Abstract
Background: China was certified malaria-free by the World Health Organization on 30 June 2021. However, due to imported malaria, maintaining a malaria-free status in China is an ongoing challenge. There are critical gaps in the detection of imported malaria through the currently available tools, especially for non-falciparum malaria. In the study, a novel point-of-care Rapid Diagnostic Test designed for the detection of imported malaria infections was evaluated in the field. Methods: Suspected imported malaria cases reported from Guangxi and Anhui Provinces of China during 2018–2019 were enrolled to evaluate the novel RDTs. Diagnostic performance of the novel RDTs was evaluated based on its sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, and Cohen’s kappa coefficient, using polymerase chain reaction as the gold standard. The Additive and absolute Net Reclassification Index were calculated to compare the diagnostic performance between the novel RDTs and Wondfo RDTs (control group). Results: A total of 602 samples were tested using the novel RDTs. Compared to the results of PCR, the novel RDTs presented sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and diagnostic accuracy rates of 78.37%, 95.05%, 94.70%, 79.59%, and 86.21%, respectively. Among the positive samples, the novel RDTs found 87.01%, 71.31%, 81.82%, and 61.54% of P. falciparum, P. ovale, P. vivax, and P. malariae, respectively. The ability to detect non-falciparum malaria did not differ significantly between the novel and Wondfo RDTs (control group). However, Wondfo RDTs can detect more P. falciparum cases than the novel RDTs (96.10% vs. 87.01%, p < 0.001). After the introduction of the novel RDTs, the value of the additive and absolute Net Reclassification Index is 1.83% and 1.33%, respectively. Conclusions: The novel RDTs demonstrated the ability to distinguish P. ovale and P. malariae from P. vivax which may help to improve the malaria post-elimination surveillance tools in China.
1. Introduction
Malaria remains a serious public health problem worldwide and is caused by Plasmodium parasites. It is reported that malaria cases were still on the rise between 2020 and 2021. However, the rate of increase is lower than that of 2019–2020; there were an estimated 247 million malaria cases in 2021 in 84 malaria endemic countries, this number was 245 million in 2020 and 232 million in 2019, and an estimated 619,000 malaria deaths [1], this number was 625,000 in 2020 and 568,000 in 2019. The African region accounts for 95% of the global malaria burden and 96% of malaria deaths. More seriously, during the COVID-19 pandemic, many factors, such as the stagnation of malaria prevention and control, the humanitarian crisis, the inadequacy of the health system, the shortage of funds, the biological threat, and the decline in the effectiveness of key disease control tools, such as drug impregnated mosquito nets, are hindering the realization of the goal of eliminating malaria globally. On the one hand, from 2000 to 2015, with the widespread application of malaria prevention and control interventions, the global incidence rate of malaria decreased by 27%, and the malaria mortality rate decreased by 50%. However, by 2017, the incidence rate had risen again, and the decline in the number of deaths had stalled [1]. on the other hand, in May 2015, the World Health Assembly released the global technical strategy for malaria 2016–2030, which set the most ambitious targets for malaria control and elimination thus far, namely reducing global malaria incidence and mortality rates by at least 90% by 2030 [2]. According to the requirements, by 2020, the incidence rate of malaria cases should be reduced by at least 40% and the mortality by at least 75%, but this key milestone goal has not been achieved [1]. Although the global decline in the malaria burden has stalled since 2015, 12 countries have been certified as malaria free since 2000 [1]. This includes China, which was certified malaria-free on June 30, 2021 by the World Health Organization (WHO) [3]. In addition, 13 countries reported zero indigenous cases for three consecutive years during this period.
With globalization and increased international movement, imported malaria cases continue to be reported in China, highlighting the challenges faced in preventing malaria re-establishment [4,5]. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, approximately 3000 imported malaria cases were reported each year, with Africa (89.1%) being the most common source [6]. These imported cases were mainly caused by overseas labourers [7], and the majority of infections were male (96.2%) [6]. In contrast, in some Western developed countries, the majority of cases are among individuals who contracted the infection while visiting friends and relatives [8,9]. Interestingly, recent evidence has shown that the proportion of imported malaria cases caused by non-falciparum malaria, especially Plasmodium ovale (P. ovale), increased to levels higher than expected [10]. Moreover, the proportion peaked at nearly 15% in 2018 in China [11].
Anhui Province is located in the southeastern part of China, in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze and Huai Rivers, with an area of 140,100 km2 and a land area of 139,400 km2. It is a transitional region between warm temperate and subtropical climates, with a distinct monsoon climate. Anhui Province was once one of the key malaria endemic provinces in China, which seriously affected people’s physical health and socio-economic development. Anhui Province is an unstable malaria endemic area, and historically, the Huaibei Plain was an endemic area for P. vivax; in the hilly areas of the Jianghuai River, there are many cases of daily malaria, and some areas have the presence of P. falciparum; the mountainous areas in southern Anhui are mainly characterized by P. vivax. Prior to the 1970s, there were cases of P. falciparum and a small number of P. malariae. After nearly 70 years of prevention and control, the basic elimination of P. falciparum was achieved in 1996. The last local infection case in the province was reported in 2013. Since 2014, there have been no local cases of malaria reported in the province, and all cases have been imported cases. Among them, there were 68–190 reported cases from 2011 to 2019, mainly of P. falciparum, with reports of the other three species and mixed infections [12].
