Epidemiological Profile of a Human Hepatitis E Virus Outbreak in 2018, Chattogram, Bangladesh
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Case Definition and Data Collection Procedures
2.4. HEV Infection Data
2.5. Remotely Sensed Environmental Data and Extraction
2.6. Data Analysis
2.6.1. Descriptive Analyses
2.6.2. Temporal Cross-Correlation between HEV Infection Incidence and Environmental Factors
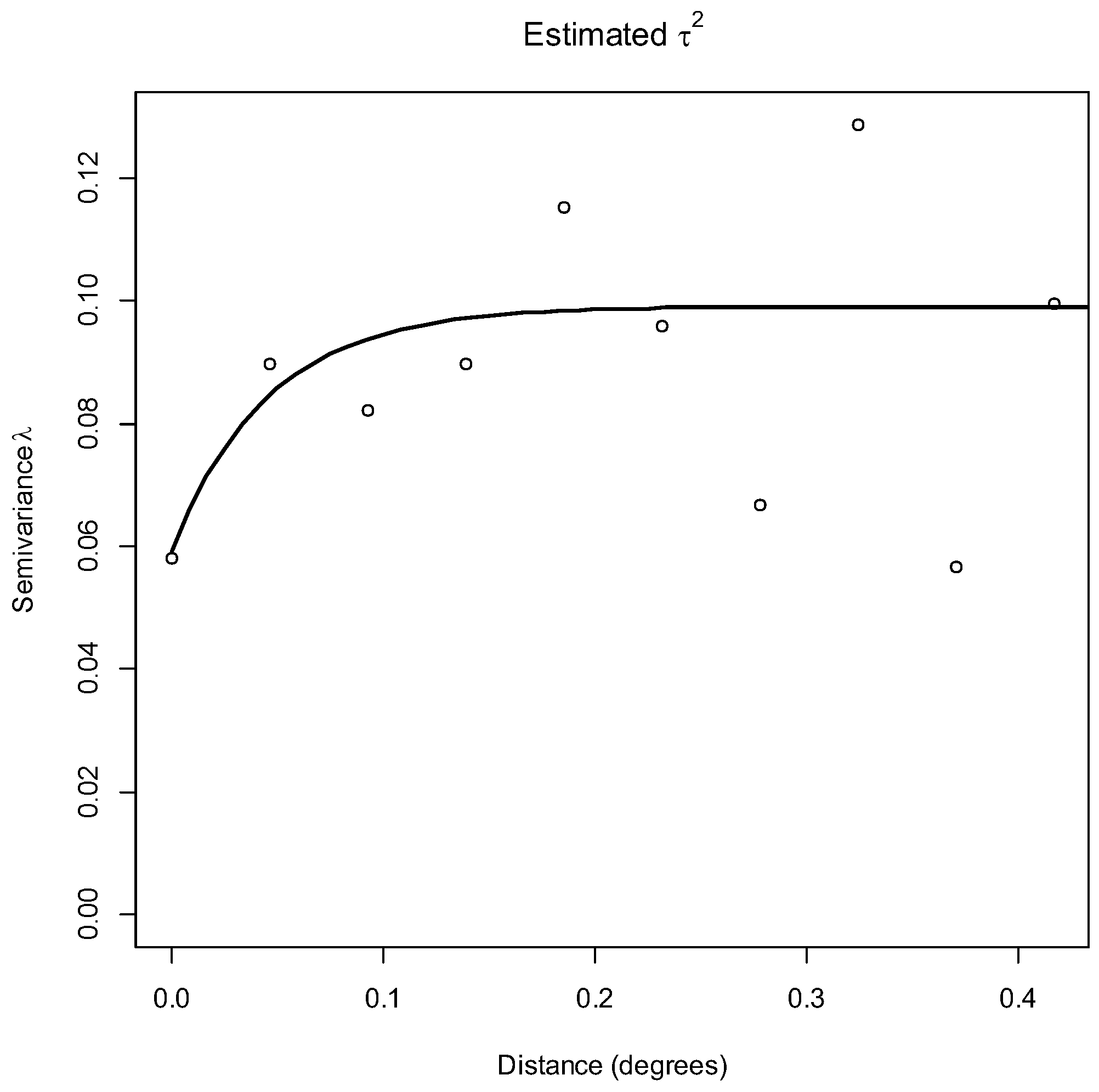
2.6.3. Spatial Analysis Pipeline
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analyses
