History, Rats, Fleas, and Opossums. II. The Decline and Resurgence of Flea-Borne Typhus in the United States, 1945–2019
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Decline of Flea-Borne Typhus, 1945–1990
3. The Advent of New Rodenticides and Integrated Rodent Control
4. Two Immunization Campaigns Against Flea-Borne Typhus
5. Advances in Diagnostic Testing for Flea-Borne Typhus
6. Nomenclature of Flea-Borne Typhus and Its Etiological Agent
7. The Treatment of Flea-Borne Typhus
8. Another Organism Causing Flea-Borne Typhus Is Discovered
9. Epidemiologic Trends in Current High-Incidence Areas (Texas, California, Hawaii). General Considerations
10. Flea-Borne Typhus in Texas, 1940s to Present
11. Flea-Borne Typhus in California, 1915–2019
12. Flea-Borne Typhus in Hawaii
13. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Image Credits
Abbreviations
| ANTU | Alpha-Naphthylthiourea |
| CC | Corpus Christi (Texas) |
| CDC | Center for Disease Control (of the United States) |
| CF | complement fixation (serologic test) |
| DDT | dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane |
| FBT | flea-borne typhus |
| HDH | Hawaii Dept of Health |
| NIH | National Institutes of Health (of the United States) |
| OC | Orange County (California) |
| PABA | para-aminobenzoic acid |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| PTU | phenylthiourea |
| RMSF | Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever |
| TGR | Typhus group rickettsioses |
| TDHS | Texas Dept of Health Services |
| TNR | trap-neuter-return |
| WFt | Weil-Felix test |
References
- Chueng, T.A.; Koch, K.R.; Anstead, G.M.; Agarwal, A.N.; Dayton, C.L. Case Report: Early doxycycline therapy for potential rickettsiosis in critically ill patients in flea-borne typhus-endemic areas. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 101, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, A.F. Epidemiology of murine typhus. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 1990, 35, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.D.; Banajee, K.H.; Foil, L.D.; Macaluso, K.R. Transmission mechanisms of an emerging insect-borne rickettsial pathogen. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstead, G.M. History, rats, fleas, and opossums: The ascendency of flea-borne typhus in the United States, 1910–1944. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smadel, J.E. Status of the rickettsioses in the United States. Ann. Intern. Med. 1959, 51, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, H.D. The changing picture of murine typhus in the United States. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1958, 70, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, T.G.; Rawlings, J.A.; Taylor, J.; Davis, B.L. Endemic typhus in Texas. Texas Med. 1983, 79, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Typhus fevers. Historical trends. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/typhus/murine/history.html (accessed on 5 September 2019).
- White, P.C., Jr. A brief historical review of murine typhus in Virginia and the United States. Va. Med. Mon. 1970, 97, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Cushing, E.C. History of Entomology in World War II; Smithsonian Institution: Washington, DC, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Busvine, J.R. Disease Transmission by Insects: Its Discovery and 90 Years of Efforts to Prevent It; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Stuart-Harris, C.H. Rickettsial Diseases. In Virus and Rickettsial Diseases of Man, 4th ed.; Bedson, S., Downie, A.W., MacCallum, F.O., Stuart-Harris, C.H., Eds.; Edward Arnold Publishers: London, UK, 1967; pp. 410–449. [Google Scholar]
- Soper, F.L.; Davis, W.A.; Markham, F.S.; Riehl, L.A. Typhus fever in Italy, 1943–1945, and its control with louse powder. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1947, 45, 305–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.E. The use of DDT to control murine typhus fever in San Antonio, Texas. Public Health Rep. 1947, 62, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas Morning News. Texas Almanac and State Industrial Guide; A.H. Belo Corp.: Dallas, TX, USA, 1940–1941. [Google Scholar]
- Dallas Morning News. Texas Almanac and State Industrial Guide; A.H. Belo Corp.: Dallas, TX, USA, 1945–1946. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D.R. San Antonio. The vicissitudes of boosterism. In Sunbelt Cities. Politics and Growth Since World War II.; Bernard, R.M., Rice, B.R., Eds.; University of Texas Press: Austin, TX, USA, 1983; pp. 235–254. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, D.E.; Pollard, M. The distribution of murine typhus in rats and in humans in San Antonio. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1946, 26, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, C.C. Charles Franklin Craig: Fifty years of work and service in tropical medicine. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1952, 1, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christian, J.J. In memoriam: David E. Davis, 1913–1994. Auk 1995, 112, 491–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.E.; Pollard, M. Prevalence of typhus complement-fixing antibodies in human serums in San Antonio, Tex. Public Health Rep. 1946, 61, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.E. Observations on rat ectoparasites and typhus fever in San Antonio, Texas. Public Health Rep. 1951, 66, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.L. Texas Ready to Lay Real Siege to Typhus Scourge, Gets U.S. Aid; Lubbock Morning Avalanche: Lubbock, TX, USA, 13 July 1945. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Rat Eradication Only Preventative of Typhus Fever; Shiner Gazette: Shiner, TX, USA, 15 May 1947. [Google Scholar]
- Wiley, J.S.; Fritz, R.F. Tentative report on expanded murine typhus fever control operations in southern states. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1948, 28, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, C.O. Results of cooperative state-federal typhus control programs. CDC Bull. 1950, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- United States Public Health Service. DDT for the control of murine typhus fever. Atlanta, GA, USA, 1946. Available online: http://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/20784 (accessed on 15 July 2016).
- Wiley, J.S. A preliminary report concerning DDT dusting and murine typhus fever in nine southeastern states. Public Health Rep. 1948, 63, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werkheiser, A.C. New Orleans rids docks of rats. Murine typhus deterred. J. Environ. Health 1973, 36, 234–236. [Google Scholar]
- Strandtmann, R.W.; Eben, D.J. A survey of typhus in rats and rat ectoparasites in Galveston, Texas. Tex. Rep. Biol. Med. 1953, 11, 144–151. [Google Scholar]
- Love, G.J.; Smith, W.W. Murine typhus investigations in Southwestern Georgia: A review. Public Health Rep. 1960, 75, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.W. Rat, flea, and murine typhus recurrence following eradication measures. Public Health Rep. 1958, 73, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, E.L.; Morlan, H.B.; Utterback, B.C.; Schubert, J.H. Evaluation of county-wide DDT dusting operations in murine typhus control (1946 through 1949). Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1951, 41, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mohr, C.O.; Smith, W.W. Eradication of murine typhus fever in a rural area: Preliminary report. Bull. WHO 1957, 16, 255–266. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, D.E.; Christian, J.J. Population consequences of a sustained yield program for Norway Rats. Ecology 1958, 39, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.W.A.; Pal, R. Insecticide Resistance in Arthropods; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Ganzel, B. Farming in the 1940s: Aerial crop dusting. Wessels Living History Farm. Available online: https://livinghistoryfarm.org/farminginthe40s/pests_04.html (accessed on 30 March 2020).
- Casida, J.E.; Quistad, G.B. Golden age of insecticide research: Past, present, or future? Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1998, 43, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimmer, J.D.; Gammon, D.W. Insecticides. In Kirk-Othmer Concise Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 5th ed.; Kirk, R.E., Othmer, D.F., Seidel, A., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 1351–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Helms, D. Pest Control. In The Encyclopedia of Southern Culture; Wilson, C.R., Ferris, W., Eds.; University of North Carolina Press: Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 1989; pp. 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G.T. Living in the Environment, 12th ed.; Wadsworth/Thomson Learning: Belmont, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rickard, E.R.; Worth, C.B. Typhus Epidemiological Studies in Florida (RG 5.3: Series 200); Rockefeller Archive Center: Sleepy Hollow, NY, USA, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, E.A. What health officers can do to promote rat extermination. Am. J. Public Health 1921, 11, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Keiner, C. Wartime rat control, rodent ecology, and the rise and fall of chemical rodenticides. Endeavor 2005, 29, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. Elton, Charles Sutherland. Encyclopedia.com. Available online: http://www.encyclopedia.com/people/history/historians-miscellaneous-biographies/charles-s-elton (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- Davis, D.H. Current methods of controlling rodents and fleas in the campaign against bubonic plague and murine typhus. J. R. Sanit. Inst. 1949, 69, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emlen, J.T., Jr. Baltimore’s community rat control program. Am. J. Public Health 1947, 37, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kelly, D.J.; Richards, A.L.; Temenak, J.D.; Strickman, D.; Dasch, G.A. The past and present threat of rickettsial diseases to military medicine and international public health. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, S145–S169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.J.; Paris, D.H.; Newton, P.N. A systematic review of mortality from untreated scrub typhus (Orientia tsutsugamushi). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, J.C. Rodent control with 1080, ANTU, and other war-developed toxic agents. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1946, 36, 1427–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Link, V.B.; Mohr, C.O. Rodenticides in bubonic-plague control. Bull. World Health Organ. 1953, 9, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalmbach, E.R. “Ten-eighty”, a war-produced rodenticide. Science 1945, 102, 232–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J.H. 1080 (sodium fluoroacetate) poisoning of rats on ships. Public Health Rep. 1950, 65, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, D.M.; van Allen, A. Typhus Fever in California, 1916–1948, Inclusive; State of California Dept of Public Health: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Hood, G.A. Zinc phosphide—A new look at an old rodenticide for field rodents. In Proceedings of the 5th Vertebrate Pest Conference; Marsh, R.E., Ed.; University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 1972; Available online: http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/vpc5/16 (accessed on 6 March 2016).