Guangxi is located in the southern part of China, bordering Guangdong and Hunan in the southeast and northeast, Yunnan and Vietnam in the west and southwest, and Guizhou Province in the north. The average annual temperature is 16.5–23.1 °C. There are 14 cities and 111 counties in the province, with a total area of 236,000 km and a total population of 56.95 million in 2019. Throughout history, Guangxi has been a severely prevalent area for malaria, with major outbreaks occurring in 1954, 1963, and 1971. Throughout history, malaria in Guangxi was mainly caused by P. vivax and P. falciparum. After the founding of New China, after more than 70 years of prevention and control, the incidence rate dropped from 296.7/10,000 in 1954 to less than 1/10,000 in 1987; The last local infection case was reported in 2012, and since 2013 there have been no local infection cases reported in the province. All cases occurred as imported cases, mainly from African and Southeast Asian countries and regions. Among them, a total of 3195 malaria cases were reported in Guangxi from 2010 to 2019, with the main species being P. falciparum, while the other three species and mixed infections were all reported as well [13,14].
In China, when suspected malaria patients presenting with symptoms of malaria, especially combined with a history of travel to a malaria-endemic area, seek medical care, the physician provides a diagnostic test for malaria, commonly microscopy or rapid diagnostic test (RDTs) [15]. However, due to their morphological similarity, P. ovale is easily and commonly misdiagnosed as an infection of P. vivax [16,17], which may lead to an inappropriate case management treatment response. For someone self-diagnosing for malaria, RDTs are available in Chinese pharmacies; however, these also cannot differentiate between P. malariae, P. ovale, and P. vivax infections. Thus, prompt and precise diagnostic tools that can detect and differentiate non-falciparum malaria species are needed.
In this study, a novel point-of-care RDT was designed for the detection of imported malaria infections and was evaluated using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) as the gold standard. We believe that the newly designed diagnostic tool can benefit the prevention of malaria re-establishment in the future.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Setting, Participants and Design
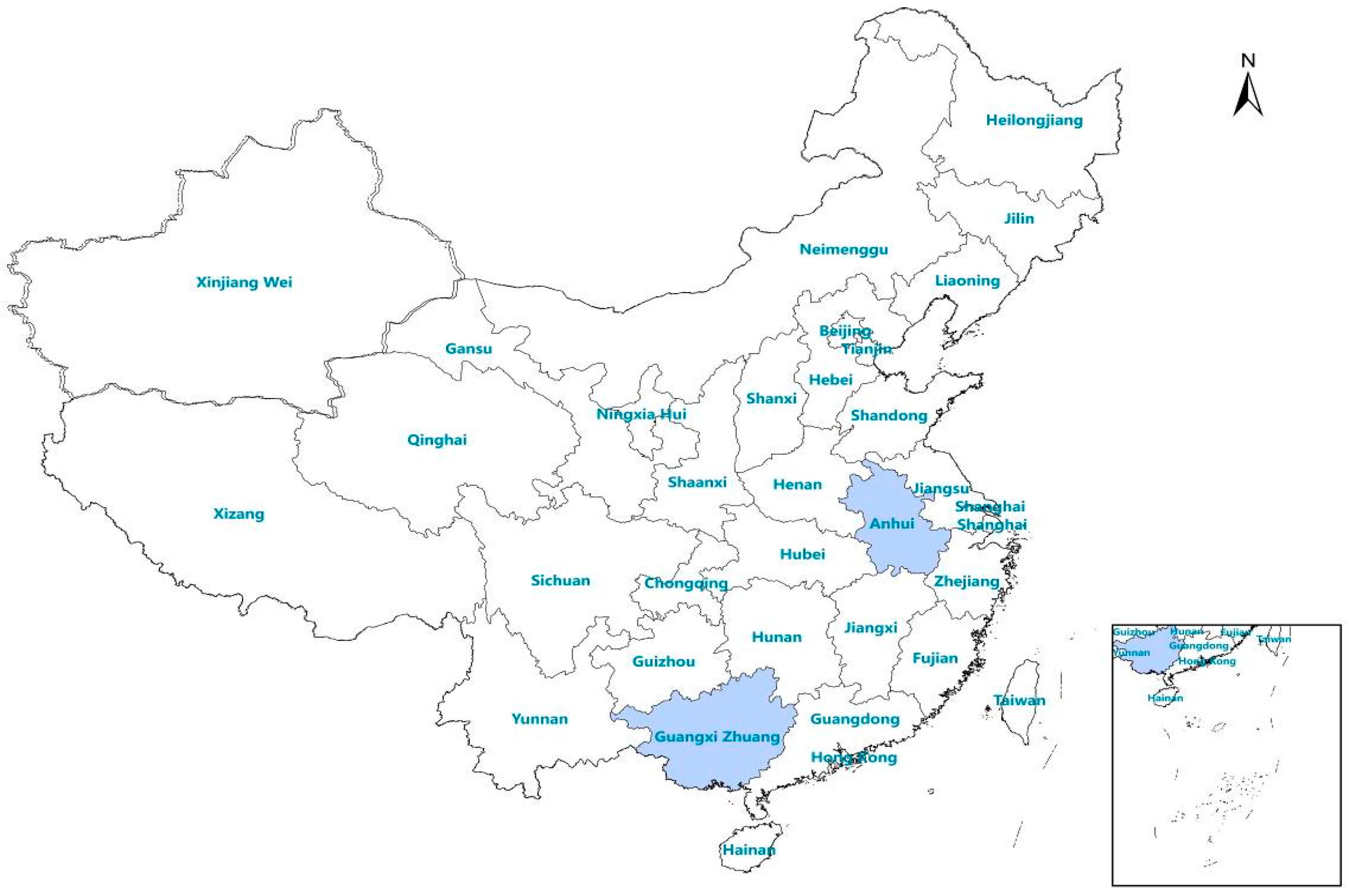
