Anti-Toxoplasma gondii and Anti-Neospora caninum Antibodies in Urban Traction Equids in Northeast Brazil: Seroprevalence and Risk Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
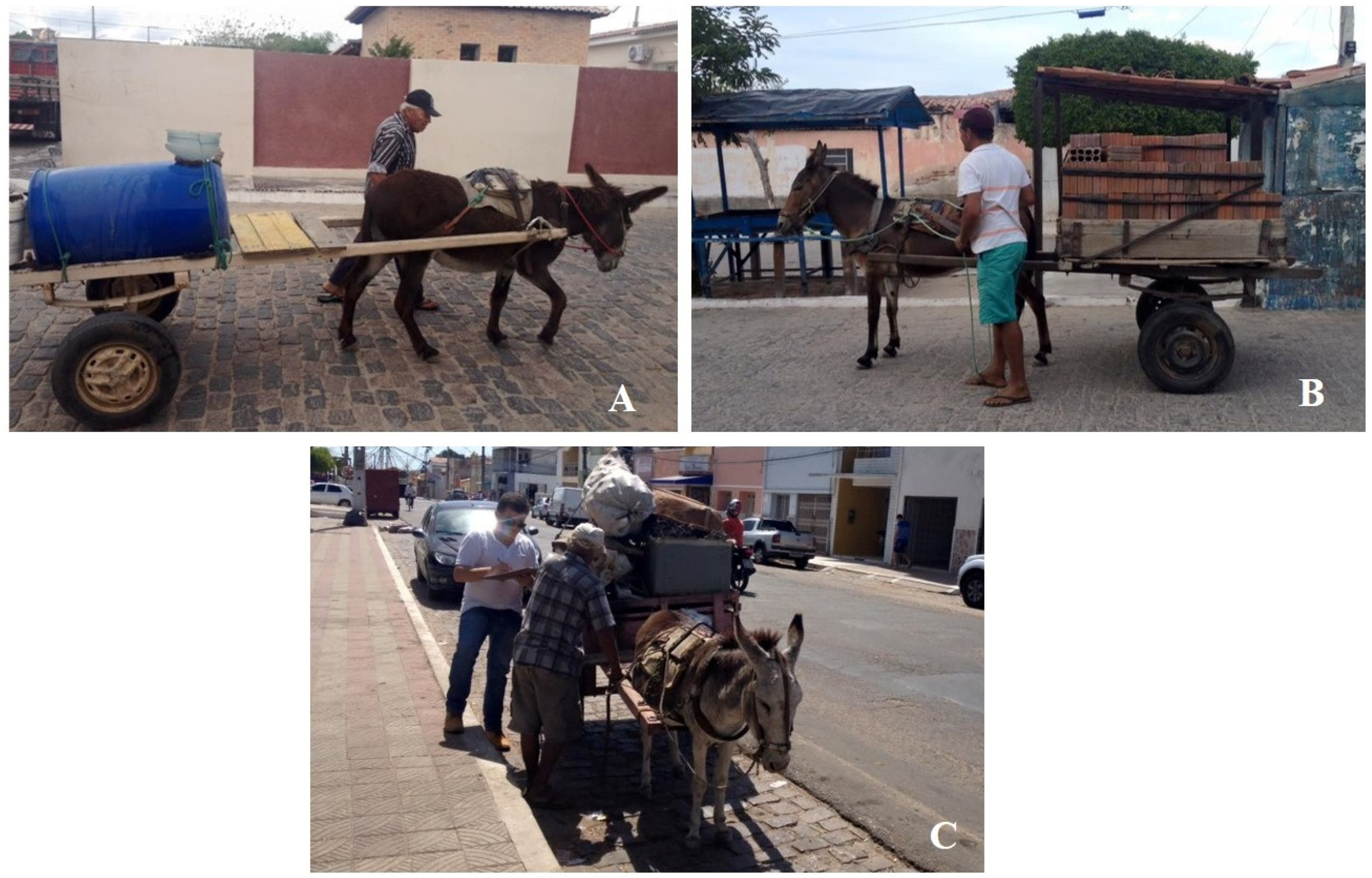
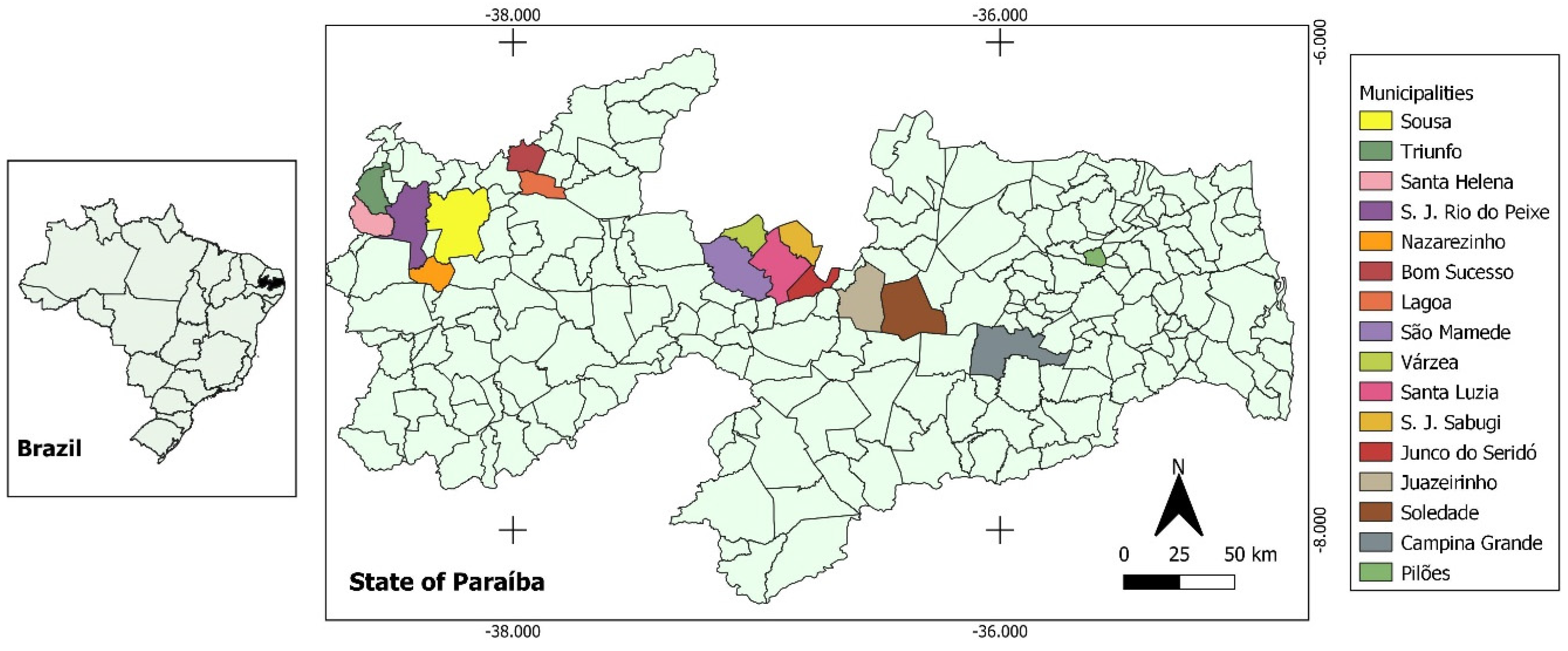
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Sample Selection
2.3. Serological Analyses
2.4. Epidemiological Questionnaire
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tavares, T.C.; Pimentel, M.M.L.; Câmara, F.V.; Lopes, K.R.; Dias, R.V.C. Análise biométrica dos equinos utilizados para tração no Município de Mossoró—RN, Brasil. Rev. Bras. Hig. Sanid. Anim. 2015, 9, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, D.S. Neosporosis: An emerging protozoal disease of horses. Equine Vet. J. 2011, 211, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camossi, L.G.; Silva, A.V.; Langoni, H. Inquérito sorológico para toxoplasmose em equinos na região de Botucatu-SP. Comunicação. Arq. Bras. Med. Veterinária Zootec. 2010, 62, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughattas, S.; Bergaoui, R.; Essid, R.; Aoun, K.; Bouratbine, A. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection among horses in Tunisia. Parasites Vectors 2011, 4, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valença, S.R.F.A.; Valença, R.M.B.; Pinheiro Junior, J.W.; Albuquerque, P.P.F.; Souza Neto, O.L.; Mota, R.A. Risk Factors for Occurrence of Anti-Neospora spp. Antibodies in Horses from Alagoas, Brazil. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2015, 35, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.C.; Vidotto, O.; Ferreira, E.P.; Ribeiro, L.P.S.; Mongruel, A.C.B.; Vieira, T.S.W.J.; Freire, R.L.; Mota, R.A.; Vieira, R.F.C. Serosurvey of anti-Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in sport horses from Paraiba state, Northeastern Brazil. Acta Parasitol. 2017, 62, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, T.R.; Sarturi, C.; Stelmachtchuk, F.N.; Andersson, E.; Norlander, E.; De Oliveira, F.L.C.; Portela, J.M.; Marcili, A.; EmaNuelson, U.; Gennari, S.M.; et al. Prevalence of antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora spp. In equids of Western Para. Brazil. Acta Trop. 2019, 189, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langoni, L.; Silva, A.V.; Pezerico, S.B.; Lima, V.Y. Utilization of modified agglutination test and indirect immunofluorescent antibody test for the detection of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in naturally exposed horses. Braz. J. Vet. Res. Sci. 2007, 44, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.J.M.; Rosa, M.H.F.; Bruhn, F.R.P.; De Garcia, A.M.; Rocha, C.M.B.M.; Guimarães, A.M. Seroepidemiology of Sarcocystis neurona, Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora spp. among horses in the south of the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Braz. J. Veterenary Parasitol. 