- Wiley, J.S. Recent developments in murine typhus fever control. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1946, 36, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. Request and release slip for 1080 rodenticide. Malaria Control in War Areas Field Bull. 1946, Jan-Feb-Mar, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Vaccination of typhus personnel. Malaria Control in War Areas Field Bull. 1946, Jan-Feb-Mar, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, J.M. Development of the Communicable Disease Center. CDC Bull. 1946, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. We pay the Pied Piper. Am. J. Publ. Health 1948, 38, 1576–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Dept of Interior. Krug Appeals to Governors and Mayors on Rat Control. Press release, 2 March 1948. Available online: http://www.fws.gov/news/Historic/NewsReleases/1948/19480302.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2016).
- United States Dept of Interior. 200th City Signs for Rat Campaign. Press release, 4 April 1948. Available online: https://www.fws.gov/news/index.cfm?first=284 (accessed on 13 June 2012).
- United States Dept of Interior. 400 Cities Join Rat Campaign. Press release, 21 April 1948. Available online: https://www.fws.gov/news/index.cfm?first=284 (accessed on 6 March 2019).
- Blackwood, P.E. National urban rat control campaign. Sci. Educ. 1948, 32, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boston, R.J. Present status of typhus fever in Georgia. J. Med. Assoc. Ga. 1952, 41, 24–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Biehler, D.D. Pests in the City: Flies, Bedbugs, Cockroaches, and Rats; University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, D.E. The characteristics of rat populations. Q. Rev. Biol. 1953, 28, 373–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emlen, J.T.; Stokes, A.W.; Davis, D.E. Methods for estimating populations of Brown Rats in urban habitats. Ecology 1949, 30, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellton, H.L. Integrating public health and commercial rodent control. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1951, 41, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, F.E. Book review. Rat-borne diseases prevention and control. CDC Bull. 1950, 9, 24–25. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Training services. CDC Bull. 1950, 9, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Bote, G.S.; Laird, D.S. Roddy, the Rat; a Story of the Spread of Typhus Fever and of Ways of Getting Rid of Rats; Florida State Board of Health: Jacksonville, FL, USA, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- United States Dept of Health, Education, and Welfare. Communicable Disease Center Training Program Bulletin, July 1961 to June 1962; Communicable Disease Center: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- United States Army and Communicable Disease Center. T.F. 8-1673. Practical Rat Control: Ratproofing (film), 1950. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4lgS0X0YfPg (accessed on 6 April 2019).
- United States Army and Communicable Disease Center. T.F. 8-1674. Practical Rat Control: Rat Killing (film), 1950. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g9Zs_H6H6n0 (accessed on 6 April 2019).
- Anonymous. Typhus control training courses. Malaria Control War Areas Field Bull. 1946, Jan-Feb-Mar, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Stahmann, M.A.; Huebner, C.F.; Link, K.P. Studies on the hemorrhagic sweet clover disease. V. Identification and synthesis of the hemorrhagic agent. J. Biol. Chem. 1941, 138, 513–527. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, W.J.; Gaines, T.B. Control of Norway Rats with residual rodenticide Warfarin. Public Health Rep. 1950, 65, 1537–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirmohamed, M. Warfarin: Almost 60 years old and still causing problems. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 62, 509–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burris, R.H. Karl Paul Link (31 January 1901–21 November 1978); National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; Available online: http://www.nasonline.org/publications/biographical-memoirs/memoir-pdfs/link-karl.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2019).
- University of Wisconsin Archives. Paul Karl Link, 1945. Available online: https://search.library.wisc.edu/digital/A6IZE6FL5M6WI58K (accessed on 1 October 2018).
- University of Wisconsin Archives. WARF Display at Farm and Home Exhibit. Available online: https://search.library.wisc.edu/digital/AABKOKTHF2P4479B (accessed on 1 October 2018).
- Anonymous. Those destructive rats. Tex. Health Bull. 1953, 6, 18–19. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, J.P. Typhus eradication demonstration project, Geneva County. J. Med. Assoc. State Ala. 1953, 22, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Phair, J.J. Comment in: Brigham, G.D.; Dyer, R.E. Endemic typhus fever in native rodents. JAMA 1938, 110, 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, R.E. Relevant Characteristics of Zinc Phosphide as a Rodenticide. In Proceedings of the Eighth Great Plains Wildlife Damage Control Workshop, Rapid City, SD, USA, 28–30 April 1987; Oresk, D.W., Schenbeck, G.L., Cefkin, R., Eds.; United States Department of Agriculture: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1987. Available online: http://digitalcommons.unl.edu/gpwdcwp/80/ (accessed on 26 August 2015).
- Greene, H.; McCroan, J.E. Residual typhus fever in Georgia. J. Med. Assoc. Ga. 1953, 42, 216–218. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, W.H.; Hines, V.D. Murine typhus fever in Southwest Georgia, January 1945–January 1953. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1954, 3, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, C.O.; Good, N.E.; Schubert, J.H. Status of murine typhus infection in domestic rats in the United States, 1952, and relation to infestation by Oriental Rat Fleas. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1953, 43, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.C., Jr. Murine typhus in the United States. Mil. Med. 1965, 130, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, H.D.; Wiseman, J.S. Fleas of Public Health Importance and Their Control; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1962; Available online: www.cdc_7681_DS1.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2018).
- Sherman, I.L.; Langmuir, A.D. Usefulness of communicable disease reports. Public Health Rep. 1952, 67, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fite, G.C. Cotton Fields No More. Southern Agriculture 1865–1980; University of Kentucky Press: Lexington, KY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Flynt, J.W. Dixie’s Forgotten People: The South’s Poor Whites; Indiana University Press: Bloomington, IN, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Tindall, G.B. The emergence of the new South 1913–1945 (Volume X). In A History of the South; Stephenson, W.H., Coulter, E.M., Eds.; Louisiana State University Press: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, E.F. The Southern Metropolis 1940–1976. In The City in Southern History. The Growth of Urban Civilization in the South; Brownell, B.A., Goldfield, D.R., Eds.; Kennikat Press: Port Washington, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Goldfield, D.R. Promised Land. The South Since 1945; Harlan Davidson: Arlington Heights, IL, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Roland, C.P. The Improbable Era. The South Since World War II; University of Kentucky Press: Lexington, KY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Beyer, G.H. Housing and Society; MacMillan: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, D.E. A perspective on rat control. Public Health Rep. 1952, 67, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anonymous. Rat Control Rejected. CQ Almanac 1967, 23rd ed.; Congressional Quarterly: Washington, DC, USA, 1968; pp. 13–446. Available online: http://library.cqpress.com/cqalmanac/cqal67-1314584 (accessed on 1 September 2016).
- McLaughlin, M. The Pied Piper of the ghetto: Lyndon Johnson, environmental justice, and the politics of rat control. Urban Hist. 2011, 37, 541–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anonymous. Urban rat control-United States. MMWR 1978, 28, 208–215. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Urban rat control-United States. MMWR 1982, 31, 259–260. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Urban rat control-United States. MMWR 1982, 31, 157. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. R.E.D. Facts. Sodium Fluoroacetate. Available online: https://www3.epa.gov/pesticides/chem_search/reg_actions/reregistration/fs_PC-075003_1-Jun-95.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2019).
- National Association of County and City Health Officials. Rodent Control and Public Health: An Assessment of U.S. Local Rodent Control Programs. Research Brief 2015. Available online: www.cdc.gov/nceh/ehs/docs/vector-profiles/assess-rodent-programs.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2019).
- Hawaii Dept of Health. Rodents: Rats and Mice. Available online: https://health.hawaii.gov/docd/files/2017/03/rodent-control-foldout-brochure.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2019).
- Louisiana Dept of Health. Murine Typhus Annual Report 2018. Available online: http://www.ldh.la.gov/assets/oph/Center-PHCH/Center-CH/infectiousepi/Annuals/MurineTyphus_LAIDAnnual.pdf (accessed on 17 March 2019).