3.2. Temporal Variation in HEV Infection and Associated Risk Factors
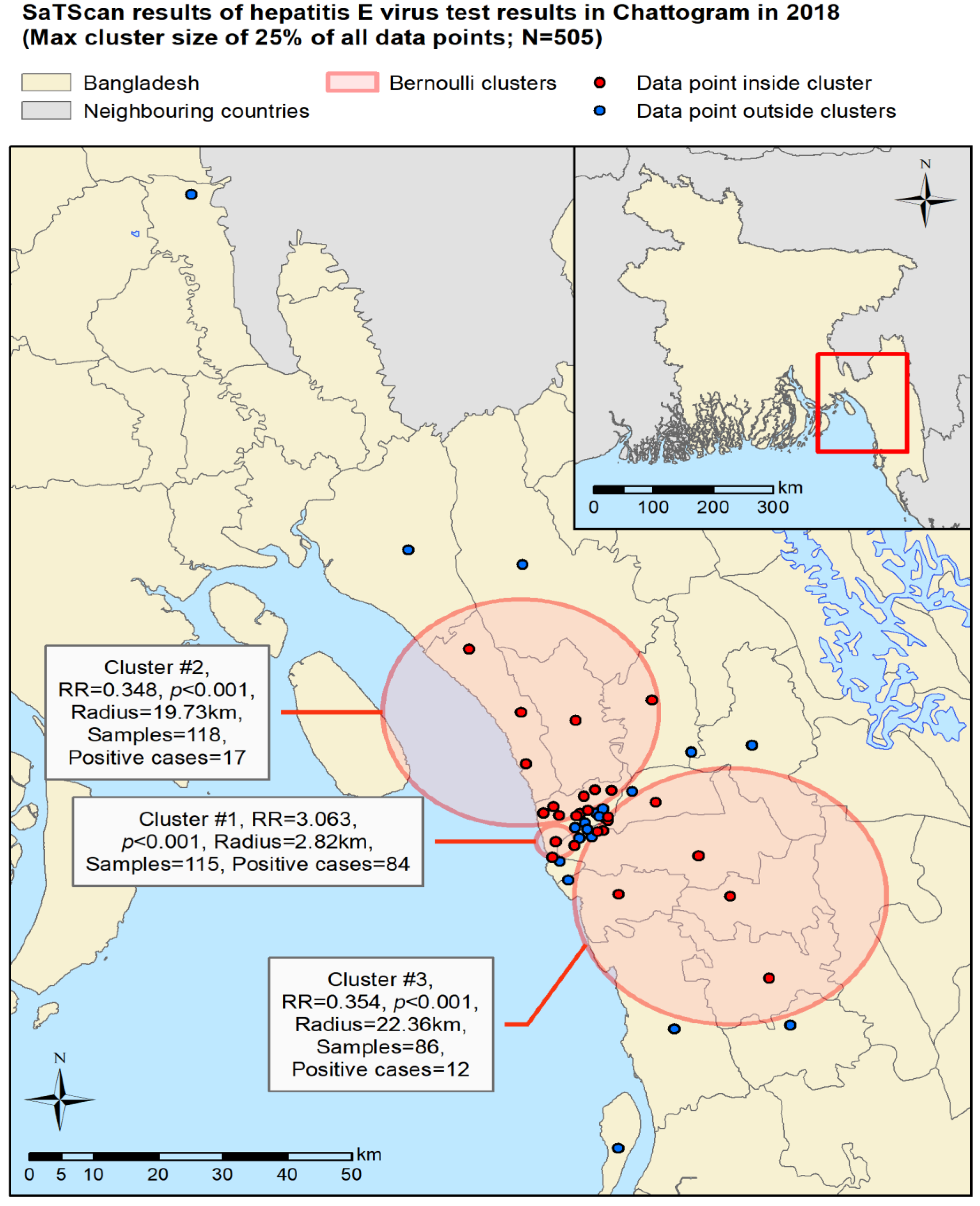
3.3. Spatial Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. Overall Findings
4.2. Association between Risk of HEV Infection and Demographics
4.3. Association between Risk of HEV Infection and Drinking Water Source and Boiling of Water
4.4. Association between Risk of HEV Infection and Climate
4.5. Possible Confounding Risk Factors of HEV Infection
4.6. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis E. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-e (accessed on 7 May 2022).