2016, 25, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, P.A.; Sverlow, K.; Anderson, M.A.; Rowe, J.; Bondurant, R.; Tuter, G.; Breitmeyer, R.; Palmer, C.; Thurmond, M.; Ardans, A. Detection of serum antibody responses in cattle with natural and experimental Neospora infections. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1993, 5, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, R.A.; Weiss, R.R.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Locatelli-Dittrich, R.; Laskoski, L.M.; Bertol, M.A.F.; Koch, M.O.; Alban, S.M.; Green, K.T. Association of Antibodies against Neospora caninum in Mares with Reproductive Problems and Presence of Seropositive Dogs as a Risk Factor. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 202, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 4th ed.; Prentice Hall: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S. Applied Logistic Regression, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, S.; Silva, N.Q.B.; Silveira, I.; Labruna, M.B.; Gennari, S.M.; Pena, H.F.J. Occurrences of antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora spp., and Sarcocystis neurona in horses and dogs in the municipality of Pauliceia, São Paulo, Brazil. Braz. J. Vet. Res. Anim. Sci. 2017, 54, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennari, S.M.; Esmerini, P.O.; Lopes, M.G.; Soares, H.S.; Vitaliano, S.N.; Cabral, A.D.; Pena, H.F.J.; Horta, M.C.; Cavalcante, P.H.; Fortes, K.P.; et al. Occurrence of antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii and its isolation and genotyping in donkeys, mules, and horses in Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 209, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gennari, S.M.; Pena, H.F.J.; Lindsay, D.S.; Lopes, M.G.; Soares, H.S.; Cabral, A.D.; Vitaliano, S.N.; Amaku, M. Prevalence of antibodies against Neospora spp. and Sarcocystis neurona in donkeys from northeastern Brazil. Braz. J. Veterenary Parasitol. 2016, 25, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, I.F.; Crispim, C.G.; Millar, P.R.; Juliano, R.S.; Nogueira, M.F.; Araujo, M.T.B.D.; Marques-Santos, F.; Amendoeira, M.R.R. Toxoplasmose ovina e equina: Ocorrência de anticorpos em animais criados em centro de pesquisa na região do Pantanal Sul Mato-grossense, Brasil. Veterinária Zootec. 2021, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.W.L.; Vilela, V.L.R.; Feitosa, T.F. Parasitic profile of traction equids in the semi-arid climate of Paraíba State, Northeastern, Brazil. Braz. J. Veterenary Parasitol. 