- Bradley, G.H.; Wiley, J.S. The control of murine typhus in the United States. In Rickettsial Diseases of Man; Moulton, F.R., Ed.; American Association for the Advancement of Science: Washington, DC, USA, 1948; pp. 229–240. [Google Scholar]
- Irons, J.V.; Murphy, J.J.N.; Davis, D.E. The distribution of endemic typhus in rats in Lavaca County, Texas. Public Health Rep. 1948, 63, 692–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, R.M.; Ogden, L.J.; Eads, R.B. Entomological studies on typhus in Lavaca County, Texas. Tex. Rep. Biol. Med. 1948, 6, 444–452. [Google Scholar]
- Sadusk, J.F., Jr. Typhus fever in the United States Army following immunization: Incidence, severity of disease, modification of clinical course, and serologic diagnosis. JAMA 1947, 133, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. All of Hallettsville Citizens Immunized Against Typhus Fever; The Weimar Mercury: Weimar, TX, USA, 23 March 1945. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. People Here to Receive Free Typhus Vaccine Shots; Lavaca County Tribune: Hallettsville, TX, USA, 23 February 1945. [Google Scholar]
- Irons, J.V.; Cox, G.W. An epidemiological investigation of typhus fever in Texas, 1943–1945. Tex. State J. Med. 1946, 42, 332–336. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.W.; Schulze, W.H. Endemic typhus in Baltimore. South. Med. J. 1948, 41, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxcy, K.F. Clinical observations on endemic typhus (Brill’s Disease) in Southern United States. Public Health Rep. 1926, 41, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, A. Technique and interpretation of the Weil-Felix test in typhus fever. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1944, 37, 321–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, J.H. Serological diagnosis of typhus. CDC Bull. 1950, 9, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Reece, C.D. Typhus fever in Texas. Tex. State J. Med. 1934, 30, 192–195. [Google Scholar]
- Bohls, S.W. Typhus fever in Texas. South Med. J. 1935, 28, 1162–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, H.A.; Wright, H.E.; Wayne, F. Specificity of the Weil-Felix reaction. Tex. State J. Med. 1926, 29, 278–281. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, J.G.; McDade, J.E. Rickettsia and Coxiella. In Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 6th ed.; Murray, P.R., Baron, E.J., Pfaller, M.A., Tenover, F.C., Yolken, R.H., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; pp. 678–685. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, B.A. Burrows Textbook of Microbiology; W. B. Saunders Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz Casteñada, M. Studies on the mechanism of immunity in typhus fever. Complement-fixation in typhus fever. J. Immunol. 1936, 31, 285–291. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, H.R. Use of yolk sac of developing chick embryo as medium for growing rickettsiae of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever and Typhus Groups. Public Health Rep. 1938, 53, 2241–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigham, G.D.; Bengtson, I.A. A Study of the complement fixation and Weil-Felix reactions in wild rats as related to the isolation of the virus of endemic typhus. Public Health Rep. 1945, 60, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtson, I.A. Complement fixation in endemic typhus fever. Public Health Rep. 1941, 56, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, V.A. Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever, History of a Twentieth-Century Disease; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Berge, T.O. Employment of soluble antigen in screening tests for typhus complement fixation. Public Health Rep. 1948, 63, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tankeshwar, A. Complement Fixation Test: Principle, Procedure and Results. Available online: http://microbeonline.com/complement-fixation-test-principle-procedure-results/ (accessed on 12 April 2016).
- Taylor, J.P. Epidemiology of murine typhus in Texas. 1980 through 1984. JAMA 1986, 255, 2173–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillip, R.N.; Casper, E.A.; Ormsbee, R.A.; Peacock, M.G.; Burgdorfer, W. Microimmuno-fluorescence test for the serological study of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever and typhus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1976, 3, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.W. The Weil-Felix test is archaic and misleading-reply. JAMA 1986, 255, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggers, R.J.; Martin, M.C.; Bouyer, D. Rickettsia felis infection rates in an east Texas population. Tex. Med. 2005, 101, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Silpapojakul, K.; Pradutkanchana, J.; Pradutkanchana, S.; Kelly, D.J. Rapid, simple serodiagnosis of murine typhus. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1995, 89, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, D.H.; Dumler, J.S. State of the art of diagnosis of rickettsial diseases: The use of blood specimens for diagnosis of scrub typhus, spotted fever group rickettsiosis, and murine typhus. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 29, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, K.M.; Jiang, J.; Rozmajzl, P.J.; Azad, A.F.; Macaluso, K.R.; Richards, A.L. Development of quantitative real-time PCR assays to detect Rickettsia typhi and Rickettsia felis, the causative agents of murine typhus and flea-borne spotted fever. Mol. Cell. Probes 2007, 21, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, S.; Castonguay-Vanier, J.; Moore, C.E.; Thongyoo, N.; Newton, P.N.; Paris, D.H. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for Rickettsia typhi (the causal agent of murine typhus): Problems with diagnosis at the limit of detection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bengtson, I.A.; Topping, N.H. Complement-fixation in rickettsial diseases. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1942, 32, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newhouse, V.F.; Shepard, C.C.; Redus, M.D.; Tzianabos, T.; McDade, J.E. A comparison of the complement fixation, indirect fluorescent antibody, and microagglutination tests for the serological diagnosis of rickettsial diseases. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1979, 28, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phakhounthong, K.; Mukaka, M.; Dittrich, S.; Tanganuchitcharnchai, A.; Day, N.P.; White, L.J.; Newton, P.N.; Blacksell, S.D. The temporal dynamics of humoral immunity to Rickettsia typhi infection in murine typhus patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 781.e9–781.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halle, S.G.; Dasch, G.A.; Weiss, E. Sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibody against typhus rickettsiae, Rickettsia prowasekii and Rickettsia typhi. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1977, 6, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mooser, H. Essai sur l’histoire naturelle du typhus exanthematique. Arch. Inst. Pasteur Tunis 1932, 21, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, K.O.; Evert, N.; Mayes, B.; Fonken, E.; Erickson, T.; Garcia, M.N.; Sidwa, T. Typhus group rickettsiosis Texas, USA, 2003–2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legendre, K.P.; Macaluso, K.R. Rickettsia felis: A review of transmission mechanisms of an emerging pathogen. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 2, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdad, M.Y.; Stenos, J.; Graves, S. Rickettsia felis, an emerging flea-transmitted human pathogen. Emerg. Health Threat. J. 2011, 4, 7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, L.; Nguyen, K.; Velten, R.; Bennett, S.; Fogarty, C.; Sun, S.; Cummings, R. The Orange County Vector Control District’s involvement in flea-borne typhus. Proc. Papers Mosquito Vector Control Assoc. Calif. 2013, 82, 128–129. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, E. History of Rickettsiology. In Biology of Rickettsial Diseases; Walker, D.H., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988; pp. 16–32. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, E.; Strauss, B.S. The Life and Career of Howard Taylor Ricketts. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1991, 13, 1241–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, J.L. Estudos sobre o typho exanthematico de São Paulo. Mem. Inst. São Paulo 1931, 6, 3–135. [Google Scholar]
- Mooser, H. Experiments relating to pathology and etiology of Mexican typhus (tabardillo). I. Clinical course and pathologic anatomy of tabardillo in guinea pigs. J. Infect. Dis. 1928, 43, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, C.B. Nomenclature of the pathogenic rickettsiae. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1943, 37, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Skerman, V.B.D.; McGowen, V.; Sneath, P.H.A. Approved list of bacterial names. Internat. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1980, 30, 225–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topping, N.H. Experimental Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever and endemic typhus treated with Prontosil or sulfapyridine. Public Health Rep. 1939, 54, 1143–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, B.M.; Pullen, R.L. Endemic (murine) typhus fever: Clinical observations of 180 cases. Ann. Intern. Med. 1945, 23, 520–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiff, D.; Pinkerton, H. Inhibition of growth of typhus rickettsiae in the yolk sac by penicillin. Exp. Biol. Med. 1944, 55, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, J.C. The Treatment of Rickettsial Diseases of Man. In Rickettsial Diseases of Man; Moulton, F.R., Ed.; American Association for the Advancement of Science: Washington, DC, USA, 1948; pp. 169–177. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Rivera, R.S.; Acosta, C.G.; Collazo, P.J.; Lebron, A.P. Effect of para-aminobenzoic acid on murine typhus a clinical study of 60 cases. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1949, 217, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.K. The use of para-aminobenzoic acid in endemic (murine) typhus. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1946, 131, 1114–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.D.; Arnold, W.T. Para-aminobenzoic acid in the treatment of endemic typhus fever. Tex. State J. Med. 1946, 42, 314–316. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich, J.; Bartz, Q.R.; Smith, R.M.; Joslyn, D.A.; Burkholder, P.R. Chloromycetin, a new antibiotic from a soil actinomycete. Science 1947, 106, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsfall, J.G. Paul Rufus Burkholder 1903–1972. A Biographical Memoir; National Academy of Sciences: Washington, DC, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Smadel, J.E.; Jackson, E.B. Chloromycetin, an antibiotic with chemotherapeutic activity in experimental rickettsial and viral infections. Science 1947, 106, 418–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, H.L., Jr.; Woodward, T.E.; Smadel, J.E. Chloramphenicol (chloromycetin) in the treatment of murine typhus. JAMA 1950, 143, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.L.; Levy, S.B. The discovery of the tetracyclines. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1241, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sneader, W. Drug Discovery: A History; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Duggar, B.M. Aureomycin: A product of the continuing search for new antibiotics. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1948, 51, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finlay, A.C.; Hobby, G.L.; P’an, S.Y.; Regna, P.P.; Routien, J.B.; Seeley, D.B.; Shull, G.M.; Sobin, B.A.; Solomons, I.A.; Vinson, J.W.; et al. Terramycin, a new antibiotic. Science 1950, 111, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, V.; Ruiz-Sanchez, F.; Ruiz-Sanchez, A.; McDermott, W. Aureomycin in typhus and brucellosis. Am. J. Med. 1949, 6, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilder, R.M. The rickettsial diseases: Discovery and conquest. Arch. Pathol. 1950, 49, 479–489. [Google Scholar]
- Ley, H.L., Jr.; Smadel, J.E. Antibiotic therapy of rickettsial diseases. Antibio. Chemother. 1954, 4, 792–802. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Joseph E. Smadel, M.D. The American Association of Immunologists website. Available online: https://www.aai.org/About/History/Past-Presidents-and-Officers/JosephESmadel (accessed on 6 March 2019).
