemented | MOHS has continued its efforts to increase the local production and uninterrupted supply of soaps and alcohol-based hand rub to health facilities. |
| Formulating HAI surveillance strategy | Partially implemented | The WHO acquired funds from US CDC to develop the first HAI surveillance strategy for Sierra Leone, which is ongoing. |
| Access to microbiological laboratories | Not implemented |
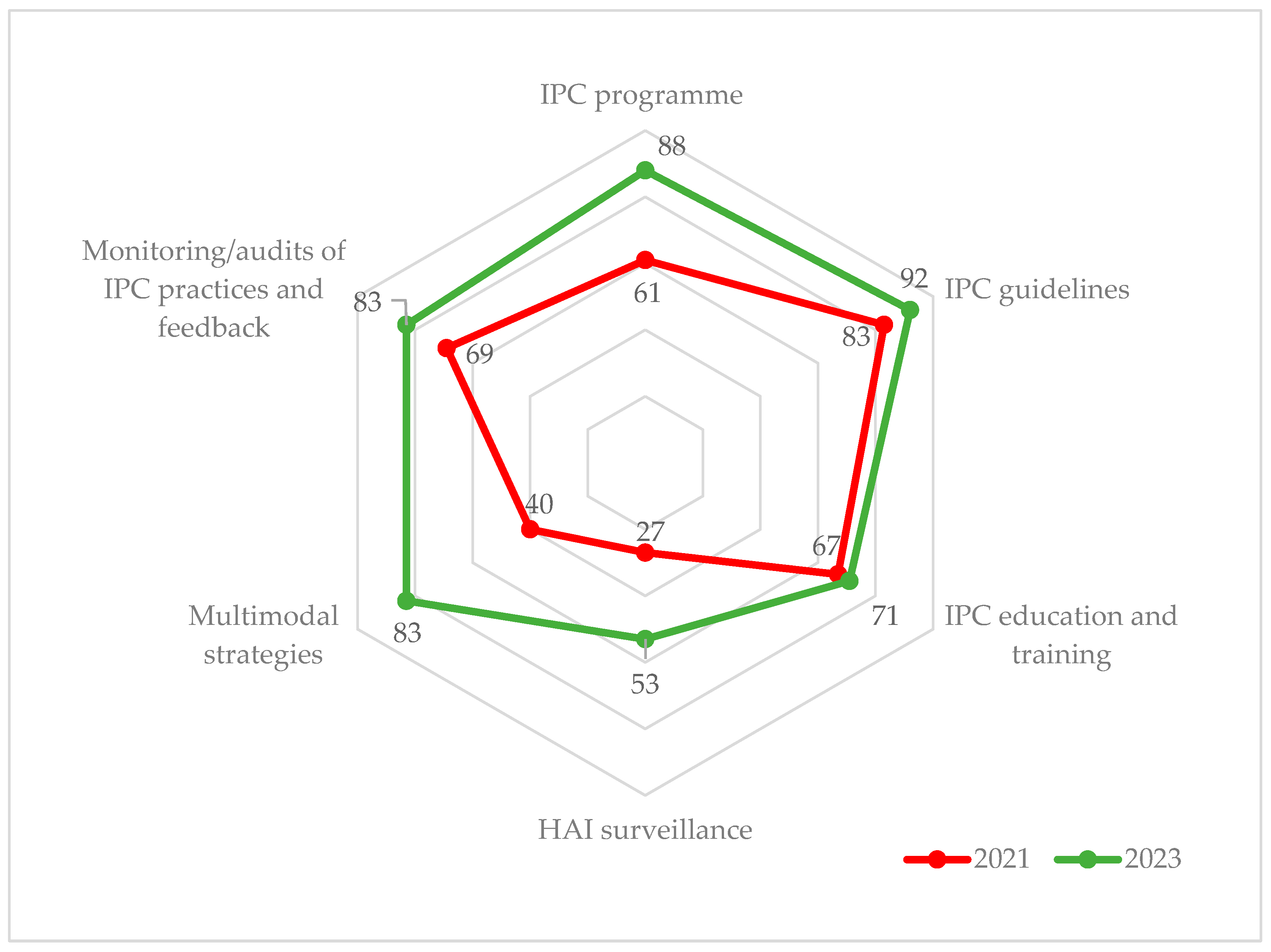
| IPC Components a | 2021 | 2023 | % Change d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade b | % Score c | Grade b | % Score c | ||
| IPC program | Intermediate | 61 | Advanced | 88 | 27 |
| IPC guidelines | Advanced | 83 | Advanced | 92 | 9 |
| IPC education and training | Intermediate | 67 | Intermediate | 71 | 4 |
| HAI surveillance | Basic | 27 | Intermediate | 53 | 26 |
| Multimodal strategies | Basic | 40 | Advanced | 83 | 43 |
| Monitoring/audits of IPC practices and feedback | Intermediate | 69 | Advanced | 83 | 14 |
| Overall score (%) | Intermediate | 58 | Advanced | 78 | 20 |
| IPC Core Components | Sub-Components | 2021 * | 2023 * |
|---|---|---|---|
| i. IPC Program | Organization and leadership of the program | 63% | 75% |
| Defined scope of responsibilities | 71% | 100% | |
| Linkages with other programs and professional organizations | 50% | 88% | |