The provinces of Anhui and the Guangxi Autonomous Region were selected as study areas for the evaluation of the novel RDTs (Figure 1). Historically, malaria was highly prevalent in Anhui province [12], which presents a high risk of re-establishment of malaria. Guangxi is a border province in southern China that exports large numbers of migrant workers to Africa. Since 2013, the number of imported malaria cases in Guangxi Province has been among the highest in China [5].
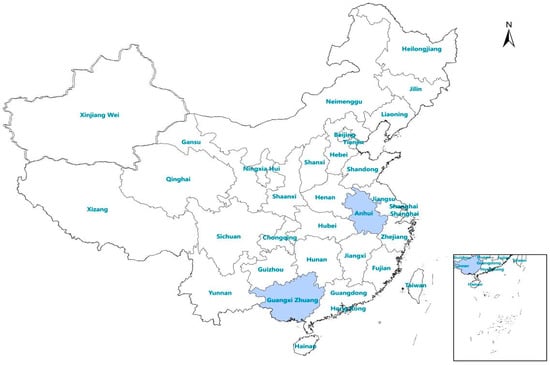
Figure 1.
Location of the study area in China.
In China, each suspected malaria case should be mandatorily reported through the China Information System for Disease Control and Prevention (CISDCP) [18]. This is a real-world study based on the surveillance system of malaria in China. All suspected imported malaria patients reported in Anhui and Guangxi provinces from 2018 to 2019 were enrolled as participants in the study. Individuals were contacted by telephone to obtain verbal informed consent. An imported case was defined as a malaria infection acquired outside the country (in this study, China).
In China, when a suspected case is reported through the network, the blood samples, including whole blood and smears that were collected from the patient before anti-malarial treatment [19], are sent to the provincial reference laboratory for final confirmation using microscopic examination and polymerase chain (PCR) reaction according to the malaria diagnostic criteria in China [20]. In this study, the real-time PCR method, used in the form of commercial real-time PCR Kits (Shanghai ZJ Bio-tech Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), was taken as the gold standard to detect the malaria infection and further distinguish between Plasmodium species. The kits, targeting the 18s rRNA gene, were designed by referring to a previous study and provided internal control [21]. Before PCR test, DNA was extracted using the QIAamp DNA Mini kit (QIAGEN Inc., Hilden, Germany) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. Then, PCR was performed in a 40.4-μL reaction mixture containing 35 μL reaction mix, 0.4 μL enzyme mix, 1 μL internal control, and 4 μL DNA template. The reaction conditions were as follows: 37 °C for 2 min and 94 °C for 2 min, followed by 40 cycles at 93 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 60 s. On the other hand, a commercial test strip (Diagnostic Kit for Malaria, Guangzhou Wondfo Biotech Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China) detecting Pf-HRP2 (Human histidine rich protein 2) and Pan- lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) was taken as control in comparison to the novel RDTs in the laboratory setting. An imported case was defined as a malaria infection acquired outside the country (in this study, China).