- Anonymous. Ruiz Sanchez Francisco. Gobierno del Estado de Jalisco website. Available online: Jalisco.gob.mx/es/jalisco/jaliscienses%20distinguidos/ruiz-sanchez-francisco (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- Hochstein, F.A.; Stephens, C.R.; Conover, L.H.; Regna, P.P.; Pasternack, R.; Gordon, P.N.; Pilgrim, F.J.; Brunings, K.J.; Woodward, R.B. The structure of terramycin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1953, 75, 5455–5475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, R.; Ling, R.C.; Day, N.P.; McGready, R.; Paris, D.H. Revisiting doxycycline in pregnancy and early childhood--time to rebuild its reputation? Expert Opin. Drug Safety 2016, 15, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikas, A.; Kastanakis, S.; Pediaditis, J.; Tselentis, Y.; Manios, A.; Doukakis, S. Comparison of the effectiveness of five different antibiotic regimens on infection with Rickettsia typhi: Therapeutic data from 87 cases. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 70, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Green, J.S.; Singh, J.; Cheung, M.; Adler-Shohet, F.C.; Ashouri, N. A cluster of pediatric endemic typhus cases in Orange County, California. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2011, 30, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, M.L.; Ritterhoff, R.J.; Hoffman, R.J. A fatal case of aplastic anemia following chloramphenicol (chlormycetin) therapy. Ann. Intern. Med. 1950, 33, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallerstein, R.O.; Condit, P.K.; Kasper, C.K.; Brown, J.W.; Morrison, F.R. Statewide study of chloramphenicol therapy and fatal aplastic anemia. JAMA 1969, 208, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laferl, H.; Fournier, P.E.; Seiberl, G.; Pichler, H.; Raoult, D. Murine typhus poorly responsive to ciprofloxacin: A case report. J. Travel Med. 2006, 9, 103–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolley, J.A.; Pelayo, R.; Hatfield, T.J.; McNulty, J. Murine typhus in a pregnant woman. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 116, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, P.N.; Keolouangkhot, V.; Lee, S.J.; Choumlivong, K.; Sisouphone, S.; Choumlivong, K.; Vongsouvath, M.; Mayxay, M.; Chansamouth, V.; Davong, V.; et al. A prospective, open-label, randomized trial of doxycycline versus azithromycin for the treatment of uncomplicated murine typhus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.R.; Azad, A.F.; Schmidtmann, E.T. Infection of colonized cat fleas, Ctenocephalides felis (Bouché), with a Rickettsia-like microorganism. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1990, 43, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, A.F.; Sacci, J.B.; Nelson, W.M.; Dasch, G.A.; Schmidtmann, E.T.; Carl, M. Genetic characterization and transovarial transmission of a typhus-like rickettsia found in cat fleas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.G.; Sacci, J.B.; Schriefer, M.E.; Andersen, E.M.; Fujioka, K.K.; Sorvillo, F.J.; Barr, A.R.; Azad, A.F. Typhus and typhus-like rickettsiae associated with opossums and their fleas in Los Angeles County, California. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 1758–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.A.; Sacci, J.B.; Schriefer, M.E.; Endris, R.G.; Azad, A.F. Molecular identification of rickettsia-like microorganisms associated with colonized cat fleas (Ctenocephalides felis). Insect Mol. Biol. 2007, 3, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, J.B.; Chomel, B.; Nicholson, W.; Foley, J.E. Serological survey of vector-borne zoonotic pathogens in pet cats and cats from animal shelters and feral colonies. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2006, 8, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schriefer, M.E.; Sacci, J.B.; Dumler, J.S.; Bullen, M.G.; Azad, A.F. Identification of a novel rickettsial infection in a patient diagnosed with murine typhus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reif, K.E.; Macaluso, K.R. Ecology of Rickettsia felis: A review. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Znazen, A.; Raoult, D. Flea-Borne Spotted Fever. In Infectious Disease and Therapy; Informa UK Limited: Colchester, UK, 2007; pp. 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, L.D.; Macaluso, K.R. Rickettsia felis, an emerging flea-borne rickettsiosis. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2016, 3, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thepparit, C.; Hirunkanokpun, B.S.; Popov, V.L.; Foil, L.D.; Macaluso, K.R. Dissemination of blood meal acquired Rickettsia felis in cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinby, G.E.; Schubert, J.H. Epidemiologic and serologic appraisal of murine typhus in the United States, 1948-1951. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1953, 43, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergie, J.E.; Purcell, K.; Wanat, D. Murine typhus in South Texas children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2000, 19, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, W.H.; Emmons, R.W.; Brooks, J.E. The changing ecology of murine (endemic) typhus in Southern California. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1970, 19, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.; Chapman, A.A. Typhus-like fever contracted from o’possum fleas. Tex. State Med. J. 1935, 31, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Brigham, G.D. Susceptibility of the opossum (Didelphis virginiana) to the virus of typhus fever. Public Health Rep. 1936, 51, 333–337. [Google Scholar]
- Boostrom, A.; Beier, M.S.; Macaluso, J.A.; Macaluso, K.R.; Sprenger, D.; Hayes, J.; Radulovic, S.; Azad, A.F. Geographic association of Rickettsia felis-infected opossums with human murine typhus, Texas. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjemian, J.; Parks, S.; McElroy, K.; Campbell, J.; Eremeeva, M.E.; Nicholson, W.L.; McQuiston, J.; Taylor, J. Murine typhus in Austin, Texas, USA, 2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, R.; Krueger, L.; Nguyen, K.; Fogarty, C.; Bennett, S.; Hosea, R.C.; Hearst, M. The Conflicting Roles of Vector Control and Animal Control Agencies in Mitigating the Rise of Human Cases of Flea-borne Typhus in Orange County, California. In Proceedings of the 26th Vertebrate Pest Conference, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–6 March 2014; Volume 26, pp. 316–322. [Google Scholar]
- Texas Department of Health Services. Statistics of Communicable and Infectious Diseases; Texas Department of Health Services: Austin, TX, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Waldrop, R.H.; Ogden, L.J. A survey to determine the prevalence and distribution of typhus in rats in Texas. CDC Bull. 1951, 10, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Texas Department of Health Services. Flea-borne Typhus Cases in Texas by County Reported, 2008–2018. Available online: https://www.dshs.texas.gov/IDCU/disease/murine_typhus/Statistics.aspx (accessed on 26 March 2019).
- Older, J.J. The epidemiology of murine typhus in Texas, 1969. JAMA 1970, 214, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttery, C.M.; Magnuson, L.W.; McLerran, G.; Villarreal, T. Endemic (murine) typhus in Corpus Christi. Tex. Med. 1984, 80, 53–54. [Google Scholar]
- Schriefer, M.E.; Sacci, J.J.B.; Taylor, J.P.; Higgins, J.A.; Azad, A.F. Murine typhus: Updated roles of multiple urban components and a second typhuslike rickettsia. J. Med. Entomol. 1994, 31, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, K.; Fergie, J.; Richman, K.; Rocha, L. Murine typhus in children, South Texas. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 926–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCormack, J. Corpus Christi has Possum Collection Program; San Antonio Express News: San Antonio, TX, USA, 23 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Blanton, L.S.; Vohra, R.F.; Bouyer, D.H.; Walker, D.H. Re-emergence of murine typhus in Galveston, Texas, USA, 2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 484–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, L.S.; Idowu, B.M.; Tatsch, T.N.; Henderson, J.M.; Bouyer, D.H.; Walker, D.H. Opossums and cat fleas: New insights in the ecology of murine typhus in Galveston, Texas. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, T.; Da Silva, J.; Nolan, M.S.; Marquez, L.; Munoz, F.M.; Murray, K.O. Newly recognized pediatric cases of Typhus Group Rickettsiosis, Houston, Texas, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 2068–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Texas Dept of State Health Services. Typhus Health Alert—Nov. 30, 2017. Increased Flea-Borne (Murine) Typhus Activity in Texas. Available online: https://www.dshs.texas.gov/news/releases/2017/HealthAlert-11302017.aspx (accessed on 6 June 2018).
