Incorporating Direct Rapid Immunohistochemical Testing into Large-Scale Wildlife Rabies Surveillance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
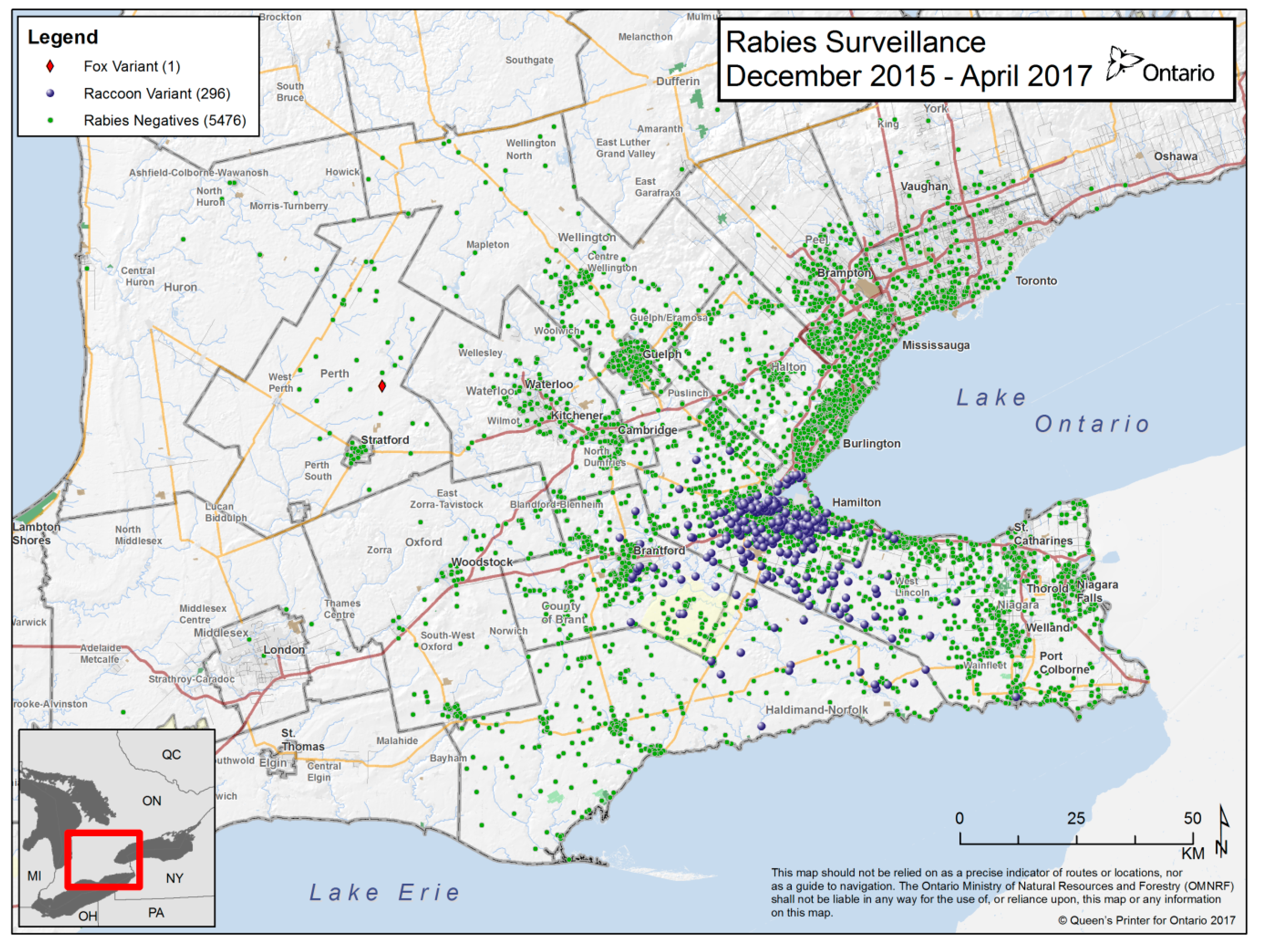
3.1. Surveillance Samples
3.2. dRIT Performance in Comparison with FAT
3.3. Cost
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lembo, T.; Niezgoda, M.; Velasco-Villa, A.; Cleaveland, S.; Ernest, E.; Rupprecht, C.E. Evaluation of a direct, rapid immunohistochemical test for rabies diagnosis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupprecht, C.E.; Cliquet, F.; Fehlner-Gardiner, C.; Fooks, A.R.; Mueller, T.; Sabeta, C.; Slate, D. Progress in the development of a direct rapid immunohistochemical test for diagnosing rabies. Bull. OIE 2014, 2014, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Healthy Wildlife: The Blog of the Canadian Wildlife Health Cooperative. Available online: http://blog.healthywildlife.ca/drit-and-rabies-surveillance-in-quebec/ (accessed on 29 May 2017).
- Niezgoda, M.; Rupprecht, C.E. Standard Operating Procedure for the Direct Rapid Immunohistochemistry Test for the Detection of Rabies Virus Antigen. National Laboratory Training Network Course; US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2006; pp. 1–16.
- Fehlner-Gardiner, C.; Nadin-Davis, S.; Armstrong, J.; Muldoon, F.; Bachmann, P.; Wandeler, A. ERA vaccine-derived cases of rabies in wildlife and domestic animals in Ontario, Canada, 1989–2004. J. Wildl. Dis. 2008, 44, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| FAT Positive | FAT Negative | Total | |
| dRIT positive | 297 | 10 | 307 |
| dRIT negative | 0 | 550 | 550 |
| Total | 297 | 560 | |
| Value | 95% CI | ||
| dRIT Sensitivity | 100.0% | 98.77%–100.00% | |
| dRIT Specificity | 98.21% | 97.74%–99.14% | |
| Kappa | 0.9744 | 0.9587–0.9902 | |
| Negative agreement | 0.9910 | - | |
| Positive agreement | 0.9834 | - | |
| Overall agreement | 0.9883 | - |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Middel, K.; Fehlner-Gardiner, C.; Pulham, N.; Buchanan, T. Incorporating Direct Rapid Immunohistochemical Testing into Large-Scale Wildlife Rabies Surveillance. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2017, 2, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed2030021
Middel K, Fehlner-Gardiner C, Pulham N, Buchanan T. Incorporating Direct Rapid Immunohistochemical Testing into Large-Scale Wildlife Rabies Surveillance. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 2017; 2(3):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed2030021
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiddel, Kevin, Christine Fehlner-Gardiner, Natalie Pulham, and Tore Buchanan. 2017. "Incorporating Direct Rapid Immunohistochemical Testing into Large-Scale Wildlife Rabies Surveillance" Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease 2, no. 3: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed2030021
APA StyleMiddel, K., Fehlner-Gardiner, C., Pulham, N., & Buchanan, T. (2017). Incorporating Direct Rapid Immunohistochemical Testing into Large-Scale Wildlife Rabies Surveillance. Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease, 2(3), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/tropicalmed2030021