2.2. Interpretation of the Results for RDTs
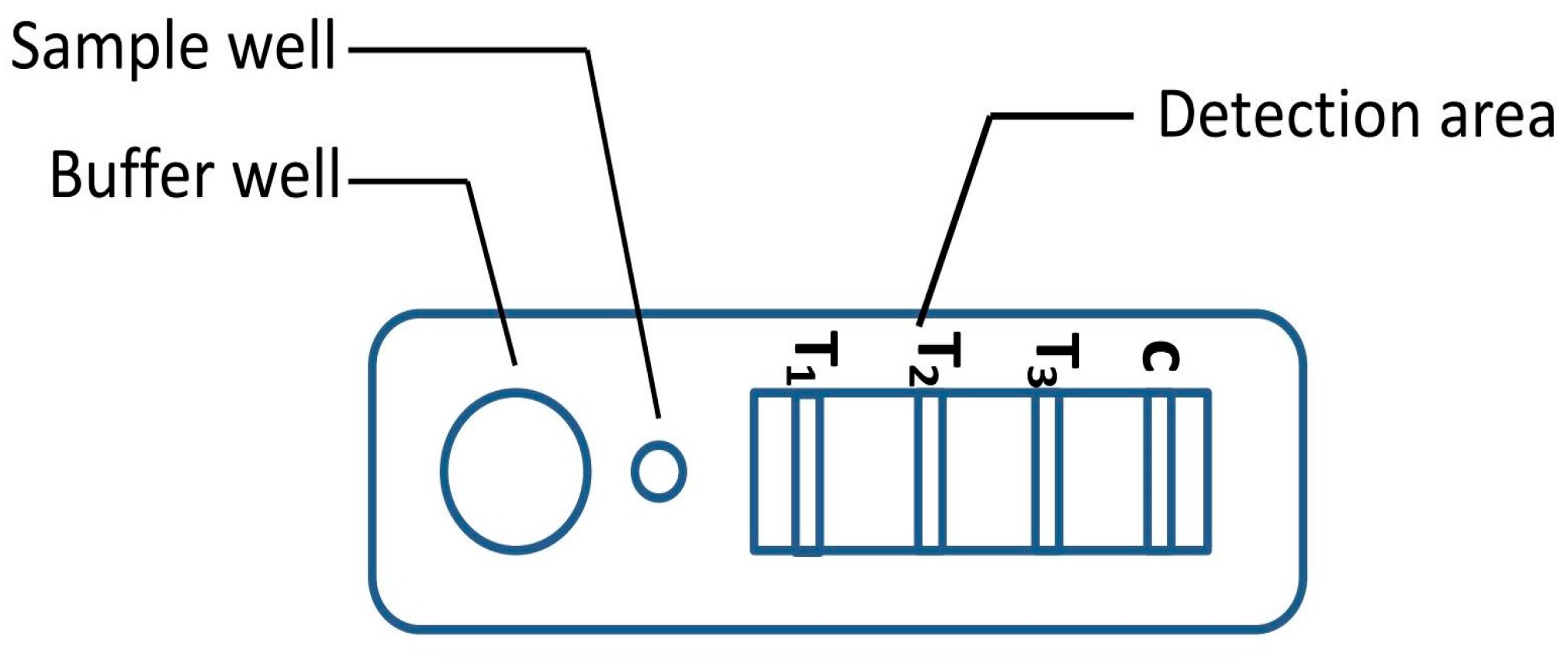
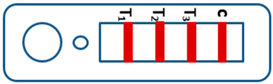
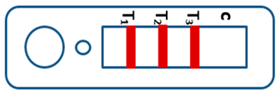
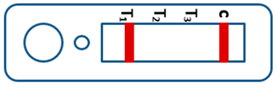
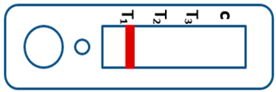
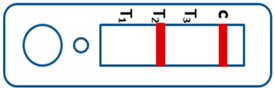
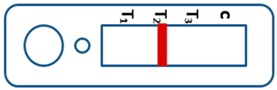
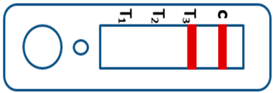
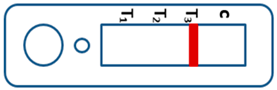
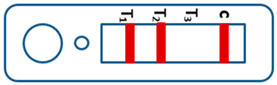
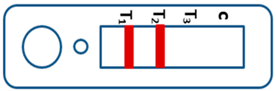
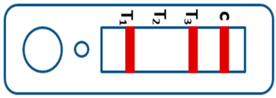
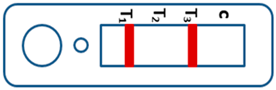
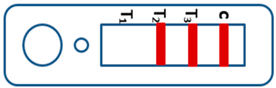
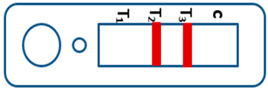
A novel malaria RDT was designed by the National Institute of Parasitic Diseases, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention and tested in this study. It is not yet officially available commercially. The novel RDT (Figure 2) is an immunochromatographic test strip, and has one control line and three test lines (“T1”, “T2”, and “T3”), detecting Pf-HRP2, Pv-speciifc LDH, and Pan-LDH, respectively. If the infection was caused by P. vivax, T2 and T3 line were simultaneously positive, whereas, if the infections were P. ovale and/or P. malariae, only the “T3” line was positive, with a negative “T2” line. Using the combination of “T2” and “T3” test lines, the novel mRDT can distinguish P. vivax from P. ovale and/or P. malariae (Table 1). Wondfo RDTs have one control line (“C”) and two detection lines (“T1” and “T2”). Additionally, the T1 and T2 lines indicate P. falciparum and Plasmodium infections, respectively. Blood samples from participants were tested simultaneously with novel and Wondfo RDTs in the provincial laboratory reference as directed by the manufacturer.