- Maxcy, K.F. The distribution of endemic typhus (Brill’s disease) in the United States. Public Health Rep. 1928, 43, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wekesa, J.W.; Nelson, K.; Brisco, A.; Cook, M.; Fujioka, K. History of flea-borne typhus in Los Angeles County, California. Proc. Mosquito Vector Control Assoc. Calif. 2016, 84, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Meleney, H.E.; French, R.S. Endemic typhus fever in Southern California. Calif. West. Med. 1945, 62, 116–119. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, M.D.; Van Allen, A. Typhus fever in California, 1916–1945, inclusive: An epidemiologic and field laboratory study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1947, 45, 335–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meleney, H.E. Recent extension of endemic typhus fever in the Southern United States. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1941, 31, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, A.H. New plans for vector control in California. J. Natl. Malar. Soc. 1948, 7, 231–235. [Google Scholar]
- Mohr, C.O.; Good, N.E. Distribution of domestic rats with murine typhus antibodies in the United States. CDC Bull. 1951, 10, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Schwan, T.G.; Nelson, B.C.; Thompson, D. Fleas on roof rats in six areas of Los Angeles County, California: Their potential role in the transmission of plague and murine typhus to humans. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1985, 34, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpathy, S.; Hayes, E.; Williams, A.; Hu, R.; Krueger, L.; Bennett, S.; Tilzer, A.; Velten, R.; Kerr, N.; Moore, W.; et al. Detection of Rickettsia felis and Rickettsia typhi in an area of California endemic for murine typhus. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009, 15, 218–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorvillo, F.J.; Gondo, B.; Emmons, R.; Ryan, P.; Waterman, S.H.; Tilzer, A.; Andersen, E.M.; Murray, R.A.; Barr, A.R. A suburban focus of endemic typhus in Los Angeles County: Association with seropositive domestic cats and opossums. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1993, 48, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civen, R.; Ngo, V. Murine typhus: An unrecognized suburban vector-borne disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, W.J.; Krause, W.A. The Opossum: Its Amazing Story; University of Missouri: Columbia, MO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Peirce, P. Curry Plant Not Source of Indian Spice Mix. SFGate, 26 November 2008. Available online: http://www.sfgate.com/homeandgarden/article/Curry-plant-not-source-of-Indian-spice-mix-3183510.php (accessed on 15 October 2016).
- Jameson, E.W., Jr.; Peeters, H.J. Mammals of California; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- California Dept of Public Health. Human Flea-Borne Typhus Cases in California (2001–2020); California Dept of Public Health: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.cdph.ca.gov/Programs/CID/DCDC/CDPH%20Document%20Library/Flea-borneTyphusCaseCounts.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Reporter, R.; Dassey, D.E.; Mascola, L. Murine typhus still exists in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 23, 205–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhold, R.W.; Jessup, D.A. Zoonotic diseases associated with free-roaming cats. Zoonoses Public Health 2012, 60, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, R.; Krueger, L.; Nguyen, K.; Morgan, T.; Fogarty, C.; Sun, S.; Servin, K.; Ostrowski, E.; Hearst, M. Orange County Vector Control and the County’s Feral Cat TNR Program: Ne’er the Twain Shall Meet? In Proceedings of the 27th Vertebrate Pest Conference, California Digital Library (CDL), Newport Beach, CA, USA, 7–10 March 2016; Volume 27, pp. 280–287. [Google Scholar]
- Orange County Grand Jury, 2014–2015 Final Report. Available online: http://www.ocgrandjury.org/pdfs/2014_2015_GJreport/1415_Final_Report.pdf (accessed on 9 July 2019).
- Anonymous. Feral cats not to blame in Southern California murine typhus scare; Animal People, 1 June 2012. Available online: http://newspaper.animalpeopleforum.org/2012/06/01/feral-cats-not-to-blame-in-southern-california-murine-typhus-scare/ (accessed on 8 November 2016).
- Kelley, J.A. Feral cats dodge a bullet in Southern California; Catster, 4 June 2012. Available online: http://www.catster.com/the-scoop/feral-cats-dodge-a-bullet-in-southern-california (accessed on 30 November 2016).
- Mullins, K.; Krueger, L.; Maina, A.N.; Cummings, R.; Williams, G.; Drusys, A.; Jiang, J.; Richards, A.L.; Dhillon, M. Rickettsial infections among cats and cat fleas in Riverside County, California. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.; Maina, A.N.; Brisco, A.; Foo, C.; Croker, C.; Ngo, V.; Civen, R.; Richards, A.L.; Fujioka, K.; Wekesa, J.W. A 2015 outbreak of flea-borne rickettsiosis in San Gabriel Valley, Los Angeles County, California. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.; Reporter, R.; Rood, M.P.; Linscott, A.J.; Mascola, L.M.; Hogrefe, W.; Purcell, R.H. Prevalence study of antibody to ratborne pathogens and other agents among patients using a free clinic in downtown Los Angeles. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186, 1673–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, K.F.; Rood, M.P.; Krueger, L.; Eremeeva, M.E. Urban focus of Rickettsia typhi and Rickettsia felis in Los Angeles, California. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noden, B.H.; Radulovic, S.; Higgins, J.A.; Azad, A.F. Molecular Identification of Rickettsia typhi and R. felis in co-infected Ctenocephalides felis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). J. Med. Entomol. 1998, 35, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremeeva, M.E.; Warashina, W.R.; Sturgeon, M.M.; Buchholz, A.E.; Olmstead, G.K.; Park, S.Y.; Effler, P.V.; Karpathy, S.E. Rickettsia typhi and R. felis in rat fleas (Xenopsylla cheopis), Oahu, Hawaii. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1613–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, K.F.; Wekesa, J.W.; Nwadike, C.N.; Zambrano, M.L.; Karpathy, S.E.; Cecil, D.; Burns, J.; Hu, R.; Eremeeva, E. Rickettsia felis in cat fleas, Ctenocephalides felis parasitizing opossums, San Bernardino County, California. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2012, 26, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billeter, S.A.; Metzger, M.E. Limited evidence for Rickettsia felis as a cause of zoonotic flea-borne rickettsiosis in Southern California. J. Med. Entomol. 2017, 54, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Los Angeles County Dept of Public Health. Health Alert: Outbreak of Flea-Borne Typhus in Downtown Los Angeles, 4 October 2018. Available online: http://publichealth.lacounty.gov/eprp/Health%20Alerts/LAHAN%20Typhus%2010.4.18%20final.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2019).
- County of Los Angeles Public Health. Guidance on Action for Cities to Help Prevent Endemic Flea-Borne Typhus Infections, 22 March 2019. Available online: http://www.publichealth.lacounty.gov/acd/docs/TyphusLettertoCitiesMarch2019.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2020).
- Karlamangla, S.L.A. Typhus Outbreak Adds Fuel to the Debates Over Homelessness and Housing; LA Times (online) 11 October 2018. Available online: https://www.latimes.com/local/california/la-me-ln-typhus-outbreak-20181011-story.html (accessed on 6 March 2019).
- Smith, D.; Zahniser, D. Filth from Homeless Camps is Luring Rats to L.A. City Hall, Report says; LA Times, 3 June 2019. Available online: https://www.latimes.com/local/lanow/la-me-ln-rats-homelessness-city-hall-fleas-report-20190603-story.html (accessed on 10 June 2019).
- Kandel, J. Typhus Epidemic Worsens in Los Angeles. A Veteran City Prosecutor is Among the Latest Victims; NBC News Los Angeles, 1 February 2019. Available online: https://www.nbclosangeles.com/news/local/Typhus-Epidemic-Worsens-in-Los-Angeles-505166301.html (accessed on 10 March 2019).
- Blankstein, A.; Romero, D. Typhus Outbreak in Los Angeles County Surpasses 100 Patients; NBC News, 30 October 2018. Available online: https://www.nbcnews.com/news/us-news/typhus-outbreak-los-angeles-county-surpasses-100-patients-n926496 (accessed on 6 March 2019).
- Fox News Channel. California Screaming. Tucker Carlson Tonight, 5 February 2019. Available online: https://video.foxnews.com/v/5998442627001/#sp=show-clips (accessed on 6 June 2019).
- Fox News Channel. Life in the Typhus Zone. Tucker Carlson Tonight, 8 March 2019. Available online: https://video.foxnews.com/v/6011822064001/#sp=show-clips (accessed on 8 March 2019).