2018, 27, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llano, H.A.B.; Soares, R.M.; Acevedo-Gutierrez, L.Y.; Rodas, J.D.; Polo, G.; Borges-Silva, W.; Jesus, R.F.; Gondim, L.F.P. Seroepidemiology of Sarcocystis neurona and Neospora spp. in horses, donkeys, and mules from Colombia. Acta Trop. 2021, 220, 105970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.M.; Ayaz, M.M.; Ahmed, A.N.; Rasheed, I.; Faraz, A.; Akram, Q.; Akhtar, S.; Maqbool, A.; Tabassum, S.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors for IgG antibodies to Neospora spp. in three types of equids from Southern Punjab, Pakistan. Acta Trop. 2018, 188, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.P.B.; Pacheco, P.S. Caracterização, inserção e resistência de muares. Nucl. Anim. 2017, 9, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.L.F. Hábitos Peculiares de Comportamento dos Asininos e Muares; Associação Brasileira de Criadores de Jumento Pêga: Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- James, K.E.; Smith, W.A.; Packham, A.E.; Conrad, P.A.; Pusterla, N. Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence and association with equine protozoal myeloencephalitis: A case-control study of Californian horses. Vet. J. 2017, 224, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bártová, E.; Machacová, T.; Sedlák, K.; Budíková, M.; Mariani, U.; Veneziano, V. Seroprevalence of antibodies of Neospora spp. and Toxoplasma gondii in horses from southern Italy. Folia Parasitol. 2015, 62, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Murata, F.H.A.; Cerqueira-Cezar, C.K.; Kwok, O.C.H. Toxoplasma gondii infections in horses, donkeys, and other equids: The last decade. Res. Vet. Sci. 2020, 132, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirosh-Levy, S.; Steinman, A.; Minderigiu, A.; Arieli, O.; Savitski, I.; Fleiderovitz, L.; Edery, N.; Schvartz, G.; Mazuz, L.M. High Exposure to Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora spp. in Donkeys in Israel: Serological Survey and Case Reports. Animals 2020, 10, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munhoz, A.D.; Souza, M.A.; Costa, S.C.L.; Freitas, J.S.; Silva, A.N.D.; Lacerda, L.C.; Cruz, R.D.S.; Albuquerque, G.R.; Pereira, M.J.S. Factors associated with the distribution of natural Toxoplasma gondii infection among equids in Northeastern Brazil. Braz. J. Veterenary Parasitol. 2019, 28, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, Z.; Borujeni, M.P.; Ghorbanpoor, M.; Mashhadi, A.R.G. Seroprevalence and risk factors of brucellosis in Arabian horses. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, R.; Winslow, G.M. IgM in microbial infections: Taken for granted? Immunol. Lett. 2009, 125, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ni, H.-B.; Ren, W.-X.; Jiang, J.; Gong, Q.-L.; Zhang, X.-X. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in horses: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Trop. 2020, 201, 105222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, E.M.C.; Furman, K.E.; Lara, M.; Cunha, E.M.S.; Finger, M.A.; Busch, A.P.B.; De Barros, I.R.; Deconto, I.; DornBusch, P.T.; Biondo, A.W. Detection of Neospora sp. antibodies in cart horses from urban areas of Curitiba, Southern Brazil. Braz. J. Veterenary Parasitol. 2012, 21, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bártová, E.; Sedlák, K.; Kobédová, K.; Budíková, M.; Joel Atuman, Y.; Kamani, J. Seroprevalence and risk factors of Neospora spp. and Toxoplasma gondii infections among horses and donkeys in Nigeria, West Africa. Acta Parasitol. 2017, 62, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomares, C.; Ajzenberg, D.; Bornard, L.; Bernardin, G.; Hasseine, L.; Darde, M.L.; Marty, P. Toxoplasmosis and horse meat, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1327–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machacová, T.; Bártová, E.; Di Loria, A.; Sedlák, K.; Guccione, J.; Fulgione, D.; Veneziano, V. Seroprevalence and risk factors of Neospora spp. in donkeys from Southern Italy. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 198, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waap, H.; De Oliveira, U.V.; Nunes, T.; Gomes, J.; Gomes, T.; Barwald, A.; Munhoz, A.D.; Schares, G. Serological survey of Neospora spp. and Besnoitia spp. in horses in Portugal. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2020, 20, 100391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable/ Category | Total Equids | Positives Anti-T. gondii | % (CI) | p | Positives Anti-N. caninum | % (CI) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | |||||||
| Horse | 76 | 12 | 15.8 (9.7–21.9) | 0.748 | 3 | 4 (2.2–5.8) | 0.889 |
| Donkey | 91 | 13 | 14.3 (10.8–17.8) | 5 | 5.5 (3.6–7.4) | ||
| Mule | 155 | 19 | 12.2 (10–14.4) | 8 | 5.1 (3.5–6.7) |
| Positivity of Anti-T. gondii Antibodies | |||||
| Titration | 1:64 | 1:128 | 1:256 | 1:512 | 1:1.024 |
| Total (%) | 31 (70.4) | 9 (20.4) | 1 (2.3) | 1 (2.3) | 2 (4.6) |
| Positivity of Anti-N. caninum Antibodies | |||||
| Titration | 1:50 | 1:100 | 1:200 | 1:400 | 1:800 |
| Total (%) | 15 (93.7) | 1 (6.3) | - | - | - |
| Variable/Category | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total of Equids | Positive Anti-T. gondii (%) | p | OR | CI | p | |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male | 138 | 19 (13.8) | >0.999 | |||
| Female | 184 | 25 (13.6) | ||||
| Age | ||||||
| ≤4 years | 72 | 14 (19.4) | 0.177 * | 0.460 | 0.20–1.05 | 0.063 |
| 5–9 years | 130 | 13 (10) | Ref. | |||
| 10–13 years | 120 | 17 (14.2) | 0.841 | 0.37–1.88 | 0.671 | |
| Feed | ||||||
| Pasture | 144 | 20 (13.9) | 0.992 | |||
| Pasture + Corn | 140 | 19 (13.6) | ||||