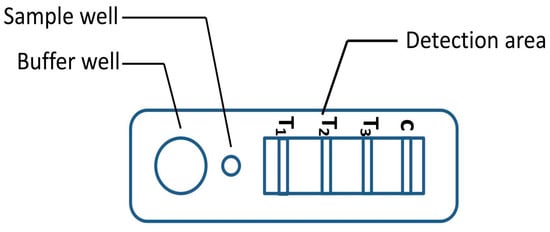
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the novel malaria RDTs.

Table 1.
Interpretation of the results of the novel malaria RDTs.
2.3. Data Analysis
The categorical data are presented as percentages. Values are presented as the mean ± standard deviation for data that were normally distributed. Differences in proportions were compared using McNemar’s χ2 test. Taking the results of PCR as the gold standard, the diagnostic performances of the novel and Wondfo RDTs were presented with the following parameters: sensitivity, specificity, positive (PPV) and negative predictive values (NPV), and Cohen’s kappa coefficient, with their respective 95% confidence intervals. The formula for calculating PPV and NPV is: PPV = (true positives)/(true positives + false positives), NPV = (true negatives)/(true negatives + false negatives), respectively. Additive Net Reclassification Index (NRI) and absolute NRI are calculated to compare diagnostic performance between the Novel and Wondfo RDTs [22]. All statistical tests were two-sided, and p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The study data were recorded and entered into an Excel database (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA), and analysis was performed using SPSS 26.0 statistical software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The thematic map of geographic distribution was created by MapInfo 15.0 (Pitney Bowes Inc., Troy, NY, USA).
3. Results
During the study period, a total of 602 blood samples collected from suspected malaria cases were tested to evaluate the performance of the novel and Wondfo RDTs. Cases came from 26 African and 2 Asian countries, with Africa (600; 99.67%) being the most common region of origin. The five countries of origin of infection were Ghana (115; 19.10%), Nigeria (55; 9.14%), Ivory Coast (53; 8.80%), Angola (51; 8.47%), and Mozambique (50; 8.31). Of these, 154 (P. falciparum), 123 (P. ovale), 22 (P. vivax), 13 (P. malariae), and 7 (mixed infections) samples tested positive. The remaining 283 cases were confirmed negative by PCR. The mean age of the participants was 42.2 ± 9.1 years, and 578 participants (96.0%) were males.
3.1. Diagnostic Performance of the Novel and Wondfo RDTs
Compared to the results of PCR, the novel RDTs presented sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and diagnostic accuracy rates of 78.37%, 95.05%, 94.70%, 79.59%, and 86.21%, respectively. Those of the Wondfo RDTs were 86.21%, 89.05%, 89.87%, 85.14%, and 87.54%, respectively. In terms of sensitivity, Wondfo RDTs outperformed the novel RDTs (86.21% vs. 78.37%), whereas the opposite is true for specificity (89.05% vs. 95.05%) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Diagnostic performance of Novel and Wondfo RDTs for malaria in a laboratory setting.
Both RDTs were able to detect all four Plasmodium species from the blood samples which were collected. Compared to the PCR gold standard, the Wondfo RDTs detected 96.01% (P. falciparum), 72.13% (P. ovale), 90.91%(P. vivax), and 92.31%(P. malariae), while the novel RDTs identified 87.01% (P. falciparum), 71.31%(P. ovale), 81.82%(P. vivax), and 61.54% (P. malariae) of cases. Their ability to detect non-falciparum malaria did not differ significantly, but Wondfo RDTs detected more P. falciparum infections than the novel RDTs (96.10% vs. 87.01%) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Detection ability of novel and Wondfo RDTs for different malaria species in a laboratory setting.
3.2. Additive NRI and Absolute NRI
The additive NRI and absolute NRI were calculated to assess the improvement due to the novel RDTs introduced in the field, compared to Wondfo RDTs. The values of the additive NRI and absolute NRI are 1.83% and 1.33%, respectively. The results showed that there was no difference in diagnostic ability between the Novel and Wondfo RDTs (all p > 0.05) (Table 4).

Table 4.
Comparison of diagnostic ability between the Novel and Wondfo RDTs.