- Paul, W.; Supharerk, T.; Thammasin, I.; Wikrom, K. Hepatitis E in Southeast Asia. Siriraj Hosp. Gaz. 2020, 72, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. (Ed.) Hepatitis E Virus; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Waterborne Outbreaks of Hepatitis E: Recognition, Investigation and Control: Technical Report. 2014. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789241507608 (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- Rein, D.B.; Stevens, G.A.; Theaker, J.; Wittenborn, J.S.; Wiersma, S.T. The global burden of hepatitis E virus genotypes 1 and 2 in 2005. Hepatology 2012, 55, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkakoti, J.; Hazam, R.K.; Mohammad, A.; Kumar, A.; Kar, P. Does high viral load of hepatitis E virus influence the severity and prognosis of acute liver failure during pregnancy? J. Med. Virol. 2013, 85, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurley, E.S.; Hossain, M.J.; Paul, R.C.; Sazzad, H.M.S.; Islam, M.S.; Parveen, S.; Faruque, L.I.; Husain, M.; Ara, K.; Jahan, Y.; et al. Outbreak of Hepatitis E in Urban Bangladesh Resulting in Maternal and Perinatal Mortality. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denner, J. Hepatitis E virus (HEV)-The future. Viruses 2019, 11, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Labrique, A.B.; Zaman, K.; Hossain, Z.; Saha, P.; Yunus, M.; Hossain, A.; Ticehurst, J.; Nelson, K.E. Population Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus Antibodies in Rural Bangladesh. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 81, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carratalà, A.; Joost, S. Population density and water balance influence the global occurrence of hepatitis E epidemics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haque, F.; Banu, S.S.; Ara, K.; Chowdhury, I.A.; Chowdhury, S.A.; Kamili, S.; Rahman, M.; Luby, S.P. An outbreak of hepatitis E in an urban area of Bangladesh. J. Viral Hepat. 2015, 22, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yugo, D.M.; Meng, X.J. Hepatitis E virus: Foodborne, waterborne and zoonotic transmission. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 4507–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuthi, M.F.R.; Biwas, M.; Bahar, M.N. Assessment of supply water quality in the Chittagong city of Bangladesh. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2009, 4, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kmush, B.; Wierzba, T.; Krain, L.; Nelson, K.; Labrique, A.B. Epidemiology of Hepatitis E in Low- and Middle-Income Countries of Asia and Africa. Semin. Liver Dis. 2013, 33, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.H. Hepatitis E: Major Outbreaks in Bangladesh. 2018. Available online: https://iedcr.gov.bd/nbph/issue-sections/1ff3b5d9-35dd-4bb3-bb71-33797ea1b5f4 (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Sarkar, J. Seroprevalence of Hepatitis-E Virus Infection among Patients Attending Different Hospitals at Chattogram, 2018. Master’s Thesis, Chattogram Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Chattogram, Bangladesh, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A. Hepatitis E Outbreak in Chittagong City. 2018. Available online: https://archive.dhakatribune.com/health/2018/06/27/hepatitis-e-outbreak-in-chittagong-city (accessed on 12 June 2022).
- Daily Sun. Hepatitis E Breaks Out in Port City. 2018. Available online: https://www.daily-sun.com/printversion/details/318535/Hepatitis-E-breaksout-in-port-city (accessed on 12 June 2022).