- Fox News Channel. Los Angeles Plagued with Trash, Rats and Typhoid Fever, Fox and Friends First, 3 June 2019. Available online: https://video.foxnews.com/v/6043968559001/#sp=show-clips (accessed on 10 June 2019).
- Braslow, S. How the Homeless Ended Up Being Blamed for Typhus. Los Angeles Magazine, 12 February 2019. Available online: https://www.lamag.com/citythinkblog/typhus-los-angeles-homeless/ (accessed on 30 May 2019).
- LeDuff, C. Up, Down, In and Out in Beverly Hills: Rats; New York Times: New York, NY, USA, 17 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Los Angeles Dept of Public Health Vector Management Program. The Norway Rat in Downtown Los Angeles. Available online: http://www.publichealth.lacounty.gov/eh/docs/Specialized/Vector Management/norway_Rat.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2019).
- Fennel, E.A. Endemic typhus in Hawaii. JAMA 1934, 102, 1135–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doolittle, S.E. Endemic typhus fever in Hawaii. Ann. Intern. Med. 1941, 14, 2091–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higa, H.H.; Broadhurst, A.M. Prevalence of rodent endemic typhus on the Island of Maui. Hawaii Med. J. 1976, 35, 366–371. [Google Scholar]
- Alicata, J.E.; Breaks, V. Typhus fever in Honolulu. Hawaii Med. J. 1942, 2, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Mohr, C.O. Entomological background of the distribution of murine typhus and murine plague in the United States 1. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1951, 31, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manea, S.J.; Sasaki, D.M.; Ikeda, J.K.; Bruno, P.P. Clinical and epidemiological observations regarding the 1998 Kauai murine typhus outbreak. Hawaii Med. J. 2001, 60, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet, D.D. Certain aspects of medical entomology in Hawaii. Proc. Hawaiian Entomol. Soc. 1948, 13, 225–233. Available online: https://scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/bitstream/10125/16173/1/PHES13_225-233.pdf (accessed on 13 February 2019).
- Cole, L.C.; Koepke, J.A. Problems of interpretation of the data of rodent-ectoparasite surveys. Public Health Rep. 1947, 202, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, R.W.; Paradiso, J.L. Walker’s Mammals of the World, 4th ed.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Paz, G.F.; Avelar, D.M.; Reis, I.A.; Linardi, P.M. Dynamics of Ctenocephalides felis felis (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) infestations on urban dogs in Southeastern Brazil. J. Med. Entomol. 2015, 52, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anonymous. Maui Information Guide. Maui Weather by Region, Cycle, Month. Available online: https://www.mauiinformationguide.com/hawaii-weather.php (accessed on 21 May 2019).
- Anonymous. Murine Typhus—Hawaii, 2002. MMWR 2003, 52, 1224–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Hawaii Dept of Health. Summary of Reported Cases of Notifiable Diseases, 1990–2017. Available online: http://health.hawaii.gov/docd/resources/reports/summary-of-reported-cases-of-notifiable-diseases/ (accessed on 1 May 2019).
- Brennan, B.M. Rodents and Rodent Control in Hawaiʻi. Cooperative Extension, University of Hawaii at Manoa, November, 1980. Available online: https://cms.ctahr.hawaii.edu/epp/Education/Study-Guide-Packets/Rodent (accessed on 20 December 2020).
- Silpapojakul, K.; Chayakul, P.; Krisanapan, S. Murine typhus in Thailand: Clinical features, diagnosis and treatment. QJM Int. J. Med. 1993, 86, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


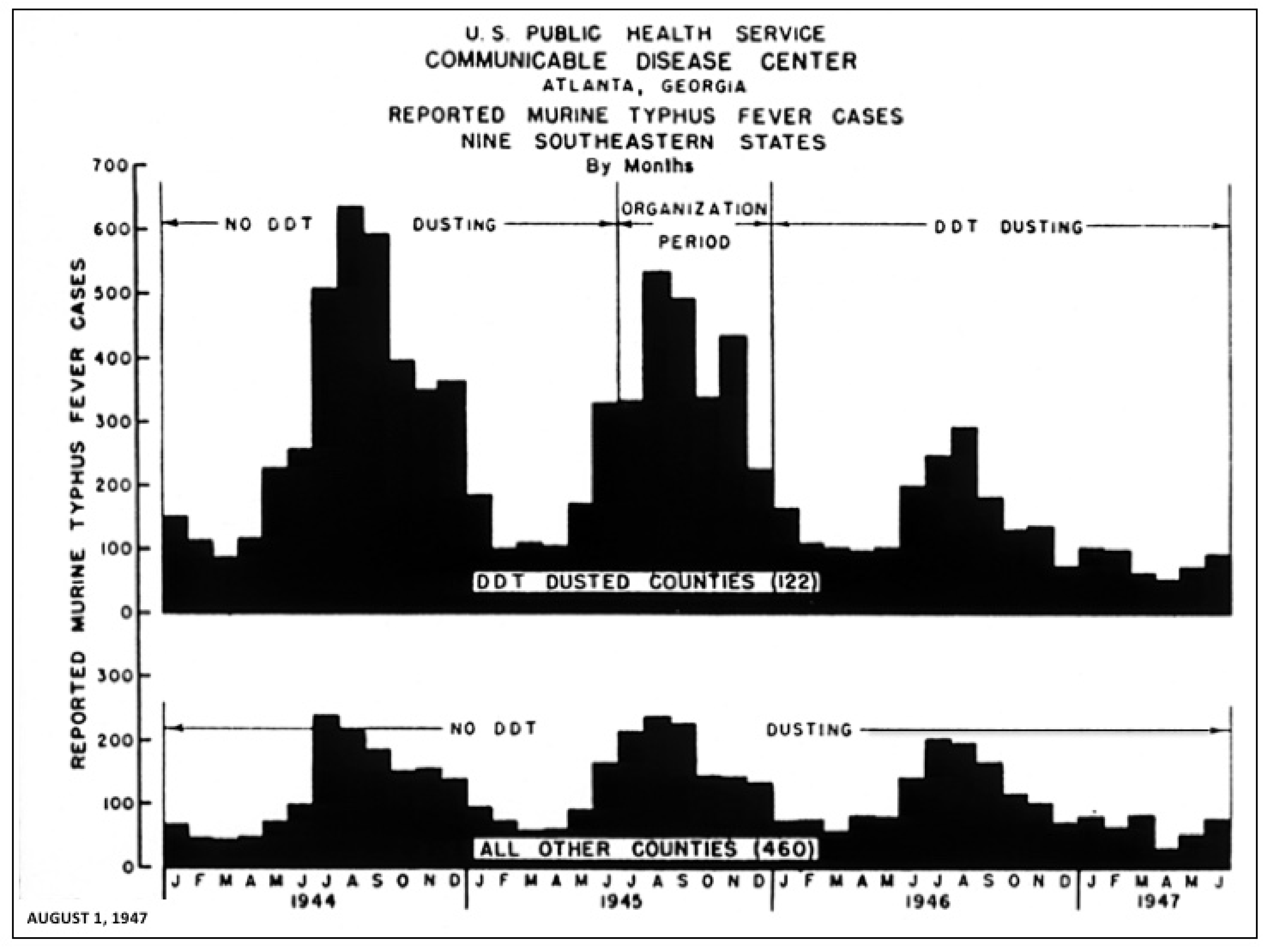



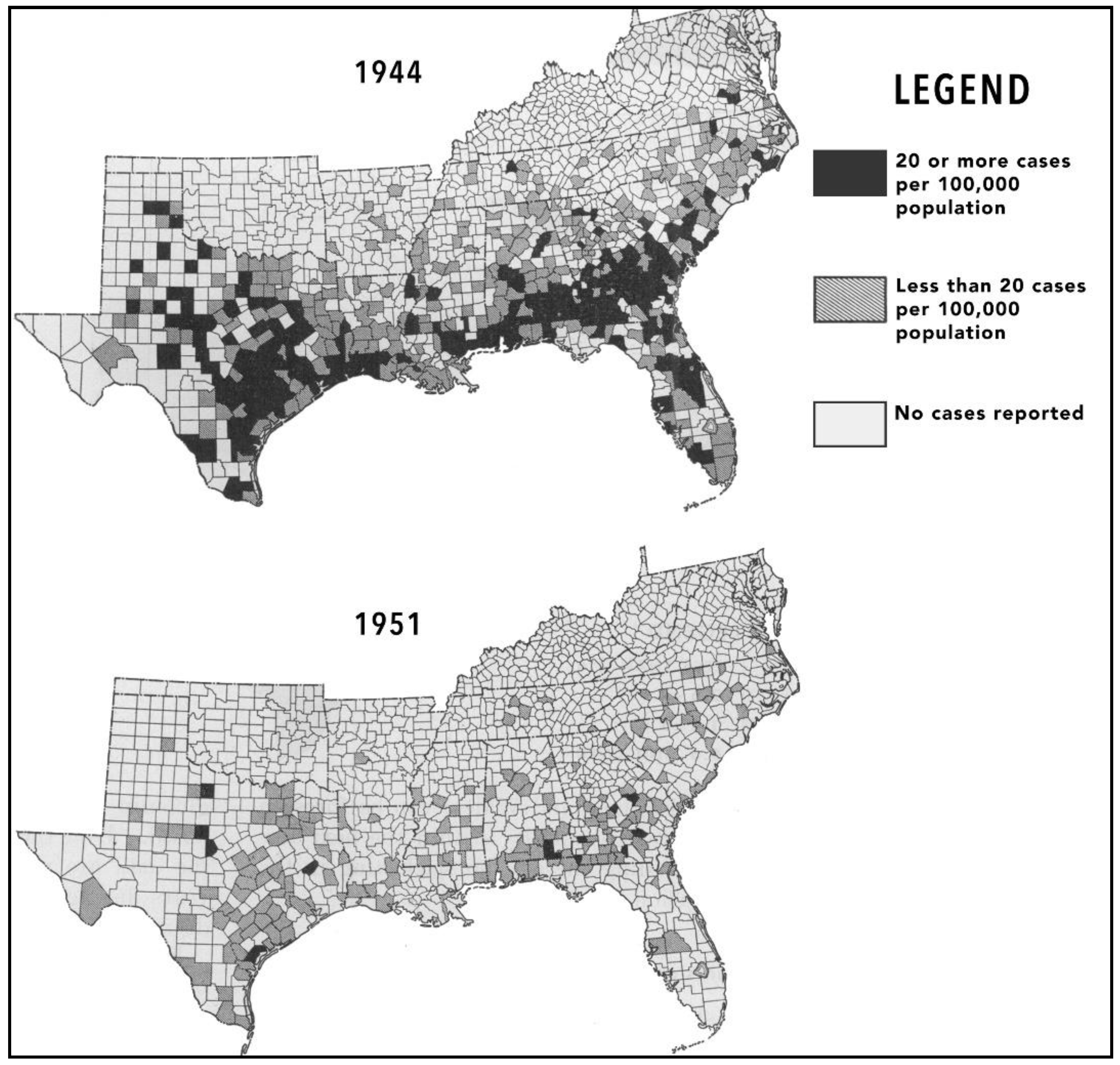




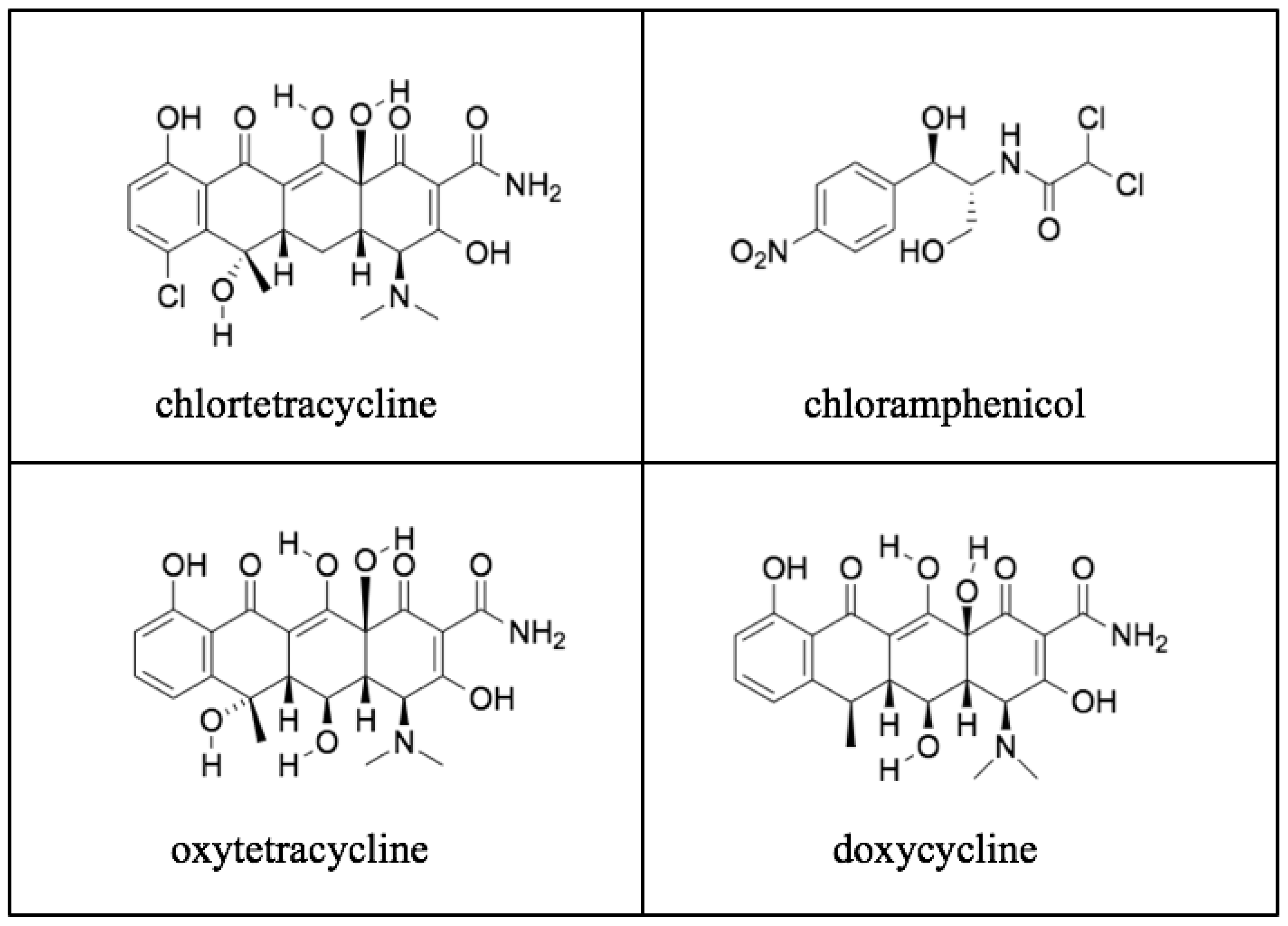