| ii. IPC Guideline | Development, dissemination, and implementation of national technical guidelines | 100% | 100% |
| Education and training of relevant healthcare workers on IPC guidelines | 67% | 67% | |
| Monitoring of guideline adherence | 100% | 100% | |
| iii. IPC Education and Training | Supporting and facilitating IPC education and training at the facility level | 100% | 100% |
| National curricula and IPC training and education | 100% | 100% | |
| Monitoring of training and education | 0% | 0% | |
| Implementation of training and education | 67% | 83% | |
| iv. HAI Surveillance | Coordination of surveillance at the national level | 43% | 43% |
| National objectives of surveillance | 20% | 80% | |
| Prioritized HAIs for surveillance | 17% | 50% | |
| Methods of surveillance | 67% | 100% | |
| v. Multimodal Strategies | National and sub-national coordination in support of local implementation of IPC improvement interventions | 100% | 100% |
| National and sub-national facilitation in support of local implementation of IPC improvement interventions | 60% | 80% | |
| Program and accreditation linkages | 0% | 50% | |
| vi. Monitoring/Audits of IPC Practices and Feedback | Monitoring/audit and feedback framework for IPC | 50% | 67% |
| Monitoring/audit indicators | 75% | 100% | |
| Monitoring/audit and feedback process and reporting | 83% | 83% |
 Inadequate;
Inadequate;  Basic;
Basic;  Intermediate;
Intermediate;  Advanced.