- Alam, H.M.; Maruf, A.; Khan, M.H.; Billah, M.M.; Uzzaman, M.S.; Flora, M.S. Hepatitis outbreak in Halishahor, Chattagram, Bangladesh. In Proceedings of the 9th Southeast Asia & Western Pacific Bi-regional TEPHINET Scientific Conference, Vientiane, Laos, 5–9 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dhewantara, P.W.; Hu, W.; Zhang, W.; Yin, W.-W.; Ding, F.; Mamun, A.A.; Soares Magalhães, R.J. Climate variability, satellite-derived physical environmental data and human leptospirosis: A retrospective ecological study in China. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, R.S.; Delmelle, E.; Eberth, J.M. Advances in spatial epidemiology and geographic information systems. Ann. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, G.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, B. Identifying flood-related infectious diseases in Anhui Province, China: A spatial and temporal analysis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopka, T.J.; Goulart, M.A.; Meyers, D.J.; Hutcheson, M.; Barton, K.; Onofrey, S.; Church, D.; Donahue, A.; Chui, K.K.H. Identifying and characterizing hepatitis C virus hotspots in Massachusetts: A spatial epidemiological approach. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, B.; Liu, J.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Mao, Y. Spatio-temporal epidemiology of viral hepatitis in China (2003-2015): Implications for prevention and control policies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khatun, M.A.; Rashid, M.B.; Hygen, H.O. Climate of Bangladesh. 2018. Available online: http://bmd.gov.bd/file/2016/08/17/pdf/21827.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Bangladesh Meteorological Department. Normal Monthly Humidty. 2018. Available online: http://bmd.gov.bd/file/2016/08/17/pdf/21827.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics. Bangladesh Population and Housing Census 2011-National Report Volume-03: Urban Area Report. 2014. Available online: http://www.bbs.gov.bd/site/page/47856ad0-7e1c-4aab-bd78-892733bc06eb/Population-and-Housing-Census (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Beijing Wantai Biological Pharmacy Enterprise Co., Ltd. Hepatitis E Virus Markers ELISAs. 2020. Available online: https://www.ystwt.cn/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/Wantai-HEV-IgG-ELISA.pdf (accessed on 7 May 2022).
- Vermote, E. MODIS/Terra Surface Reflectance 8-Day L3 Global 500m SIN Grid V061. 2021. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mod09a1v061/ (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Li, X.; Asrar, G.R. A global seamless 1 km resolution daily land surface temperature dataset (2003–2020). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Stocker, E.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Tan, J. Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for GPM (IMERG), Version 06B. 2020. Available online: https://arthurhouhttps.pps.eosdis.nasa.gov/gpmdata/YYYY/MM/DD/gis/ (accessed on 19 March 2022).
- Jarvis, A.; Reuter, H.I.; Nelson, A.; Guevara, E. Hole-filled Seamless SRTM Data V4. 2008. Available online: https://srtm.csi.cgiar.org (accessed on 26 March 2022).
- Hijmans, R. DIVA-GIS. 2022. Available online: https://www.diva-gis.org/ (accessed on 26 March 2022).
- Environmental Systems Research Institute. ArcGIS Desktop: Release 10.8.1. 2020. Available online: https://www.esri.com (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2021. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Kulldorf, M. SaTScan™ v10.0.2: Software for the Spatial and Space-Time Scan Statistics. 2022. Available online: https://www.satscan.org (accessed on 26 April 2022).