4. Discussion
The last indigenous malaria case in China was reported in 2016 and local transmission has been interrupted since 2017 [23]. China was certified malaria-free by the WHO in 2021 and is facing continued challenges due to imported malaria, particularly among male workers visiting Africa. Therefore, performing and sustaining a sensitive surveillance system that can detect suspected malaria cases in a prompt and accurate manner is the key. However, the inability to properly detect and distinguish malaria parasites is a huge barrier [24]. In field practice, microscopy and RDTs are common diagnosis methods for malaria in the health care setting in China. However, sustaining microscopy competency is extremely difficult due to the limited accumulation of experience [25]. RDT has the characteristics of easy operation and intuitive reading; therefore, it is the diagnostic method for malaria that has been recommended by the WHO. Further, RDTs, a vital supplement, extend access to diagnostic tools in areas where microscopy cannot be reliably maintained. RDT has been recommended to provide parasite diagnosis for suspected malaria cases by WHO [26].
For malaria detection, RDT that can distinguish between the types of malaria parasites, live and dead infections, and the sexual stage of parasitemia will be very helpful for diagnosis and guide intervention measures. The main challenge is in the field of low-level parasitemia. The examination of the life cycle stage of malaria parasite infection has identified many key targets, including the HRP2 protein (P. falciparum), parasite lactate dehydrogenase (pLDH, Plasmodium genus), and malaria parasite aldolase (Plasmodium genus). Therefore, distinguishing between P. falciparum and other species is not a simple task [27]. Piper conducted research on how existing combinations of pLDH antibodies perform in the differential diagnosis of P. falciparum, pan specificity, and malaria parasites, showing that differences in reactivity may be related to small differences on the surface of pLDH, with subtle amino acid changes being the cause of species specificity [28].
There is evidence to suggest that, in countries with low malaria transmission, due to the long-term absence of malaria cases, the awareness and vigilance of health systems and the preparedness of health workers towards the correct management of suspected malaria will decrease [29].
In China, infections caused by P. falciparum, P. vivax, P. malariae, and P. ovale have still been reported for many years. The malaria surveillance system needs to introduce RDTs with the ability to detect four species. However, thus far, only two Pf/Pan tests (Wondfo and BinaxNOW® Malaria) have been registered in the National Medical Products Administration that could be used in health facilities. Wondfo RDTs are used more in the market for price reasons, and presented a better performance for detecting P. ovale compared to CareStart pLDH PAN and SD BIOLINE Pf/Pan RDTs [30]. According to the manufacturer’s instructions, Wonfo RDTs can distinguish P. falciparum from non-falciparum species. However, they could not further differentiate non-falciparum species. P. vivax, a common species in all malaria-endemic areas, is distributed nationwide and is the main species related to the risk of malaria reintroduction. Due to their morphological similarity, P. ovale is easily and commonly misdiagnosed as an infection of P. vivax in the field, further leading to inappropriate interventions. A novel RDT has been designed to fulfil the gap in field practice.
Related studies have shown that, although the protein sequence of pLDH is very conservative within the same species, there are certain differences in the protein sequence of pLDH among the four human malaria parasites. Usually, the detection antibodies in RDT are monoclonal antibodies that are prepared based on a specific pLDH antigen of a certain insect species. Therefore, when detecting unknown samples, if the patient is infected with other insect species in the body, the detection antibodies in RDT cannot specifically bind to the antigen in the sample, resulting in false negative test results. The specificity experiment results showed that the monoclonal antibody of PfLDH only reacted with the samples of P. falciparum and did not react with the samples of P. vivax (P. vi-vax); similarly, PvLDH antibodies only react with P. vivax samples and do not react with P. falciparum samples [31].
In this study, the diagnostic performance of the novel RDTs was assessed using blood samples collected from the field. The novel RDTs found 87.01% of P. falciparum, 71.31% of P. ovale, 81.82% of P. vivax, and 61.54% of P. malariae infections. The diagnostic performance of the novel RDTs for non-falciparum species was similar to that of the Wondfo RDTs. Importantly, the novel RDTs had the ability to distinguish P. ovale and P. malariae infections from P. vivax. Although improvements are still needed to improve the novel RDTs, we believe that significant progress has been made in this initial development and through this diagnostic evaluation.
Although the diagnostic sensitivity of the novel RDTs for P. falciparum was lower than for Wondfo RDTs (87.01% vs. 96.10%), P. falciparum is the dominant species of imported malaria [4]. Novel RDTs need to fulfil the gap in future practical applications. The value of additive NRI and absolute NRI are 1.83% and 1.33%, respectively, which means that there are no obvious additional benefits to the introduction of the novel RDTs in the field.