| Pasture + Commercial Food | 38 | 5 (13.1) | ||||
| Contact with Cats | ||||||
| Yes | 274 | 39 (14.2) | 0.649 | |||
| No | 48 | 5 (10.4) | ||||
| Time of Work | ||||||
| ≤3 years | 40 | 1 (2.5) | 0.025 * | Ref. | ||
| ≥4 years | 282 | 43 (15.2) | 6.050 | 4.38–8.54 | <0.0001 | |
| Variable/Category | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total of Equids | Positives Anti-N. caninum (%) | p | OR | CI | p | |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male | 138 | 4 (2.9) | 0.195 * | 1.139 | 0.48–2.63 | 0.7595 |
| Female | 184 | 12 (6.5) | Ref. | |||
| Age | ||||||
| ≤4 years | 72 | 2 (2.8) | 0.475 | |||
| 5–13 years | 129 | 6 (4.6) | ||||
| 10–13 years | 120 | 8 (6.7) | ||||
| Feed | ||||||
| Pasture | 144 | 8 (5.5) | 0.882 | |||
| Pasture + Corn | 140 | 6 (4.2) | ||||
| Pasture + Commercial Food | 38 | 2 (5.3) | ||||
| Contact with dogs | ||||||
| Yes | 237 | 14 (5.9) | 0.254 | |||
| No | 85 | 2 (2.3) | ||||
| Time of Work | ||||||
| ≤3 years | 40 | 1 (2.5) | 0.703 | |||
| ≥4 years | 282 | 15 (5.3) | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, P.W.L.; Oliveira, C.S.M.; Bezerra, R.A.; Alvares, F.B.V.; Formiga, V.H.A.S.; Martins, M.R.D.D.; Feitosa, T.F.; Vilela, V.L.R. Anti-Toxoplasma gondii and Anti-Neospora caninum Antibodies in Urban Traction Equids in Northeast Brazil: Seroprevalence and Risk Factors. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8040234
Costa PWL, Oliveira CSM, Bezerra RA, Alvares FBV, Formiga VHAS, Martins MRDD, Feitosa TF, Vilela VLR. Anti-Toxoplasma gondii and Anti-Neospora caninum Antibodies in Urban Traction Equids in Northeast Brazil: Seroprevalence and Risk Factors. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2023; 8(4):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8040234
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Paulo Wbiratan Lopes, Clarisse Silva Menezes Oliveira, Roberto Alves Bezerra, Felipe Boniedj Ventura Alvares, Victor Hugo Alves Sousa Formiga, Marianne Rachel Domiciano Dantas Martins, Thais Ferreira Feitosa, and Vinícius Longo Ribeiro Vilela. 2023. "Anti-Toxoplasma gondii and Anti-Neospora caninum Antibodies in Urban Traction Equids in Northeast Brazil: Seroprevalence and Risk Factors" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 8, no. 4: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8040234
APA StyleCosta, P. W. L., Oliveira, C. S. M., Bezerra, R. A., Alvares, F. B. V., Formiga, V. H. A. S., Martins, M. R. D. D., Feitosa, T. F., & Vilela, V. L. R. (2023). Anti-Toxoplasma gondii and Anti-Neospora caninum Antibodies in Urban Traction Equids in Northeast Brazil: Seroprevalence and Risk Factors. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 8(4), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed8040234