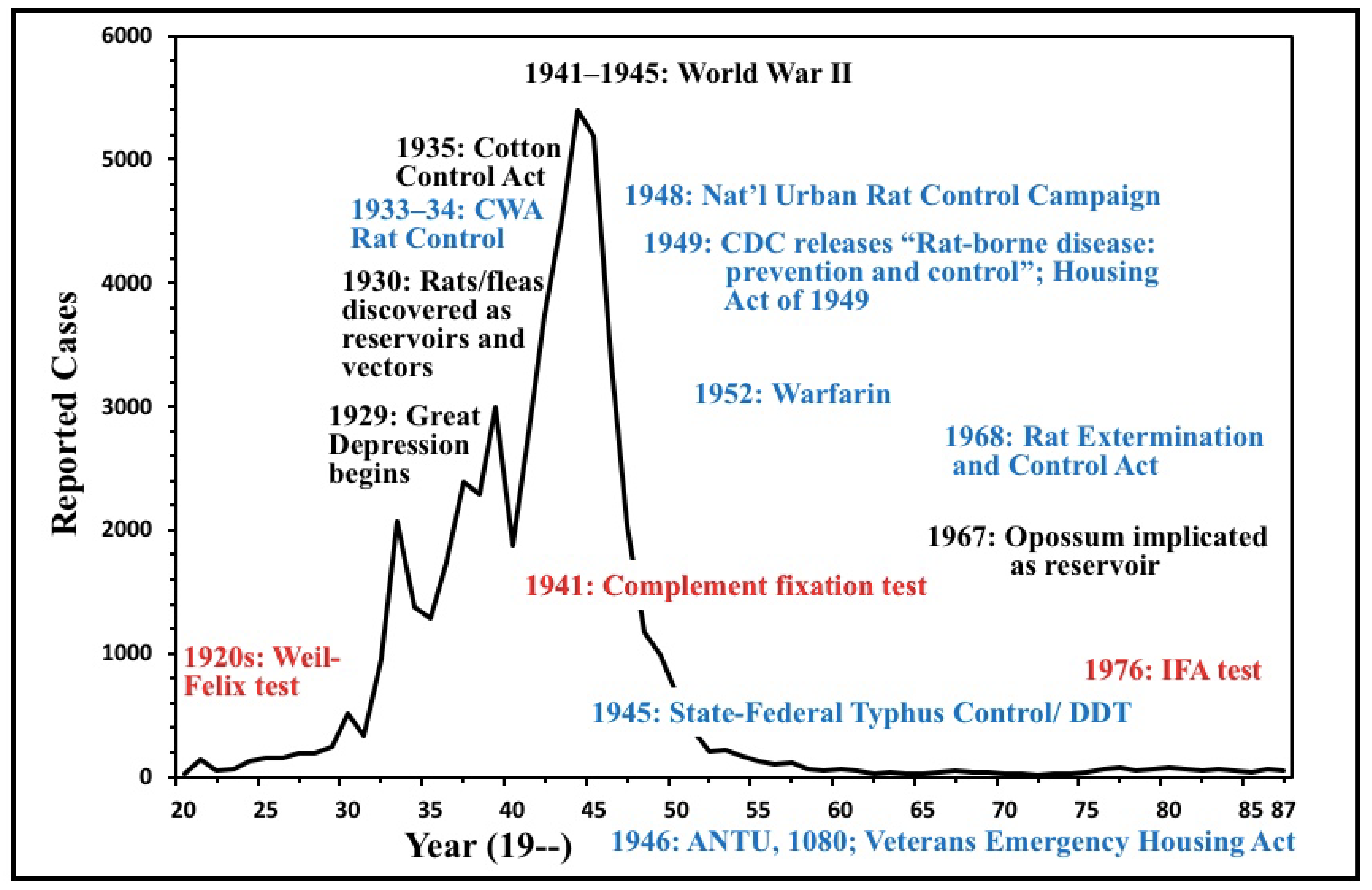
| YEAR | Cases | YEAR | Cases | YEAR | Cases | YEAR | Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1920 | 31 | 1940 | 1878 | 1960 | 68 | 1980 | 81 |
| 1921 | 143 | 1941 | 2784 | 1961 | 46 | 1981 | 59 |
| 1922 | 48 | 1942 | 3736 | 1962 | 32 | 1982 | 58 |
| 1923 | 65 | 1943 | 4528 | 1963 | 35 | 1983 | 62 |
| 1924 | 130 | 1944 | 5401 | 1964 | 30 | 1984 | 53 |
| 1925 | 154 | 1945 | 5193 | 1965 | 28 | 1985 | 37 |
| 1926 | 160 | 1946 | 3365 | 1966 | 33 | 1986 | 67 |
| 1927 | 199 | 1947 | 2050 | 1967 | 52 | 1987 | 49 |
| 1928 | 196 | 1948 | 1171 | 1968 | 36 | ||
| 1929 | 239 | 1949 | 985 | 1969 | 36 | ||
| 1930 | 511 | 1950 | 685 | 1970 | 27 | ||
| 1931 | 333 | 1951 | 378 | 1971 | 23 | ||
| 1932 | 957 | 1952 | 205 | 1972 | 18 | ||
| 1933 | 2070 | 1953 | 221 | 1973 | 32 | ||
| 1934 | 1374 | 1954 | 163 | 1974 | 26 | ||
| 1935 | 1287 | 1955 | 135 | 1975 | 44 | ||
| 1936 | 1733 | 1956 | 98 | 1976 | 69 | ||
| 1937 | 2394 | 1957 | 114 | 1977 | 76 | ||
| 1938 | 2294 | 1958 | 71 | 1978 | 46 | ||
| 1939 | 2996 | 1959 | 51 | 1979 | 69 |
| Test | Year Devised | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weil-Felix Test (WFt) | 1915 [119] | requires minimal equipment; generally positive in the first week of infection [120] | two or more sequential sera were needed for better accuracy [122,123]; cross-reaction between rickettsial infections [120]; poor sensitivity and specificity [124] |
| Complement Fixation (CF) | 1936 [126]; not practical until 1941 [129] | able to differentiate species of rickettsiae; CF antibodies may be present up to ≥5 years after the illness [141]. | delayed positivity (second week) [120]; technically difficult [131]; lower sensitivity than IFA [133] |
| Indirect Immuno-fluorescence Assay (IFA) | 1976 [134] | considered current gold standard; IgG sensitivity ≥83%; specificity ≥ 93% [142]; median half-life of R. typhi IgG was 177 days [143] | paired sera for confirmation; negative results during the first 7–14 days of infection; cross-reaction with other rickettsiae [138]; requires fluorescence microscope and reference laboratory |
| Latex Agglutination | 1995 [137] | rapid; requires minimal equipment | less sensitive than IFA [144] |
| Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) | 1977 [144] | rapid; requires minimal equipment | comparable sensitive to IFA in some studies [144], but inadequate validation [138] |
| Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) | 2007 [139] | potential for early diagnosis | low sensitivity when using blood samples [140,143] |
| Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification | 2014 [140] | potential for rapid, point-of-care assay; does not require thermocycler | low sensitivity when using blood samples (48%) [140] |
| YEAR | Cases | Decade Total | YEAR | Cases | Decade Total | YEAR | Cases | Decade Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1940 | B | − | 1970 | 16 | 321 | 2000 | 53 | 994 |
| 1941 | B | − | 1971 | 17 | 2001 | 29 | ||
| 1942 | 1204 c | 8625 (1942–1949) | 1972 | 13 | 2002 | 53 | ||
| 1943 | 1452 d | 1973 | 28 | 2003 | 30 | |||
| 1944 | 1740 d | 1974 | 12 | 2004 | 66 | |||
| 1945 | 1844 e | 1975 | 30 | 2005 | 100 | |||
| 1946 | 1147 | 1976 | 58 | 2006 | 146 | |||
| 1947 | 610 | 1977 | 55 | 2007 | 169 | |||
| 1948 | 344 | 1978 | 33 | 2008 | 157 | |||
| 1949 | 284 | 1979 | 59 | 2009 | 191 | |||
| 1950 | 222 | 805 | 1980 | 61 | 436 | 2010 | 135 | 3159 (2010–2018) |
| 1951 | 164 | 1981 | 50 | 2011 | 286 | |||
| 1952 | 84 | 1982 | 41 | 2012 | 263 | |||
| 1953 | 82 | 1983 | 46 | 2013 | 222 | |||
| 1954 | 64 | 1984 | 37 | 2014 | 308 | |||
| 1955 | 52 | 1985 | 25 | 2015 | 324 | |||
| 1956 | 51 | 1986 | 52 | 2016 | 364 | |||
| 1957 | 38 | 1987 | 34 | 2017 | 519 f | |||