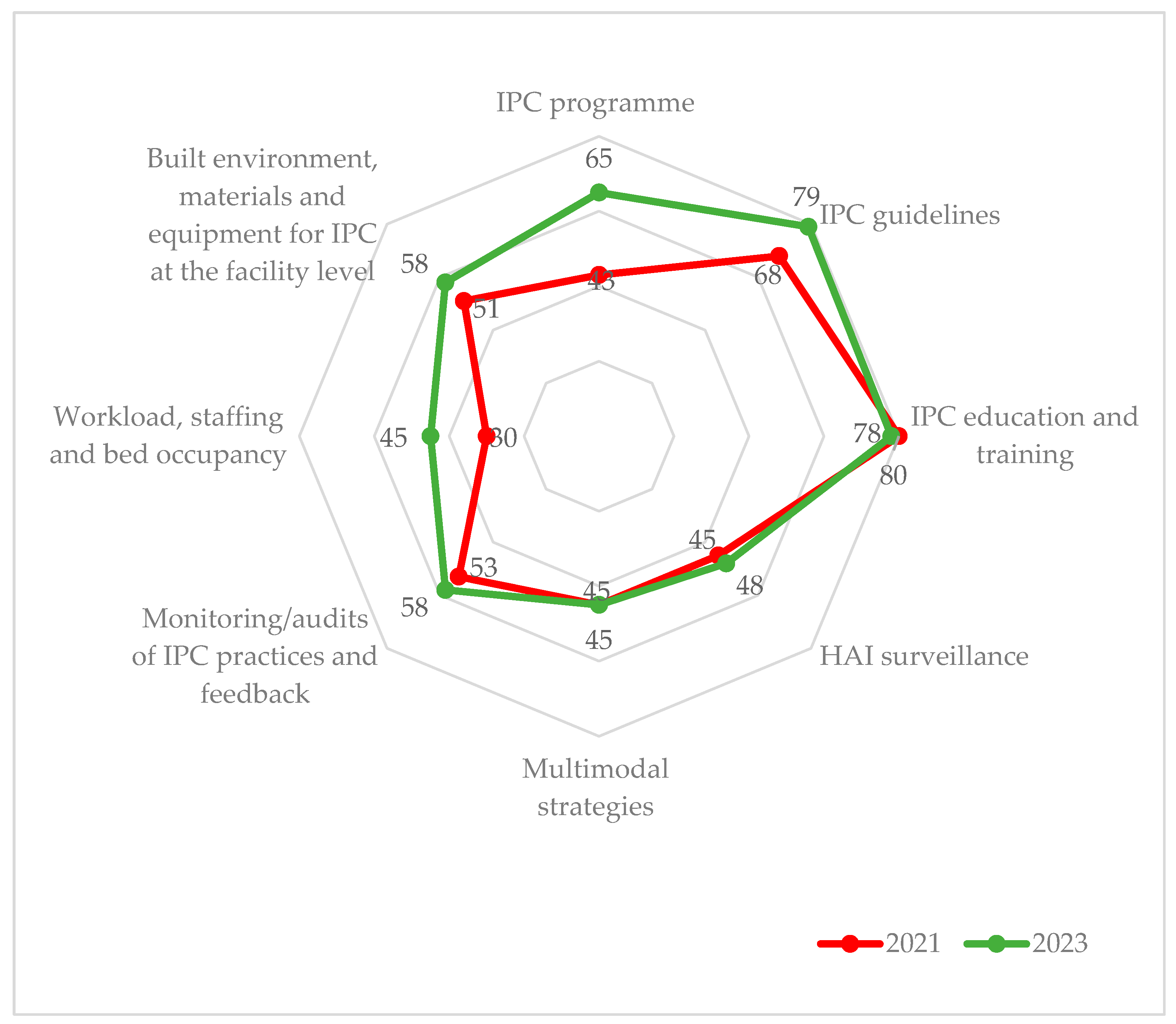
Advanced.| IPC Components a | 2021 | 2023 | % Change d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade b | Median % Score c | Grade b | Median % Score c | ||
| IPC program | Basic | 43 | Intermediate | 65 | 22 |
| IPC guidelines | Intermediate | 68 | Advanced | 79 | 11 |
| IPC education and training | Advanced | 80 | Advanced | 78 | -2 |
| HAI surveillance | Basic | 45 | Basic | 48 | 3 |
| Multimodal strategies | Basic | 45 | Basic | 45 | 0 |
| Monitoring/audits of IPC practices and feedback | Intermediate | 53 | Intermediate | 58 | 5 |
| Workload, staffing, and bed occupancy | Basic | 30 | Basic | 45 | 15 |
| Built environment, materials, and equipment for IPC | Intermediate | 51 | Intermediate | 58 | 7 |
| Overall score (%) | Basic | 50 | Intermediate | 59 | 9 |
| IPC Core Components | Sub-Components | Median Percentage Score * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 2023 | ||
| i. IPC Program | IPC program at facility | 50% | 75% |
| Functional IPC committee | 100% | 100% | |
| Senior facility leadership commitment and support, with a budget allocated specifically for the IPC activities | 0% | 0% | |
| ii. IPC Guideline | Expertise in IPC to develop or adapt guidelines | 0% | 100% |
| Availability of IPC guidelines | 57% | 93% | |
| Consistent with national/international guidelines | 100% | 100% | |
| iii. IPC Education and Training | Availability of personnel with the IPC expertise to lead IPC training | 100% | 100% |
| Frequency of IPC training | 67% | 33% | |
| IPC training integrated in the clinical practice and training of other specialties | 0% | 50% | |
| iv. HAI Surveillance | Surveillance as a defined component of IPC program | 100% | 100% |
| HAI surveillance performed | 14% | 29% | |
| Methods of surveillance | 40% | 40% | |
| v. Multimodal Strategies | Use of multimodal strategies to implement IPC interventions | 100% | 100% |
| Multimodal strategy elements implemented in an integrated way | 40% | 40% | |
| A multidisciplinary team for implementing IPC multimodal strategies | 0% | 0% | |
| vi. Monitoring/Audits of IPC Practices and Feedback | A well-defined monitoring plan, with clear goals, targets and activities | 0% | 100% |
| Monitoring of IPC processes and indicators | 44% | 44% | |
| Feedback of auditing reports on the state of the IPC activities/performance | 60% | 80% | |