P. ovale and P. malariae were commonly considered as the ‘bashful’ malaria parasites, due to their low prevalence and limited geographic distribution [32]. However, the introduction of more sensitive molecular methods has provided more evidence that their geographic distribution is larger than previously speculated [33,34]. Further, scientific knowledge about the two species is very limited compared to P. falciparum and P. vivax. Developing diagnostic tools that target the two main species of Plasmodium is challenging. One factor significantly impacting its success is that parasitaemia is typically very low in infections caused by P. ovale and P. malariae (sub-microscopic malaria infections). According to a previous study, P. malariae only invades aged red blood cells (0.1% parasitaemia) and P. ovale preferentially invades youthful red blood cells (1% parasitaemia) [35]. This implies that the concentration of specific antigens targeted by novel RDTs may be lower than the threshold value. For example, in our field assessment, novel RDTs only found 61.54% infections of P. malariae.
Our study has two main limitations. First, limitations around clinical and patient-level RDTs occur frequently in non-endemic settings, especially in the presence of treatment delays [36]. Therefore, the performance of the novel RDTs may be underestimated. Second, the number of P. malariae and P. vivax cases is small.
5. Conclusions
The diagnostic power of novel RDTs for non-falciparum species detection was comparable to the Wondfo RDTs, and demonstrated the ability to distinguish P. ovale and P. malariae from P. vivax. We believe that the newly designed RDTs can benefit POR practices within China and other malaria-eliminating and POR countries with further improvements.
Author Contributions
S.L.(Shizhu Li)., D.W. and K.L. designed the study and developed the protocol. Y.S. and C.C. analyzed and S.L. (Shenning Lu). interpreted the data. F.L., Y.Q. and F.S. organized and supervised the study in field. J.L. and S.W. conducted the study in field, and entered the data. K.L., S.W. and T.Z. wrote the first draft of the paper and prepared the final manuscript with S.L (Shenning Lu). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Study on the prevalence of important infectious diseases in Africa (2016 ZX10004222), China–Africa cooperation project on malaria control under the Project No. 2020-C4-0002-3 and the programme of the Chinese Center for Tropical Diseases Research (No.131031104000160004) as well as UNICEF/UNDP/World Bank/WHO Special Programme for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases (TDR) Small Grant (WHO Reference 2021/1104003–0). Funder of the event is not involved in the manuscript review.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of NAME OF The National Institute of Parasitic Diseases(NIPD), Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention(WHO Collaborating Centre for Tropical Diseases) Ethics Review Committee (protocol code 20190115 and date of approval 2019.2.27) for studies involving humans.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge all participants for their contribution of time and patience in the study. We acknowledge the staffs of the Institute of Parasitic Diseases, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Center for Disease Control and Prevention (GXCDC), and the Anhui Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention for logistic support, and the clinical and laboratory staff of Shanglin County Center for Disease Control and Prevention for their hard work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. World Malaria Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Technical Strategy for Malaria 2016–2030; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.-N. China declared malaria-free: A milestone in the world malaria eradication and Chinese public health. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2021, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Feng, X.-Y.; Zhou, S.-S.; Tang, L.-H.; Xia, Z.-G. Establishing and applying an adaptive strategy and approach to eliminating malaria: Practice and lessons learnt from China from 2011 to 2020. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, L.; Tu, H.; Zhou, S.S.; Xia, Z.G. From elimination to post-elimination: Characteristics, challenges and re-transmission preventing strategy of imported malaria in China. China Trop. Medicine. 2021, 21, 5–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Feng, J.; Zhang, S.S.; Xia, Z.-G.; Zhou, S.-S. Epidemiological characteristics of malaria and the progress towards its elimination in China in 2018. Chin. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Dis. 2019, 37, 241–247. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, S.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Z.; Geng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Lai, S.; et al. Epidemiologic features of overseas imported malaria in the People’s Republic of China. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mace, K.E.; Lucchi, N.W.; Tan, K.R. Malaria Surveillance—United States, 2018. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2022, 71, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, R.H.; Neave, P.E.; Jones, C.O. Imported malaria among people who travel to visit friends and relatives: Is current UK policy effective or does it need a strategic change? Malar. J. 2015, 14, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, S.Q.; Wang, D.Q.; Auburn, S.; Lu, S.N.; Xu, X.; Lyu, X.; Yu, C.; Tian, C.; Li, S.; et al. Epidemiological profile of Plasmodium ovale spp. imported from Africa to Anhui Province, China, 2012–2019. Malar. J. 2021, 20, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Tu, H.; Zhang, L.; Xia, Z.; Zhou, S. Imported Malaria Cases—China, 2012–2018. China CDC Wkly. 2020, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, J.J.; Li, W.D. Course of malaria control and elimination in Anhui Province. J. Trop. Dis. Parasitol. 