- Selker, R.; Love, J.; Dropmann, F.; Moreno, V. jmv R Package (version 2.3.4). 2022. Available online: https://www.jamovi.org/jmv/ (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software: Release 13. 2013. Available online: https://www.stata.com (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Pfeiffer, D.; Robinson, T.P.; Stevenson, M.; Stevens, K.B.; Rogers, D.J.; Clements, A.C.A. Chapter 6: Spatial variation in risk. In Spatial Analysis in Epidemiology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 76–77. [Google Scholar]
- Talaat, M.; Afifi, S.; Reaves, E.J.; Abu Elsood, H.; El-Gohary, A.; Refaey, S.; Hammad, R.; Abdel Fadeel, M.; Kandeel, A. Evidence of sustained reductions in the relative risk of acute hepatitis B and C virus infections, and the increasing burden of hepatitis a virus infection in Egypt: Comparison of sentinel acute viral hepatitis surveillance results, 2001–2017. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyessa, A.B.; Mengesha, M.; Belay, D.; Tayachew, A.; Ayele, W.; Beyene, B.; Kassa, W.; Zemelak, E.; Demissie, G.; Amare, B.; et al. Epidemiology of influenza in Ethiopia: Findings from influenza sentinel surveillance and respiratory infection outbreak investigations, 2009–2015. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azman, A.S.; Paul, K.K.; Bhuiyan, T.R.; Koyuncu, A.; Salje, H.; Qadri, F.; Gurley, E.S. Hepatitis E in Bangladesh: Insights From a National Serosurvey. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, S805–S812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anower, A.K.M.; Ahmed, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Hasan, A.; Islam, M.A.; Rahman, L. Hygienic Farming System Improved Pig-Rearers Livelihood Status in South-West Region of Bangladesh. Int. J. Avian Wildl. Biol. 2017, 2, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, T.C.; Eom, K.S.; Choe, S.; Islam, S.; Sabuj, S.S.; Saha, E.; Tuhin, R.H.; Ndosi, B.A.; Kang, Y.; Kim, S.; et al. Insights to helminth infections in food and companion animals in Bangladesh: Occurrence and risk profiling. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2022, 17, e00245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank. Climate Change in Bangladesh: Impact on Infectious Diseases and Mental Health. 2021. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/feature/2021/10/07/climate-change-in-bangladesh-impact-on-infectious-diseases-and-mental-health (accessed on 9 May 2022).
- Nahar, N.; Uddin, M.; Sarkar, R.A.; Gurley, E.S.; Khan, M.S.U.; Hossain, M.J.; Sultana, R.; Luby, S.P. Exploring pig raising in Bangladesh: Implications for public health interventions. Vet. Ital. 2013, 49, 7–17. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Poel, W.H.M. Food and environmental routes of Hepatitis E virus transmission. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 4, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meester, M.; Tobias, T.J.; Bouwknegt, M.; Kusters, N.E.; Stegeman, J.A.; van der Poel, W.H.M. Infection dynamics and persistence of hepatitis E virus on pig farms-a review. Porcine Health Manag. 2021, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, L.C.; DiCaprio, E. Hepatitis E Virus: An Emerging Foodborne Pathogen. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, N.; Khan, M.S.U.; Hossain, M.B.; Sazzad, H.M.S.; Rahman, M.Z.; Ahmed, F.; Zeidner, N.S. Serological evidence of hepatitis E virus infection in pigs and jaundice among pig handlers in Bangladesh. Zoonoses Public Health 2017, 64, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, Z.; Hook, S.; Hulley, G. MODIS/Terra Land Surface Temperature/Emissivity 8-Day L3 Global 1 km SIN Grid V061. 2021. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/products/mod11a2v061/ (accessed on 19 March 2022).