| 1958 | 30 | 1988 | 30 | 2018 | 738 f | |||
| 1959 | 18 | 1989 | 30 | 2019 | g | − | ||
| 1960 | 50 | 246 | 1990 | 36 | 348 | |||
| 1961 | 21 | 1991 | 22 | |||||
| 1962 | 12 | 1992 | 18 | |||||
| 1963 | 21 | 1993 | 12 | |||||
| 1964 | 15 | 1994 | 9 | |||||
| 1965 | 18 | 1995 | 53 | |||||
| 1966 | 20 | 1996 | 41 | |||||
| 1967 | 37 | 1997 | 70 | |||||
| 1968 | 23 | 1998 | 45 | |||||
| 1969 | 29 | 1999 | 42 | |||||
| YEAR | Hawaii | Honolulu | Kuaui | Maui | TOTAL | Decade Total | Avg No. Cases/Yr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 42 | 4.2 |
| 1991 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 6 | ||
| 1992 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | ||
| 1993 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 1994 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 5 | ||
| 1995 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3 | ||
| 1996 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 1997 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | ||
| 1998 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 9 | ||
| 1999 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | ||
| 2000 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 235 | 23.5 |
| 2001 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | ||
| 2002 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 41 | 48 | ||
| 2003 | 0 | 13 | 11 | 18 | 42 | ||
| 2004 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 20 | 32 | ||
| 2005 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 42 | 47 | ||
| 2006 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 16 | 18 | ||
| 2007 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 12 | 18 | ||
| 2008 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 10 | ||
| 2009 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 8 | 11 | ||
| 2010 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 65 (2010–2018) | 7.2 (2010–2018) |
| 2011 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 13 | 14 | ||
| 2012 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 6 | 9 | ||
| 2013 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 4 | ||
| 2014 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 7 | ||
| 2015 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 8 | ||
| 2016 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 6 | ||
| 2017 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 8 | ||
| 2108 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 8 | ||
| 2019 d | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ||
| TOTAL | 3 | 58 | 34 | 246 | 341 | 341 | 11.8 |
| % of total | 0.9 | 17.0 | 10.0 | 72.1 | 100 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anstead, G.M. History, Rats, Fleas, and Opossums. II. The Decline and Resurgence of Flea-Borne Typhus in the United States, 1945–2019. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed6010002
Anstead GM. History, Rats, Fleas, and Opossums. II. The Decline and Resurgence of Flea-Borne Typhus in the United States, 1945–2019. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2021; 6(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed6010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnstead, Gregory M. 2021. "History, Rats, Fleas, and Opossums. II. The Decline and Resurgence of Flea-Borne Typhus in the United States, 1945–2019" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 6, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed6010002
APA StyleAnstead, G. M. (2021). History, Rats, Fleas, and Opossums. II. The Decline and Resurgence of Flea-Borne Typhus in the United States, 1945–2019. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 6(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed6010002