2020, 18, 65–69, 80. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wei, S.-j.; Zhang, W.-w.; Lin, K.-m.; Yan, H.; Feng, X.-y. Analysis of malaria epidemiological characteristics in Guangxi Province in 2010–2019. Chin. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Dis. 2020, 38, 589–594. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, L.; Kangmin, L.; Shujia, W.; Weiwe, Z.; Xiangyan, F.; Hui, Y. An overview of malaria control in Guangxi Zhuang autonomous region for 70 years. J. Trop. Med. 2020, 20, 997–1000, 1012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Cotter, C.; Sun, X.; Bennett, A.; Gosling, R.D.; Xiao, N. Adapting the local response for malaria elimination through evaluation of the 1-3-7 system performance in the China–Myanmar border region. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.-N.; Zhang, L.-L.; Ruan, W.; Chen, H.-L.; Lu, Q.-Y.; Yang, T.-T. Species identification in 5 imported cases previously diagnosed as Vivax malaria by parasitological and nested PCR techniques. Chin. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Dis. 2013, 31, 221–223, 234. [Google Scholar]
- Chavatte, J.-M.; Tan, S.B.H.; Snounou, G.; Lin, R.T.P.V. Molecular characterization of misidentified Plasmodium ovale imported cases in Singapore. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Jin, S.; Wu, Z.; Chin, D.P.; Koplan, J.P.; Wilson, M.E. Emergence and control of infectious diseases in China. Lancet 2008, 372, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, S.; Cheng, Z.; Xiao, N.; Cotter, C.; Hwang, J.; Li, X.; Yin, S.; Wang, J.; Bai, L.; et al. Transmission riskfrom imported Plasmodium vivax malaria in the China–Myanmar borderregion. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1861–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health and Family Planning Commission of China. Diagnosis of Malaria; National Health and Family Planning Commission of China: Beijing, China, 2015. (In Chinese)
- Perandin, F.; Manca, N.; Calderaro, A.; Piccolo, G.; Galati, L.; Ricci, L.; Medici, M.C.; Arcangeletti, M.C.; Snounou, G.; Dettori, G.; et al. Development of a real-time PCR assay for detection of Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax, and Plasmodium ovale for routine clinical diagnosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1214–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba, A.C.; Agoritsas, T.; Walsh, M.; Hanna, S.; Iorio, A.; Devereaux, P.J.; McGinn, T.; Guyatt, G. Discrimination and Calibration of Clinical Prediction Models: Users’ Guides to the Medical Literature. JAMA 2017, 318, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Feng, J.; Tu, H.; Yin, J.H.; Xia, Z.G. Malaria epidemiology in China in 2020. Chin. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Dis. 2021, 39, 195–199. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Yan, H.; Li, M. Prompt and precise identifcation of various sources of infection in response to the prevention of malaria re-establishment in China. Infect. Dis. Poverty. 2022, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, G.; Zhu, G.; Cao, C.; Miao, P.; Cao, Y.; Wang, W.; Gu, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, S.; Zhou, H.; et al. The challenge of maintaining microscopist capacity at basic levels for malaria elimination in Jiangsu Province, China. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for the Treatment of Malaria, 3rd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, D.; Wongsrichanalai, C.; Barnwell, J.W. Ensuring quality and access for malaria diagnosis: How can it be achieved? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, S7–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piper, R.C.; Buchanan, I.; Choi, Y.H.; Makler, M.T. Opportunities for improving pLDH-based malaria diagnostic tests. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, H.; Majdzadeh, R.; Ahmadi, A.; Esmaeili, E.D.; Naghili, B.; Mansournia, M.A. Health workers readiness and practice in malaria case detection and appropriate treatment: A meta-analysis and meta-regression. Malar. J. 2021, 20, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Tang, F.; Zhu, H.; Lu, F.; Xu, S.; Cao, Y.; Gu, Y.; He, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, G.; et al. Assessment of false negative rates of lactate dehydrogenase-based malaria rapid diagnostic tests for Plasmodium ovale detection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Zhigui, X.; Ahuisen, Z. Analysis of inconsistence of plasmodium detection in some malaria cases. Chin. J. Paraist Dis. 2019, 37, 464–471. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, I.; Zimmerman, P.A.; Reeder, J.C. Plasmodium malariae and Plasmodium ovale-the “bashful” malaria parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2007, 23, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguike, M.C.; Betson, M.; Burke, M.; Nolder, D.; Stothard, R.; Kleinschmidt, I.; Proietti, C.; Bousema, T.; Ndounga, M.; Tanabe, K.; et al. Plasmodium ovale curtisi and Plasmodium ovale wallikeri circulate simultaneously in African communities. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oriero, E.C.; Amenga-Etego, L.; Ishengoma, D.S.; Amambua-Ngwa, A. Plasmodium malariae, current knowledge and future re-search opportunities on a neglected malaria parasite species. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 47, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerlin, D.H.; Gatton, M.L. Preferential Invasion by Plasmodium Merozoites and the Self-Regulation of Parasite Burden. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota-Sullivan, K.; Blecker-Shelly, D.L. Use of the Rapid BinaxNOW Malaria Test in a 24-Hour Laboratory Associated with Accurate Detection and Decreased Malaria Testing Turnaround Times in a Pediatric Setting Where Malaria Is Not Endemic. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1567–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).