| vii. Workload, Staffing, and Bed Occupancy | Assessment of hospital staffing needs | 0% | 0% |
| Hospital bed occupancy | 43% | 54% | |
| viii. Built Environment, Materials, and Equipment for IPC at the Facility Level | Water availability and access | 42% | 50% |
| Functioning hand hygiene and sanitation facilities | 67% | 58% | |
| Patient placement and personal protective equipment (PPE) in health care settings | 67% | 67% | |
| Medical waste management, and sewage | 50% | 53% | |
| Decontamination and sterilization | 50% | 67% | |
 Inadequate;
Inadequate;  Basic;
Basic;  Intermediate;
Intermediate;  Adequate.
Adequate.Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Margao, S.; Fofanah, B.D.; Thekkur, P.; Kallon, C.; Ngauja, R.E.; Kamara, I.F.; Kamara, R.Z.; Tengbe, S.M.; Moiwo, M.; Musoke, R.; et al. Improvement in Infection Prevention and Control Performance Following Operational Research in Sierra Leone: A Before (2021) and After (2023) Study. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8070376
Margao S, Fofanah BD, Thekkur P, Kallon C, Ngauja RE, Kamara IF, Kamara RZ, Tengbe SM, Moiwo M, Musoke R, et al. Improvement in Infection Prevention and Control Performance Following Operational Research in Sierra Leone: A Before (2021) and After (2023) Study. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2023; 8(7):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8070376
Chicago/Turabian StyleMargao, Senesie, Bobson Derrick Fofanah, Pruthu Thekkur, Christiana Kallon, Ramatu Elizabeth Ngauja, Ibrahim Franklyn Kamara, Rugiatu Zainab Kamara, Sia Morenike Tengbe, Matilda Moiwo, Robert Musoke, and et al. 2023. "Improvement in Infection Prevention and Control Performance Following Operational Research in Sierra Leone: A Before (2021) and After (2023) Study" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 8, no. 7: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8070376
APA StyleMargao, S., Fofanah, B. D., Thekkur, P., Kallon, C., Ngauja, R. E., Kamara, I. F., Kamara, R. Z., Tengbe, S. M., Moiwo, M., Musoke, R., Fullah, M., Kanu, J. S., Lakoh, S., Kpagoi, S. S. T. K., Kamara, K. N., Thomas, F., Mannah, M. T., Katawera, V., & Zachariah, R. (2023). Improvement in Infection Prevention and Control Performance Following Operational Research in Sierra Leone: A Before (2021) and After (2023) Study. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 8(7), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8070376