- Shiff, S.; Helman, D.; Lensky, I.M. Worldwide continuous gap-filled MODIS land surface temperature dataset. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Environmental Variable | Resolution | Temporal Range | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Land surface temperature (LST) | 1 km | Daily | [30] |
| Precipitation | 0.1 degrees | Daily | [31] |
| Elevation | 0.00083 degrees | N/A | [32] |
| Inland water bodies 1 | Vector | N/A | [33] |
| Modified normalised difference water index (MNDWI) 2 | 500 m | 8 day average | [29] |
| Normalised difference vegetation index (NDVI) 2 | 500 m | 8 day average | [29] |
| Variable | Category | HEV Test Result | Proportion of All Patients (N = 505) | Pearson’s Chi-Squared Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seronegative | Seropositive | Total | ||||
| Age | 0–20 | 59 (68.60%) | 27 (31.40%) | 86 | 17.03% | chi2 = 4.78, p = 0.189 |
| 21–40 | 182 (65.00%) | 98 (35.00%) | 280 | 55.45% | ||
| 41–60 | 65 (58.56%) | 46 (41.44%) | 111 | 21.98% | ||
| 61+ | 22 (78.57%) | 6 (21.43%) | 28 | 5.54% | ||
| Sex | Male | 169 (58.89%) | 118 (41.11%) | 287 | 56.83% | chi2 = 10.74, p = 0.001 |
| Female | 159 (72.94%) | 59 (27.06%) | 218 | 43.17% | ||
| Source of drinking water | Shallow tube well | 181 (83.41%) | 36 (16.59%) | 217 | 42.97% | chi2 = 90.71, p < 0.001 |
| Deep tube well | 74 (73.27%) | 27 (26.73%) | 101 | 20.00% | ||
| WASA | 73 (39.04%) | 114 (60.96%) | 187 | 37.03% | ||
| Boiling of water | No | 248 (59.05%) | 172 (40.95%) | 420 | 83.17% | chi2 = 38.19, p < 0.001 |
| Yes | 80 (94.12%) | 5 (5.88%) | 85 | 16.83% | ||
| Variable | Predictor | Coefficient | Standard Error | p-Value | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (reference: male) | Female | −0.118 | 0.034 | 0.001 | (−0.186, −0.051) |
| Age category (reference: 0–20 years) | 21−40 | 0.035 | 0.047 | 0.458 | (−0.057, 0.127) |
| 41−60 | 0.146 | 0.055 | 0.007 | (0.039, 0.253) | |
| 60+ | −0.108 | 0.083 | 0.190 | (−0.271, 0.054) | |
| Source of drinking water (reference: shallow tube well) | Deep tube well | 0.124 | 0.047 | 0.009 | (0.032, 0.216) |
| WASA | 0.444 | 0.047 | 0.000 | (0.353, 0.535) | |
| Boiling of drinking water (reference: no) | Yes | −0.504 | 0.047 | 0.000 | (−0.596, −0.412) |
| Environment time Lag effect | Precipitation (lag 8 days) | 0.086 | 0.023 | 0.000 | (0.041, 0.131) |
| Precipitation (lag 48 days) | −0.098 | 0.024 | 0.000 | (−0.145, −0.051) | |
| Precipitation (lag 72 days) | 0.022 | 0.018 | 0.206 | (−0.012, 0.057) | |
| MNDWI (lag 40 days) | 0.049 | 0.021 | 0.022 | (0.007, 0.091) | |
| LST (lag 8 days) | 0.029 | 0.020 | 0.155 | (−0.011, 0.069) | |
| Intercept | 0.235 | 0.049 | 0.000 | (0.140, 0.330) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Owada, K.; Sarkar, J.; Rahman, M.K.; Khan, S.A.; Islam, A.; Hassan, M.M.; Soares Magalhães, R.J. Epidemiological Profile of a Human Hepatitis E Virus Outbreak in 2018, Chattogram, Bangladesh. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7080170
Owada K, Sarkar J, Rahman MK, Khan SA, Islam A, Hassan MM, Soares Magalhães RJ. Epidemiological Profile of a Human Hepatitis E Virus Outbreak in 2018, Chattogram, Bangladesh. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2022; 7(8):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7080170
Chicago/Turabian StyleOwada, Kei, Joyantee Sarkar, Md. Kaisar Rahman, Shahneaz Ali Khan, Ariful Islam, Mohammad Mahmudul Hassan, and Ricardo J. Soares Magalhães. 2022. "Epidemiological Profile of a Human Hepatitis E Virus Outbreak in 2018, Chattogram, Bangladesh" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 7, no. 8: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7080170
APA StyleOwada, K., Sarkar, J., Rahman, M. K., Khan, S. A., Islam, A., Hassan, M. M., & Soares Magalhães, R. J. (2022). Epidemiological Profile of a Human Hepatitis E Virus Outbreak in 2018, Chattogram, Bangladesh. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 7(8), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed7080170









